Java Shiro 权限绕过
前言:这篇作为Shiro的权限绕过的笔记
这篇文章作为之前笔记Filter权限绕过笔记的拓展,Filter权限绕过笔记:https://www.cnblogs.com/zpchcbd/p/14815501.html
参考文章:https://shiro.apache.org/security-reports.html
参考文章:https://www.anquanke.com/post/id/240033
参考文章:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/359199157
参考文章:https://blog.riskivy.com/shiro-权限绕过漏洞分析(cve-2020-1957)/
什么是Shiro
Apache Shiro是一个强大且易用的Java安全框架,执行身份验证、授权、密码和会话管理。使用Shiro的易于理解的API,您可以快速、轻松地获得任何应用程序,从最小的移动应用程序到最大的网络和企业应用程序。
关于Shiro漏洞历史线
CVE-2016-4437(shiro-550)
Apache Shiro before 1.2.5, when a cipher key has not been configured for the “remember me” feature, allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or bypass intended access restrictions via an unspecified request parameter.
CVE-2016-6802(权限绕过)
Apache Shiro before 1.3.2 allows attackers to bypass intended servlet filters and gain access by leveraging use of a non-root servlet context path.
CVE-2019-12422(shiro-721)
Apache Shiro before 1.4.2, when using the default “remember me” configuration, cookies could be susceptible to a padding attack.
CVE-2020-1957(权限绕过)
Apache Shiro before 1.5.2, when using Apache Shiro with Spring dynamic controllers, a specially crafted request may cause an authentication bypass.
CVE-2020-11989(权限绕过)
Apache Shiro before 1.5.3, when using Apache Shiro with Spring dynamic controllers, a specially crafted request may cause an authentication bypass.
CVE-2020-13933(权限绕过)
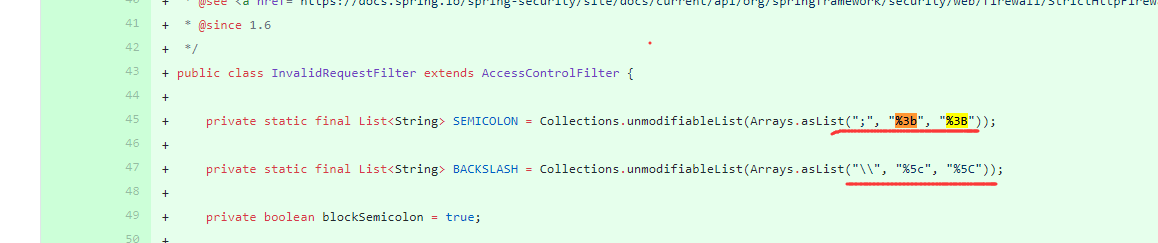
Apache Shiro before 1.6.0, when using Apache Shiro, a specially crafted HTTP request may cause an authentication bypass.
CVE-2020-17510(权限绕过)
Apache Shiro before 1.7.0, when using Apache Shiro with Spring, a specially crafted HTTP request may cause an authentication bypass.
If you are NOT using Shiro’s Spring Boot Starter (shiro-spring-boot-web-starter), you must configure add the ShiroRequestMappingConfig auto configuration to your application or configure the equivalent manually.
CVE-2020-17523(权限绕过)
Apache Shiro before 1.7.1, when using Apache Shiro with Spring, a specially crafted HTTP request may cause an authentication bypass.
环境搭建
第一步
第二步
第三步:
第四步:
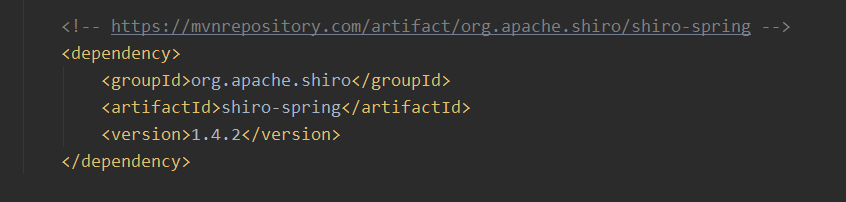
maven添加依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.shiro/shiro-spring -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.4.2</version>
</dependency>
前置知识点
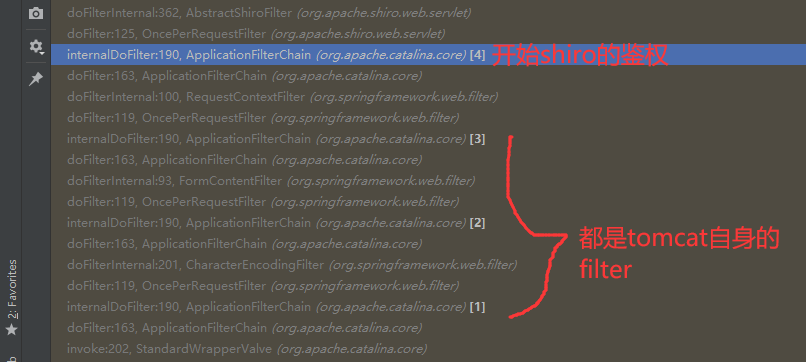
在tomcat和shiro的filter中,哪个会先进行执行?后进行执行?
我这里看到堆栈的调用链,所以调用的过程是从下往上,那么就是tomcat相关的filter先执行,接着才是shiro的filter执行
关于Shiro拦截器
Shiro框架通过拦截器功能来实现对用户访问权限的控制和拦截。
Shiro中常见的拦截器有anon,authc等拦截器,还有其他的,这里是探讨关于authc拦截器的绕过。
1.anon为匿名拦截器,不需要登录就能访问,一般用于静态资源,或者移动端接口
2.authc为登录拦截器,需要登录认证才能访问的资源。
...
关于shiro的拦截匹配模式
Shiro的URL路径表达式为Ant格式,org.springframework.util.AntPathMatcher
/hello:只匹配url,比如 http://demo.com/hello
/h?:只匹配url,比如 http://demo.com/h+任意一个字符
/hello/*:匹配url下,比如 http://demo.com/hello/xxxx 的任意内容,不支持匹配多层路径
/hello/**:匹配url下,比如 http://demo.com/hello/xxxx http://demo.com/hello/xxxx/aaaa ,支持匹配多层路径
shiro是如何运行的?
我这里也不太懂shiro,这里就正常的看下shiro源码是如何运行的就可以了,简单的学下
shiroConfig需要通过ShiroFilterFactoryBean类来进行配置,一个正常的ShiroConfig.java如下所示
@Configuration
public class ShiroConfig {
@Bean
MyRealm myRealm(){
return new MyRealm();
}
@Bean
public DefaultWebSecurityManager manager(){
