vue8-vuex、路径配置别名、promise
目录
十三、路径配置别名
vue-cli2
-
配置别名:\build\webpack.base.conf.js
resolve: { extensions: ['.js', '.vue', '.json'], alias: { '@': resolve('src'), 'assets': resolve('src/assets'), 'components': resolve('src/components'), 'views': resolve('src/views'), } }, -
项目中使用
-
html中: 前面要加 ~
<tab-bar-item path="/home" activeColor="blue"> <img slot="item-icon" src="~assets/images/tabbar/home.png" alt="首页" /> <img slot="item-icon-active" src="~assets/images/tabbar/home_active.png" alt /> <div slot="item-text">首页</div> </tab-bar-item> -
import中使用
import TabBarItem from "components/tabbar/TabBarItem";
-
vue-cli3
- 根目录下新建vue.config.js
- 在vue.config.js中的chainWebpack中配置config.resolve.alias.set('@', resolve('src')).set('components', resolve('src/components'));
十四、promise
是什么?
是异步编程的一种解决方案
什么时候使用异步呢?
- 网络请求
- 回调函数的时候
promise用法
- 构造器有一个参数,是函数,这个函数有两个参数都是函数
- resolve:异步请求成功调的函数,被调用之后会调用then()
- then:来处理业务代码,参数是一个函数,可通过resolve来传入data
- reject:异步失败的时候调的函数,也可以传输数据到catch
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('传入then 中的 data')
}, 1500)
}).then(data => {
console.log(data);
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
// resolve('内部的resolve')
reject('内部的reject')
}, 1500)
})
}).catch(data => {
console.log(data);
})
-
promise异步完成后会有三种状态
- pendding等待
- fullfill 完全满足
- reject 拒绝|次品
-
promise的另一种写法
- then中也可以传两个函数,第一个是成功,第二个是失败
new Promise((resolve, reject) => { setTimeout(() => { resolve('传入then 中的 data') // reject('失败') }, 1500) }).then(data => { console.log(data); },reject => { console.log(reject); }) -
再简化
- new Promise(resolve) ==>Promise.resolve(data) ==> data
- throw 'msg'也会被catch()捕获
// new Promise(resolve) ==>Promise.resolve(data) ==> data
//throw 'msg'也会被catch()捕获
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('第一层...')
}, 1500)
}).then(data => {
console.log(data);
return Promise.resolve('第二层...')
// return Promise.reject('额鹅鹅鹅')
throw 'dsadsa'
}).then(data=>{
console.log(data);
return 'aaa'
}).then(data=>{
console.log(data);
}).catch(err=>{
console.log(err);
})
- Promise.all([PromiseInstance...])
- 多个异步请求同时等待成功后才执行后续代码
- 像是java-juc的栅栏
Promise.all([
new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
resolve('1111111')
},1000)
}),
new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
resolve('222222')
},2000)
})
]).then(data=>{
//1111111,222222
console.log(data.toString())
})
十五、vuex
介绍
- 是什么?
- 是为vue程序提供一个集中状态管理模式和库
- 充当应用程序中所有组件的特殊共享变量的集中存储
- 这些共享状态都是响应式的
- vuex修改状态的流程
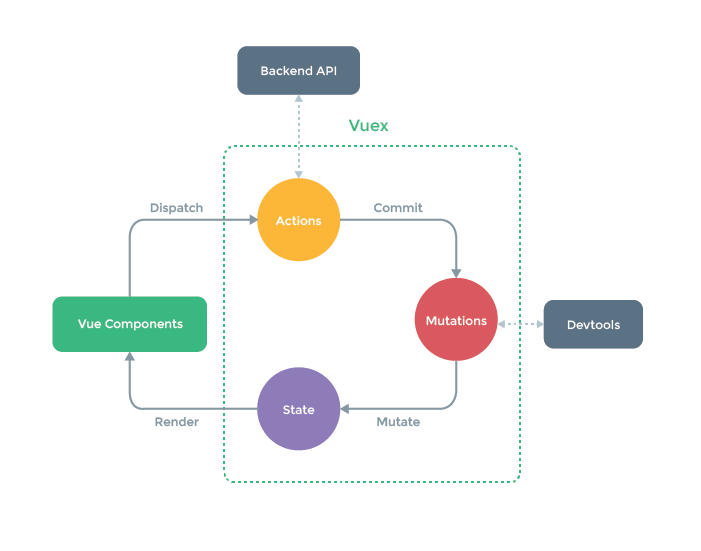
-
通过提交 mutation 的方式,而非直接改变
store.state.count,是因为我们想要更明确地追踪到状态的变化。这个简单的约定能够让你的意图更加明显,这样你在阅读代码的时候能更容易地解读应用内部的状态改变。此外,这样也让我们有机会去实现一些能记录每次状态改变,保存状态快照的调试工具。有了它,我们甚至可以实现如时间穿梭般的调试体验。由于 store 中的状态是响应式的,在组件中调用 store 中的状态简单到仅需要在计算属性中返回即可。触发变化也仅仅是在组件的 methods 中提交 mutation。
-
actions步骤可以省略,一般异步的操作放在actions中完成后放在mutations中
-
mutations只能是同步的操作,devtools监听不到异步操作
使用步骤
store用法
state用法
state中所有的已定义的属性都是响应式的,新加入的不被响应:因为属性初始化后,都被一个dep对象=【watcher,watcher..】监控,后面加入的不受监控
-
npm install vuex --save -
新建、src/store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
//1.安装,底层会调用Vuex.install
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 2.创建对象
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
}, mutations: {
//state必须传,默认会传进来
increment(state) {
state.count++
}
}, actions: {}, getters: {}, modules: {}
