BFS广度优先遍历-寻找最短路径(无权图)
前言:BFS广度优先遍历-寻找最短路径学习和实现笔记
dijkstra是bfs的升级版,就是说如果求最短路径,当图从无权值变成有权值时,bfs不再适用了,于是我们用dijkstra方法。换句话说,对于无权值图,dijkstra方法跟bfs是一致的。你可以画个无权图,用dijkstra走一遍,发现其实这就是bfs。
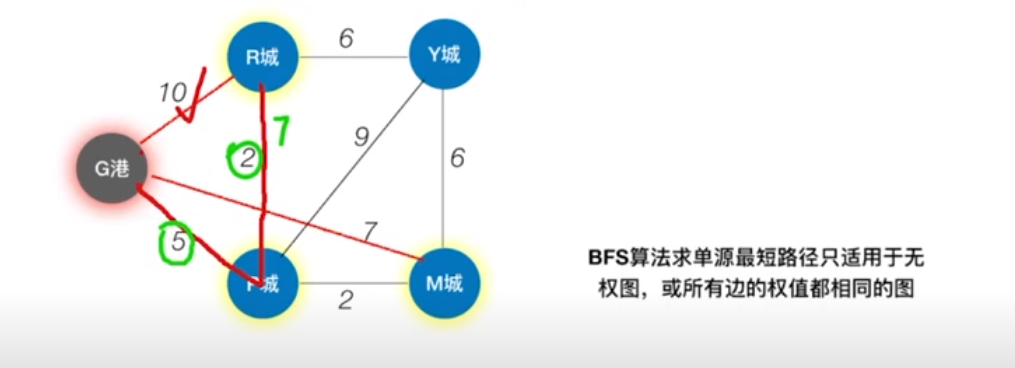
这里举个例子,就比如如下图所示,如果是从G港开始走的话,那么想要求到R城的最短路径,如果是BFS的话那么直接就是G-R之间最短,但是实际上在有权图中的话,G-P-R才是最短的,当用dijkstra算法来寻找的时候,dijkstra算法能够算出带有有权值的图的最短路径!
其实之前已经实现过关于图的BFS广度优先遍历算法了,其中在寻找最短路径实现,只需要加以修改一点内容即可
这里需要多创建一个结构体来记录每次遍历完当前顶点的邻接矩阵,然后需要从一个顶点到另外一个顶点之间的路径距离
其实就是只需要在每次在判断当前顶点的邻接顶点的时候,通过结构体来判断与当前顶点之间的距离即可,然后再每次顶点与原顶点的基础上再加上指定顶点到当前顶点的距离
typedef struct _VexPath{
int pathValue; // 路径长度
int preVex; // 前驱节点
}VexPath;
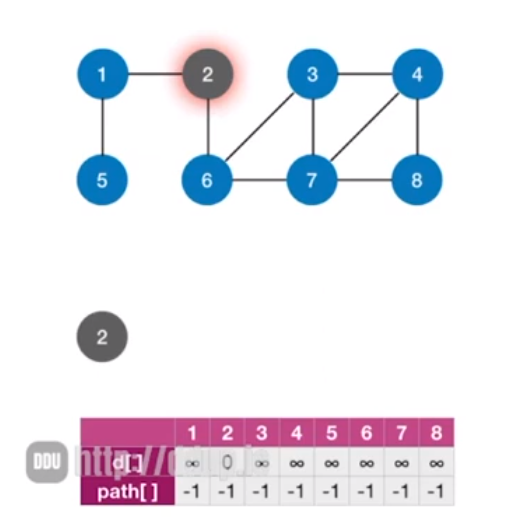
这样说可以不太好理解,这里通过一个图来进行观察演示,初始状态如下,如下图所示,因为这里找的是从顶点2出发,顶点2和自身的距离是0,所以这里距离就设置为0
-
这里要找的是从顶点2出发,来找无权图之间各个顶点之间的最短路径
-
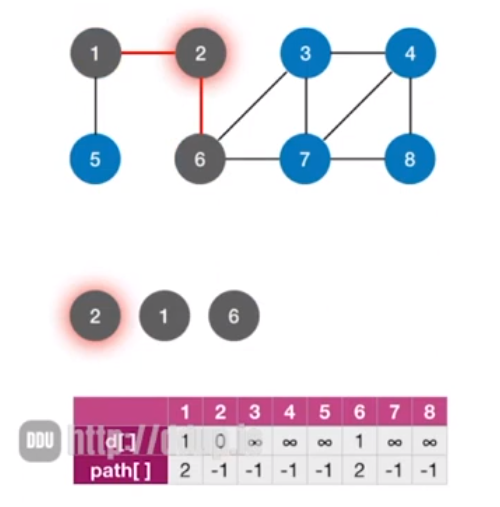
首先与顶点2相邻的顶点有顶点1和顶点6,那么就会将顶点1和顶点6对应的距离+1,并且将顶点1和顶点6的前驱节点设置为顶点2的下标,这里通过队列来进行存储顶点1和顶点6
- 接着第二次的时候,队列中取出顶点1来进行上述一样的操作,直到队列中的元素为空
比如BFS优先遍历和寻找最短路径的区别代码如下所示:
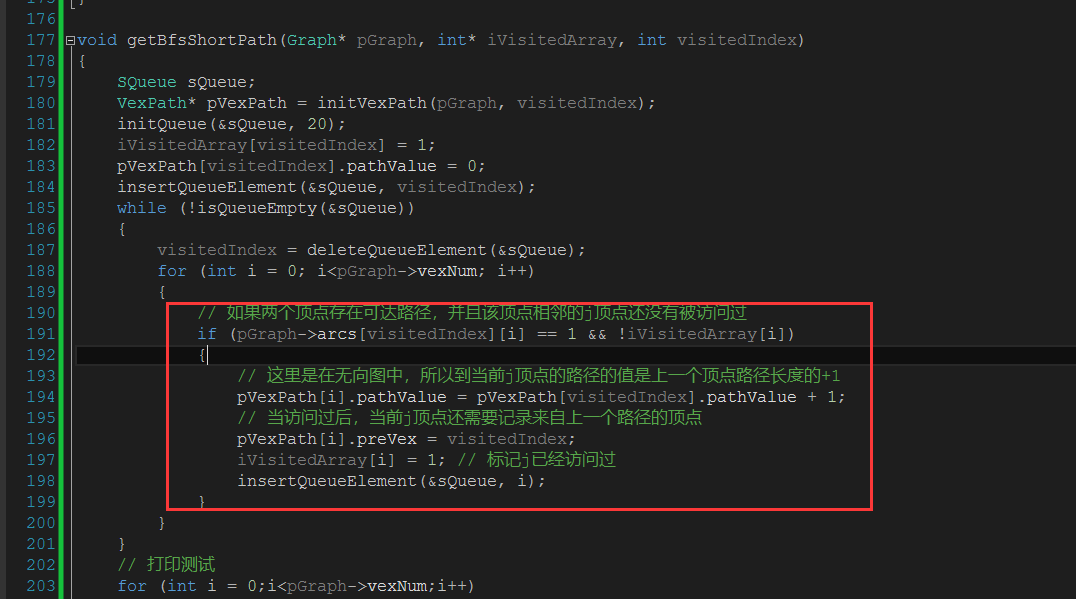
BFS寻找最短路径实现
最终的实现代码如下
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define MAX 32676
typedef int ElemType;
typedef int Status;
typedef char VexType;
typedef struct _Graph
{
int vexNum;
int arcNum;
int** arcs;
char* vexs;
}Graph, *PGraph;
typedef struct _SQueue{
ElemType* pQueue;
int rear;
int front;
int currentLength;
int initLength;
}SQueue, *PSQueue;
Status initQueue(SQueue* psQueue, int iSize)
{
if (psQueue == NULL)
return ERROR;
psQueue->pQueue = (ElemType*)malloc(iSize*sizeof(int));
psQueue->front = 0;
psQueue->rear = 0;
psQueue->currentLength = 0;
psQueue->initLength = iSize;
return OK;
}
Status insertQueueElement(SQueue* psQueue, ElemType elem)
{