DefaultWebSecurityManager manager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
manager.setRealm(myRealm());
return manager;
}
@Bean
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean filterFactoryBean(){
ShiroFilterFactoryBean factoryBean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
factoryBean.setSecurityManager(manager());
factoryBean.setUnauthorizedUrl("/login");
factoryBean.setLoginUrl("/login");
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("/login", "anon");
factoryBean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(map);
return factoryBean;
}
}
对于路径的访问权限的控制都是基于ShiroFilterFactoryBean类来进行配置的
@Bean
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean filterFactoryBean(){
ShiroFilterFactoryBean factoryBean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
factoryBean.setSecurityManager(manager());
factoryBean.setUnauthorizedUrl("/login");
factoryBean.setLoginUrl("/login");
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("/login", "anon");
factoryBean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(map);
return factoryBean;
}
这里可以来到ShiroFilterFactoryBean类中,看它是如何作用的,该类中存在一个getObject方法
public Object getObject() throws Exception {
if (instance == null) {
instance = createInstance();
}
return instance;
}
其中createInstance方法是来创建相关Shiro Filter,结果是返回一个继承了AbstractShiroFilter的SpringShiroFilter对象
protected AbstractShiroFilter createInstance() throws Exception {
log.debug("Creating Shiro Filter instance."); // 创建shiro Filter的实例
SecurityManager securityManager = getSecurityManager();
if (securityManager == null) {
String msg = "SecurityManager property must be set.";
throw new BeanInitializationException(msg);
}
if (!(securityManager instanceof WebSecurityManager)) {
String msg = "The security manager does not implement the WebSecurityManager interface.";
throw new BeanInitializationException(msg);
}
FilterChainManager manager = createFilterChainManager();
PathMatchingFilterChainResolver chainResolver = new PathMatchingFilterChainResolver();
chainResolver.setFilterChainManager(manager);
return new SpringShiroFilter((WebSecurityManager) securityManager, chainResolver);
}
SpringShiroFilter这个对象是继承了AbstractShiroFilter,而这个AbstractShiroFilter中存在一个doFilterInternal,这个方法我自己有了解,因为Filter的内存文章中tomcat这个其中的InternaldoFilter就是去调用我们每个Filter对象中实现的doFilter方法的一个方法,而这里的doFilterInternal可能不太一样,它是通过executeChain来进行链式调用传入的chain参数,这个chain是一个FilterChain对象
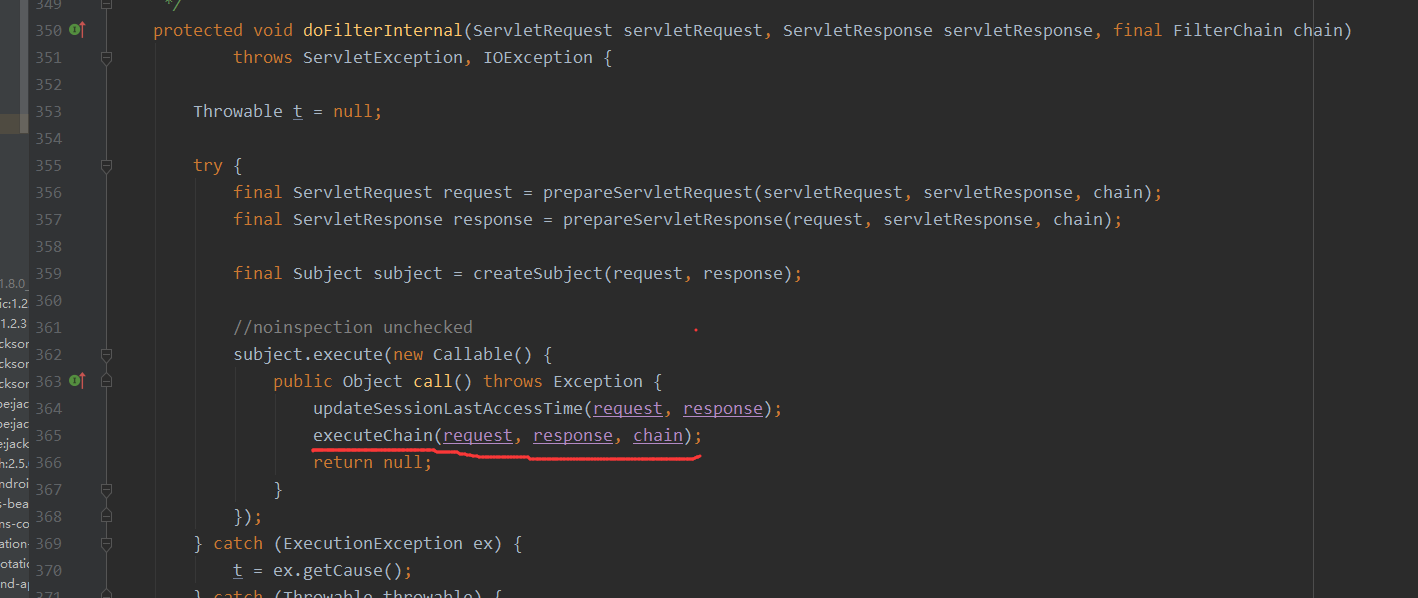
其中executeChain方法来对传入的FilterChain对象进行处理调用doFilter方法
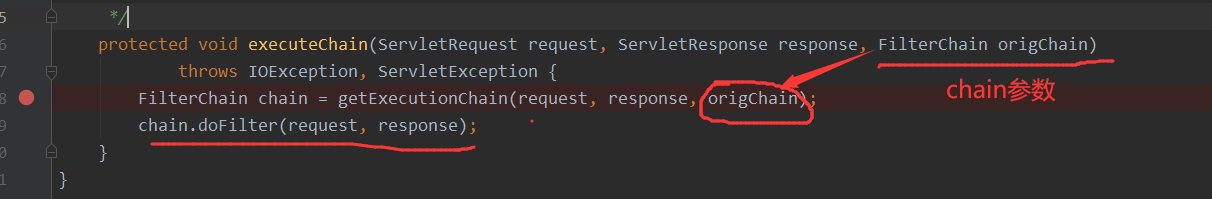
此时前面的tomcat的Filter对象中的doFilter已经走完了,tomcat的走完了才开始走shiro的filter(PS:此时tomcat的过滤器并不是完全走完,还有最后一个在shiro的后面)
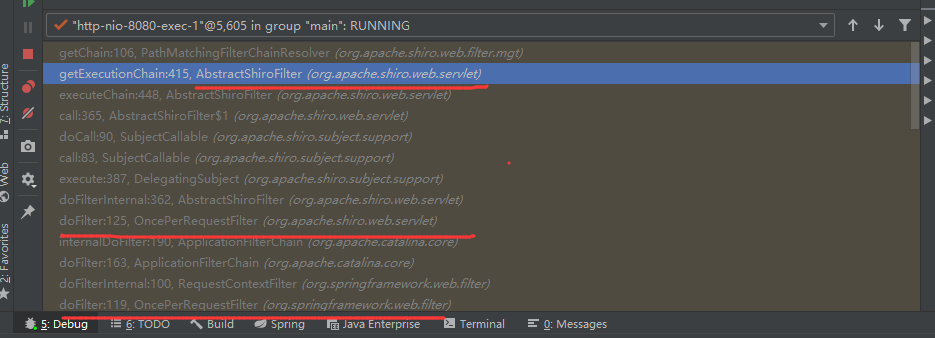
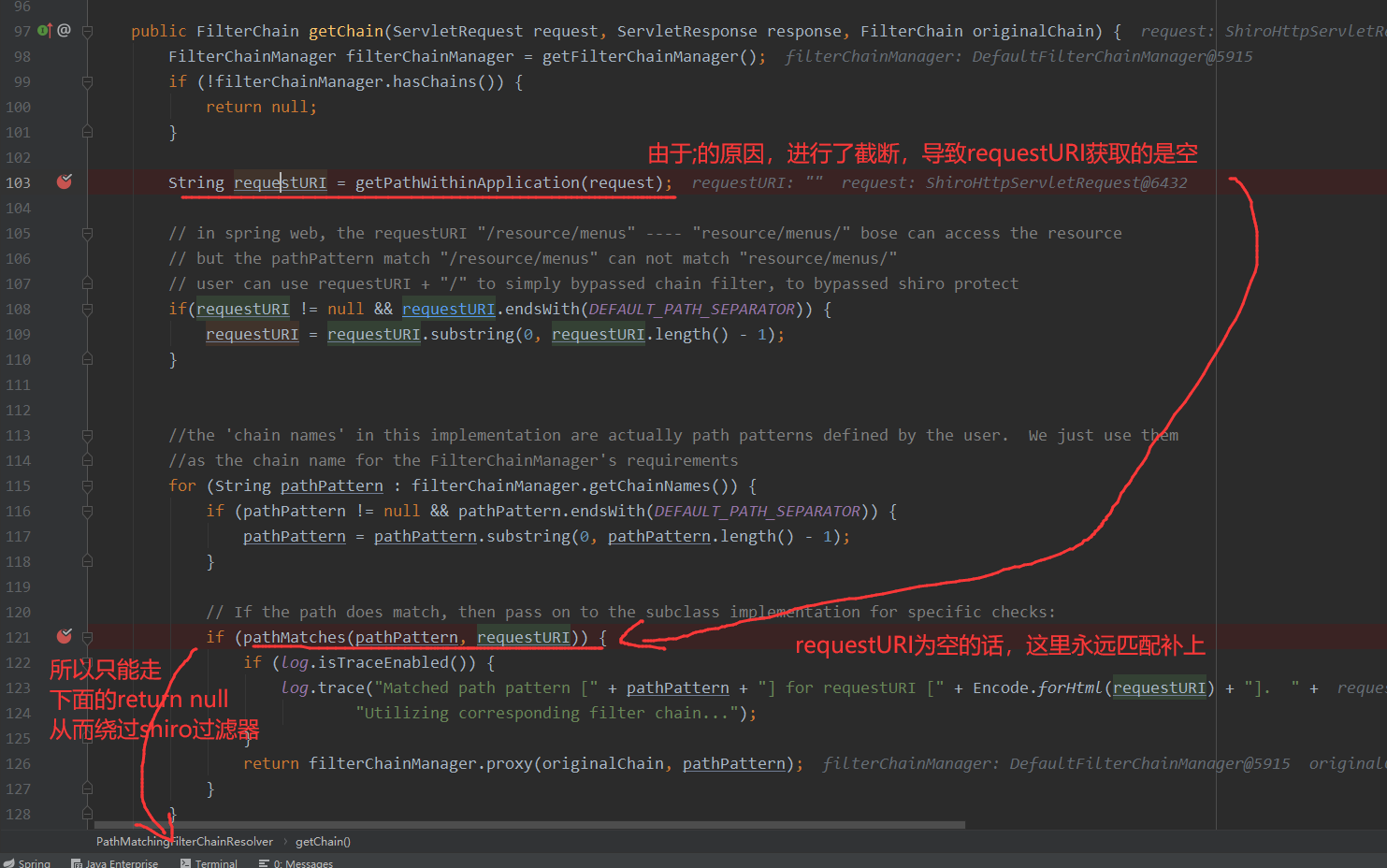
接着就是getExecutionChain方法,其中就会通过FilterChainResolver的getChain方法来进行解析,从这里开始shiro的拦截器就开始进行发挥作用了,这里如果是被正确的拦截了,那么原始的chain则会被替换为shiro的filterChainManager.proxy(originalChain, pathPattern)所返回的FilterChain,如果没有被拦截则最后不会被替换,还是走原来的chain
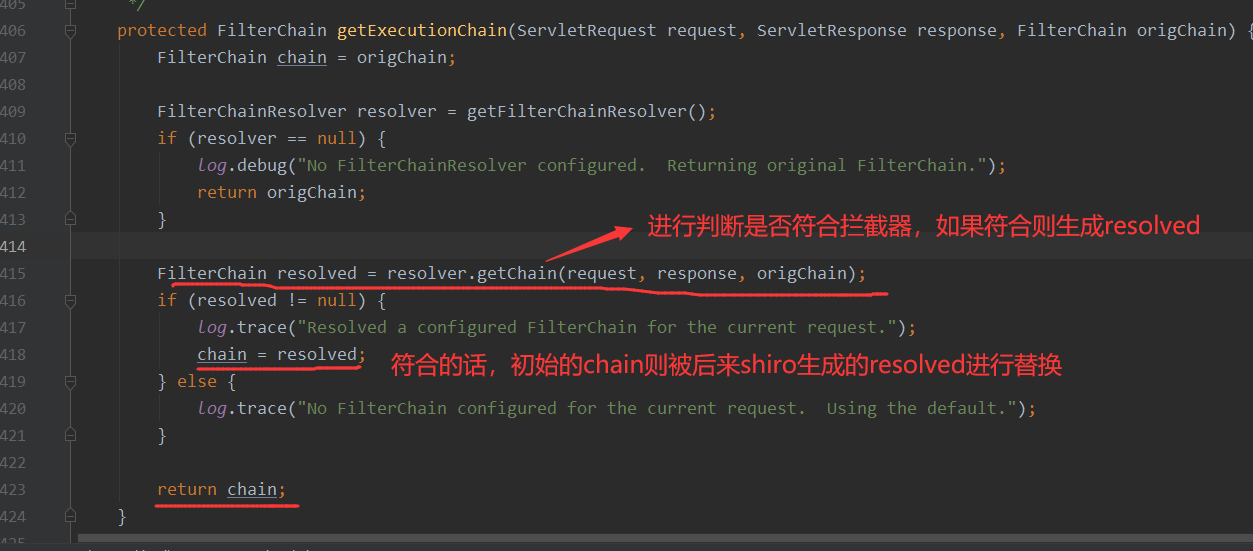
那么shiro是如何判断是否被拦截的?可以继续看
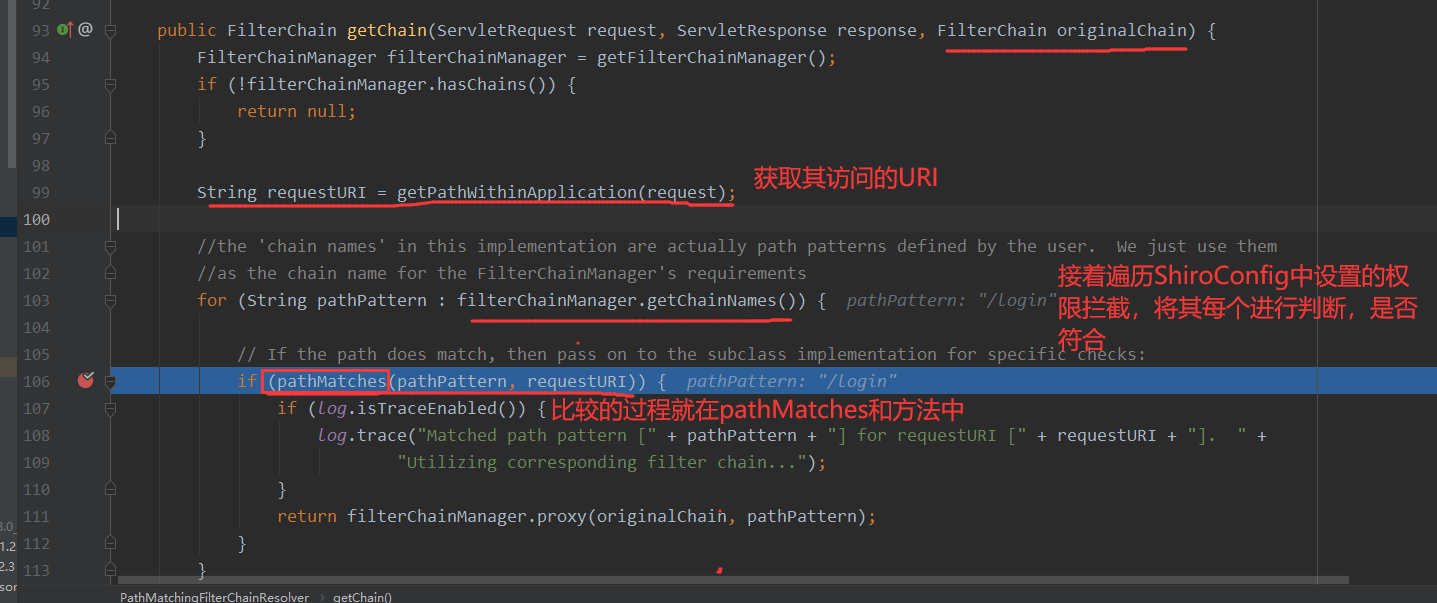
继续跟到pathMatches方法中去看,他会用自己的一个路径匹配器PathMatcher来进行比较
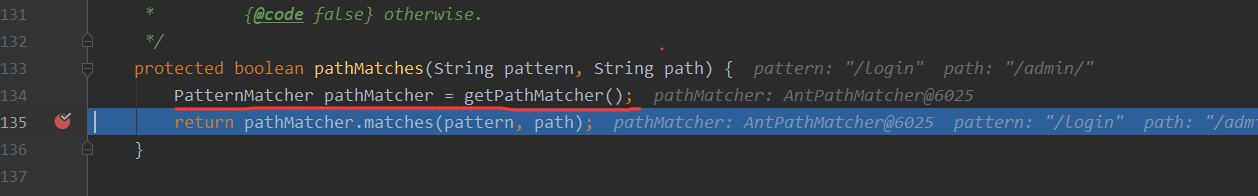
最后doMatch方法获取 需要校验的路径 和 当前客户端访问的路径来进行比较,是否是需要进行拦截的
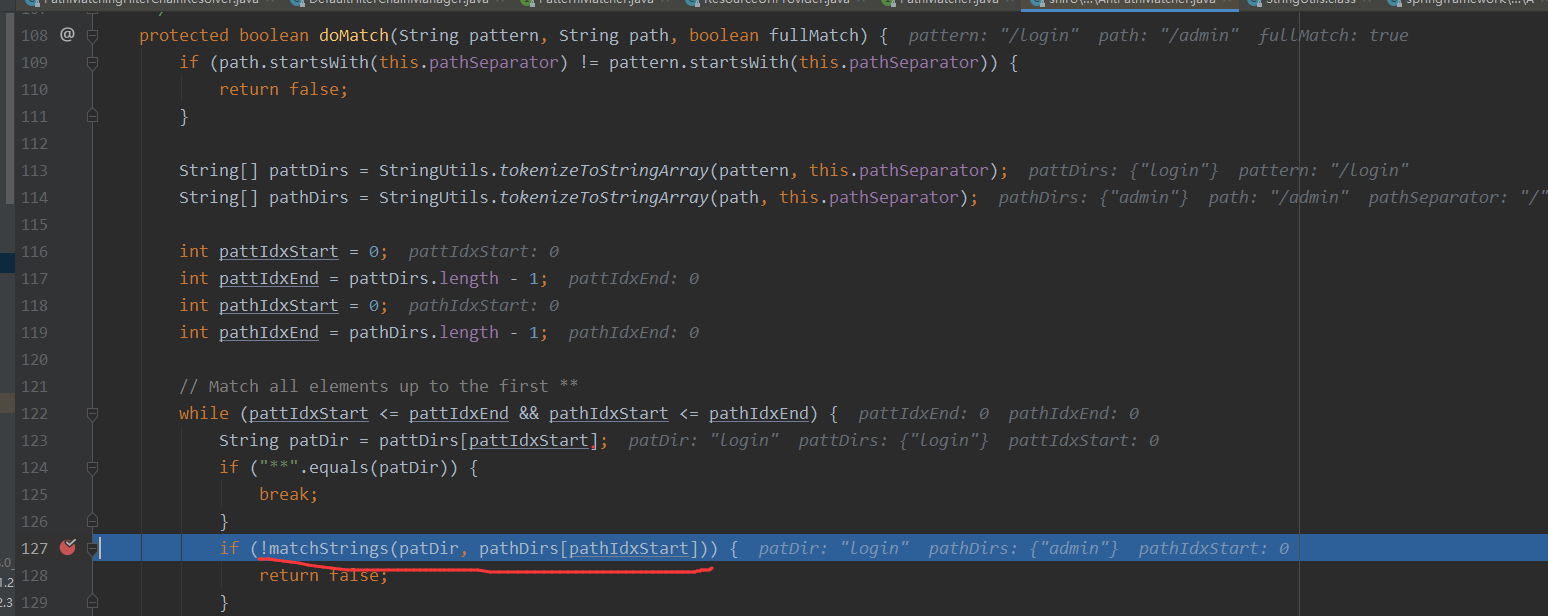
判断是否需要拦截,具体根据其中的matchStrings方法来进行判别,到这里一次请求的判断就结束了
接下来看漏洞分析...
