Bridging Qemu Image To Real Network Using Tap Interface
http://brezular.com/2011/06/19/bridging-qemu-image-to-the-real-network-using-tap-interface/
In this tutorial I would like to show how to bridge operation system (OS) that is running inside a virtual machine (guest), with OS running on physical hardware (host). A virtual machine is created and virtualized by Qemu emulator, installed on the host.
By default, when a Qemu virtual machine is started without specifying NIC options, one single network interface is created on he guest OS. The interface connects a guest OS with with a host OS using a NAT mode. The NAT causes that traffic leaving guest OS is passed out of the guest network interface without any restrictions but only established traffic is allowed to enter guest network interface. All the traffic coming from the host to the guest that is not established, is discarded. An IP address of the guest network interface is assigned automatically from an internal Qemu DHCP server and it is typically 10.0.2.15/24 with default gateway IP address 10.0.2.2.
Our goal is to create such a configuration which allows traffic being initialized from both directions. This type of connection between is called bridged connection and the both - guest and host IP addresses are assigned from the same subnet. To create a bridged connection between the guest and host we have to create a virtual tap interface on host and Qemu must be told to bridge a guest interface with a tap interface. Then we can create a bridge virtual interface and bridge an existing host Ethernet interface and tap interface together. The Fedora Linux package bridge-utils can be used to do this job.
Host OS Configuration - Fedora Linux
1/ Install bridge-utils package
The bridge utility creates a virtual bridge interface that forwards traffic between tap and Ethernet interface.
sudo yum install bridge-utils
2/ Install tunctl package
The tunctl utility is used to create and manage virtual TUN/TAP interfaces. It is required that a generic TUN/TAP driver is either built-in to kernel, or available as a module. To check the availability of this module do the following:
ls -la /dev/net/tun
If you get error message no such file or directory, load a module to a Linux kernel with the modprobe tun command. After that a module should be presented in the output of lsmod command.
sudo yum install tunctl
3/ Create bridge device virbr0
sudo brctl addbr virbr0
4/ Create virtual tap0 interface
Tap interface is persistent and owned by user
brezular
/usr/sbin/tunctl -t tap0 -u brezular
5/ Add eth0 and tap0 to the bridge and bring the interfaces up
sudo brctl addif virbr0 eth0
sudo brctl addif virbr0 tap0
sudo ifconfig eth0 up
sudo ifconfig tap0 up
sudo ifconfig virbr0 up
Note: Check if tap0 and eth0 are properly bridged.
brctl show
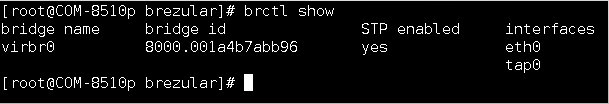
Picture 1 - Bridging Ethernet and Virtual TAP Interface
6/ Assign IP address to virbr0 interface and remove IP address eth0 interface
Only the bridge interface virbr0 should have an IP address assigned.
sudo ifconfig virbr0 172.16.1.2/16
sudo ifconfig eth0 0.0.0.0 promisc
Note: If you run DHCP server in your network, issue the following command to assign IP address to the interface virbr0.
sudo dhclient virbr0
Configure a default route if connection to the Internet is required. In the example below, the default gateway IP address is the last usable IP address for the subnet 172.16.0.0/16.
sudo route add default gw 172.16.255.254
7/ Disable L2 traffic filtering - ebtables, bridge-nf, arptables
Change value 1 to 0 for all the files in directory /proc/sys/net/bridge/.
cd /proc/sys/net/bridge; ls
bridge-nf-call-arptables bridge-nf-call-iptables
bridge-nf-call-ip6tables bridge-nf-filter-vlan-tagged
sudo su
for f in bridge-nf-*; do echo 0 > $f; done
8/ Start Guest OS - Core Linux
Qemu guest virtual machine have to be started with the parameters that instruct Qemu to bridge a tap0 interface with a guest network interface. Below is deprecated "vlan" command syntax.
/usr/local/bin/qemu-system-x86 -m 128M -enable-kvm -boot c -hda /home/brezular/qemu-tinycore-linux.img -net nic,vlan=0,macaddr=00:aa:00:60:00:01,model=e1000 -net tap,vlan=0,ifname=tap0,script=no
The new Qemu versions use "netdev" syntax.
/usr/local/bin/qemu-system-x86 -m 128M -enable-kvm -boot c -hda /home/brezular/qemu-tinycore-linux.img -netdev tap,id=net0,ifname=tap0,script=no,downscript=no -device e1000,netdev=net0,mac=00:aa:00:60:00:01
Explanation:
-boot c -> boot from the hard disk
-m 128M -> 128 MB RAM allocated for the image
-enable-kvm ->enable hardware virtualization
Guest OS Configuration - Core Linux
1/ Configure IP address for eth0 interface (it is on the same subnet as virbr0)
sudo su
ifconfig eth0 172.16.1.1/16 up





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通