if (psQueue->currentLength == psQueue->initLength)
return ERROR;
psQueue->pQueue[(psQueue->rear) % psQueue->initLength] = elem;
psQueue->currentLength++;
psQueue->rear = (psQueue->rear + 1) % psQueue->initLength;
return OK;
}
int getQueueCurrentLength(SQueue* psQueue)
{
return psQueue->currentLength;
}
ElemType deleteQueueElement(SQueue* psQueue)
{
ElemType elem;
if (getQueueCurrentLength(psQueue) == 0)
return ERROR;
elem = psQueue->pQueue[psQueue->front];
psQueue->currentLength--;
psQueue->front = (psQueue->front + 1) % psQueue->initLength;
return elem;
}
ElemType getHeadQueueElement(SQueue* psQueue)
{
if (psQueue->currentLength != psQueue->initLength)
return ERROR;
return psQueue->pQueue[psQueue->front];
}
void travelQueueElement(SQueue* psQueue)
{
while (psQueue->currentLength != 0)
{
printf("current elem -> %d\n", deleteQueueElement(psQueue));
}
}
Status isQueueEmpty(SQueue* psQueue)
{
if (psQueue->front == psQueue->rear)
return OK;
return ERROR;
}
Graph* initGraph(int vexNum)
{
Graph* pGraph = NULL;
if (pGraph == NULL)
{
pGraph = (Graph*)malloc(sizeof(Graph));
memset(pGraph, 0, sizeof(Graph));
if (pGraph == NULL)
return NULL;
pGraph->vexNum = vexNum; //
pGraph->vexs = (char*)malloc(sizeof(pGraph->vexNum));
memset(pGraph->vexs, 0, sizeof(pGraph->vexNum));
pGraph->arcNum = 0; //
pGraph->arcs = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*)* pGraph->vexNum);
memset(pGraph->arcs, sizeof(int*)* pGraph->vexNum, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < pGraph->vexNum; i++)
{
pGraph->arcs[i] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)* pGraph->vexNum);
memset(pGraph->arcs[i], 0, sizeof(int)*pGraph->vexNum);
}
}
return pGraph;
}