CVE-2016-6802(SHIRO-682)
参考:https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/SHIRO-682

影响版本: shiro<1.5.0
漏洞原理:shiro与spring的URI中末尾的/不同导致的权限绕过
其中*表示匹配零个或多个字符串,/*可以匹配/hello,但匹配不到/hello/因为*通配符无法匹配路径。
假设/hello接口设置了authc拦截器,访问/hello将会被进行权限判断,如果请求的URI为/hello/呢,/*的URL路径表达式将无法正确匹配导致放行,然后进入到spring(Servlet)拦截器,而spring中 /hello 形式和 /hello/形式的URL访问的资源是一样的,从而导致了绕过。
漏洞分析:
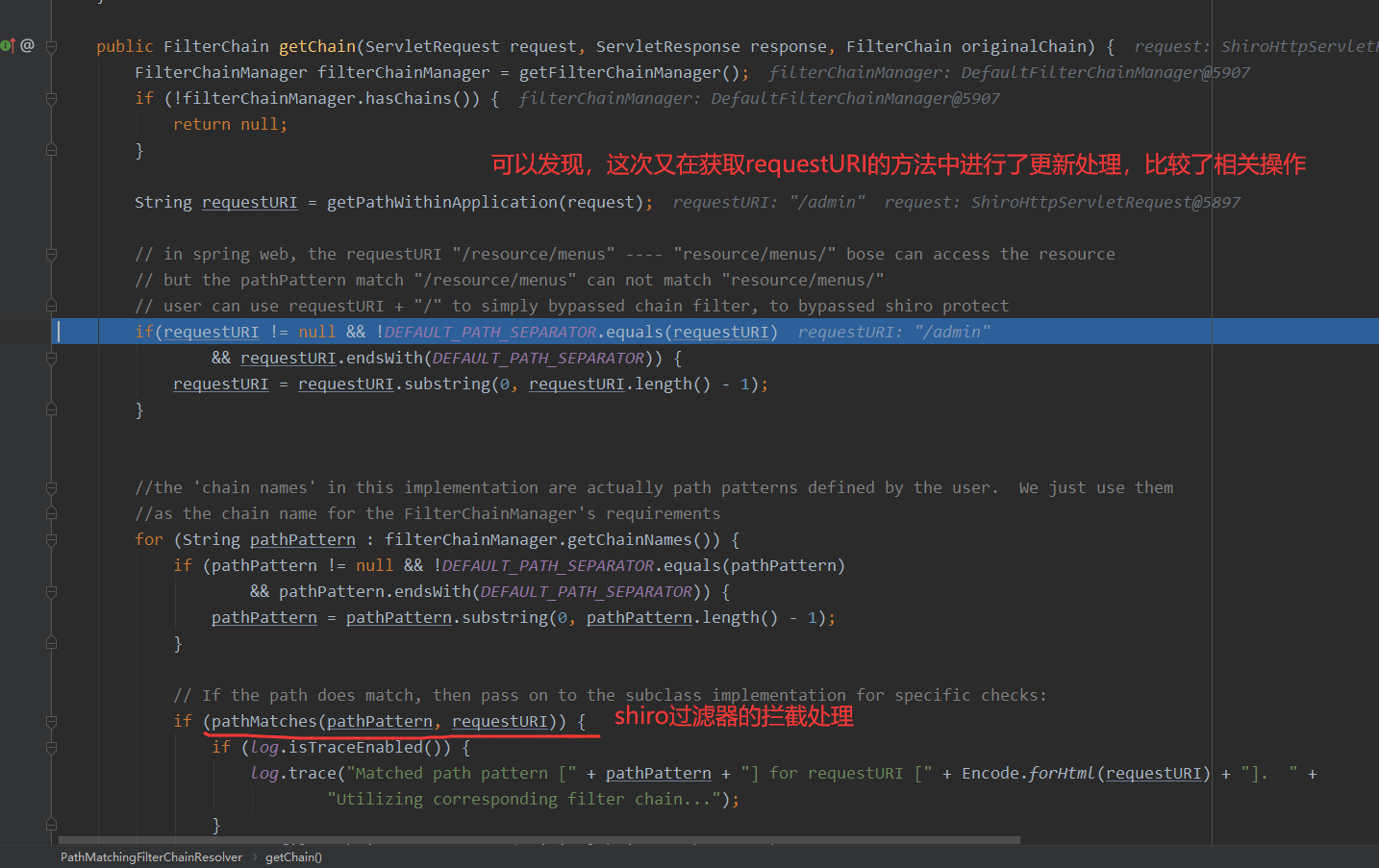
这里的话从getChain方法开始看,这里会先获取相关的URI,然后传入pathMatches来进行比较
我们设置一个权限拦截器,如下所示:
@Bean
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean filterFactoryBean(){
ShiroFilterFactoryBean factoryBean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
factoryBean.setSecurityManager(manager());
factoryBean.setUnauthorizedUrl("/login");
factoryBean.setLoginUrl("/login");
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("/admin", "authc"); // 新增的拦截器
factoryBean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(map);
return factoryBean;
}
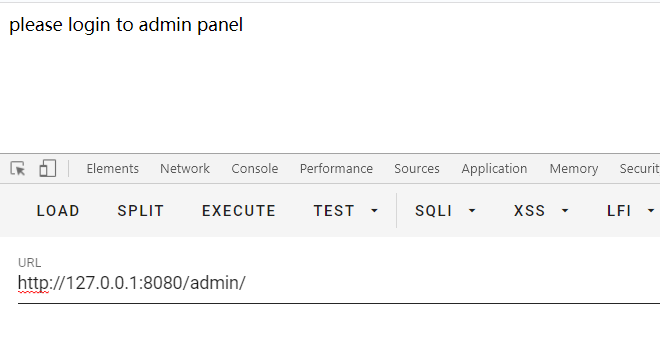
访问:http://127.0.0.1:8080/admin/
首先来到的地方还是getChain
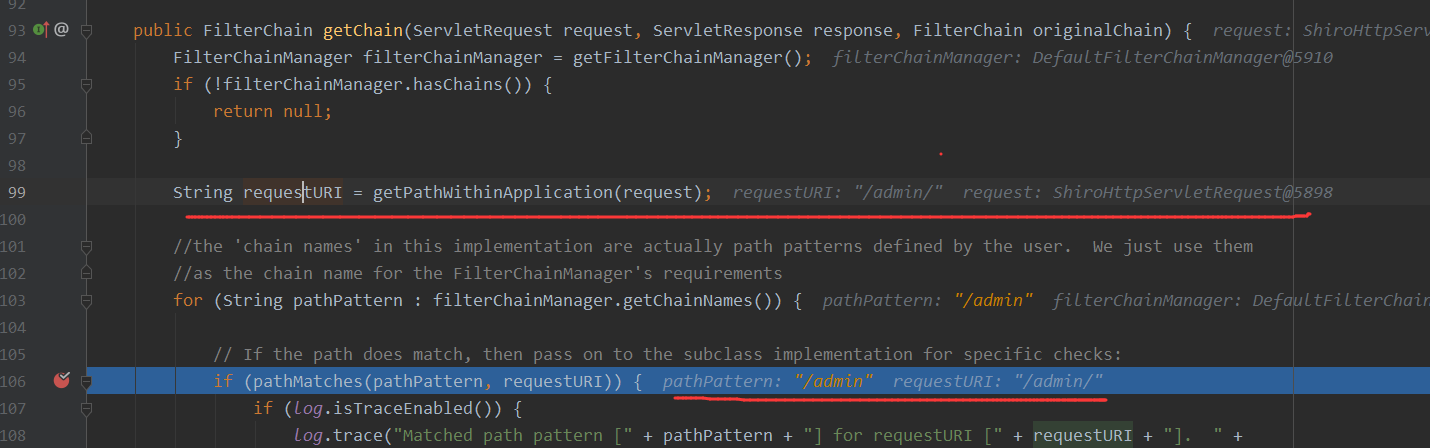
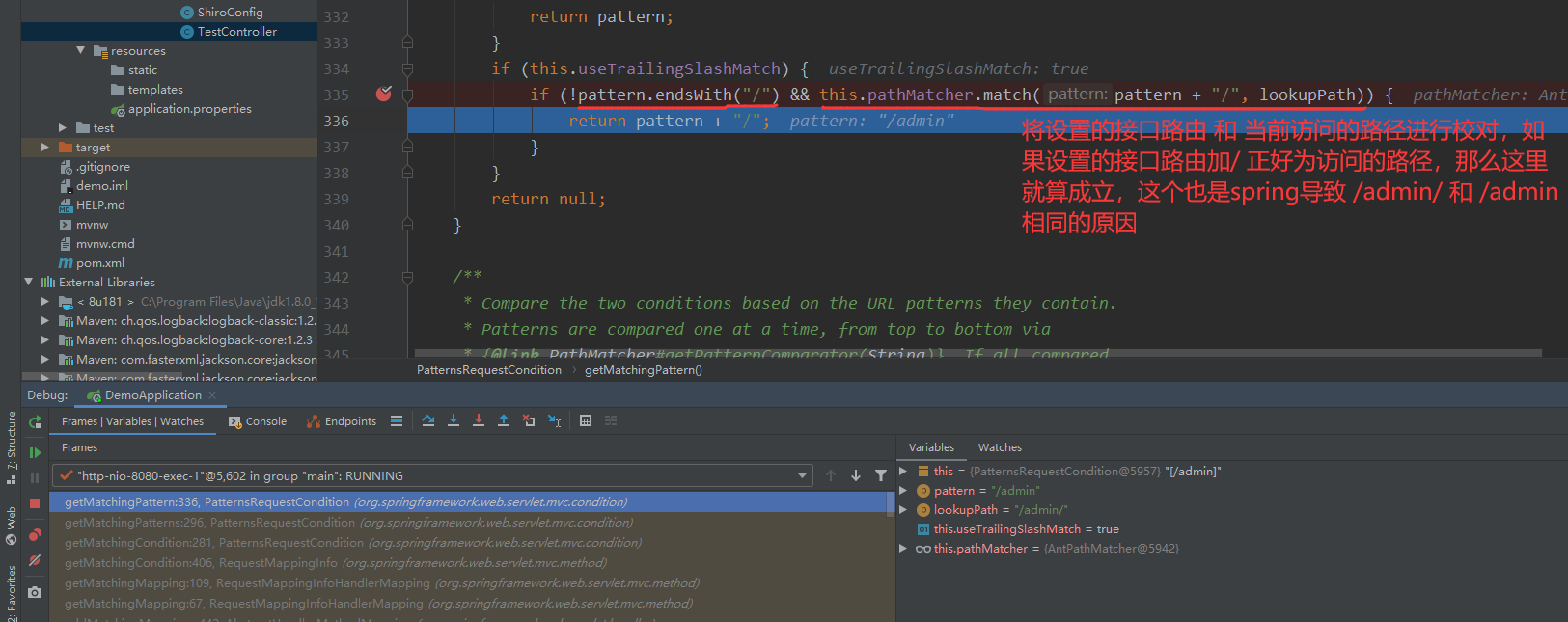
跟到doMatches 这里调用的是doMatch,这里/admin/和/admin经过tokenizeToStringArray返回的数据是一样的
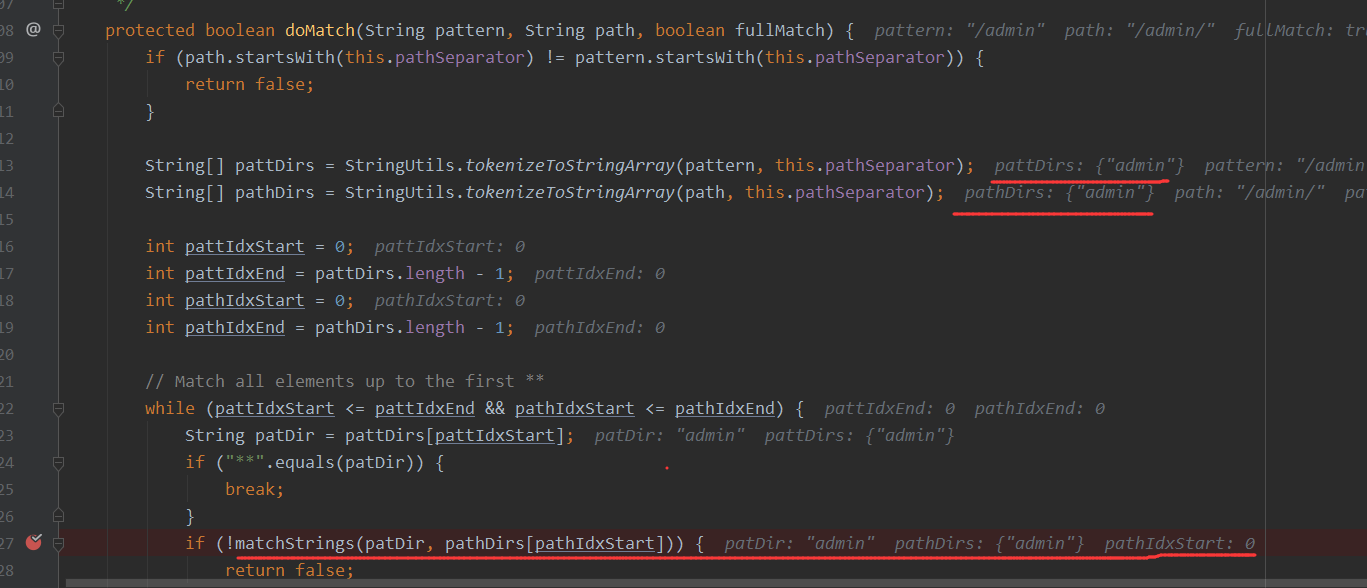
/admin/和/admin经过tokenizeToStringArray返回的数据是一样的,但是接着后面就是会进行判断,如果结尾存在/,则返回为False
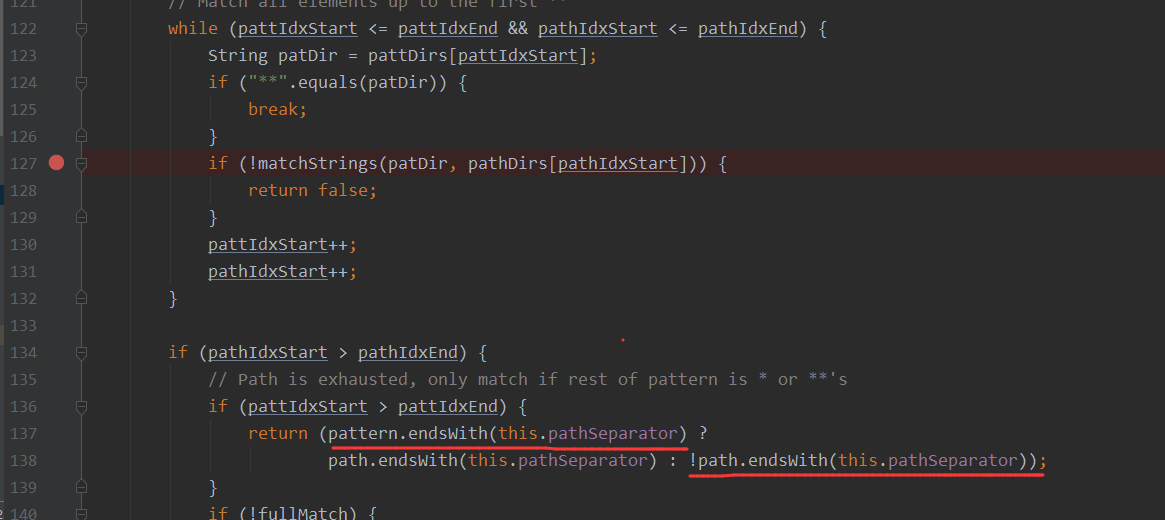
返回为False,就不会走shiro的拦截器了,最后就成功绕过了,shiro的过滤器拦截
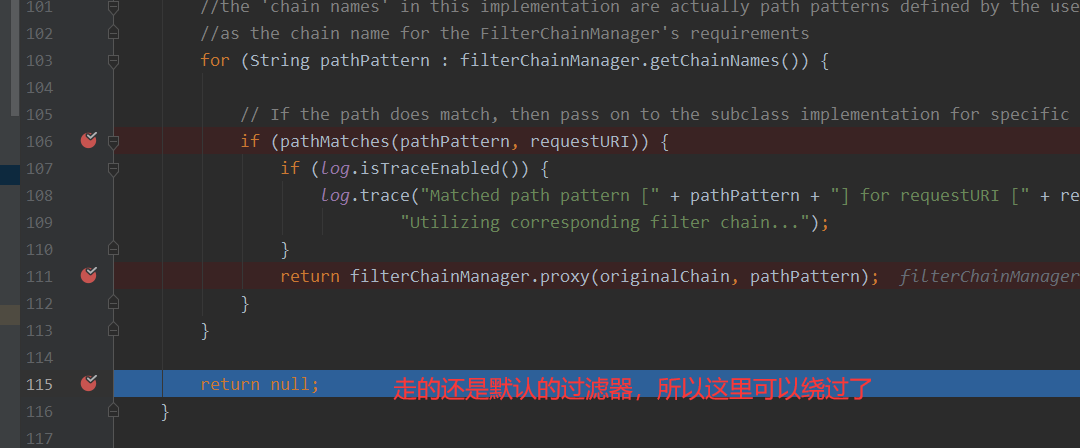
而正常的访问:http://127.0.0.1:8080/admin ,则会被shiro的拦截器捕获
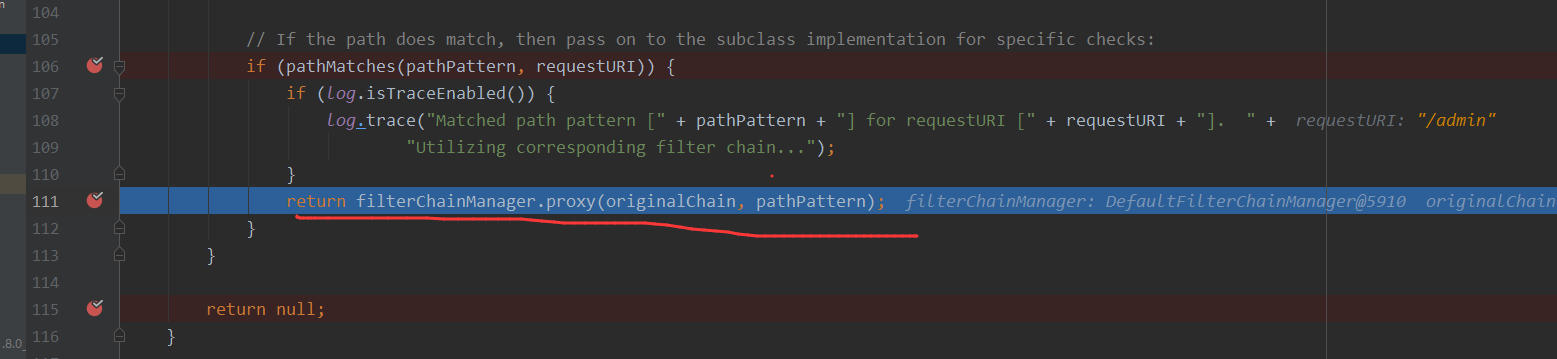
问题思考
在CVE-2016-6802(SHIRO-682)中,通过后面加/,来绕过了shiro的拦截器,那么此时的URI则是http://127.0.0.1:8080/admin/,那么又为什么可以访问到接口为admin接口的资源呢?
