红帽7 Apache服务部署静态网站
httpd 服务程序的功能是允许用户访问网站内容,因此 SELinux 肯定会默认放行用户对网
第一步:把虚拟机中安装系统的光盘设备中的系统镜像挂载到/media/cdrom
[root@localhost Desktop]# mkdir -p /media/cdrom [root@localhost Desktop]# mount /dev/cdrom /media/cdrom mount: /dev/sr0 is write-protected, mounting read-only
第二步:使用 Vim 文本编辑器创建 Yum 仓库的配置文件
[root@localhost Desktop]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/rhel7.repo [rhel7] name=rhel7 baseurl=file:///media/cdrom enabled=1 gpgcheck=0
第三步:动手安装 Apache 服务程序。注意,使用 yum 命令进行安装时,跟在命令后面的Apache 服务的软件包名称为 httpd。如果直接执行 yum install apache 命令,则系统会报错。

[root@localhost Desktop]# yum install httpd Loaded plugins: langpacks, product-id, subscription-manager ………………省略部分输出信息……………… Dependencies Resolved =============================================================================== Package Arch Version Repository Size =============================================================================== Installing: httpd x86_64 2.4.6-17.el7 rhel 1.2 M Installing for dependencies: apr x86_64 1.4.8-3.el7 rhel 103 k apr-util x86_64 1.5.2-6.el7 rhel 92 k httpd-tools x86_64 2.4.6-17.el7 rhel 77 k mailcap noarch 2.1.41-2.el7 rhel 31 k Transaction Summary =============================================================================== Install 1 Package (+4 Dependent packages) Total download size: 1.5 M Installed size: 4.3 M Is this ok [y/d/N]: y Downloading packages: ………………省略部分输出信息……………… Complete!
第四步:启用 httpd 服务程序并将其加入到开机启动项中,使其能够随系统开机而运行,从而持续为用户提供 Web 服务
[root@localhost Desktop]# systemctl start httpd [root@localhost Desktop]# systemctl enable httpd ln -s '/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service' '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user. target.wants/httpd.service'
然后打开Firefox浏览器,在地址栏里输入 127.0.0.1 并按回车,就可以看到用于提供 Web 服务的 httpd 服务程序的默认页面了

1、配置服务文件参数
配置文件
| 参数 | 存放位置 |
| 服务目录 | /etc/httpd |
| 主配置文件 | /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf |
| 网站数据目录 | /var/www/html |
| 访问日志 | /var/log/httpd/access_log |
| 错误日志 | /var/log/httpd/error_log |
配置 httpd 服务程序时最常用的参数以及用途描述
| 参数 | 用途 |
| ServerRoot | 服务目录 |
| ServerAdmin | 管理员邮箱 |
| User | 运行服务的用户 |
| Group | 运行服务的用户组 |
| ServerName | 网站服务器的域名 |
| DocumentRoot | 网站数据目录 |
| ErrorLog | 错误日志文件 |
| Directory | 网站数据目录的权限 |
| Listen | 监听的 IP 地址与端口号 |
| DirectoryIndex | 默认的索引页页面 |
| CustomLog | 访问日志文件 |
| Timeout | 网页超时时间,默认为 300 秒 |
DocumentRoot 参数用于定义网站数据的保存路径,其参数的默认值是把网站数据存放到/var/www/html 目录中;而当前网站普遍的首页面名称是 index.html,因
此可以向/var/www/html 目录中写入一个文件,替换掉 httpd 服务程序的默认首页面,该操作会立即生效。
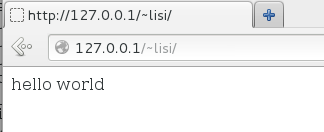
[root@localhost Desktop]# echo "hello world" > /var/www/html/index.html
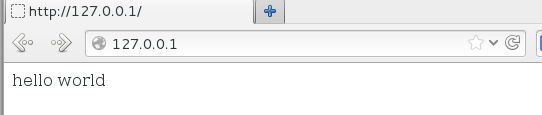
在默认情况下,网站数据是保存在/var/www/html 目录中,而如果想把保存网站数据的目录修改为/home/wwwroot 目录,该怎么操作呢?