})
// 3.导出store对象
export default store
- main.js挂载插件
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import store from "./store";
Vue.config.productionTip = false
/* eslint-disable no-new */
new Vue({
el: '#app',
store,
render: h => h(App)
})
- App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<h2>{{$store.state.count}}</h2>
<button @click="increment">+</button>
<hello-vuex></hello-vuex>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import HelloVuex from "./components/HelloVuex";
export default {
name: 'App',
methods:{
increment(){
this.$store.commit('increment')
}
},
components: {
HelloVuex
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
- HelloVuex.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>{{$store.state.count}}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "HelloVuex"
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
getters用法
有点像computed的概念
- App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<h2>{{$store.state.count}}</h2>
<button @click="increment">+</button>
<h2>年龄大于20:{{$store.getters.more20Person}}</h2>
<h2>年龄大于20个数:{{$store.getters.more20PersonCount}}</h2>
<h2>年龄大于age个数:{{$store.getters.moreAgePerson(13)}}</h2>
<hello-vuex></hello-vuex>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import HelloVuex from "./components/HelloVuex";
export default {
name: 'App',
methods:{
increment(){
this.$store.commit('increment')
}
},
components: {
HelloVuex
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
- store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
//1.安装,底层会调用Vuex.install
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 2.创建对象
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0,
persons: [
{name: 'a', age: 12},
{name: 'b', age: 23},
{name: 'c', age: 32},
{name: 'd', age: 24}
]
}, mutations: {
//state必须传,默认会传进来
increment(state) {
state.count++
}
},
actions: {},
//最多只能写两个参数时state,getters,默认会传进来
getters: {
more20Person(state) {
return state.persons.filter(per=>per.age>20)
},
more20PersonCount(state,getters){
// 这里不用写括号
return getters.more20Person.length
},
//返回一个函数可以传动态的参数
moreAgePerson(state){
return (age)=>{
return state.persons.filter(per=>per.age>age)
}
}
},
modules: {}
})
// 3.导出store对象
export default store
mutations
- 官方规定修改state只能用mutations
- 分为两部分函数名叫做字符串时间类型
- 代码块叫做回调函数
- 可以传多个参数第一个是store,后面的自定义叫做payload(负载 )
//store/index.js
mutations: {
//state必须传,默认会传进来
increment(state) {
state.count++
},
add(state,num){
state.count +=num
}
}
//app.vue
methods:{
increment(){
this.$store.commit('increment')
},
add(num){
this.$store.commit('add',num)
}
}
第二种提交风格
- 提交的参数会当成一个对象来取
inc(num){
this.$store.commit({
type:'inc',
num
})
}
mutations: {
//state必须传,默认会传进来
increment(state) {
state.count++
},
add(state,num){
state.count +=num
},
//当成对象处理参数
inc(state,payLoad){
state.count +=payLoad.num
}
}
响应式操作
update(state){
//响应式
// state.persons.push({name:'e',age:99})
//响应式
// state.person={name:'f',age:101}
//新加的属性不会被监控,只有在其他任意的属性变化一次后他会刷新一次
// state.person.add=111
// state.person['address']=222
//删除一个对象的属性
// delete state.person.age
//vue set value是响应式的,key必须是字符串
// Vue.set(state.person,'asd','vue set value是响应式的')
Vue.delete(state.person,'age')
}
mutations中方法的官方定义
-
避免写错,定义一个常量对象,在使用的文件中导入
-
定义
[const](){}
//mutation-type.js
export const INCREMENT='increment'