这里就要引出sprng的路径处理的过程了...
接着来看spring是如何处理URI的,此时我们已经到了如下的位置
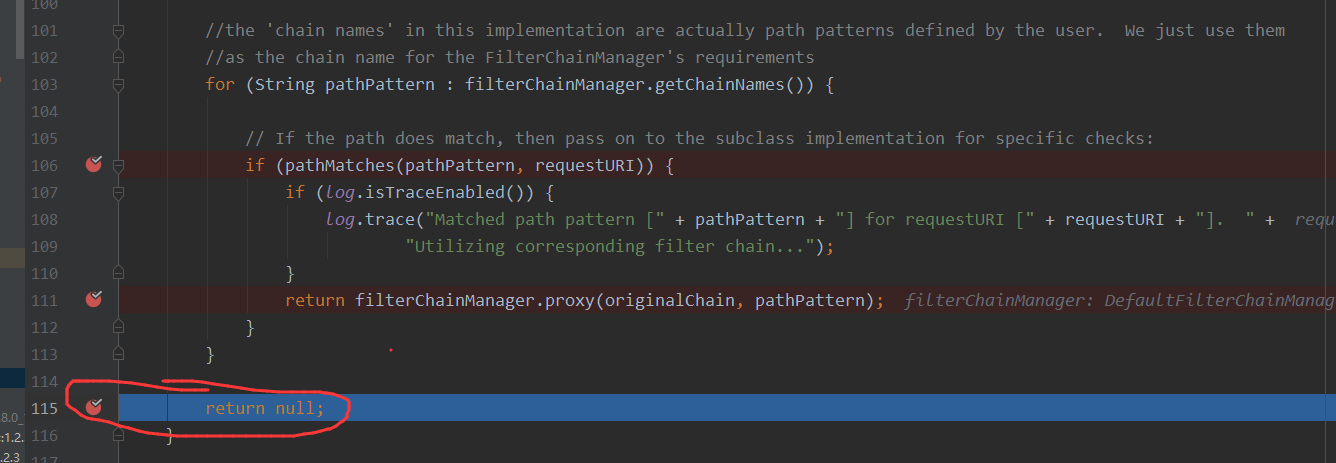
F8走出来,到此shiro的过滤拦截器已经执行完成了,又开始进行转发请求的操作chain.doFilter(request, response)
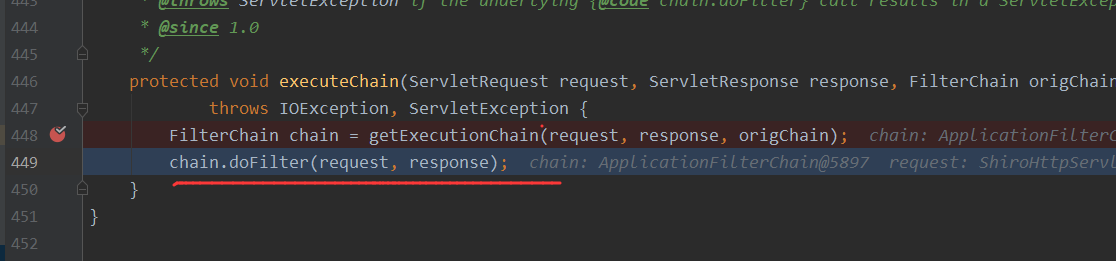
到这里可以继续看下过滤器的数量,shiro过滤器走的是filterFactoryBean,那么此时还有最后一个过滤器还没走,Tomcat WebSocket (JSR356) Filter
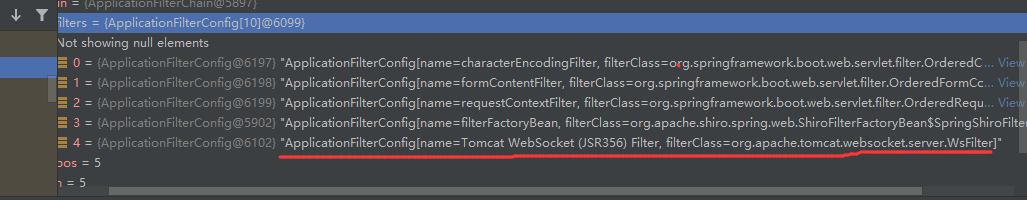
走完最后一个Tomcat Filter之后,请求被转发到了spring中,这里的话,断在org/springframework/web/util/UrlPathHelper.java#getLookupPathForRequest方法上,此时在Shiro包装的HttpServlet来进行处理,这里则返回了/admin/
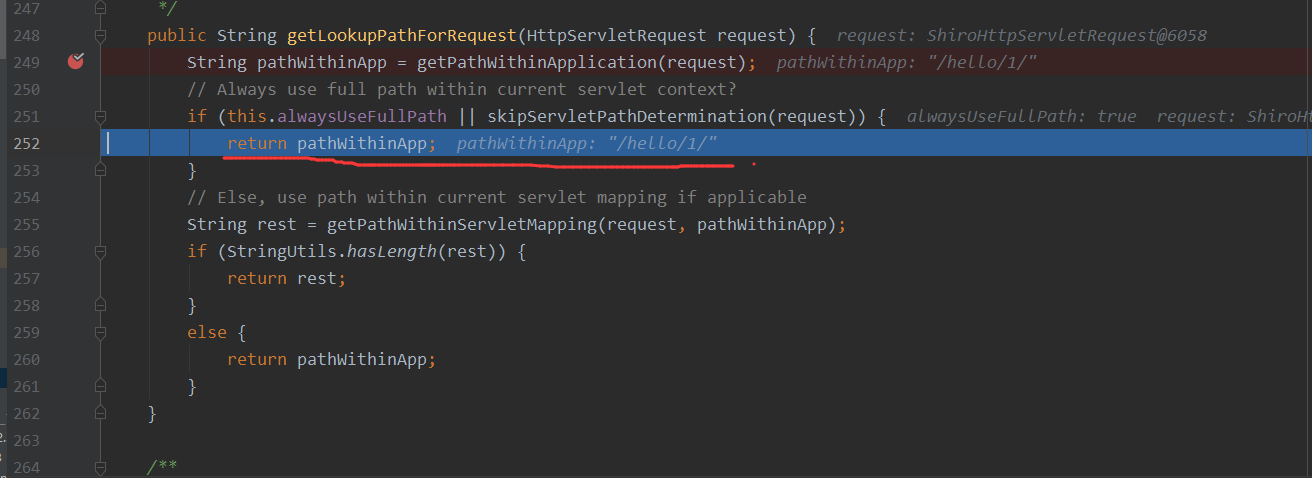
接着F8一直走到lookupHandlerMethod,来调用对应接口的方法,这个地方就是重点,看他如何处理这个/admin/,这里就不跟了,可以自己跟下,调用链如下,我的springboot版本2.5.2
getMatchingPattern:336, PatternsRequestCondition (org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition)
getMatchingPatterns:296, PatternsRequestCondition (org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition)
getMatchingCondition:281, PatternsRequestCondition (org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition)
getMatchingCondition:406, RequestMappingInfo (org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method)
getMatchingMapping:109, RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping (org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method)
getMatchingMapping:67, RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping (org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method)
addMatchingMappings:442, AbstractHandlerMethodMapping (org.springframework.web.servlet.handler)
lookupHandlerMethod:402, AbstractHandlerMethodMapping (org.springframework.web.servlet.handler)
官方修复方法:
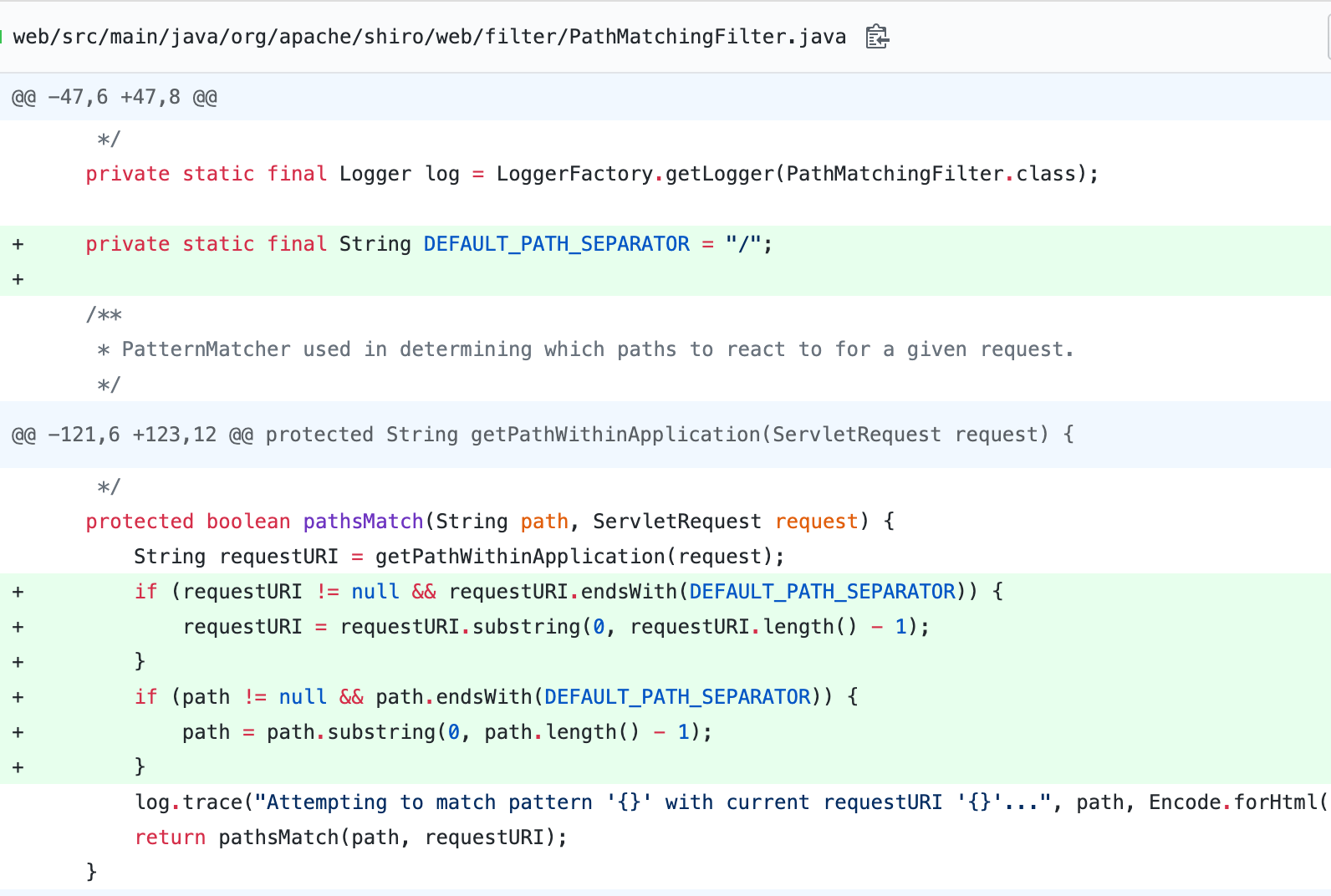
1.5.0版本修复源自tomsun28提交的PR代码,代码修复位置为pathsMatch:125, PathMatchingFilter (org.apache.shiro.web.filter),该修复方式是通过判断requestURI是否以/为结尾,如果以/结尾的话,则去掉尾部的/符号在与URL表达式进行比较。
也就是当requestURI为/hello/1/等以/为结尾的URI的时候,都会被清除最后的/号,再进行URL路径匹配。
可能自己会试下访问:http://127.0.0.1:8080/admin//
但是在request.getRequestURI函数即是在后面多个/的时候,获取到的结尾还是一个/,接着又被取length-1,那么这里就没办法了。
CVE-2020-1957
影响版本: shiro<1.5.2
漏洞原理:shiro与spring的URI中对;处理不同,导致绕过
类型: 权限绕过
因为上面大致将整个shiro的流程都讲了一遍了,现在主要分析的就是漏洞本身了!
