数据库高级查询
1.连接查询,对结果集列的扩展
select * from info
①select * from info,nation #形成笛卡尔积(学名)
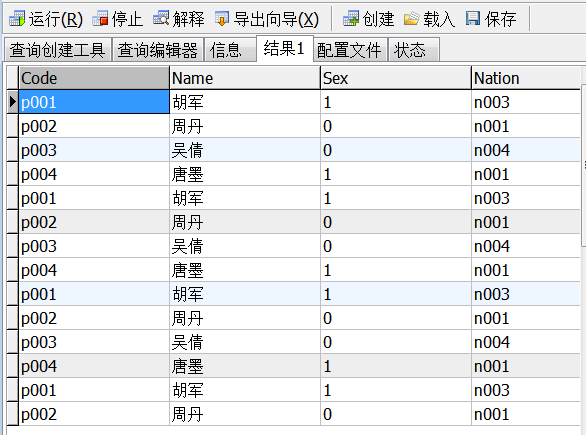 简单查询
简单查询
②select * from info,nation where info.nation=nation.code
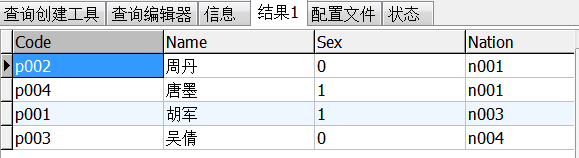
info.nation=nation.code:
 属于
属于 等于
等于 也属于
也属于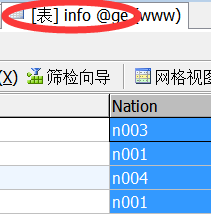
.:后面的数据属于前面的数据。
=:起到连接的作用。
③select info.code,info.name,sex,nation.name,birthday from info,nation where info.nation=nation.code
 也就是说,将第二张表的某以代号列连接到第一张表中显示。
也就是说,将第二张表的某以代号列连接到第一张表中显示。
④select * from info join nation on info.nation=nation.code
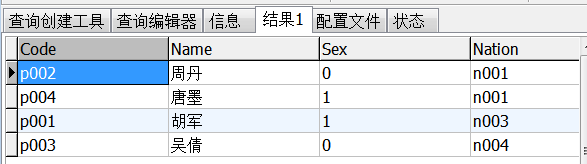 第四种属于最简便的方式。
第四种属于最简便的方式。
join:连接作用
on:在...之间
2.联合查询,对结果集行的扩展
①select code,name from info
union:联合
②select code,name from nation
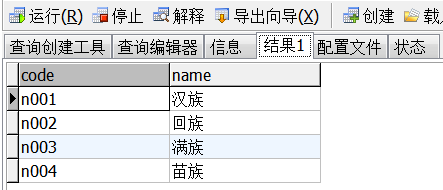 选择code列,将name列内容为nation显示。
选择code列,将name列内容为nation显示。
3.子查询
父查询:外层查询
子查询:里层查询
子查询的结果做为父查询的条件
(1)无关子查询
子查询在执行的时候和父查询没有关系,子查询可以单独执行
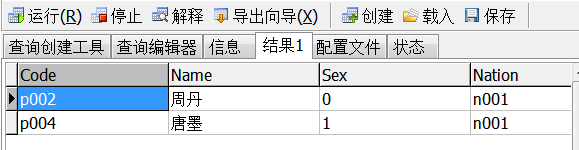
1.查询民族为‘汉族’的所有人员信息
父查询:select * from info where nation=()
子查询:select code from nation where name='汉族'
就是将子查询的查询代码放到父查询的()里再进行查询。
select * from info where nation=(select code from nation where name='汉族')
2.查询系列名为‘宝马5系’的所有汽车信息
select * from car where brand=(select brand_code from brand where brand_name='宝马5系')
(2)相关子查询
子查询在执行的时候和父查询有关系,子查询不可以单独执行
1.查询汽车表中油耗小于该系列平均油耗的所有汽车信息
父查询:select * from car where oil<(该系列平均油耗)
子查询:select avg(oil) from car where brand=该系列
select * from car as a where oil<(select avg(oil) from car as b where b.brand=a.brand)
为了区分“该系列”,将两个系列各取一个名字好进行区分。as a;as b
avg:平均