export const ADD='add'
export const INC='inc'
export const UPDATE='update'
import {INCREMENT,ADD,UPDATE,INC} from "./mutation-type";
//app.vue
update(){
this.$store.commit({
type:UPDATE,
})
}
//index.js
mutations: {
//state必须传,默认会传进来
[INCREMENT](state) {
state.count++
},
[ADD](state,num){
state.count +=num
},
//当成对象处理参数
[INC](state,payLoad){
state.count +=payLoad.num
},
[UPDATE](state){
Vue.delete(state.person,'age')
}
}
actions
- mutations的异步方法修改的数据,插件是跟踪不到的
- 所有的异步操作都应该放在actions中处理,处理后的回调放在mutations中处理
- 修改state的唯一途径就是mutations
- actions中的默认参数是上下文context(context=store)
action处理异步操作:
//app.vue
aUpdate(){
// this.$store.dispatch('aUpdate',{
// msg:'参数信息',
// success:(data)=>{console.log(data)}
// })
//第二种方法,异步函数返回的promise对象
this.$store.dispatch('aUpdate',{
msg:'参数信息'
}).then(res=>{
console.log('完成异步操作');
console.log(res);
})
}
//index.js
actions: {
// aUpdate(context,payload) {
// // console.log('默认参数是上下文对象: ',context)
// setTimeout(function () {
// context.commit('aUpdate',payload)
// }, 1000)
// }
//第二种方式返回一个promise对象,在调用处可以使用
aUpdate(context, payload) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('aUpdate', payload)
resolve(12312)
}, 1000)
})
}
}
modules
- 只在一个state中存数据可能因为数据量过大而臃肿,所以在modules中分多个模块
- 取值$store.state. modulesName .propertise
- 子模块:
- state:需要指定模块名,可以和父模块同名
- getters : 和父模块同名会报错,可以直接访问不需要指定模块名
- actions|mutations : 和父模块名字相同都会调用,先调用父模块的,所以不要定义相同的名字
显示:app.vue
<h2>-------------state--modules的内容---------</h2>
<h2>{{$store.state.a.name}}</h2>
<h2>{{$store.getters.getModuleA}}</h2>
<h2>{{$store.getters.getModuleA_add('age')}}</h2>
<h2>{{$store.getters.getModuleA_add_root}}</h2>
<button @click="moduleA">模块a修改name</button>
<button @click="asyncUpdateModuleA">异步模块a修改name</button>
methods:{
moduleA() {
this.$store.commit('aUpdate','模块a名字修改')
},
asyncUpdateModuleA(){
this.$store.dispatch('asyncUpdateModuleA')
}
}
index.js
modules: {
a:{
//需要指定模块名,可以和父模块同名
state:{name:'module_a',person:123},
//和父模块同名会报错,可以直接访问不需要指定模块名
getters:{
getModuleA(state){
return state.name+'_getModuleA'
},
getModuleA_add(state,getters){
return (age) => {
return getters.getModuleA+age
}
},
//三个默认参数
getModuleA_add_root(state,getters,rootState){
return state.name+getters.getModuleA+'_add_'+rootState.count
}
},
// 和mutations使用差不多
actions:{
//也可以使用对象的解构,详见es6
asyncUpdateModuleA(context){
setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit('aUpdate','异步修改子模块')
},1000)
}
},
mutations:{
//和父模块名字相同都会调用,先调用父模块的,所以不要定义相同的名字
aUpdate(state,payload){
state.name=payload
console.log('child mutations 被调用')
}
},
modules:{}
},
//模块b
b:ModuleB
}
抽离index.js
- state一般是不抽取出来的
- modules是新建一个./modules/文件夹,在里面建立模块
- 抽离好的文件
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import mutations from "./mutations";
import actions from "./actions";
import getters from "./getters";
import module_a from "./modules/module_a";
//1.安装,底层会调用Vuex.install
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 2.创建对象
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0,
persons: [
{name: 'a', age: 12},
{name: 'b', age: 23},
{name: 'c', age: 32},
{name: 'd', age: 24}
],
person: {
name: 'g',
age: 100
}
},
mutations,
actions,
getters,
modules: {
a: module_a
}
})
// 3.导出store对象
export default store


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号