介绍:CVE-2020-1957则是对CVE-2016-6802的绕过
按照原来的绕过,如下图所示,发现已经无法进行绕过了
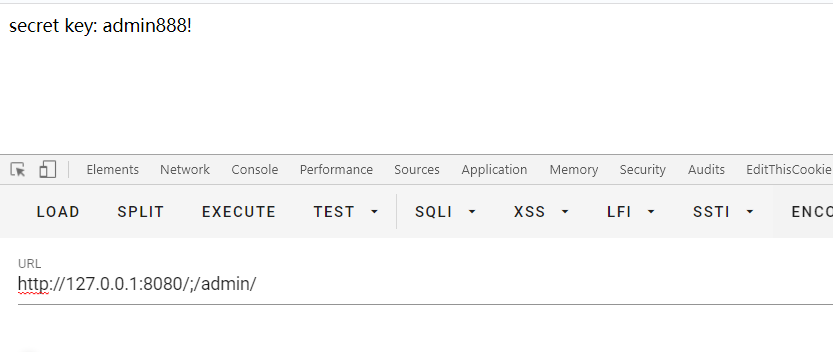
绕过方法:分号;
分析
shiro的部分
spring的部分
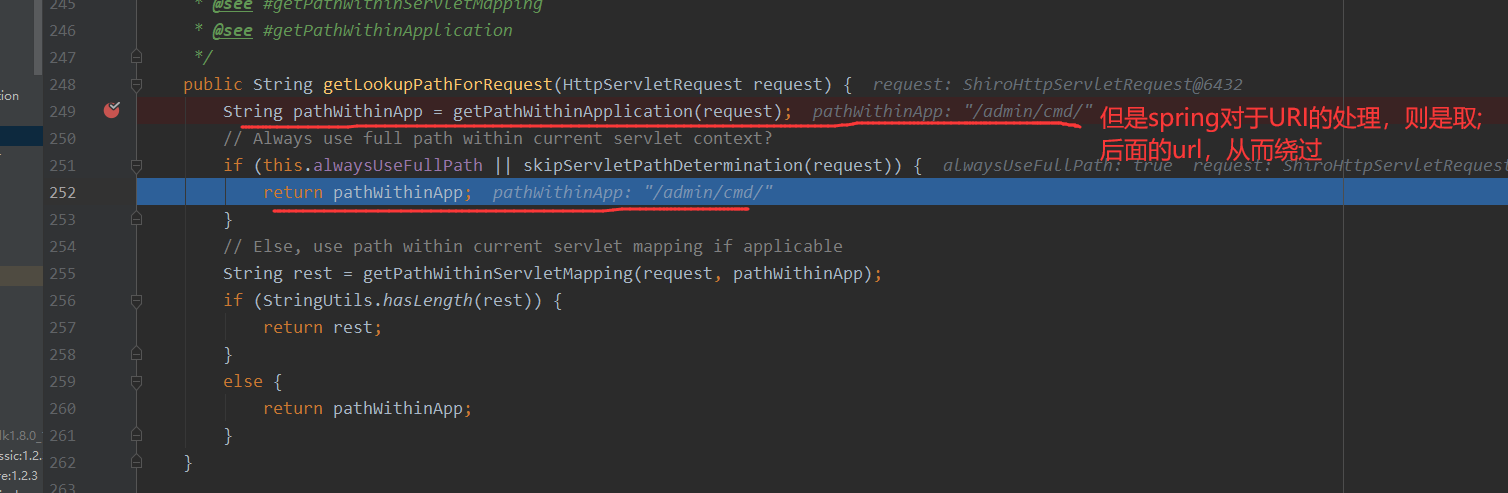
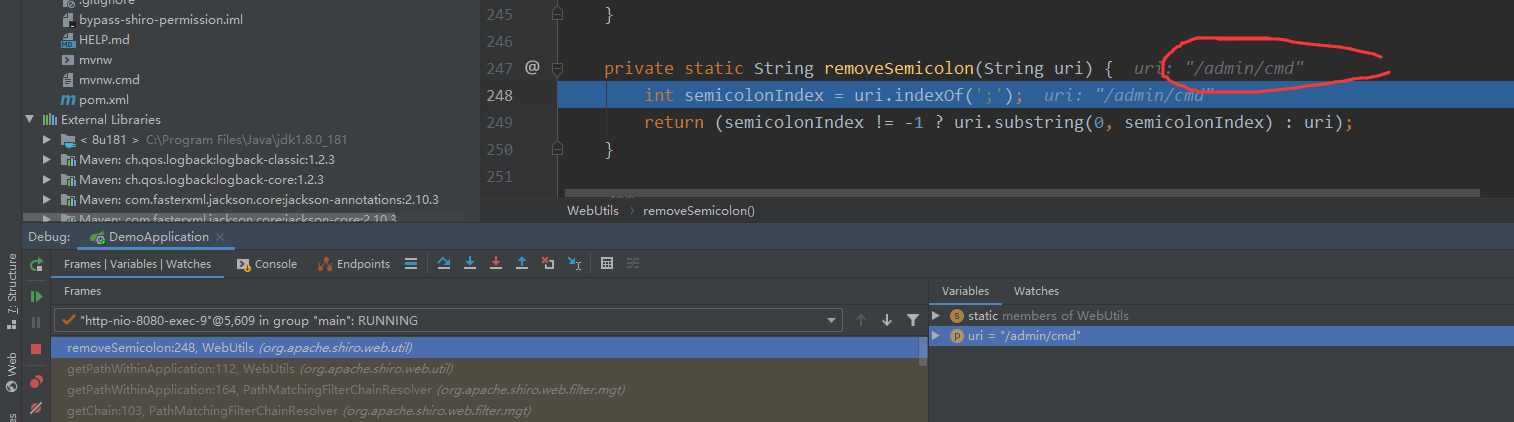
可以看下getPathWithinApplication方法是如何处理的,因为我们这里没有设置ContextPath,所以默认为空
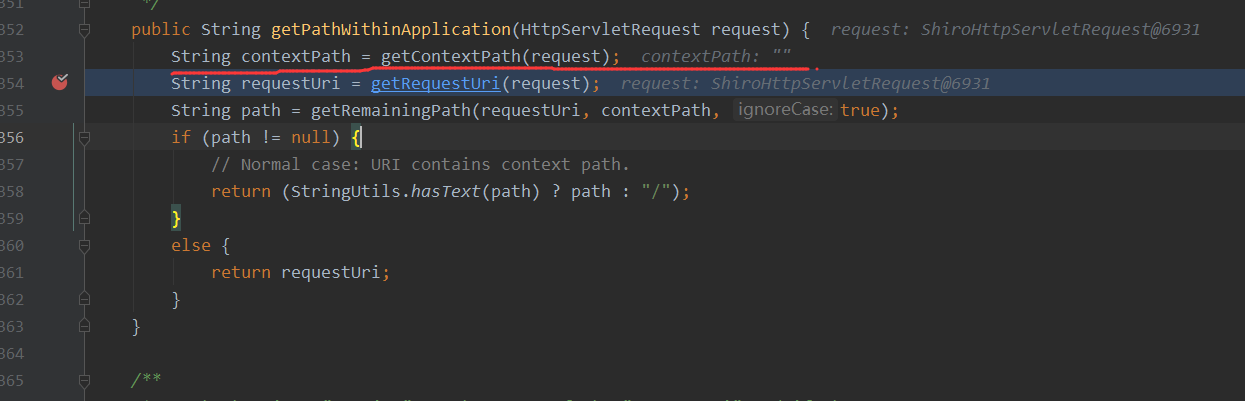
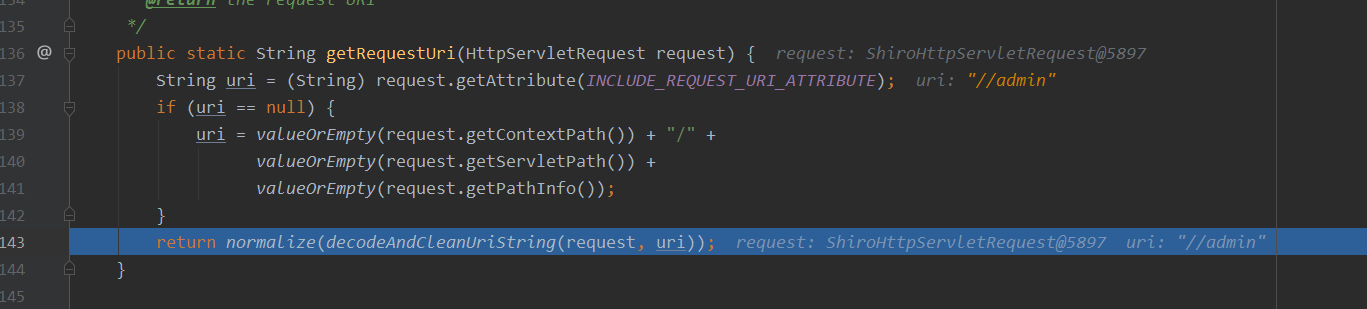
接着跟进getRequestUri方法中
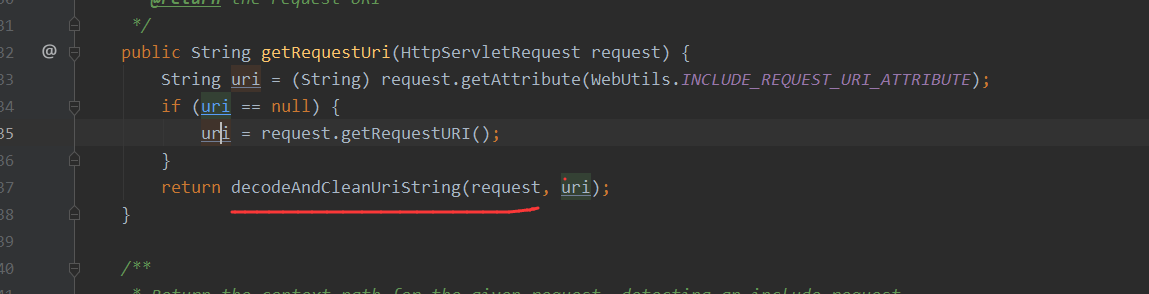
decodeAndCleanUriString方法中
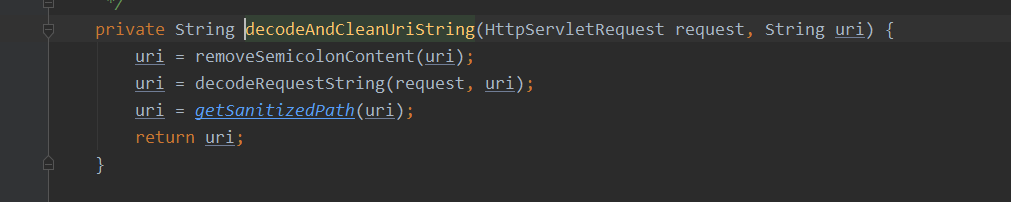
decodeAndCleanUriString方法中又调用了removeSemicolonContent,removeSemicolonContent方法中有调用了removeSemicolonContentInternal,结果返回如下
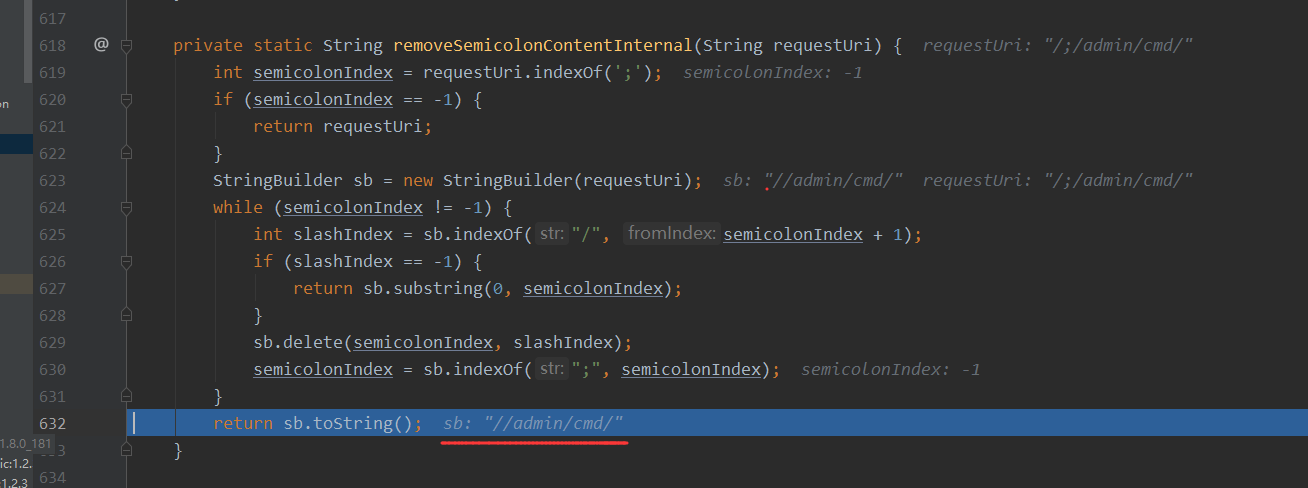
接着又是decodeRequestString,这里就是简单的URL解码,没有影响,那么这里思考下,那么我们一次的访问就是二次解码,这个点能不能在其他地方上进行利用?我也不太清楚
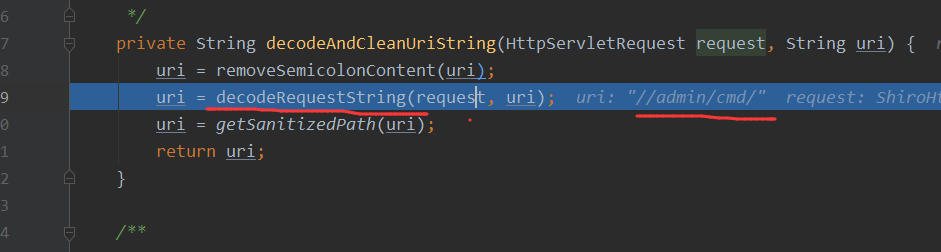
接着就是getSanitizedPath方法
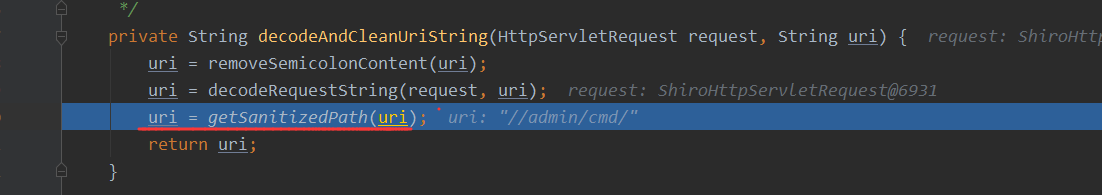
这个方法的作用则是将//转化为/,那么此时就是将//admin/cmd转化为/admin/cmd
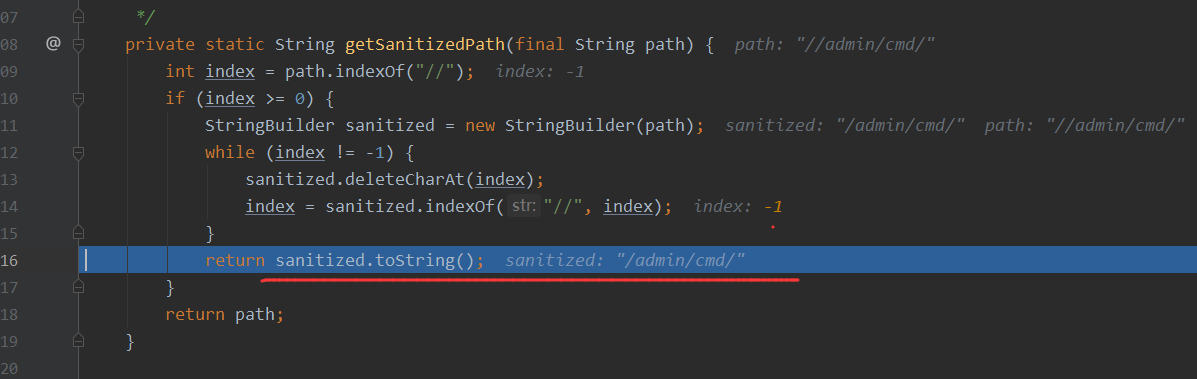
最后返回就是为/admin/cmd,一个正常的访问路径,最后进行调用从而绕过
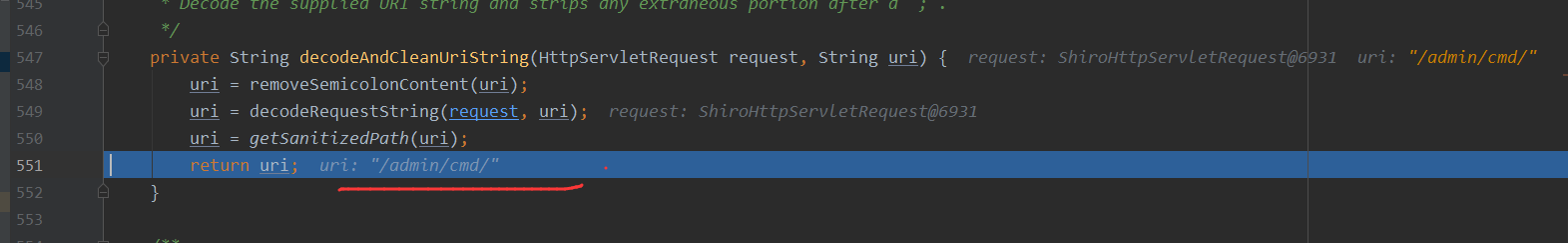
稍微总结下:
这次的绕过其实还是shiro和spring的路径处理方式不同,shiro是如何处理的?
比如http://127.0.0.1:8080/;/admin,shiro则是认为是访问http://127.0.0.1:8080/
spring是如何处理的?