Status createGraph(Graph** pGraph, char* vexs, int* arcs)
{
if (*pGraph == NULL)
return ERROR;
for (int i = 0; i<(*pGraph)->vexNum; i++)
{
*((*pGraph)->vexs + i) = *(vexs + i);
for (int j = 0; j<(*pGraph)->vexNum; j++)
{
(*pGraph)->arcs[i][j] = *(arcs + i*((*pGraph)->vexNum) + j);
printf("%d ", (*pGraph)->arcs[i][j]);
if ((*pGraph)->arcs[i][j] == 1)
(*pGraph)->arcNum++;
}
printf("\n");
}
(*pGraph)->arcNum /= 2;
return OK;
}
// BFS广度优先遍历算法的实现
// 实现的思路其实跟树的层序遍历是一样的
// 当遍历的一个点之后
Status BFS(Graph* pGraph, int* iVisitedArray, int visitedIndex)
{
SQueue sQueue;
if (pGraph == NULL)
return ERROR;
initQueue(&sQueue, 10);
iVisitedArray[visitedIndex] = 1;
insertQueueElement(&sQueue, pGraph->vexs[visitedIndex]);
while (!isQueueEmpty(&sQueue))
{
ElemType elem = deleteQueueElement(&sQueue);
printf("%c ", elem);
for (int i = 0;i<pGraph->vexNum;i++)
{
for (int j = 0;j<pGraph->vexNum;j++)
{
if (pGraph->arcs[i][j] == 1 && !iVisitedArray[j])
{
iVisitedArray[j] = 1;
insertQueueElement(&sQueue, pGraph->vexs[j]);
}
}
}
}
return OK;
}
typedef struct _VexPath{
int preVex;
int pathValue;
}VexPath;
VexPath* initVexPath(Graph* pGraph)
{
VexPath* pVexPath = (VexPath*)malloc(sizeof(VexPath) * pGraph->vexNum);
for(int i=0;i<pGraph->vexNum;i++)
{
pVexPath[i].preVex = MAX;
pVexPath[i].pathValue = -1;
}
return pVexPath;
}
void getShort(Graph* pGraph, VexPath* pVexPath, int* iVisitedArray, int visitedIndex)
{
SQueue sQueue;
initQueue(&sQueue, 10);
iVisitedArray[visitedIndex] = 1;
pVexPath[visitedIndex].pathValue = 0;
insertQueueElement(&sQueue, visitedIndex);
while (!isQueueEmpty(&sQueue))
{
visitedIndex = deleteQueueElement(&sQueue);
for (int i = 0;i<pGraph->vexNum;i++)
{
