Spring Security 入门(四):Session 会话管理
本文在 Spring Security 入门(三):Remember-Me 和注销登录 一文的代码基础上介绍Spring Security的 Session 会话管理。
Session 会话管理的配置方法
Session 会话管理需要在configure(HttpSecurity http)方法中通过http.sessionManagement()开启配置。此处对http.sessionManagement()返回值的主要方法进行说明,这些方法涉及 Session 会话管理的配置,具体如下:
invalidSessionUrl(String invalidSessionUrl):指定会话失效时(请求携带无效的 JSESSIONID 访问系统)重定向的 URL,默认重定向到登录页面。invalidSessionStrategy(InvalidSessionStrategy invalidSessionStrategy):指定会话失效时(请求携带无效的 JSESSIONID 访问系统)的处理策略。maximumSessions(int maximumSessions):指定每个用户的最大并发会话数量,-1 表示不限数量。maxSessionsPreventsLogin(boolean maxSessionsPreventsLogin):如果设置为 true,表示某用户达到最大会话并发数后,新会话请求会被拒绝登录;如果设置为 false,表示某用户达到最大会话并发数后,新会话请求访问时,其最老会话会在下一次请求时失效并根据 expiredUrl() 或者 expiredSessionStrategy() 方法配置的会话失效策略进行处理,默认值为 false。expiredUrl(String expiredUrl):如果某用户达到最大会话并发数后,新会话请求访问时,其最老会话会在下一次请求时失效并重定向到 expiredUrl。expiredSessionStrategy(SessionInformationExpiredStrategy expiredSessionStrategy):如果某用户达到最大会话并发数后,新会话请求访问时,其最老会话会在下一次请求中失效并按照该策略处理请求。注意如果本方法与 expiredUrl() 同时使用,优先使用 expiredUrl() 的配置。sessionRegistry(SessionRegistry sessionRegistry):设置所要使用的 sessionRegistry,默认配置的是 SessionRegistryImpl 实现类。
Session 会话失效处理
当用户的 Session 会话失效(请求携带着无效的 JSESSIONID 访问系统)时,可以制定相关策略对会话失效的请求进行处理。
invalidSessionUrl 方法
☕️ 修改安全配置类 SpringSecurityConfig,配置 Session 会话失效时重定向到/login/page
@EnableWebSecurity // 开启 MVC Security 安全配置
public class SpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//...
/**
* 定制基于 HTTP 请求的用户访问控制
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//...
// 开启 Session 会话管理配置
http.sessionManagement()
// 设置 Session 会话失效时重定向路径,默认为 loginPage()
.invalidSessionUrl("/login/page");
}
//...
}
☕️ 设置 Session 的失效时间
Session 的失效时间配置是 SpringBoot 原生支持的,可以在 application.properties 配置文件中直接配置:
# session 失效时间,单位是秒,默认为 30min
server.servlet.session.timeout=30m
# JSESSIONID (Cookie)的生命周期,单位是秒,默认为 -1
server.servlet.session.cookie.max-age=-1
注意:Session 的失效时间至少要 1 分钟,少于 1 分钟按照 1 分钟配置,查看源码:
public class TomcatServletWebServerFactory extends AbstractServletWebServerFactory implements ConfigurableTomcatWebServerFactory, ResourceLoaderAware {
//...
private long getSessionTimeoutInMinutes() {
Duration sessionTimeout = this.getSession().getTimeout();
// 至少 1 分钟,少于 1 分钟按照 1 分钟配置
return this.isZeroOrLess(sessionTimeout) ? 0L : Math.max(sessionTimeout.toMinutes(), 1L);
}
//...