比如http://127.0.0.1:8080/;/admin,shiro则是认位是访问http://127.0.0.1:8080/admin
这就造成了与Shiro处理⽅式的差异,Shiro是直接截断后⾯所有部分,⽽Spring只会截断【分号之后,斜杠之前】的部分
官方修复方案
shiro中的getRequestUri修改为如下:
public static String getRequestUri(HttpServletRequest request) {
String uri = (String) request.getAttribute(INCLUDE_REQUEST_URI_ATTRIBUTE);
if (uri == null) {
uri = valueOrEmpty(request.getContextPath()) + "/" +
valueOrEmpty(request.getServletPath()) +
valueOrEmpty(request.getPathInfo());
}
return normalize(decodeAndCleanUriString(request, uri));
}
private static String valueOrEmpty(String input) {
if (input == null) {
return "";
}
return input;
}
重新调试下,发现在shiro拦截器处理之前就进行了处理,如下
具体修改如下,在自定义的getRequestUri方法中用ContextPath、ServletPath、PathInfo三者拼接的⽅式获取路由,由于 ServletPath 能够正确的处理分号,通过这种⽅式来获取对应的路由能够成功修复此漏洞。
public static String getRequestUri(HttpServletRequest request) {
String uri = (String) request.getAttribute(INCLUDE_REQUEST_URI_ATTRIBUTE);
if (uri == null) {
uri = valueOrEmpty(request.getContextPath()) + "/" +
valueOrEmpty(request.getServletPath()) +
valueOrEmpty(request.getPathInfo());
}
return normalize(decodeAndCleanUriString(request, uri));
}
private static String valueOrEmpty(String input) {
if (input == null) {
return "";
}
return input;
}
CVE-2020-11989
影响版本: shiro<1.5.3
环境配置
1、shiro的版本
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.5.2</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.shiro/shiro-spring -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.5.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2、设置下context-path
在资源文件的application.properties文件中进行设置
server.servlet.context-path=/test
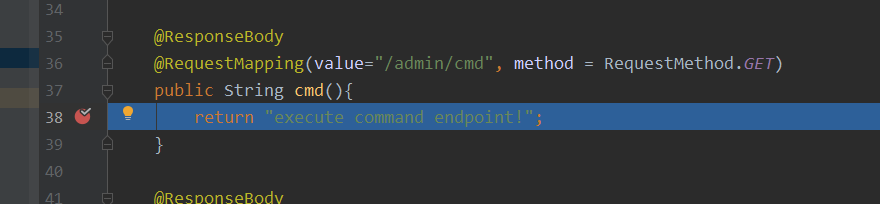
3、在多添加一个admin路径下的一个接口
TestController.java
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value="/admin/cmd", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String cmd(){
return "execute command endpoint!";
}
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value="/admin", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String admin(){
return "secret key: admin888!";
}
ShiroConfig.java
@Bean
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean filterFactoryBean(){
ShiroFilterFactoryBean factoryBean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
factoryBean.setSecurityManager(manager());
factoryBean.setUnauthorizedUrl("/login");
factoryBean.setLoginUrl("/login");
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("/login", "anon");
map.put("/admin", "authc");
map.put("/admin/*", "authc");
factoryBean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(map);
return factoryBean;
}
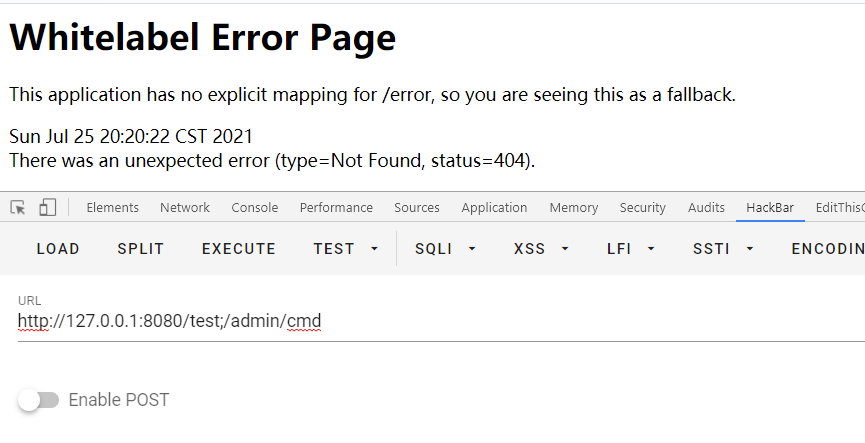
漏洞复现
根据漏洞payload访问:http://127.0.0.1:8080/test;/admin/cmd,但是发现没有进行绕过成功,而是报错了
接着查了相关的文章,我这里继续把spring-boot的版本进行替换
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.6.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
再次访问http://127.0.0.1:8080/test;/admin/cmd,这里却发现了成功绕过
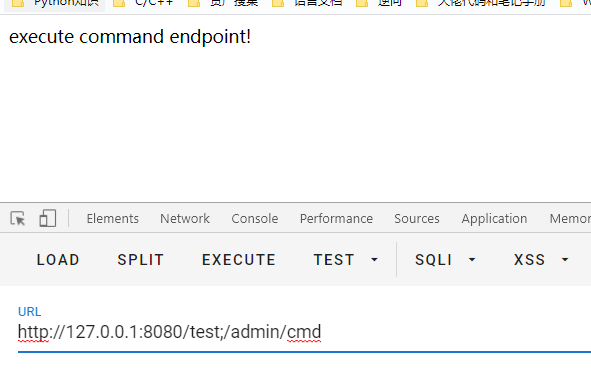
接着我在2.2.6的基础上,将context-path去掉,继续访问``http://127.0.0.1:8080/test;/admin/cmd`,这里发现又不行了
问题
1、为什么需要设置context-path,权限才能绕过?
2、为什么2.5.2的spring-boot版本不可以进行利用,却在2.2.6的版本上可以进行利用?
问题1
1、为什么需要设置context-path,权限才能绕过?
回想下对于shiro的1.5.2的漏洞代码修复,官方变动的地方为getRequestURI的方式,那么产生这个问题的肯定也是来自这里,所以这里仔细来分析这个地方,这里调试的环境为2.2.6
其实想下,它的修复方式就是通过如下来获取getRequestURI来进行获取请求路径,也就是如下代码,可以看到它是通过 ContextPath + ServletPath + getPathInfo 来进行拼接而成的
public static String getRequestUri(HttpServletRequest request) {
String uri = (String) request.getAttribute(INCLUDE_REQUEST_URI_ATTRIBUTE);
if (uri == null) {
uri = valueOrEmpty(request.getContextPath()) + "/" +
valueOrEmpty(request.getServletPath()) +
valueOrEmpty(request.getPathInfo());
}
return normalize(decodeAndCleanUriString(request, uri));
}
当没有ContextPath设定的时候,我们访问http://127.0.0.1:8080/admin;/cmd,那么此时getRequestURI处理过后就是//admin/cmd,那么这个则会被shiro过滤器所拦截
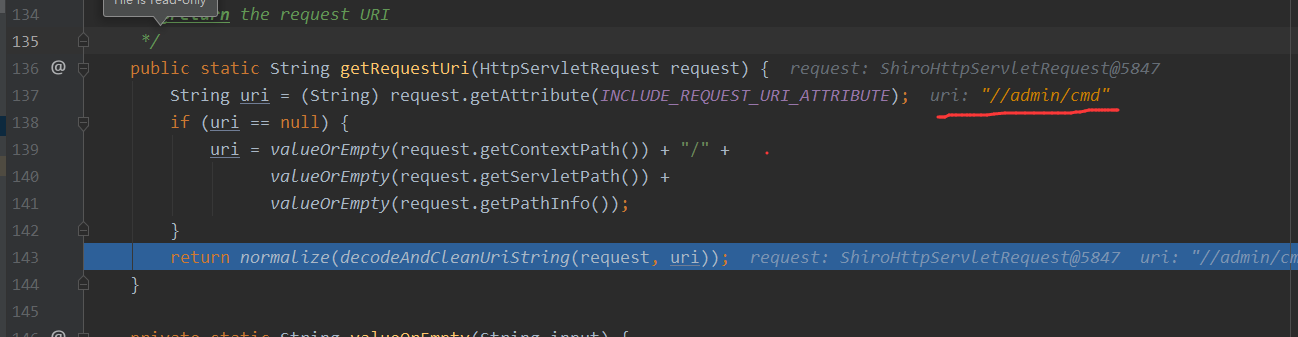
上面的图中其实还没走decodeAndCleanUriString方法,这个方法走了之后//admin/cmd,也就会成为/admin/cmd
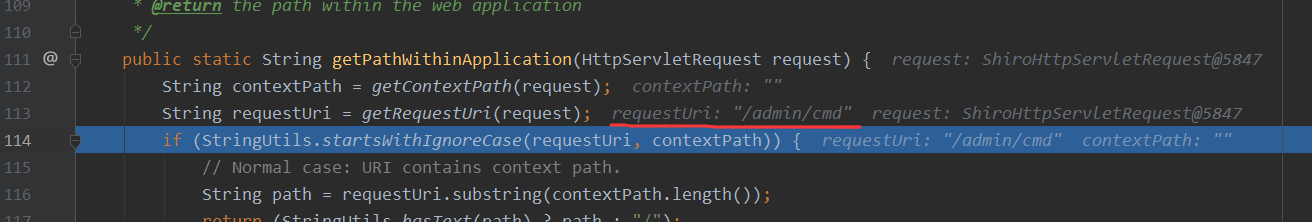
但是如果ContextPath有设定的时候,我们再来访问http://127.0.0.1:8080/test;/admin/cmd,注意的是我们这里设定的ContextPath为test,所以才这么访问,可以看到此时getRequestURI处理过后则是/test;//admin/cmd
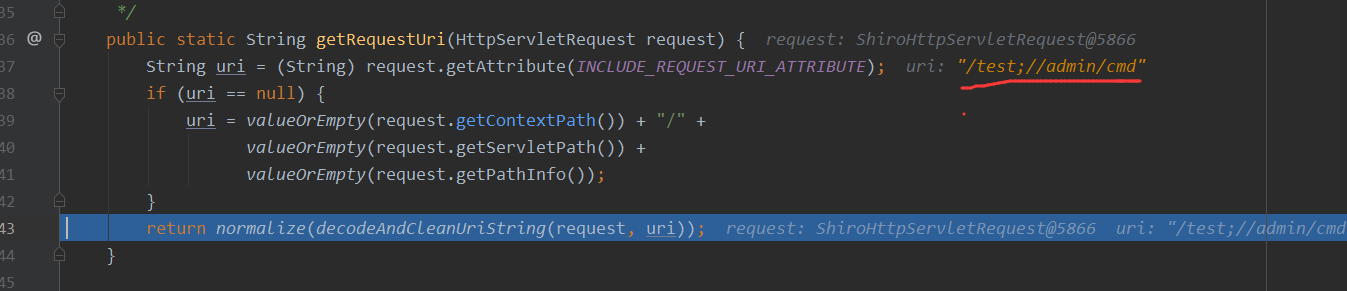
那么继续走decodeAndCleanUriString方法,这里最后就拿到了一个/test
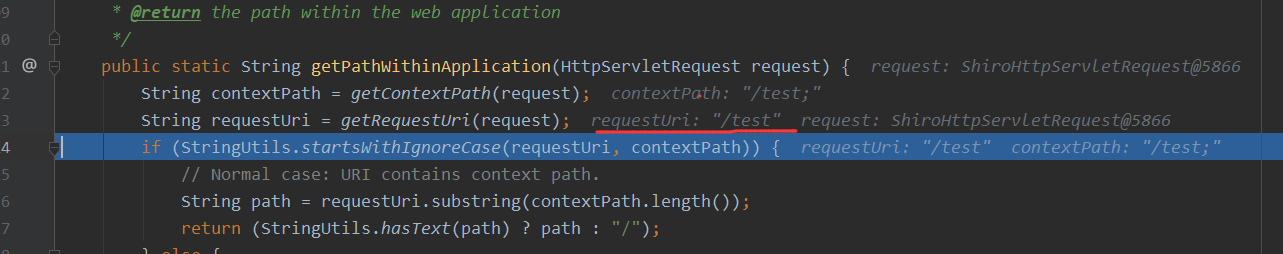
这里你就会发现获取ContextPath方法和getServletPath、getPathInfo方法不同的就是,它不会对;这个进行处理,导致decodeAndCleanUriString的时候将;后面的都去除掉,最后只剩下了一个/test
然后这里的/test,最后的结果就是在shiro过滤器中没有匹配到。
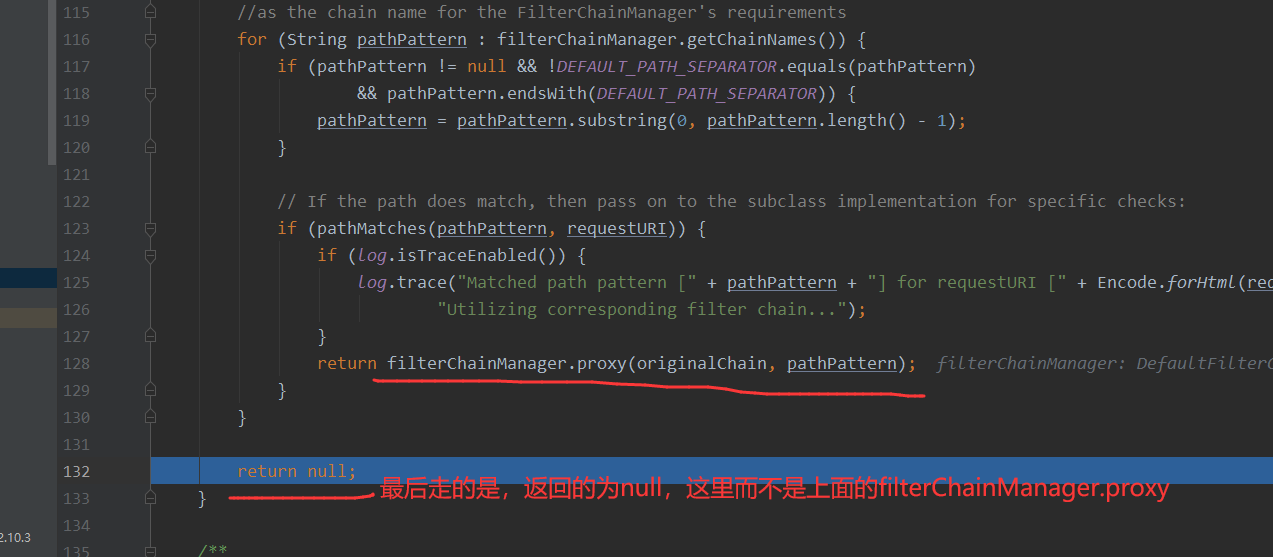
接着看spring中是如何运作的?
