HTTP协议栈
一. HTTP全称是Hyper Transfer protocol ,即超文本传输协议,当今普遍采用版本Http1.1,HTTP协议已属于应用层协议,它构建在TCP之上,处于TCP/IP架构的顶端,为了更好的理解HTTP协议,我们基于java的SocketAPI设计一个简单的应用层通信协议,来窥探协议实现的一些过程与细节。
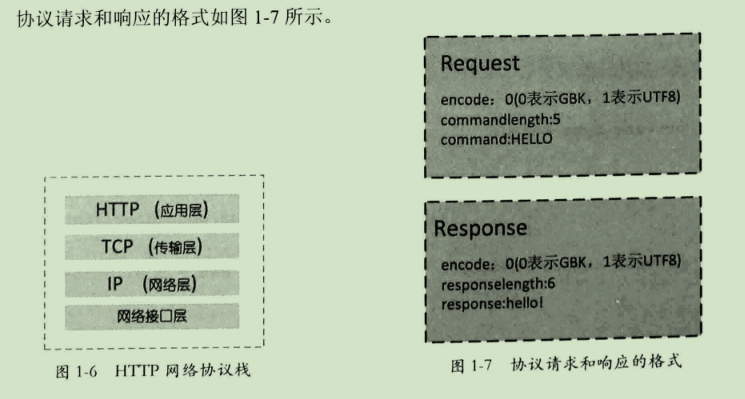
客户端向服务端发送一条命令,服务端接收到命令后,会判断命令是否为"HELLO",若是则返回客户端"hello!",否则返回客户端"bye bye"。
1.协议请求:
1 package com.zqf.fenbushi; 2 //协议请求 3 //2016110758 邹奇方 4 public class Request { 5 6 /** 7 * 协议编码 0:GBK;1:UTF-8 8 */ 9 private byte encode; 10 /** 11 * 命令 12 */ 13 private String command; 14 /** 15 * 命令长度 16 */ 17 private int commandLength; 18 19 public byte getEncode() { 20 return encode; 21 } 22 23 public void setEncode(byte encode) { 24 this.encode = encode; 25 } 26 27 public String getCommand() { 28 return command; 29 } 30 31 public void setCommand(String command) { 32 this.command = command; 33 } 34 35 public int getCommandLength() { 36 return commandLength; 37 } 38 39 public void setCommandLength(int commandLength) { 40 this.commandLength = commandLength; 41 } 42 43 }
2.协议响应:
1 package com.zqf.fenbushi; 2 //协议响应 3 //2016110758 邹奇方 4 public class Response { 5 /** 6 * 编码 7 */ 8 private byte encode; 9 /** 10 * 响应 11 */ 12 private String response; 13 /** 14 * 响应长度 15 */ 16 private int responseLength; 17 18 public byte getEncode() { 19 return encode; 20 } 21 22 public void setEncode(byte encode) { 23 this.encode = encode; 24 } 25 26 public String getResponse() { 27 return response; 28 } 29 30 public void setResponse(String response) { 31 this.response = response; 32 } 33 34 public int getResponseLength() { 35 return responseLength; 36 } 37 38 public void setResponseLength(int responseLength) { 39 this.responseLength = responseLength; 40 } 41 42 @Override 43 public String toString() { 44 return "Response [encode=" + encode + ", response=" + response + ", responseLength=" + responseLength + "]"; 45 } 46 47 }
3.客户端发送,以及服务端响应处理代码:
1 package com.zqf.fenbushi; 2 //客服端发送,以及服务端响应处理代码 3 //2016110758 邹奇方 4 import java.net.ServerSocket; 5 import java.net.Socket; 6 7 8 public class Server { 9 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 10 System.out.println("开启服务器..."); 11 ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(16789); 12 while(true) { 13 Socket client = server.accept(); 14 //读取请求数据 15 Request request = ProtocolUtil.readRequest(client.getInputStream()); 16 //封装响应数据 17 Response response = new Response(); 18 System.out.println("response"+response); 19 response.setEncode(Encode.UTF8.getValue()); 20 response.setResponse(request.getCommand().equals("HELLO") ? "hello!" : "bye bye"); 21 response.setResponseLength(response.getResponse().length()); 22 //响应到客户端 23 ProtocolUtil.writeResponse(client.getOutputStream(), response); 24 } 25 } 26 }
4.客户端:
1 package com.zqf.fenbushi; 2 //客户端 3 //2016110758 邹奇方 4 import java.net.Socket; 5 6 public class Client { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 9 //组装请求数据 10 Request request = new Request(); 11 request.setCommand("HELLO"); 12 request.setCommandLength(request.getCommand().length()); 13 request.setEncode(Encode.UTF8.getValue()); 14 Socket client = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 16789); 15 System.out.println(client); 16 17 18 //发送请求 19 ProtocolUtil.writeRequest(client.getOutputStream(), request); 20 //读取相应 21 Response response = ProtocolUtil.readResponse(client.getInputStream()); 22 System.out.println(response); 23 } 24 }
5.ProtocolUtil 类:
1 package com.zqf.fenbushi; 2 3 //2016110758 邹奇方 4 import java.io.InputStream; 5 import java.io.OutputStream; 6 7 public class ProtocolUtil { 8 9 public static void writeRequest(OutputStream out, Request request) { 10 try { 11 out.write(request.getEncode()); 12 //write一个int值会截取其低8位传输,丢弃其高24位,因此需要将基本类型转化为字节流 13 //java采用Big Endian字节序,而所有的网络协议也都是以Big Endian字节序来进行传输,所以再进行数据的传输和接收时,需要先将数据转化成Big Endian字节序 14 //out.write(request.getCommandLength()); 15 out.write(int2ByteArray(request.getCommandLength())); 16 out.write(Encode.GBK.getValue() == request.getEncode() ? request.getCommand().getBytes("GBK") : request.getCommand().getBytes("UTF8")); 17 out.flush(); 18 } catch (Exception e) { 19 