}
为了方便检验,在 application.properties 中配置 Session 的失效时间为 1 分钟:
# session 失效时间,单位是秒,默认为 30min
server.servlet.session.timeout=60
☕️ 测试
浏览器访问localhost:8080/login/page,输入正确的用户名、密码(不选择“记住我”功能)成功登录后,重定向到首页面:
之后,等待 1 分钟,刷新页面,浏览器重定向到/login/page:
invalidSessionStrategy 方法
如果想要自定义 Session 会话失效处理策略,使用该方法传入自定义策略。
⭐️ 自定义 Session 会话失效处理策略 CustomInvalidSessionStrategy
package com.example.config.security.session;
import com.example.entity.ResultData;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.web.DefaultRedirectStrategy;
import org.springframework.security.web.RedirectStrategy;
import org.springframework.security.web.session.InvalidSessionStrategy;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.servlet.http.Cookie;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 用户请求携带无效的 JSESSIONID 访问时的处理策略,即对应的 Session 会话失效
*/
@Component
public class CustomInvalidSessionStrategy implements InvalidSessionStrategy {
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
private final RedirectStrategy redirectStrategy = new DefaultRedirectStrategy();
@Override
public void onInvalidSessionDetected(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
// 清除浏览器中的无效的 JSESSIONID
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("JSESSIONID", null);
cookie.setPath(getCookiePath(request));
cookie.setMaxAge(0);
response.addCookie(cookie);
String xRequestedWith = request.getHeader("x-requested-with");
// 判断前端的请求是否为 ajax 请求
if ("XMLHttpRequest".equals(xRequestedWith)) {
// 响应 JSON 数据
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(new ResultData<>(1, "SESSION 失效,请重新登录!")));
}else {
// 重定向到登录页面
redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response, "/login/page");
}
}
private String getCookiePath(HttpServletRequest request) {
String contextPath = request.getContextPath();
return contextPath.length() > 0 ? contextPath : "/";
}
}
⭐️ 修改安全配置类 SpringSecurityConfig,配置使用自定义的 Session 会话失效处理策略
@EnableWebSecurity // 开启 MVC Security 安全配置
public class SpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//...
@Autowired
private CustomInvalidSessionStrategy invalidSessionStrategy; // 自定义 Session 会话失效策略
//...
/**
* 定制基于 HTTP 请求的用户访问控制
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//...
// 开启 Session 会话管理配置
http.sessionManagement()
// 设置 Session 会话失效时重定向路径,默认为 loginPage()
// .invalidSessionUrl("/login/page")
// 配置使用自定义的 Session 会话失效处理策略
.invalidSessionStrategy(invalidSessionStrategy);
}
//...
}
⭐️ 测试
浏览器访问localhost:8080/login/page,输入正确的用户名、密码(不选择“记住我”功能)成功登录后,重定向到首页面:

之后,等待 1 分钟,刷新页面,查看响应头:
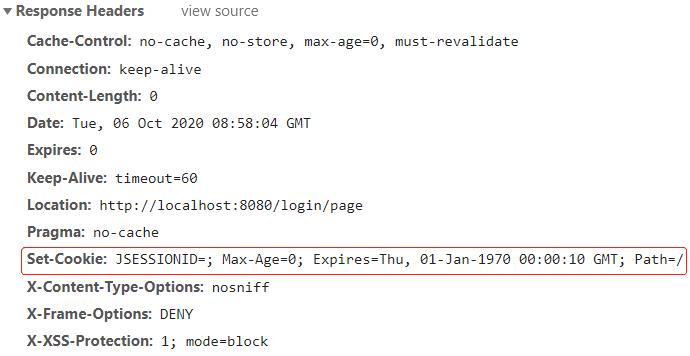
同时,浏览器重定向到/login/page:

Session 会话并发控制
Session 会话并发控制可以限制用户的最大并发会话数量,例如:只允许一个用户在一个地方登陆,也就是说每个用户在系统中只能有一个 Session 会话。为了方便检验,在 application.properties 中将 Session 的过期时间改回 30 分钟:
# session 有效期,单位是秒,默认为 30min
server.servlet.session.timeout=30m
在使用 Session 会话并发控制时,最好保证自定义的 UserDetails 实现类重写了 equals() 和 hashCode() 方法:
@Data
public class User implements UserDetails {
//...
private String username; // 用户名
//...
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) { // equals() 方法一般要重写
return obj instanceof User && this.username.equals(((User) obj).username);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() { // hashCode() 方法一般要重写
return this.username.hashCode();
}
}
我们前面实现了两种登录方式:用户名、密码登录和手机短信验证码登录,需要保证两种登录方式使用的是同一个 SessionAuthenticationStrategy 实例,也就是 MobileAuthenticationConfig 配置类中要有(1.4)的配置:
@Component
public class MobileAuthenticationConfig extends SecurityConfigurerAdapter<DefaultSecurityFilterChain, HttpSecurity> {
//...
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//...
//(1.1) 创建手机短信验证码认证过滤器的实例 filer
MobileAuthenticationFilter filter = new MobileAuthenticationFilter();
//...
//(1.4) 设置 filter 使用 SessionAuthenticationStrategy 会话管理器
// 多种登录方式应该使用同一个会话管理器实例,获取 Spring 容器已经存在的 SessionAuthenticationStrategy 实例
SessionAuthenticationStrategy sessionAuthenticationStrategy = http.getSharedObject(SessionAuthenticationStrategy.class);
filter.setSessionAuthenticationStrategy(sessionAuthenticationStrategy);
//...