还是老样子,打断点在org/springframework/web/util/UrlPathHelper.java#getLookupPathForRequest方法中,可以看到这里分析的2.2.6
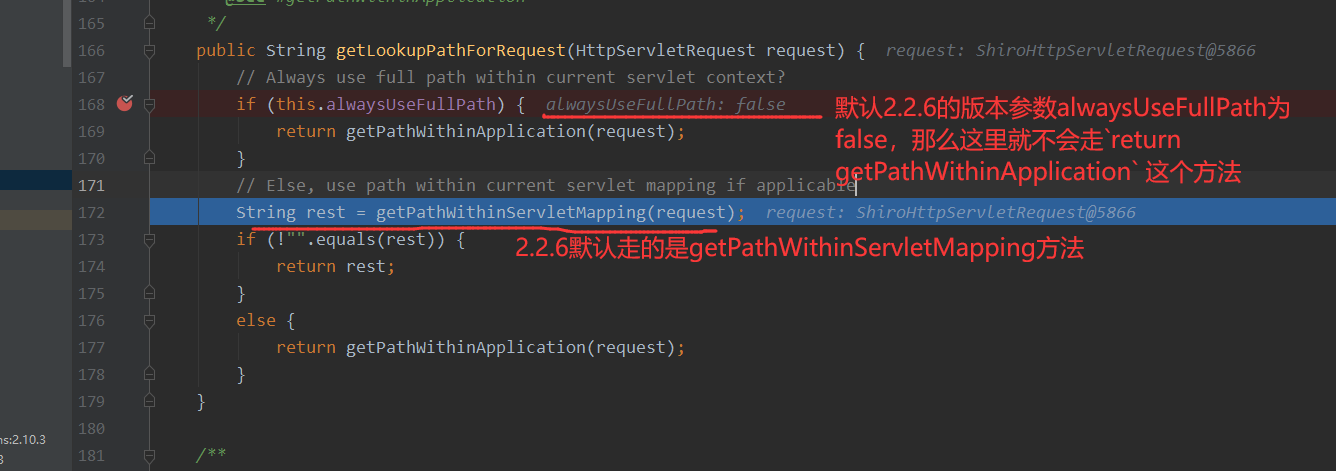
2.2.6默认走的就是getPathWithinServletMapping方法,这个方法返回的则是/admin/cmd
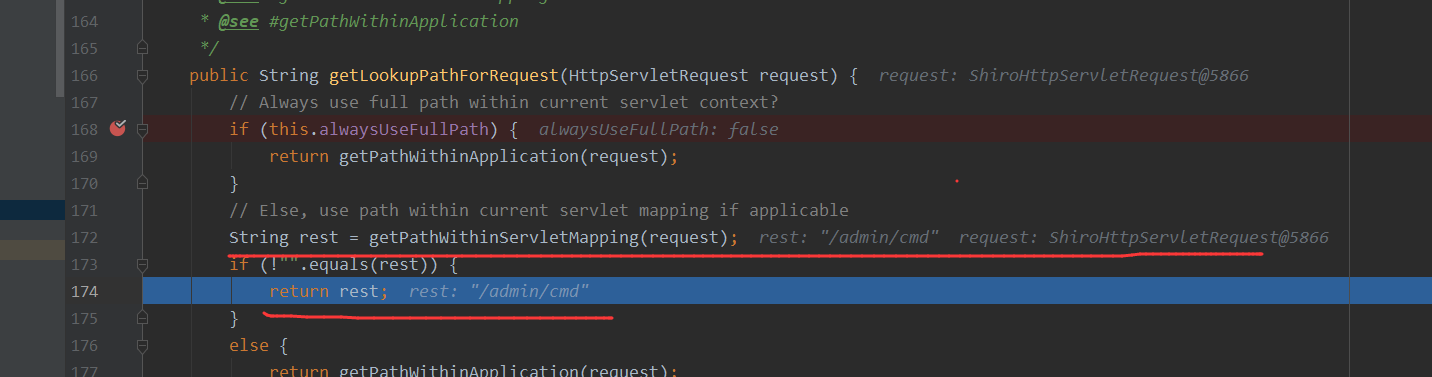
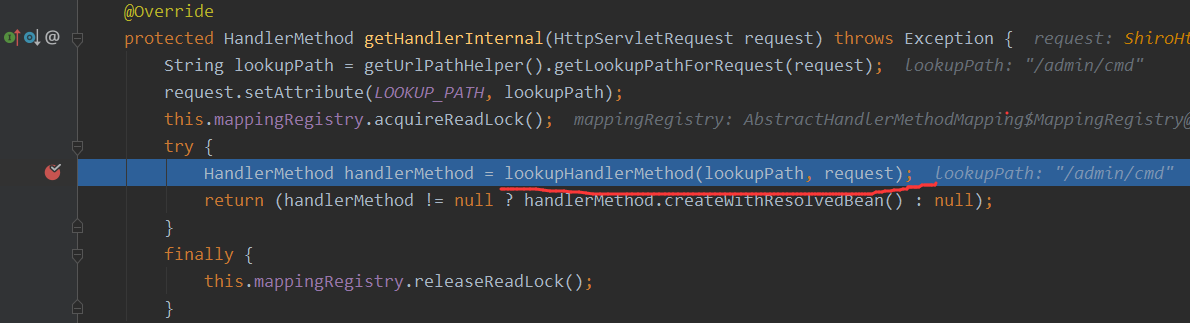
最后就是通过解析对应的controller的方法,获得对应的handler来进行反射调用
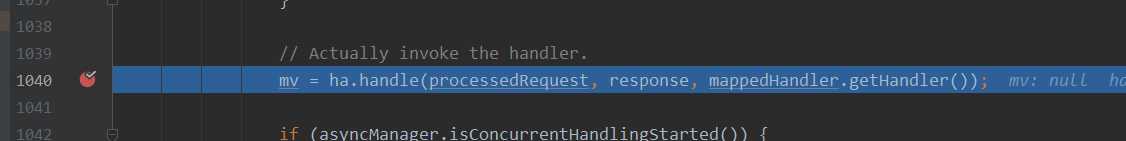
其实自己总结下:这个CVE的产生则是跟shiro和spring对ContextPath的处理方式不同产生的权限绕过,所以也就是这个漏洞为什么需要ContextPath的支持。
2、为什么2.5.2的SpringBoot版本不可以进行利用,却在2.2.6的版本上可以进行利用
继续走第二个问题,这里把SpringBoot的环境换成2.5.2进行调试
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.5.2</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
继续之前的过程,先看shiro过滤器这边的绕过,可以绕过,如下所示,获得是/test
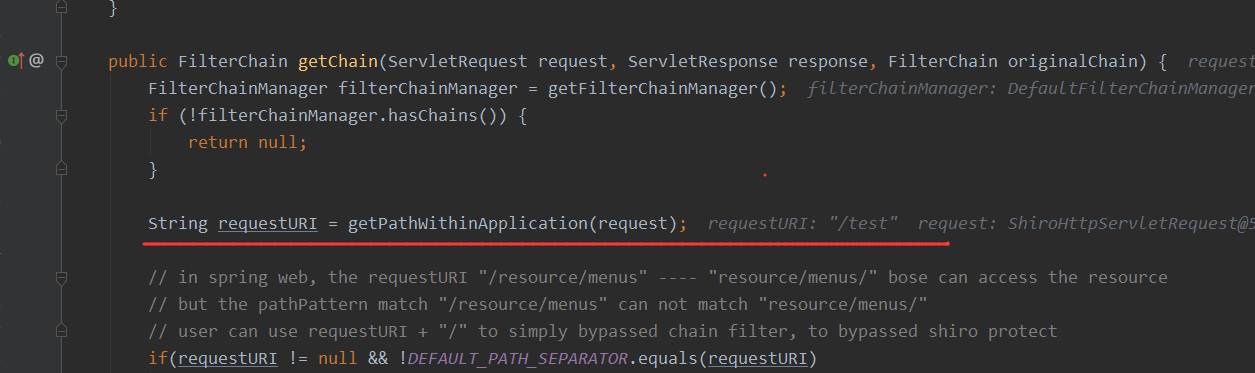
接着看spring的路由走法,可以发现跟2.2.6的走法是不同的,主要受到了alwaysUseFullPath参数值的影响

alwaysUseFullPath为true和false的区别到底是怎么样的呢?
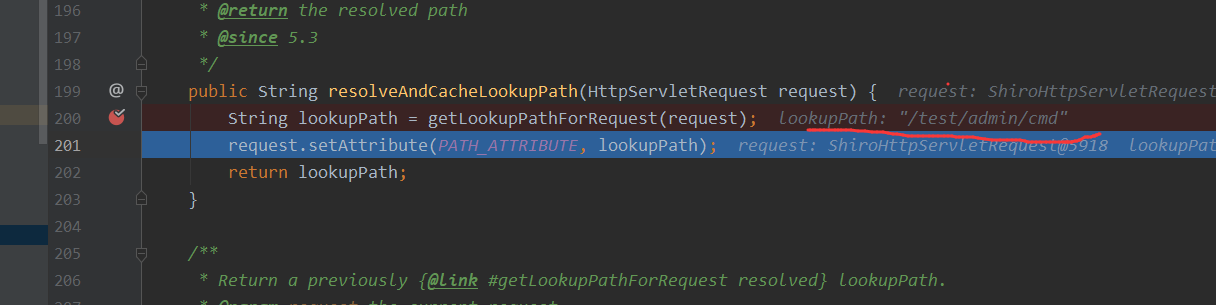
可以看到如果为true的话,下面的语句不会执行方法getPathWithinServletMapping了,而是直接返回一个getPathWithinApplication处理过后的结果,而单单只经过getPathWithinApplication方法处理的最后在调用对应方法的时候就调用不到
alwaysUseFullPath为true的时候结果为如下
alwaysUseFullPath为false的时候结果为如下
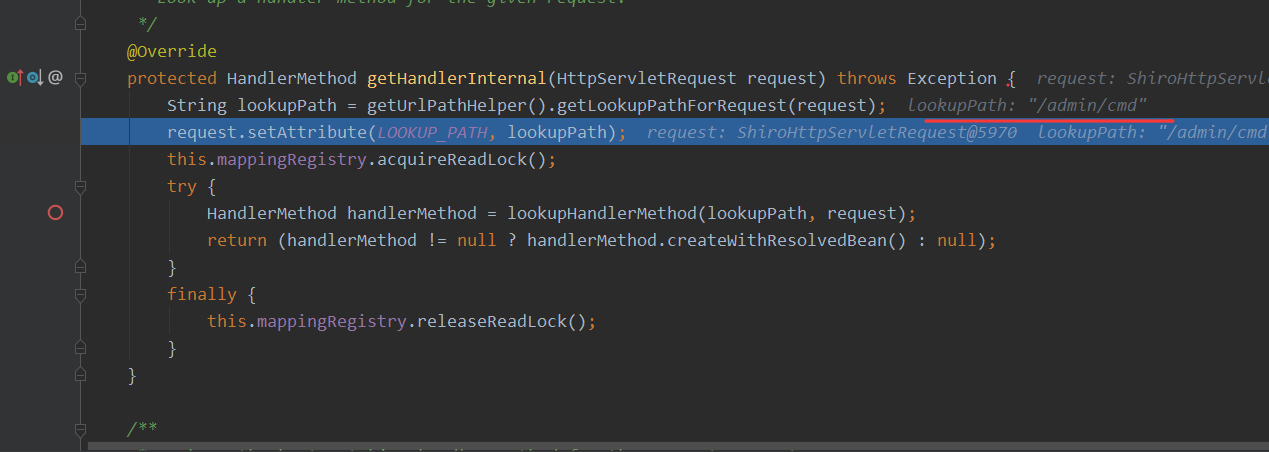
当Spring Boot版本在小于等于2.3.0.RELEASE的情况下,alwaysUseFullPath为默认值false,这会使得其获取ServletPath,所以在路由匹配时相当于会进行路径标准化包括对%2e解码以及处理跨目录,这可能导致身份验证绕过。而反过来由于高版本将alwaysUseFullPath自动配置成了true从而开启全路径,又可能导致一些安全问题。
官方修复方案
该漏洞是Shiro与Servlet对于ContextPath处理的差异,Shiro将ContextPath与其他路径拼接后代入了格式化方法进⾏处理,而该方法将分号后的所有部分都截断,这是漏洞的核心。
https://github.com/apache/shiro/compare/shiro-root-1.5.2...shiro-root-1.5.3
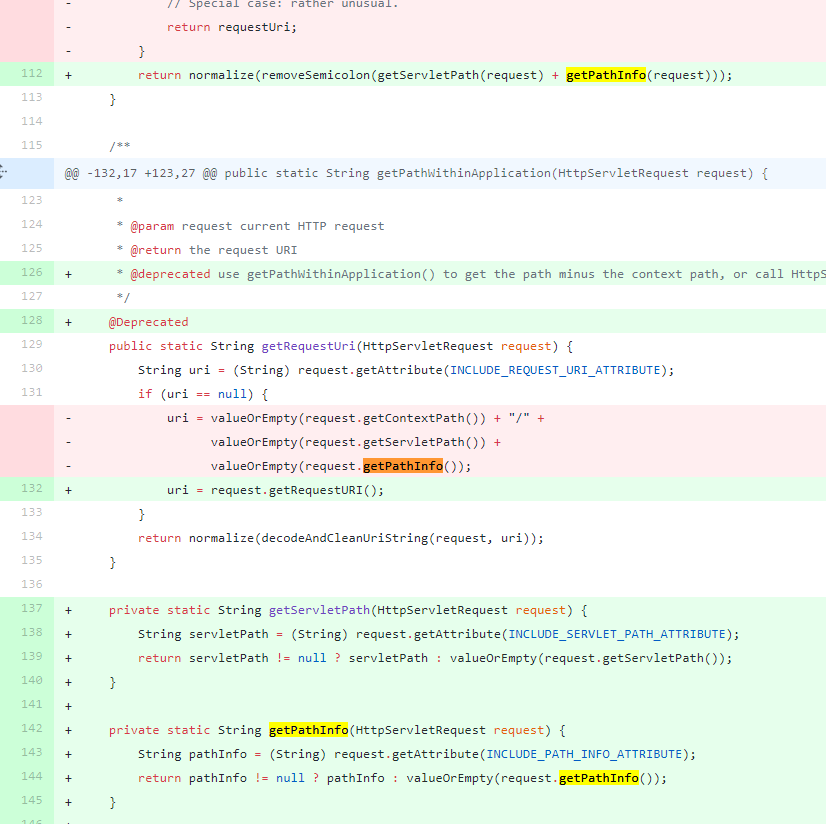
重新跟下,它是如何修复的?
访问http://127.0.0.1:8080/test;/admin/cmd
如下可以看到,这里的话在shiro处理路径的时候,getPathWithinApplication方法出来之后就是/admin/cmd,这里并不是将;后面的内容都去掉了

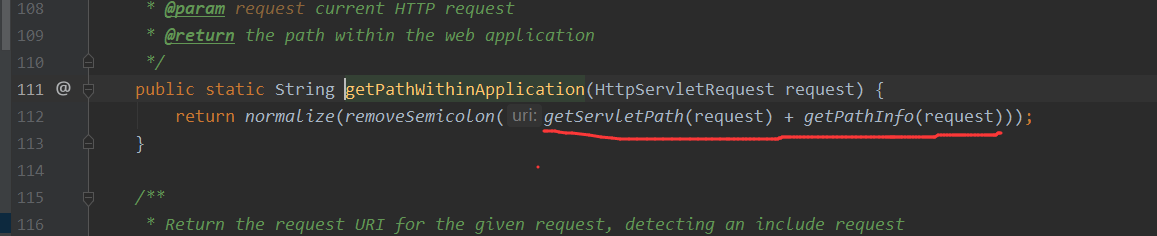
可以看下getPathWithinApplication比起上个版本是如何修复的?
