Flume—(2)实时读取本地文件到HDFS
1)案例需求
实时监控Hive日志,并上传到HDFS在。
2)需求分析

3)实现步骤:
1.Flume要想将数据输出到HDFS,必须持有Hadoop相关的jar包
将commons-configuration-1.6、commons-io-2.4、hadoop-auth-2.9.0、hadoop-common-2.9.0、hadoop-hdfs-2.9.0、htrace-core4-4.1.0-incubating 拷贝到/opt/module/flume-1.9.0/lib文件下。
2.创建flume-file-hdfs.conf文件
创建
[atguigu@hadoop102 job]$ touch flume-file-hdfs.conf
注:要想读取Linux系统中的文件,就得按照Linux命令的规则执行命令。由于Hive日志在Linux系统中所以读取文件的类型选择:exec即execute执行的意思。表示执行Linux命令来读取文件。
[atguigu@hadoop102 job]$ vim flume-file-hdfs.conf
添加内容:
# Name the components on this agent a2.sources = r2 a2.sinks = k2 a2.channels = c2
#Describe/configure the source a2.sources.r2.type = exec #定义source类型为exec可执行命令 a2.sources.r2.command = tail -F /opt/module/hive/logs/hive.log a2.sources.r2.shell = /bin/bash -c #执行shell脚本的绝对路径 #Describe the sink a2.sinks.k2.type = hdfs a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.path = hdfs://hadoop102:9000/flume-1.9.0/%Y%m%d/%H a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.filePrefix = logs- #上传文件的前缀 a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.round = true #是否按照时间滚动文件夹 a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.roundValue = 1 #多少时间单位滚动文件夹 a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.roundUnit = hour #重新定义时间单位 a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true #是否使用本地时间戳 a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.batchSize = 1000 #积攒多少个event才flush到HDFS一次 a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.fileType = DataStream #设置文件类型,可支持压缩 a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.rollInterval = 600 #多久生成一个新的文件 a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.rollSize = 134217700 #设置每个文件的滚动大小
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.rollCount = 0 #文件的滚动与event数量无关
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.minBlockReplicas = 1 #最小冗余数
#Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a2.channels.c2.type = memory
a2.channels.c2.capacity = 1000
a2.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100
#Bind the Source and sink to the channel
a2.sources.r2.channels = c2
a2.sinks.k2.channel = c2
3. 先开启flume监听端口
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume-1.9.0]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a2 --conf-file job/flume-file-hdfs.conf
4. 开启Hadoop和Hive 并操作Hive产生日志
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-2.9.0]$ sbin/start-dfs.sh [atguigu@hadoop103 hadoop-2.9.0]$ sbin/start-yarn.sh [atguigu@hadoop102 hive]$ bin/hive hive (default)>
5. 在HDFS上查看文件
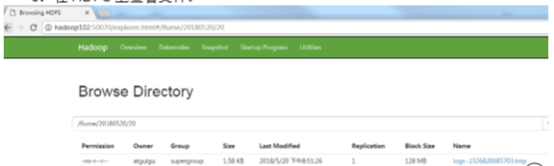
源于atguigu视频