}
}
如果没有(1.4)的配置,MobileAuthenticationFilter 默认使用的是 NullAuthenticatedSessionStrategy 实例管理 Session,而 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 使用的是 CompositeSessionAuthenticationStrategy 实例管理 Session,也就是说两种登录方式的 Session 管理是相互独立的,这是不应该出现的情况。
基本使用
场景一:如果同一个用户在第二个地方登录,则不允许他二次登录
✏️ 修改安全配置类 SpringSecurityConfig,配置用户最大并发 Session 会话数量和限制用户二次登录
@EnableWebSecurity // 开启 MVC Security 安全配置
public class SpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//...
/**
* 定制基于 HTTP 请求的用户访问控制
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//...
// 开启 Session 会话管理配置
http.sessionManagement()
// 设置 Session 会话失效时重定向路径,默认为 loginPage()
// .invalidSessionUrl("/login/page")
// 配置使用自定义的 Session 会话失效处理策略
.invalidSessionStrategy(invalidSessionStrategy)
// 设置单用户的 Session 最大并发会话数量,-1 表示不受限制
.maximumSessions(1)
// 设置为 true,表示某用户达到最大会话并发数后,新会话请求会被拒绝登录
.maxSessionsPreventsLogin(true);
// 设置所要使用的 sessionRegistry,默认为 SessionRegistryImpl 实现类
.sessionRegistry(sessionRegistry());
}
/**
* 注册 SessionRegistry,该 Bean 用于管理 Session 会话并发控制
*/
@Bean
public SessionRegistry sessionRegistry() {
return new SessionRegistryImpl();
}
/**
* 配置 Session 的监听器(注意:如果使用并发 Sessoion 控制,一般都需要配置该监听器)
* 解决 Session 失效后, SessionRegistry 中 SessionInformation 没有同步失效的问题
*/
@Bean
public HttpSessionEventPublisher httpSessionEventPublisher() {
return new HttpSessionEventPublisher();
}
//..
}
✏️ 测试
第一个浏览器访问localhost:8080/login/page,输入正确的用户名、密码成功登录后,会重定向到/index:

第二个浏览器访问localhost:8080/login/page,输入相同的用户名、密码访问,重定向/login/page?error:
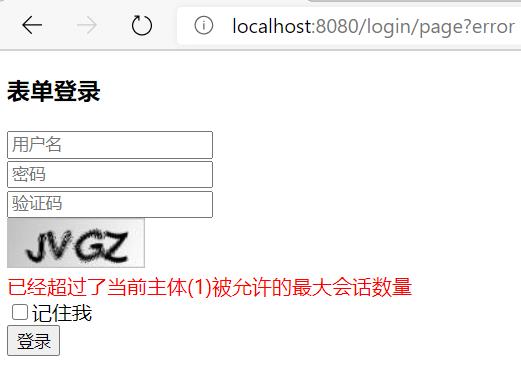
上述配置限制了同一个用户的二次登陆,但是不建议使用该配置。因为用户一旦被盗号,那真正的用户后续就无法登录,只能通过联系管理员解决,所以如果只能一个用户 Session 登录,一般是新会话登录并将老会话踢下线。
场景二:如果同一个用户在第二个地方登录,则将第一个踢下线
📚 自定义最老会话被踢时的处理策略 CustomSessionInformationExpiredStrategy:
package com.example.config.security.session;
import com.example.entity.ResultData;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationServiceException;
import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.web.DefaultRedirectStrategy;
import org.springframework.security.web.RedirectStrategy;
import org.springframework.security.web.session.SessionInformationExpiredEvent;
import org.springframework.security.web.session.SessionInformationExpiredStrategy;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 前提:Session 并发处理的配置为 maxSessionsPreventsLogin(false)
* 用户的并发 Session 会话数量达到上限,新会话登录后,最老会话会在下一次请求中失效,并执行此策略
*/
@Component
public class CustomSessionInformationExpiredStrategy implements SessionInformationExpiredStrategy {
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
private final RedirectStrategy redirectStrategy = new DefaultRedirectStrategy();
@Override
public void onExpiredSessionDetected(SessionInformationExpiredEvent event) throws IOException {
HttpServletRequest request = event.getRequest();
HttpServletResponse response = event.getResponse();
// 最老会话被踢下线时显示的信息
UserDetails userDetails = (UserDetails) event.getSessionInformation().getPrincipal();
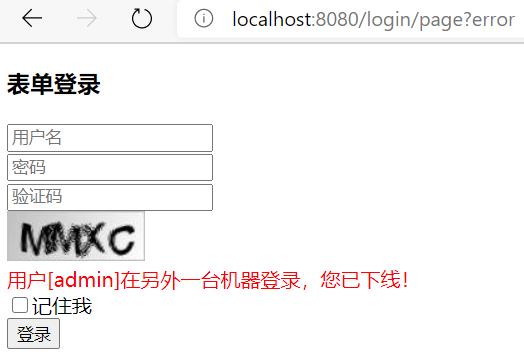
String msg = String.format("用户[%s]在另外一台机器登录,您已下线!", userDetails.getUsername());
String xRequestedWith = event.getRequest().getHeader("x-requested-with");
// 判断前端的请求是否为 ajax 请求
if ("XMLHttpRequest".equals(xRequestedWith)) {
// 认证成功,响应 JSON 数据
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(new ResultData<>(1, msg)));
}else {
// 返回到登录页面显示信息
AuthenticationException e = new AuthenticationServiceException(msg);
request.getSession().setAttribute("SPRING_SECURITY_LAST_EXCEPTION", e);
redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response, "/login/page?error");
}
}
}
📚 修改安全配置类 SpringSecurityConfig,配置最老会话被踢时的处理策略
@EnableWebSecurity // 开启 MVC Security 安全配置
public class SpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//...