第一步:建立网站数据的保存目录,并创建首页文件
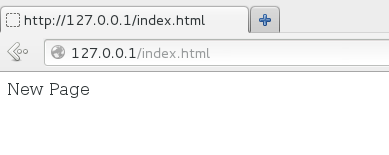
[root@localhost Desktop]# mkdir /home/wwwroot [root@localhost Desktop]# echo "New Page" > /home/wwwroot/index.html
第二步:打开 httpd 服务程序的主配置文件,将约第 119 行用于定义网站数据保存路径的参数 DocumentRoot 修改为 /home/wwwroot,同时还需要将约第 124 行用于定义目录权限的参数 Directory 后面的路径也修改为/home/wwwroot。配置文件修改完毕后即可保存并退出
[root@localhost Desktop]# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf 114 #………………省略部分输出信息……………… 115 # DocumentRoot: The directory out of which you will serve your 116 # documents. By default, all requests are taken from this directory, but 117 # symbolic links and aliases may be used to point to other locations. 118 # 119 DocumentRoot "/home/wwwroot" 120 121 # 122 # Relax access to content within /var/www. 123 # 124 <Directory "/home/wwwroot"> 125 AllowOverride None 126 # Allow open access: 127 Require all granted 128 </Directory>
………………省略部分输出信息………………
第三步:重新启动 httpd 服务程序并验证效果。但奇怪的是,为什么没看到应该显示的页面,而显示的是httpd服务程序的默认页面,按理来说,只有在网站的首页面文件不存
在或者用户权限不足时,才显示 httpd 服务程序的默认首页面。尝试访问http://127.0.0.1/index.html 页面时,竟然发现页面中显示“Forbidden,You don't have permission to access /index.html on this server.” 而这一切都是由于 SELinux 的原因
2、 SELinux 安全子系统
SELinux(Security-Enhanced Linux)是美国国家安全局在 Linux 开源社区的帮助下开发的一个强制访问控制(MAC,Mandatory Access Control)的安全子系统。SELinux
技术的目的是为了让各个服务进程都受到约束,使其仅获取到本应获取的资源。
例如,你在自己电脑上打开一个视频软件在看视频,然而它却在后台偷偷监听着浏览器中输入的密码信息,这显然不是它该做的事情,SELinux 安全子系统就是为了杜绝此类情况而
设计的,它能够从多方面监控违法行为:对服务程序的功能进行限制(SELinux 域限制可以确保服务程序做不了出格的事情);对文件资源的访问限制(SELinux 安全上下文确保文件资源只能被其所属的服务程序进行访问)。
SELinux 服务有三种配置模式
➢ enforcing:强制启用安全策略模式,将拦截服务的不合法请求。
➢ permissive:遇到服务越权访问时,只发出警告而不强制拦截。
➢ disabled:对于越权的行为不警告也不拦
[root@localhost Desktop]# vim /etc/selinux/config

SELinux 服务的主配置文件中,定义的是 SELinux 的默认运行状态,可以将其理解为系统重启后的状态,因此它不会在更改后立即生效。
getenforce 命令:获得当前 SELinux服务的运行模式
[root@localhost Desktop]# getenforce
Enforcing
为验证上面的情况确实是因为 SELinux 而导致的,使用setenforce [0|1]命令修改 SELinux 当前的运行模式(0 为禁用,1 为启用)。注意,这种修改只是临时的,在系统重启后就会失效
[root@localhost Desktop]# setenforce 0 [root@localhost Desktop]# getenforce Permissive
再次刷新网页,就会看到正常的网页内容了
httpd 服务程序的功能是允许用户访问网站内容,因此 SELinux 肯定会默认放行用户对网站的请求操作。但是,我们将网站数据的默认保存目录修改为了/home/wwwroot,而这就产生问题了。/home 目录是用来存放普通用户的家目录数据的,而现在,httpd提供的网站服务却要去获取普通用户家目录中的数据了,这显然违反了 SELinux 的监管原则。
现在,我们把 SELinux 服务恢复到强制启用安全策略模式,然后分别查看原始网站数据的保存目录与当前网站数据的保存目录是否拥有不同的 SELinux 安全上下文值
