AP World History复习提纲(unit 3~uint4)
theme 1 Humans and the environment
theme 2 cultural developments and interactions(important)
theme3 governance
- Centralizing Control In Europe: King James1 believed in the divine right of kings, a common calim from the Middle Ages that the riught to rule was given to aking by God.
- Engliand's Gentry Officials(上流社会): In England, the Tudors relied on justices of the peace, officials selected by the landed gentry to "swear that as Justices of the Peace..in all articles in the King's Commission to you directed, ye shall do equal right to the poor and to the rich after your cunning wit, and power, and after the laws and customs of the realm and statutes thereof made,". In 1689, England's rulers William and Mary signed the English Bill of Rights which iassured individual civil liberties.
- Absolutism in France: In contrast to developments in England, the French government became more absolute. Louis XIII and his minister Cardinal Richelieu moved to even greater centralization of the government and development of the system of intendants-royal officials,tax farmers. The sun king, Louis XIV espoused a theory of divine right and was a virtual dictator. He kept nobles close to him in his palace at Versailles, making it difficult for them to act independently against him.
- Reigning in Control of the Russian Empire: boyars-noble landowning class stood the top of the pyramid.
- the efforts of Ivan IV, boyar class experienced similar tensions with the rulers. Ivaj established a paramilitary force lyoal to him. - Peter the Great: the **Romanov Dynasty** took control of Russia after a period of turmoil following Ivan's death.The rise to power of **Peter I**, illustrates these conflicting ambitions.
-
Centralizing Control in the Ottoman Empire
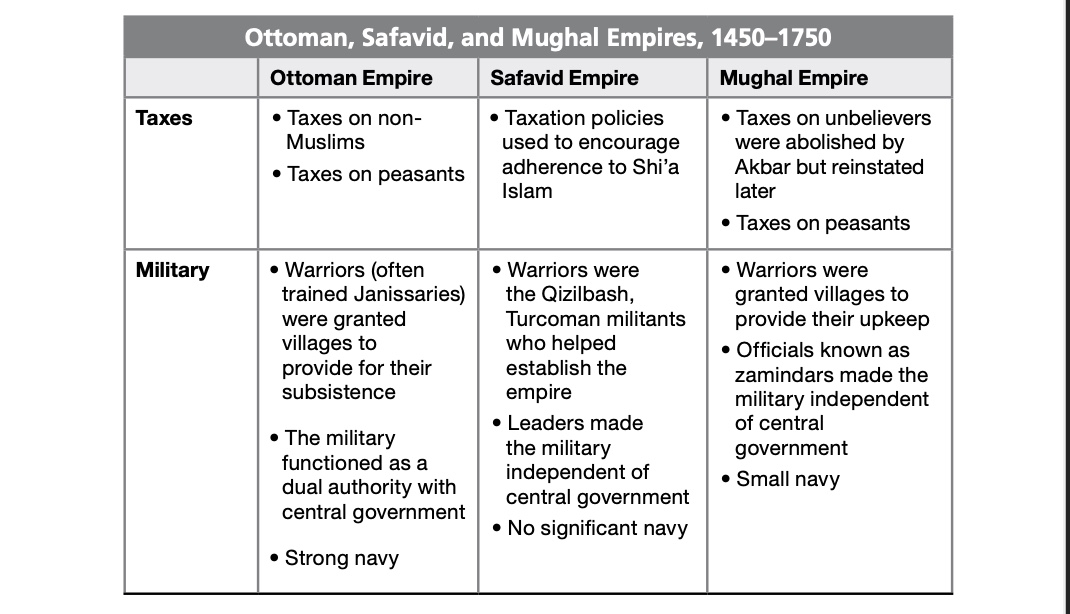
- devshirme: selection system called devshirme.Janissaries-formed elite forces in the Ottoman army.
-
Centralizing Control in East and South Asia
- Consolidating Power in Japan: military leaders called shoguns ruled Japan in the emperor's name from the 12th to the 15th centuries. Yet conflict between landholding aristocrats called daimyo left Japan in disarray. After his death in 1598, the center of power shifted to the city of Edo (Tokyo), controlled by the daimyo Tokugawa Ieyasu (ruled 1600–1616), who was declared shogun in 1603. His successors would continue to rule Japan into the mid-19th century, in an era known as the Period of Great Peace. Tokugawa shogunate set about reorganizing the governance of Japan in order to centralize control over what was essentially a feudal system.
- Consolidating Mughal Power in South Asia: Akbar proved to be the most capable of the Mughal rulers.From his capital in Delhi, he established an effcient government and a system of fairly administered laws.Paid government officials called zamindars were in charge of specific duties.
theme4 economic systems
- Financing Empires: Taxation in Russia, Otooman and Mughal Taxasion.
theme5 social interactions and organization(important)
-
Europe: The year 1450 has traditionally signified the ending of the medieval period and the begnning of the early modern period and the beginning of the early modern period.invention of the Gutenburg printing press followed by an increase in literacy.The nature of new monarchies in Europe was the result of the desire of certain leaders to centralize power by controlling stuff.
Russia: Ivan IV: set about to expand the Russian border eastward. control of the Volga: allowed the Stroganoffs(地主) to hire band of fierce peasant warriors known as Cossacks to fight the local tribes and the Siberian khan.to the pacific. -
East Asia: China. conflicts with the west.
-
Rise of the Islamic Gunpowder Empires:
- The Rule of Tamerlane: The invasion of Central Asia and the Middle East by tamerlne set the stage for the rise of the Turkic empires. The Eurasian steppes were the birthplace of ghazi deal-model for warrior life that blended the cooperative values of nomadic culture with the willingness to serve as a holy fighter for Islam.
-
The Ottoman Empire:
- Mehmed II:
- Suleiman I
-
The Safavids: An early Safavid military hero named Ismail conquered most of Persia and pushed into Iraq.He soon conuqered all of Iran and was proclaimed shah(equivalent to king or emperor).Shah Abbas: presided over the Safavid Empire at its height. women are rarely mentioned, but were permited to particpate in their societies.
-
Mughal India: Mughal Empire under Akbar was one of the richest and best governed states in the world. Castes are strict social groupings desgnated at birth.
-
Decline of the Gunpowder Empires
- Ottoman :after Suleiman's death, a European foce made up mostly of Spaniards and Venetians defeated the Ottomans in a great naval conflict known as the Battle of Lepanto.
- Safavid Decline: the leader combined lavish lifestyles and militray spending with falling revenues, resulting in a weakened economy.
- Mughal Decline: Shah Jahan's son and scuessor, inherited an empire weakened by corruption and the failure to keep up with the military innovations of external enemies.
theme6 technology and innovation
- Gunpowder Empires: large, multiethnic states in Southwest, Central, and South Asia that relied on firarms to conquer and control territories.
reasoning process: comparison
reasoning process: causation
reasoning process: continuity and change
本文作者:zplqwq
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/zplqwq/p/18091553
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步