@Autowired
private CustomSessionInformationExpiredStrategy sessionInformationExpiredStrategy; // 自定义最老会话失效策略
//...
/**
* 定制基于 HTTP 请求的用户访问控制
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//...
// 开启 Session 会话管理配置
http.sessionManagement()
// 设置 Session 会话失效时重定向路径,默认为 loginPage()
// .invalidSessionUrl("/login/page")
// 配置使用自定义的 Session 会话失效处理策略
.invalidSessionStrategy(invalidSessionStrategy)
// 设置单用户的 Session 最大并发会话数量,-1 表示不受限制
.maximumSessions(1)
// 设置为 true,表示某用户达到最大会话并发数后,新会话请求会被拒绝登录;
// 设置为 false,表示某用户达到最大会话并发数后,新会话请求访问时,其最老会话会在下一次请求时失效
.maxSessionsPreventsLogin(false)
// 设置所要使用的 sessionRegistry,默认为 SessionRegistryImpl 实现类
.sessionRegistry(sessionRegistry())
// 最老会话在下一次请求时失效,并重定向到 /login/page
//.expiredUrl("/login/page");
// 最老会话在下一次请求时失效,并按照自定义策略处理
.expiredSessionStrategy(sessionInformationExpiredStrategy);
}
/**
* 注册 SessionRegistry,该 Bean 用于管理 Session 会话并发控制
*/
@Bean
public SessionRegistry sessionRegistry() {
return new SessionRegistryImpl();
}
/**
* 配置 Session 的监听器(如果使用并发 Sessoion 控制,一般都需要配置)
* 解决 Session 失效后, SessionRegistry 中 SessionInformation 没有同步失效问题
*/
@Bean
public HttpSessionEventPublisher httpSessionEventPublisher() {
return new HttpSessionEventPublisher();
}
//...
}
📚 测试
第一个浏览器访问localhost:8080/login/page,输入正确的用户名、密码成功登录后,重定向到/index:
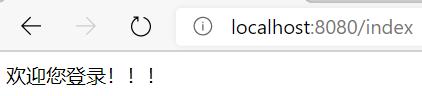
第二个浏览器访问localhost:8080/login/page,输入相同的用户名、密码成功登录后,重定向到/index:

刷新第一个浏览器页面,重定向到/login/page?error:
原理分析
✌ AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter#doFilter
public abstract class AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter extends GenericFilterBean implements ApplicationEventPublisherAware, MessageSourceAware {
private SessionAuthenticationStrategy sessionStrategy = new NullAuthenticatedSessionStrategy();
//...
// 过滤器 doFilter() 方法
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest)req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse)res;
if (!this.requiresAuthentication(request, response)) {
//(1) 判断该请求是否为 POST 方式的登录表单提交请求,如果不是则直接放行,进入下一个过滤器
chain.doFilter(request, response);
} else {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Request is to process authentication");
}
// Authentication 是用来存储用户认证信息的类,后续会进行详细介绍
Authentication authResult;
try {
//(2) 调用子类 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 重写的方法进行身份认证,
// 返回的 authResult 对象封装认证后的用户信息
authResult = this.attemptAuthentication(request, response);
if (authResult == null) {
return;
}
//(3) Session 策略处理(如果配置了用户 Session 最大并发数,就是在此处进行判断并处理)
// 默认使用的是新创建的 NullAuthenticatedSessionStrategy 实例,而 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 过滤器使用的是 CompositeSessionAuthenticationStrategy 实例
this.sessionStrategy.onAuthentication(authResult, request, response);
} catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException var8) {
this.logger.error("An internal error occurred while trying to authenticate the user.", var8);
//(4) 认证失败,调用认证失败的处理器
this.unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, var8);
return;
} catch (AuthenticationException var9) {
this.unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, var9);
return;
}
//(4) 认证成功的处理
if (this.continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication) {
// 默认的 continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication 为 false,所以认证成功之后不进入下一个过滤器
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
// 调用认证成功的处理器
this.successfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authResult);
}
}
//...