[root@localhost Desktop]# setenforce 1 [root@localhost Desktop]# ls -Zd /var/www/html -Z用于查看上下文 drwxr-xr-x. root root system_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0 /var/www/html [root@localhost Desktop]# ls -Zd /home/wwwroot drwxr-xr-x. root root unconfined_u:object_r:home_root_t:s0 /home/wwwroot
在文件上设置的 SELinux 安全上下文是由用户段、角色段以及类型段等多个信息项共同组成的。其中,用户段 system_u 代表系统进程的身份,角色段 object_r 代表文件目录的角色,类型段 httpd_sys_content_t 代表网站服务的系统文件。针对当前这种情况,我们只需要使用 semanage 命令,将当前网站目录/home/wwwroot 的SELinux 安全上下文修改为跟原始网站目录的一样就可以了
semanage 命令
semanage 命令用于管理 SELinux 的策略,格式为“semanage [选项] [文件]”。
➢ -l 参数用于查询;
➢ -a 参数用于添加;
➢ -m 参数用于修改;
➢ -d 参数用于删除。
可以向新的网站数据目录中新添加一条 SELinux 安全上下文,让这个目录以及里面的所有文件能够被 httpd 服务程序所访问到
[root@localhost Desktop]# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t /home/wwwroot -t表示具体要使用什么值 目录不能有最后那个斜杠 [root@localhost Desktop]# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t /home/wwwroot/*
执行上述设置之后,还无法立即访问网站,还需要使用 restorecon 命令将设置好的SELinux 安全上下文立即生效。在使用 restorecon 命令时,可以加上-Rv 参数对指定的目录进
行递归操作,以及显示 SELinux 安全上下文的修改过程。最后,再次刷新页面,就可以正常看到网页内容了
[root@localhost Desktop]# restorecon -Rv /home/wwwroot/ restorecon reset /home/wwwroot context unconfined_u:object_r:home_root_t:s0->unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0 restorecon reset /home/wwwroot/index.html context unconfined_u:object_r:home_root_t:s0->unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0

3、个人用户主页功能
如果想在系统中为每位用户建立一个独立的网站,通常的方法是基于虚拟网站主机功能来部署多个网站。httpd 服务程序提供的个人用户主页功能完全可以以胜任这个工作。该功能可以让系统内所有的用户在自己的家目录中管理个人的网站,而且访问起来也非常容易。
第一步:在 httpd 服务程序中,默认没有开启个人用户主页功能。需要编辑配置文件,然后在第 17 行的 UserDir disabled 参数前面加上井号(#),表示让 httpd 服务程序开启个人用户主页功能;同时再把第 24 行的 UserDir public_html 参数前面的井号(#)去掉(UserDir 参数表示网站数据在用户家目录中的保存目录名称,即 public_html 目录)。最后,
在修改完毕后记得保存。
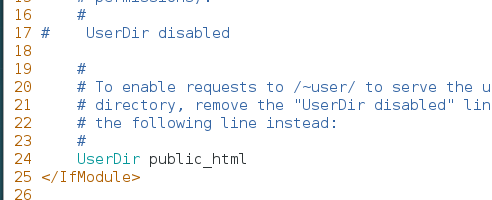
第二步:在用户家目录中建立用于保存网站数据的目录及首页面文件。另外,还需要把家目录的权限修改为 755,保证其他人也有权限读取里面的内容
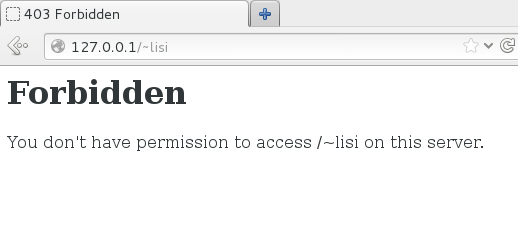
[lisi@localhost ~]$ mkdir public_html [lisi@localhost ~]$ echo "hello world" > public_html/ [lisi@localhost ~]$ echo "hello world" > public_html/index.html
第三步:重新启动 httpd 服务程序,在浏览器的地址栏中输入网址,其格式为“网址/~用户名”(其中的波浪号是必需的,而且网址、波浪号、用户名之间没有空格),从理论上来讲就可以看到用户的个人网站了。但显示的确是系统报错页面。其实还是SELinux的问题
第四步:httpd 服务程序在提供个人用户主页功能时,该用户的网站数据目录本身就应该是存放到与这位用户对应的家目录中的,所以应该不需要修改家目录的 SELinux 安全上下文。但是,还有Linux域,Linux 域确保服务程序不能执行违规的操作,只能本本分分地为用户提供服务。httpd 服务中突然开启的这项个人用户主页功能到底有没有被 SELinux 域默认允许呢?