if (pGraph->arcs[visitedIndex][i] == 1 && !iVisitedArray[i])
{
pVexPath[i].pathValue = pVexPath[visitedIndex].pathValue+1;
pVexPath[i].preVex = visitedIndex;
iVisitedArray[i] = 1;
insertQueueElement(&sQueue, i);
}
}
}
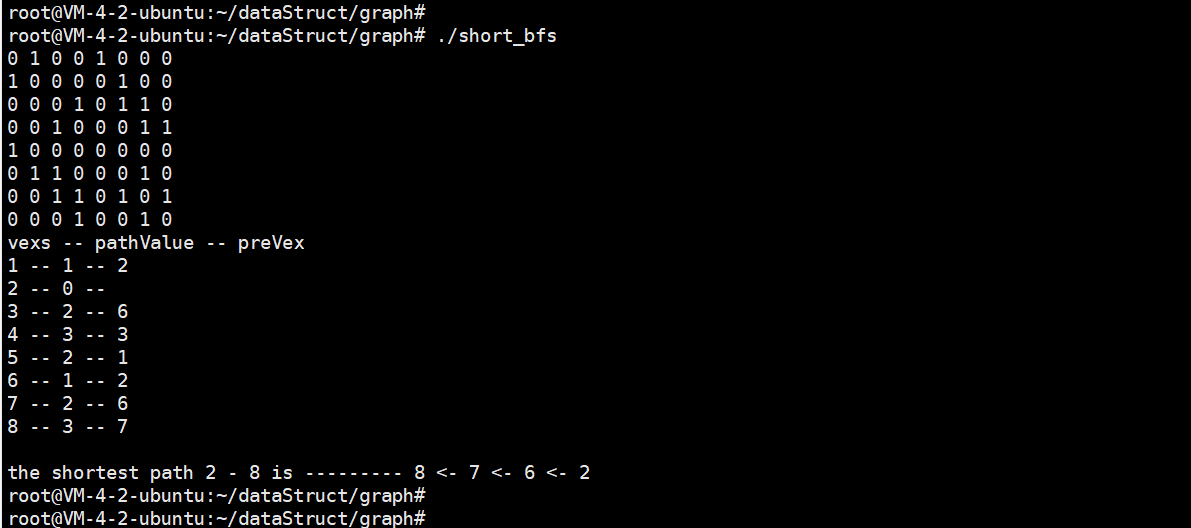
printf("vexs -- pathValue -- preVex\n");
for(int i=0;i<pGraph->vexNum;i++)
printf("%c -- %d -- %c\n", pGraph->vexs[i], pVexPath[i].pathValue, pGraph->vexs[pVexPath[i].preVex]);
}
// get vex1 how to go vex2
void getVexShortPath(Graph* pGraph, VexPath* pVexPath, int vexIndex1, int vexIndex2)
{
int iPreVex;
int vexIndex1Value = pVexPath[vexIndex1].pathValue;
printf("the shortest path %c - %c is --------- %c <- ", pGraph->vexs[vexIndex1], pGraph->vexs[vexIndex2], pGraph->vexs[vexIndex2]);
iPreVex = pVexPath[vexIndex2].preVex;
for (int i = 0;i<8;i++)
{
printf("%c <- ", pGraph->vexs[iPreVex]);
iPreVex = pVexPath[iPreVex].preVex;
if (pVexPath[iPreVex].pathValue == vexIndex1Value)
break;
}
printf("%c\n", pGraph->vexs[vexIndex1]);
}
int main()
{
int visited[8] = { 0 };
int initArcs[8][8] =
{
0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0,
1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0,
0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1,
1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0,
0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1,
0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0,
};
char initVexs[9] = "12345678";
Graph* pGraph = initGraph(8);
createGraph(&pGraph, initVexs, (int*)initArcs);
VexPath* pVexPath = initVexPath(pGraph);
getShort(pGraph, pVexPath, visited, 1);
printf("\n");
getVexShortPath(pGraph,pVexPath, 1, 7 );
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号