不对Servletpath进行处理了,这里处理的只有getServletPath(request) + getPathInfo(request)
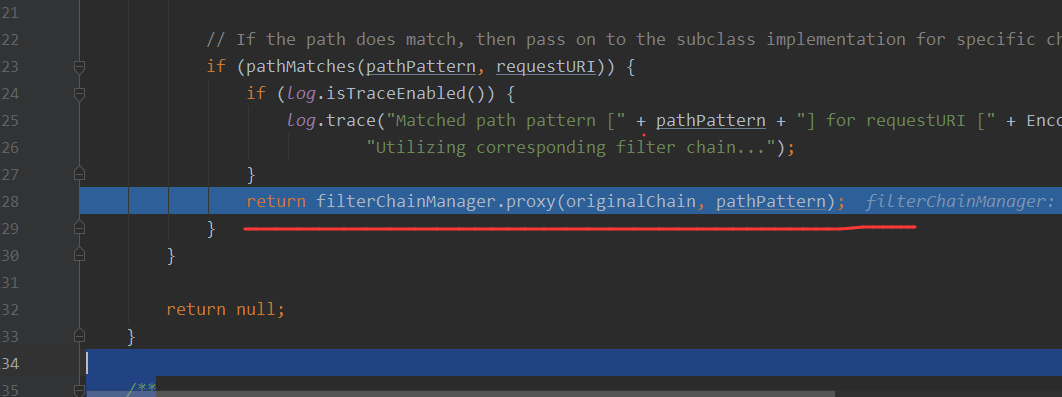
最后匹配了规则之后,走的就是shiro过滤器的地方
CVE-2020-13933
影响版本: shiro<1.6.0
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.5.3</version>
</dependency>
环境配置
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value="/hello/{index}", method= RequestMethod.GET)
public String hello1(@PathVariable String index){
// CVE-2020-13933
return "Hello World "+ index.toString() + "!";
}
@Bean
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean filterFactoryBean(){
ShiroFilterFactoryBean factoryBean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
factoryBean.setSecurityManager(manager());
factoryBean.setUnauthorizedUrl("/login");
factoryBean.setLoginUrl("/login");
Map<String, String> filterMap = new HashMap<>();
filterMap.put("/login", "anon");
// filterMap.put("/admin/*", "authc");
filterMap.put("/hello/*", "authc");
// filterMap.put("/admin", "authc");
// map.put("/static/**", "anon");
//map.put("/**", "authc");
factoryBean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(filterMap);
return factoryBean;
}
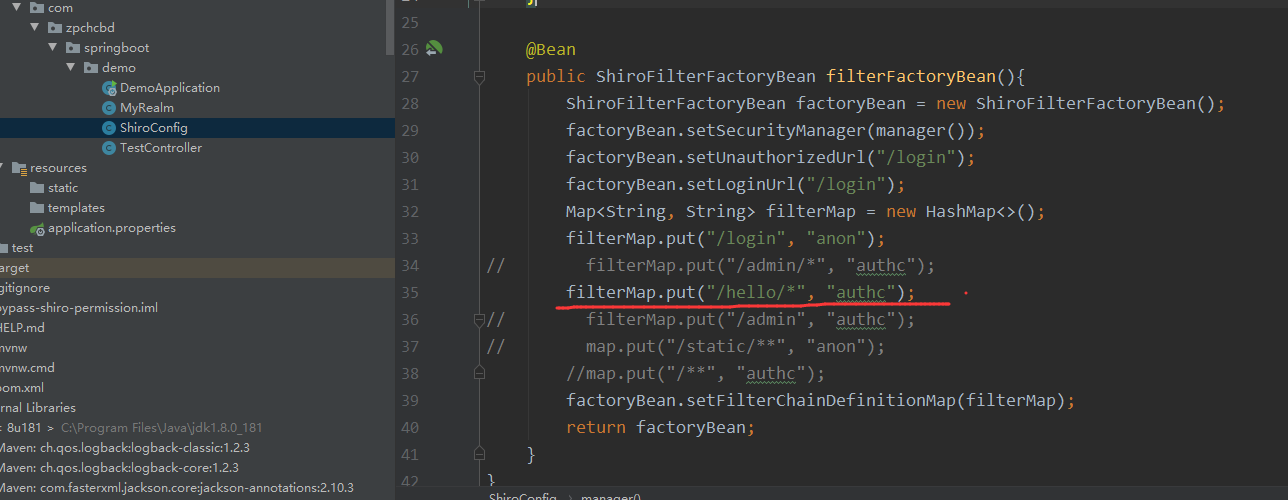
shiro分析
getServletPath():默认会将URI进⾏Urldecode
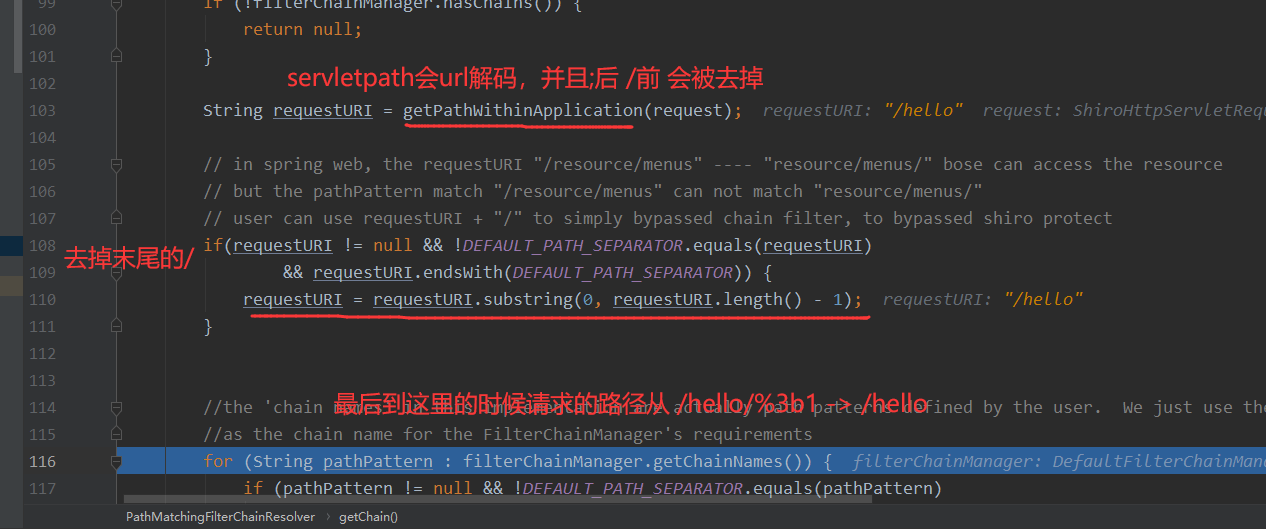
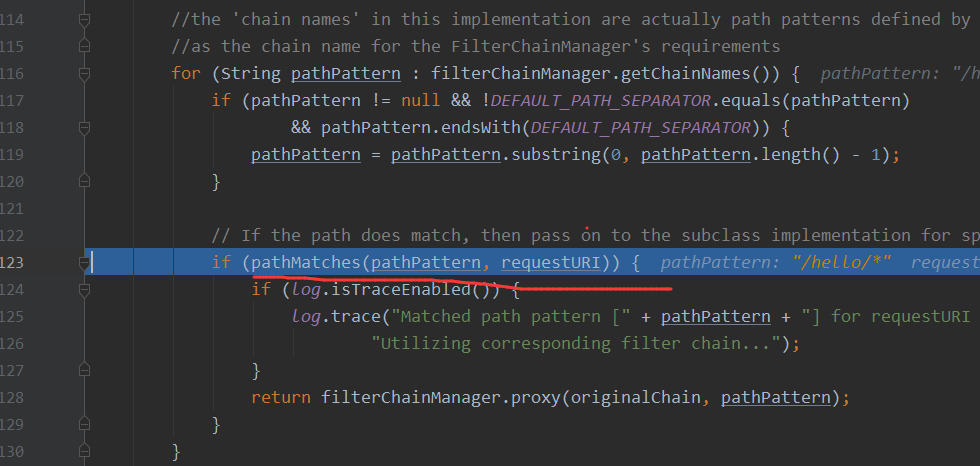
接着就是下面pathMatches方法进行相关匹配的shiro拦截器进行比较
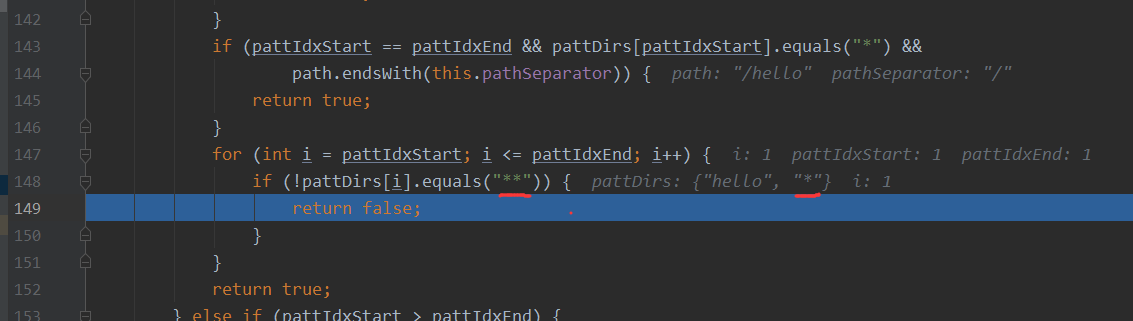
不满足,** 和 * 不等,所以返回false,从而进行绕过
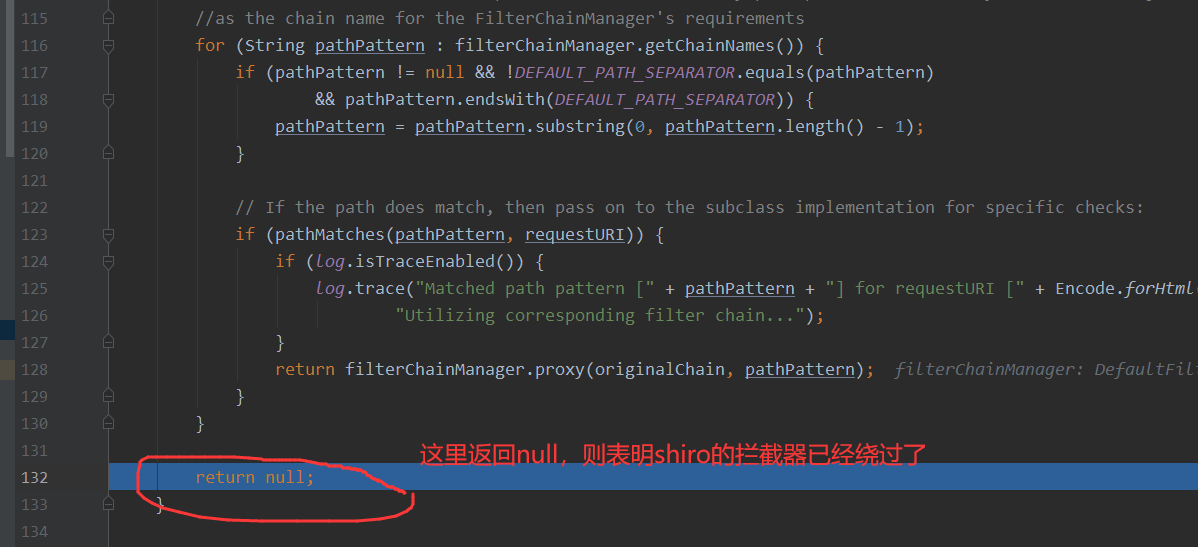
需要注意的是:
如果这两个都存在的话,那么对于访问http://127.0.0.1:8080/hello/%3b111,这种就无法绕过
filterMap.put("/hello/*", "authc");
filterMap.put("/hello","authc");
原因在于shiro的判断中pathMatches的方法的行为。
spring分析
getPathWithinServletMapping方法
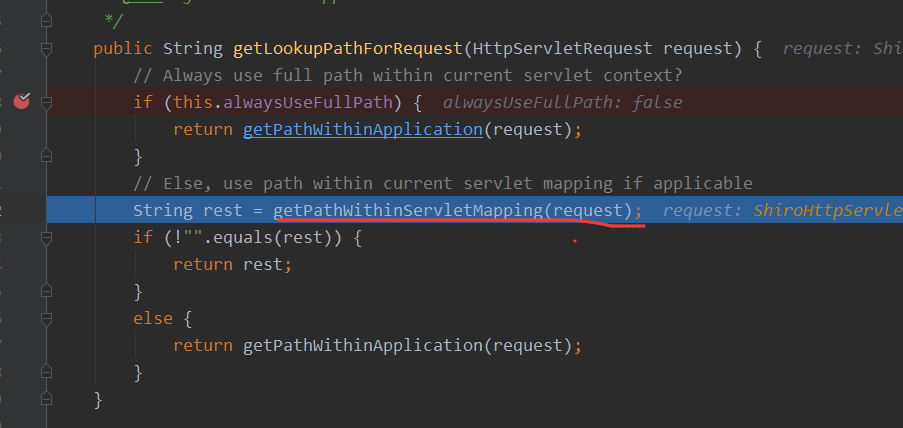
得到的路径为/hello/;1
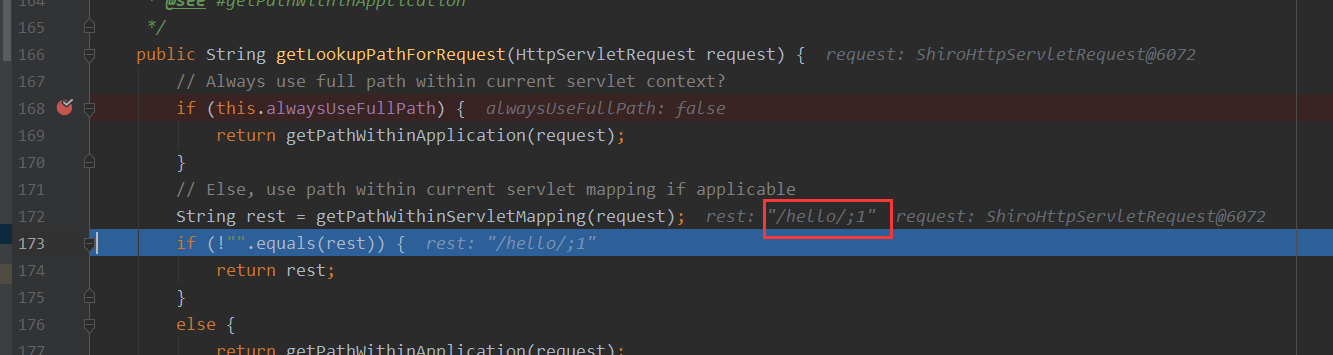
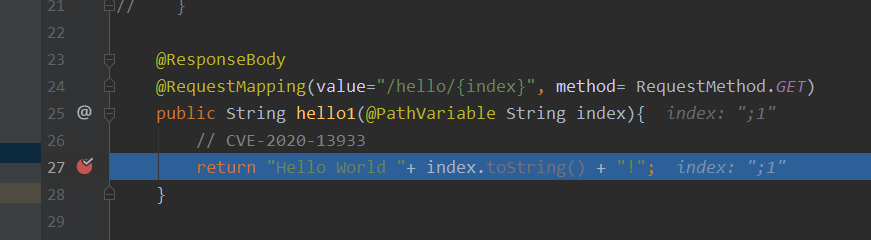
漏洞点出在Shiro会先进⾏urldecode后再进⾏分号截断,⽽Spring⾸先进⾏了分号截断,随后才会进⾏urldecode。正是两者之间微⼩的差异才导致了漏洞的产⽣。
官方修复
https://github.com/apache/shiro/compare/shiro-root-1.5.3...shiro-root-1.6.0