getsebool 命令
getsebool 命令查询并过滤出所有与 HTTP 协议相关的安全策略。其中,off 为禁止状态,on 为允许状态
[root@localhost Desktop]# getsebool -a | grep http -a表示显示所有安全策略 httpd_anon_write --> off httpd_builtin_scripting --> on httpd_can_check_spam --> off httpd_can_connect_ftp --> off httpd_can_connect_ldap --> off httpd_can_connect_mythtv --> off httpd_can_connect_zabbix --> off httpd_can_network_connect --> off httpd_can_network_connect_cobbler --> off httpd_can_network_connect_db --> off httpd_can_network_memcache --> off httpd_can_network_relay --> off httpd_can_sendmail --> off httpd_dbus_avahi --> off httpd_dbus_sssd --> off httpd_dontaudit_search_dirs --> off httpd_enable_cgi --> on httpd_enable_ftp_server --> off httpd_enable_homedirs --> off httpd_execmem --> off httpd_graceful_shutdown --> on httpd_manage_ipa --> off httpd_mod_auth_ntlm_winbind --> off httpd_mod_auth_pam --> off httpd_read_user_content --> off httpd_run_stickshift --> off httpd_serve_cobbler_files --> off httpd_setrlimit --> off httpd_ssi_exec --> off httpd_sys_script_anon_write --> off httpd_tmp_exec --> off httpd_tty_comm --> off httpd_unified --> off httpd_use_cifs --> off httpd_use_fusefs --> off httpd_use_gpg --> off httpd_use_nfs --> off httpd_use_openstack --> off httpd_use_sasl --> off httpd_verify_dns --> off named_tcp_bind_http_port --> off prosody_bind_http_port --> off
相应的安全策略是 httpd_enable_homedirs ,为关闭状态,可以用 setsebool 命令来修改 SELinux 策略中各条规则的布尔值,在 setsebool 命令后面加上-P 参数,让修改后的 SELinux 策略规则永久生效且立即生效。随后刷新网页。
[root@localhost Desktop]# setsebool -P httpd_enable_homedirs=on
有时,网站的拥有者并不希望直接将网页内容显示出来,只想让通过身份验证的用户访客看到里面的内容,这时就可以在网站中添加口令功能了。
第一步:先使用 htpasswd 命令生成密码数据库。-c 参数表示第一次生成;后面再分别添加密码数据库的存放文件,以及验证要用到的用户名称(该用户不必是系统中已有的本地账户)。
[root@localhost Desktop]# htpasswd -c /etc/httpd/passwd test New password: 输入用于网页验证的密码 Re-type new password: 再次输入 Adding password for user test
第二步:编辑个人用户主页功能的配置文件。把第 32~35 行的参数信息修改成下列内容,随后保存并退出配置文件,重启 httpd 服务程序即可生效。
[root@localhost Desktop]# vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/userdir.conf 27 # 28 # Control access to UserDir directories. The following is an example 29 # for a site where these directories are restricted to read-only. 30 # 31 <Directory "/home/*/public_html"> 32 authuserfile "/etc/httpd/passwd" #刚生成出来的密码验证文件保存路径 33 authname "Enter passwd" #当用户尝试访问个人用户网站时的提示信息 34 authtype basic 35 require user test #用户进行账户密码登录时需要验证的用户名称,和生产密码验证文件时的用户名称一样 36 </Directory> 37 [root@localhost Desktop]# systemctl restart httpd
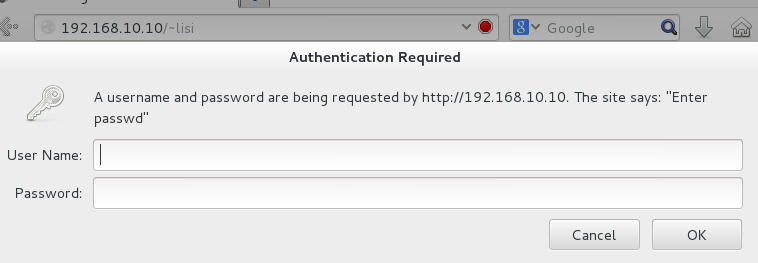
此后,当用户再想访问某个用户的个人网站时,就必须要输入账户和密码才能正常访问了。另外,验证时使用的账户和密码是用 htpasswd 命令生成的专门用于网站登录的口令密码,而不是系统中的用户密码





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号