public void setSessionAuthenticationStrategy(SessionAuthenticationStrategy sessionStrategy) {
this.sessionStrategy = sessionStrategy;
}
}
上述的(3)过程,sessionStrategy 默认使用的是新创建的 NullAuthenticatedSessionStrategy 实例,所以在前面我们要求 MobileAuthenticationFilter 使用 Spring 容器中已存在的 SessionAuthenticationStrategy 实例,两种登录方式使用同一个 CompositeSessionAuthenticationStrategy 实例管理 Session。
✌ CompositeSessionAuthenticationStrategy#onAuthentication
public class CompositeSessionAuthenticationStrategy implements SessionAuthenticationStrategy {
//...
private final List<SessionAuthenticationStrategy> delegateStrategies;
public void onAuthentication(Authentication authentication, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws SessionAuthenticationException {
SessionAuthenticationStrategy delegate;
// delegateStrategies 是 Session 处理策略集合,会调用这些策略的 onAuthentication() 方法
// 包括处理 Session 并发数的策略 ConcurrentSessionControlAuthenticationStrategy
for(Iterator var4 = this.delegateStrategies.iterator(); var4.hasNext(); delegate.onAuthentication(authentication, request, response)) {
delegate = (SessionAuthenticationStrategy)var4.next();
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Delegating to " + delegate);
}
}
}
//...
}
✌ ConcurrentSessionControlAuthenticationStrategy#onAuthentication
public class ConcurrentSessionControlAuthenticationStrategy implements MessageSourceAware, SessionAuthenticationStrategy {
//...
public void onAuthentication(Authentication authentication, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
//(1) 获取用户在系统中的 Session 列表,元素类型为 SessionInformation,该类后续会介绍
List<SessionInformation> sessions = this.sessionRegistry.getAllSessions(authentication.getPrincipal(), false);
//(2) 获取用户在系统的并发 Session 数量
int sessionCount = sessions.size();
//(3) 获取用户能够允许的最大并发 Session 数量
int allowedSessions = this.getMaximumSessionsForThisUser(authentication);
//(4) 判断当前用户的并发 Session 数量是否达到上限
if (sessionCount >= allowedSessions) {
// allowedSessions 为 -1,表示并发 Session 数量不受限制
if (allowedSessions != -1) {
//(5) 当已存在的 Session 数量等于最大并发 Session 数量时
if (sessionCount == allowedSessions) (5) 当已存在的会话数等于最大会话数时
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
Iterator var8 = sessions.iterator();
while(var8.hasNext()) {
SessionInformation si = (SessionInformation)var8.next();
//(6) 当前验证的会话如果并非新的会话,则不做任何处理
if (si.getSessionId().equals(session.getId())) {
return;
}
}
}
}
//(5) 否则,进行策略判断
this.allowableSessionsExceeded(sessions, allowedSessions, this.sessionRegistry);
}
}
}
protected void allowableSessionsExceeded(List<SessionInformation> sessions, int allowableSessions, SessionRegistry registry) throws SessionAuthenticationException {
//(1) exceptionIfMaximumExceeded 就是配置类中 maxSessionsPreventsLogin() 方法参数
if (!this.exceptionIfMaximumExceeded && sessions != null) {
// 当配置 maxSessionsPreventsLogin(false) 时,才运行此处代码
//(2) 将用户的 SessionInformation 列表按照最后一次访问时间进行排序
sessions.sort(Comparator.comparing(SessionInformation::getLastRequest));
//(3) 获取需要踢下线的 SessionInformation 列表(最老会话列表)
int maximumSessionsExceededBy = sessions.size() - allowableSessions + 1;
List<SessionInformation> sessionsToBeExpired = sessions.subList(0, maximumSessionsExceededBy);
Iterator var6 = sessionsToBeExpired.iterator();
while(var6.hasNext()) {
//(4) 将用户最老会话列表中的所有 SessionInformation 对象记为过期
// 注意这里只是标记,而不是真正的将 HttpSession 对象过期,
// 只有最老会话再次请求或者达到过期时间,HttpSession 对象才会真正失效
SessionInformation session = (SessionInformation)var6.next();
session.expireNow();
}
} else {
// 当配置 maxSessionsPreventsLogin(true) 时,运行此处代码
//(2) 当前(最新)会话的请求访问抛出异常,返回信息(超出最大并发 Session 数量)
throw new SessionAuthenticationException(this.messages.getMessage("ConcurrentSessionControlAuthenticationStrategy.exceededAllowed", new Object[]{allowableSessions}, "Maximum sessions of {0} for this principal exceeded"));
}
}
//...