System.err.println(e.getMessage()); 20 } 21 } 22 23 /** 24 * 将响应输出到客户端 25 * @param os 26 * @param response 27 */ 28 public static void writeResponse(OutputStream out, Response response) { 29 try { 30 out.write(response.getEncode()); 31 out.write(int2ByteArray(response.getResponseLength())); 32 out.write(Encode.GBK.getValue() == response.getEncode() ? response.getResponse().getBytes("GBK") : response.getResponse().getBytes("UTF8")); 33 out.flush(); 34 } catch (Exception e) { 35 System.err.println(e.getMessage()); 36 } 37 } 38 39 public static Request readRequest(InputStream is) { 40 Request request = new Request(); 41 try { 42 //读取编码 43 byte [] encodeByte = new byte[1]; 44 is.read(encodeByte); 45 byte encode = encodeByte[0]; 46 //读取命令长度 47 byte [] commandLengthByte = new byte[4];//缓冲区 48 is.read(commandLengthByte); 49 int commandLength = byte2Int(commandLengthByte); 50 //读取命令 51 byte [] commandByte = new byte[commandLength]; 52 is.read(commandByte); 53 String command = Encode.GBK.getValue() == encode ? new String(commandByte, "GBK") : new String(commandByte, "UTF8"); 54 //组装请求返回 55 request.setEncode(encode); 56 request.setCommand(command); 57 request.setCommandLength(commandLength); 58 } catch (Exception e) { 59 System.err.println(e.getMessage()); 60 } 61 return request; 62 } 63 64 public static Response readResponse(InputStream is) { 65 Response response = new Response(); 66 try { 67 byte [] encodeByte = new byte[1]; 68 is.read(encodeByte); 69 byte encode = encodeByte[0]; 70 byte [] responseLengthByte = new byte[4]; 71 is.read(responseLengthByte); 72 int commandLength = byte2Int(responseLengthByte); 73 byte [] responseByte = new byte[commandLength]; 74 is.read(responseByte); 75 String resContent = Encode.GBK.getValue() == encode ? new String(responseByte, "GBK") : new String(responseByte, "UTF8"); 76 response.setEncode(encode); 77 response.setResponse(resContent); 78 response.setResponseLength(commandLength); 79 } catch (Exception e) { 80 System.err.println(e.getMessage()); 81 } 82 return response; 83 } 84 85 public static int byte2Int(byte [] bytes) { 86 int num = bytes[3] & 0xFF; 87 num |= ((bytes[2] << 8) & 0xFF00); 88 num |= ((bytes[1] << 16) & 0xFF0000); 89 num |= ((bytes[0] << 24) & 0xFF000000); 90 return num; 91 } 92 93 public static byte[] int2ByteArray(int i) { 94 byte [] result = new byte[4]; 95 result[0] = (byte) ((i >> 24) & 0xFF); 96 result[1] = (byte) ((i >> 16) & 0xFF); 97 result[2] = (byte) ((i >> 8) & 0xFF); 98 result[3] = (byte) (i & 0xFF); 99 return result; 100 } 101 102 }
6.Encode类:
1 package com.zqf.fenbushi; 2 3 //2016110758 邹奇方 4 public class Encode { 5 6 private byte enCode; //编码,取值1表示 utf-8编码,取值0表示 gbk编码 7 8 9 public static Encode UTF8 = new Encode("utf-8"); 10 public static Encode GBK = new Encode("gbk"); 11 12 public Encode(String enCode){ 13 14 if(enCode.equals("utf-8")){ 15 this.enCode = 1; 16 } 17 if(enCode.equals("gbk")){ 18 this.enCode = 0; 19 } 20 } 21 22 public byte getValue(){ 23 24 return this.enCode; 25 26 } 27 28 //测试 29 public static void main(String[] args) { 30 31 System.out.println(Encode.UTF8.getValue()); 32 System.out.println(Encode.GBK.getValue()); 33 34 } 35 36 }
以上代码运行结果:(在客服端输入HELLO,则输出hello,输入不是HELLO,则输出为bye bye)
 (此输入为HELLO)
(此输入为HELLO)
 (此输入不是HELLO)
(此输入不是HELLO)
二.HTTP请求与响应
下图是HTTP请求与响应的过程步骤,在此不详细赘述。
三.通过HttpClient发送HTTP请求
HttpClient对HTTP协议通信的过程进行了封装,下面是简单的通过HttpClient发送HTTP GET请求,并获取服务端响应的代码:
1 //url前加上http协议头,标明该请求为http请求 2 String url = "https://www.baidu.com"; 3 //组装请求 4 HttpClient httpClient = new DefaultHttpClient(); 5 HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(url); 6 //接收响应 7 HttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(httpGet); 8 HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity(); 9 byte[] byteArray = EntityUtils.toByteArray(entity); 10 String result = new String(byteArray, "utf8"); 11 System.out.println(result);
四.使用HTTP协议的优势
随着请求规模的扩展,基于TCP协议的RPC的实现,需要考虑多线程并发、锁、I/O等复杂的底层细节,在大流量高并发的压力下,任何一个小的错误都可能被无限放大,最终导致程序宕机。而对于基于HTTP协议的实现来说,很多成熟的开源web容易已经帮其处理好了这些事情,如Apache,Tomcat,Jboss等,开发人员可将更多的精力集中在业务实现上,而非处理底层细节。