}
上述代码中,获取当前用户在系统中的 Session 列表的元素类型是 SessionInformation,而不是 HttpSession,我们查看其源码定义:
public class SessionInformation implements Serializable {
private Date lastRequest; // 最后一次访问时间
private final Object principal; // UserDetails 对象
private final String sessionId; // SessionId
private boolean expired = false; // 是否过期
// ...
}
可以发现 SessionInformation 并不是真正的 HttpSession 对象,只是对 SessionId 和用户信息的一次封装。对于该类的具体使用,需要查看 SessionRegistryImpl 类。
✌ SessionRegistryImpl
public class SessionRegistryImpl implements SessionRegistry, ApplicationListener<SessionDestroyedEvent> {
// 存放用户(UserDetails)以及其对应的所有 SessionId
private final ConcurrentMap<Object, Set<String>> principals;
// 存放 sessionId 以及其对应的 SessionInformation
private final Map<String, SessionInformation> sessionIds;
public SessionRegistryImpl() {
this.principals = new ConcurrentHashMap();
this.sessionIds = new ConcurrentHashMap();
}
public SessionRegistryImpl(ConcurrentMap<Object, Set<String>> principals, Map<String, SessionInformation> sessionIds) {
this.principals = principals;
this.sessionIds = sessionIds;
}
public List<Object> getAllPrincipals() {
return new ArrayList(this.principals.keySet());
}
// 根据用户的 UserDetails 对象获取用户在系统中的所有 SessionInformation
public List<SessionInformation> getAllSessions(Object principal, boolean includeExpiredSessions) {
//(1) 获取用户在系统中的所有 SessionId 的集合
Set<String> sessionsUsedByPrincipal = (Set)this.principals.get(principal);
if (sessionsUsedByPrincipal == null) {
return Collections.emptyList();
} else {
List<SessionInformation> list = new ArrayList(sessionsUsedByPrincipal.size());
Iterator var5 = sessionsUsedByPrincipal.iterator();
while(true) {
SessionInformation sessionInformation;
do {
do {
if (!var5.hasNext()) {
//(4) 返回用户的 sessionInformation 集合
return list;
}
String sessionId = (String)var5.next();
//(2) 根据 SessionId 查询对应的 sessionInformation 对象
sessionInformation = this.getSessionInformation(sessionId);
} while(sessionInformation == null);
} while(!includeExpiredSessions && sessionInformation.isExpired());
//(3) 注意这里要判断 SessionInformation 是否过期,未过期的才能加入 list
list.add(sessionInformation);
}
}
}
public SessionInformation getSessionInformation(String sessionId) {
Assert.hasText(sessionId, "SessionId required as per interface contract");
return (SessionInformation)this.sessionIds.get(sessionId);
}
// 实现 onApplicationEvent 接口,表明处理 SessionDestrotyedEvent 事件
public void onApplicationEvent(SessionDestroyedEvent event) {
String sessionId = event.getId();
// 当会话销毁事件被触发时,移除对应 sessionId 的相关数据
this.removeSessionInformation(sessionId);
}
public void refreshLastRequest(String sessionId) {
Assert.hasText(sessionId, "SessionId required as per interface contract");
SessionInformation info = this.getSessionInformation(sessionId);
if (info != null) {
info.refreshLastRequest();
}
}
// 注册新的会话
// SessionManagementConfigure 默认会将 RegisterSessionAuthenticationStrategy
// 添加到一个组合式的 SessionAuthenticationStartegy 中,并由
// AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter 在登录成功时调用,从而触发
// registerNewSession 动作
public void registerNewSession(String sessionId, Object principal) {
Assert.hasText(sessionId, "SessionId required as per interface contract");
Assert.notNull(principal, "Principal required as per interface contract");
if (this.getSessionInformation(sessionId) != null) {
// 如果 sessionId 存在,则移除相关 SessionInformation
this.removeSessionInformation(sessionId);
}
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Registering session " + sessionId + ", for principal " + principal);
}
// 添加 sessionId 以及其对应的 SessionInformatio
this.sessionIds.put(sessionId, new SessionInformation(principal, sessionId, new Date()));
// 添加用户(UserDetails)以及其对应的 SessionId
sessionsUsedByPrincipal
this.principals.compute(principal, (key, sessionsUsedByPrincipal) -> {
if (sessionsUsedByPrincipal == null) {
sessionsUsedByPrincipal = new CopyOnWriteArraySet();
}
((Set)sessionsUsedByPrincipal).add(sessionId);
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace("Sessions used by '" + principal + "' : " + sessionsUsedByPrincipal);
}
return (Set)sessionsUsedByPrincipal;
});
}
// 移除对应的会话信息
public void removeSessionInformation(String sessionId) {
Assert.hasText(sessionId, "SessionId required as per interface contract");
//(1) 获取 SessionId 对应的 SessionInformation 对象
SessionInformation info = this.getSessionInformation(sessionId);
if (info != null) {
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Removing session " + sessionId + " from set of registered sessions");
}
//(2) 移除 SessionId 以及其对应的 SessionInformation
this.sessionIds.remove(sessionId);
//(3) 移除用户以及其对应的 SessionId
this.principals.computeIfPresent(info.getPrincipal(), (key, sessionsUsedByPrincipal) -> {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Removing session " + sessionId + " from principal's set of registered sessions");
}
sessionsUsedByPrincipal.remove(sessionId);
if (sessionsUsedByPrincipal.isEmpty()) {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Removing principal " + info.getPrincipal() + " from registry");
}
sessionsUsedByPrincipal = null;
}
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace("Sessions used by '" + info.getPrincipal() + "' : " + sessionsUsedByPrincipal);
}
return sessionsUsedByPrincipal;
});
}
}
}
也就是说,用户每登录一个新 Session 会话都会创建一个对应的 SessionInformation 对象,该对象是 SessionId 和用户信息的封装,相关信息会缓存在 principals 和 sessionIds 这两个 Map 集合中。需要注意的是 principals 集合采用的是以用户信息(UserDetails)为 key 的设计,在 HashMap 中以对象为 key 必须重写 hashCode 和 equals 方法,所以前面我们自定义 UserDetails 实现类重写了这两个方法:
@Data
public class User implements UserDetails {
//...
private String username; // 用户名
//...
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
// 对于 UserDetails 对象而言,username 就是其唯一标识
return obj instanceof User && this.username.equals(((User) obj).username);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
// 对于 UserDetails 对象而言,username 就是其唯一标识
return this.username.hashCode();
}
}
前面也提到,当用户的并发 Session 会话数量达到上限,新会话登录时,只是将最老会话的 SessionInformation 对象标记为过期,最老会话对应的 HttpSession 对象是在该会话的下一次请求访问时才被真正销毁。而Spring Security是通过监听 HttpSession 对象的销毁事件来触发会话信息集合 principals 和 sessionIds 的清理工作,但是默认情况下是没有注册过相关的监听器,这会导致Spring Security无法正常清理过期或已注销的会话。所以,前面我们在安全配置类注册了 HttpSessionEventPublisher 的 Bean,用于监听 HttpSession 的销毁:
@EnableWebSecurity // 开启 MVC Security 安全配置
public class SpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//...
/**
* 配置 Session 的监听器(如果使用并发 Sessoion 控制,一般都需要配置)
* 解决 Session 失效后, SessionRegistry 中 SessionInformation 没有同步失效问题
*/
@Bean
public HttpSessionEventPublisher httpSessionEventPublisher() {
return new HttpSessionEventPublisher();
}
//...
}
自定义使用
✍ 统计当前用户未过期的并发 Session 数量
@Controller
public class TestController {
//...
@Autowired
private SessionRegistry sessionRegistry;
//...
@GetMapping("/test4")
@ResponseBody
public Object getOnlineSession() {
// 统计当前用户未过期的并发 Session 数量
UserDetails user = (UserDetails) SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getDetails();
List<SessionInformation> sessions = this.sessionRegistry.getAllSessions(user, false);
return new ResultData<>(sessions.size());
}
}
✍ 统计所有在线用户
@Controller
public class TestController {
//...
@Autowired
private SessionRegistry sessionRegistry;
//...
@GetMapping("/test5")
@ResponseBody
public Object getOnlineUsers() {
// 统计所有在线用户
List<String> userList = sessionRegistry.getAllPrincipals().stream()
.map(user -> ((UserDetails) user).getUsername())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return new ResultData<>(userList);
}
}
使用 Redis 共享 Session
这里使用 Redis 来实现 Session 共享,实现步骤特别简单。
💡 在 pom.xml 中添加依赖
<!-- redis 依赖启动器 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- redis 数据源 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
<version>2.8.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 使用 Redis 管理 session -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.session</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-session-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
💡 在 application.properties 添加配置
# Redis 服务器地址
spring.redis.host=localhost
# Redis 服务器连接端口
spring.redis.port=6379
# Redis 服务器连接密码(默认无)
spring.redis.password=
# Redis数据库索引(默认为0)
spring.redis.database=1
# 连接池最大连接数(使用负值表示没有限制),默认 8
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-active=100
# 连接池大阻塞等待时间(使用负值表示没有限制),默认 -1
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-wait=PT10S
# 连接池中的大空闲连接 默认 8
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-idle=10
# 连接池中的小空闲连接 默认 0
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.min-idle=1
# 连接超时时间
spring.redis.timeout=PT10S
# 使用 Redis 存储 Session,默认为 none(使用内存存储)
spring.session.store-type=redis
# 指定存储 SessionId 的 Cookie 名(使用 Redis 存储 Session 后,Cookie 名默认会变为 SESSION)
server.servlet.session.cookie.name=JSESSIONID
💡 Redis 存储 Session 默认的序列化方式为 JdkSerializationRedisSerializer,所以存入 Session 的对象都要实现 Serializable 接口。因此,要保证前面代码中的验证码 CheckCode 类实现 Serializable 接口:
// 验证码信息类
public class CheckCode implements Serializable {
private String code; // 验证码字符
private LocalDateTime expireTime; // 过期时间
//...
}
💡 测试
访问localhost:8080/login/page,查看 Redis 数据库中的 key 数据:
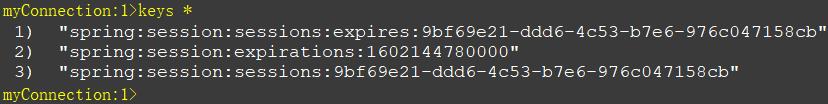
spring:session是 Redis 存储 Session 的 默认前缀,每一个 Session 都会创建 3 组数据,下面进行介绍:
☕️ 第一组:string 结构,用于记录指定 Session 的剩余存活时间
上面的例子中,spring:session:sessions:9bf69e21-ddd6-4c53-b7e6-976c047158cb就是这个 string 结构的 key,后缀的字符串是 JSEESIONID 的 base64 解码值。其 value 为空,TTL 时间为对应 Session 的剩余存活时间,如下所示:

☕️ 第二组:hash 结构,用于存储指定 Session 的数据
上面的例子中,spring:session:sessions:9bf69e21-ddd6-4c53-b7e6-976c047158cb就是这个 hash 结构的 key,后缀的字符串是 JSEESIONID 的 base64 解码值。hash 结构的 value 值本身就是一个 map 集合,其 value 如下所示:
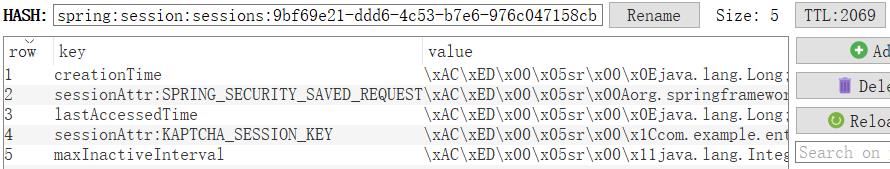
上图记录分别为 lastAccessedTime(最后访问时间)、creationTime(创建时间)、maxInactiveInterval(最大存活时间)、sessionAttr:属性名 (Session 里存储的属性数据)。
☕️ 第三组:set 结构,用于记录 Session 的过期时间
上面的例子中,spring:session:expirations:1602144780000 就是这个 set 结构的 key,后缀的字符串是一个整分钟的时间戳,其 value 是一个 set 集合,存的是这个时间戳的分钟内要失效的 Session 对应的 JSEESIONID 的 base64 解码值,例如:

remember-me 失效解释
当配置了.maximumSessions(1).maxSessionsPreventsLogin(false)要求只能一个用户 Session 登录时,我们在两个地方使用相同的账号,并且都勾选 remember-me 进行登录。最老会话的下一次请求不但会使老会话强制失效,还会使数据库中所有该用户的所有 remember-me 记录被删除。
第一个浏览器勾选 remember-me 登录后,数据库中 remember-me 记录:

第二个浏览器使用相同账号勾选 remember-me 登录后,数据库中 remember-me 记录:
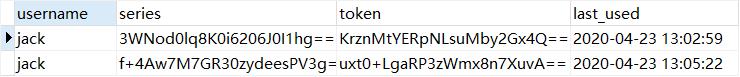
当刷新第一个浏览器,页面重定向到localhost:8080/login/page?error,显示用户在另外一个地方登录的信息,老会话被强制下线,数据库中 remember-me 记录:

可以发现,该用户的所有 remember-me 记录被删了。


