linux中LNMP架构和location用法
location
使用Nginx Location可以控制访问网站的路径,但一个server可以有多个location配置, 多个location的优先级该如何区分
location匹配符号
| 匹配符 | 匹配规则 | 优先级 |
|---|---|---|
| = | 精确匹配 | 1 |
| ^~ | 以某个字符串开头 | 2 |
| ~ | 区分大小写的正则匹配 | 3 |
| ~* | 不区分大小写的正则匹配 | 3 |
| / | 通用匹配,任何请求都会匹配到 | 4 |
[root@web02 conf.d]# vim supermary.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name _;
location ~* /python {
default_type text/html;
return 200 "Location ~*";
}
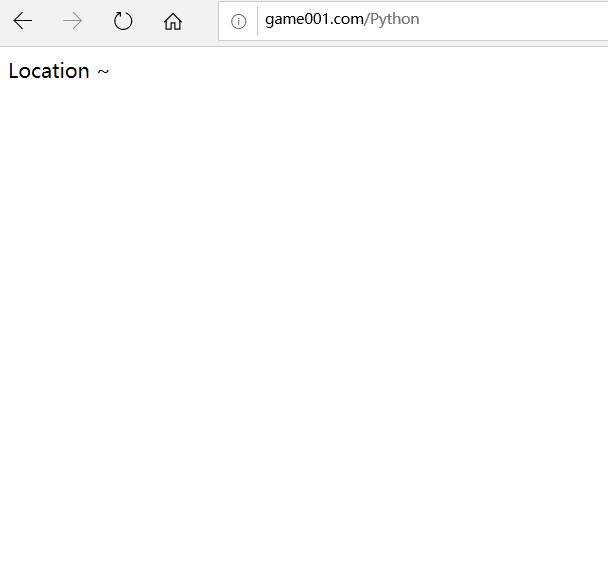
location ~ /Python {
default_type text/html;
return 200 "Location ~";
}
location ^~ /python {
default_type text/html;
return 200 "Location ^~";
}
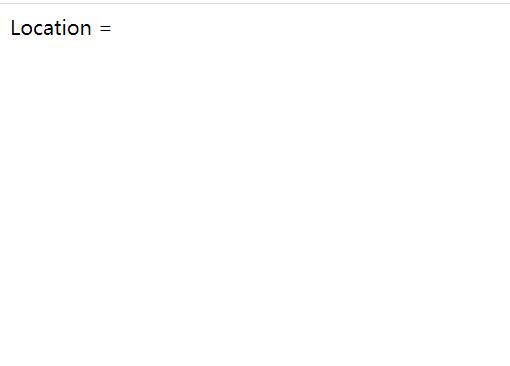
location = /python {
default_type text/html;
return 200 "Location =";
}
}
网站访问game001.com/python,每次访问之后修改配置文件,会产生一下效果.


案例
我们把超级玛丽里的images里的图片放到共享文件下/opt/imgaes然后删除超级玛丽里的images,然后这时会游戏会显示黑屏,因为找不到图片
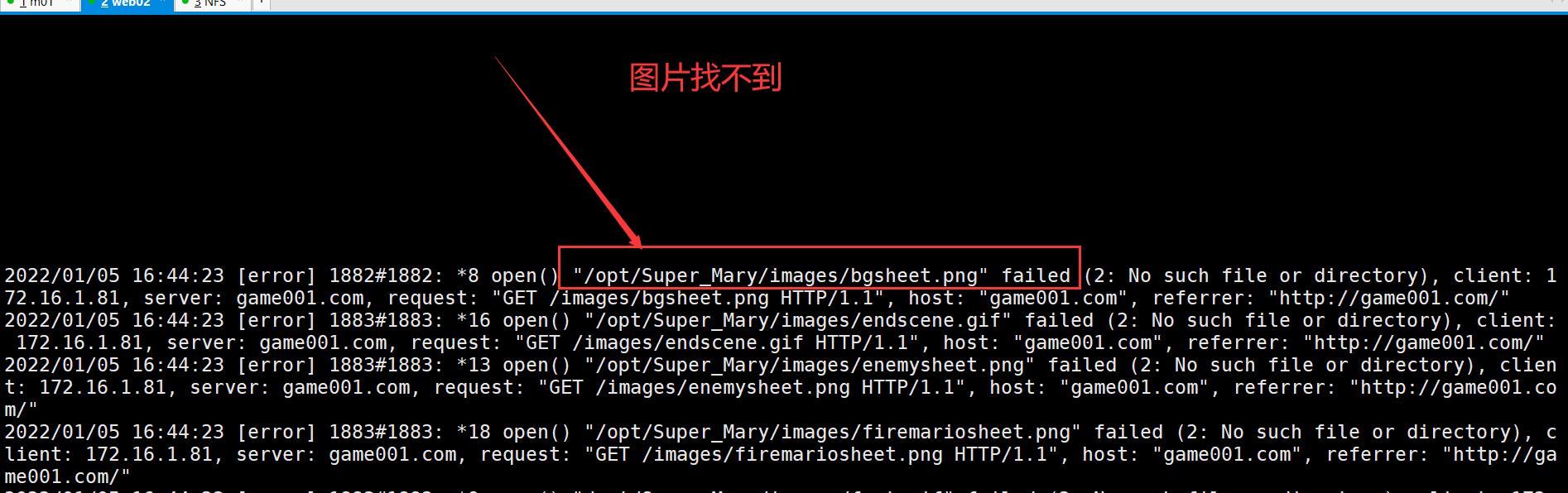
我们查看下错误日志
然后我们再做如下操作
server {
listen 80;
server_name game001.com;
location / {
root /opt/Super_Mary;
index index.html;
}
location ^~ /images { # 新写一个location 以image开头 在/opt目录下查找
root /opt;
}
}
再次访问超级玛丽游戏,就又可以游玩啦!!!

LNMP架构
1.简介
LNMP是一套技术的组合,L=Linux、N=Nginx、M=MySQL、P=PYTHON或PHP
不仅仅只有这些服务,还有很多
首先Nginx服务是不能处理动态请求,那么当用户发起动态请求时, Nginx又是如何进行处理的。
1.静态请求:请求的内容是静态文件就是静态请求
1)静态文件:文件上传到服务器,永远不会改变的文件就是静态文件
2)html就是一个标准的静态文件
2.动态请求:请求的内容是动态的就是动态请求
1)不是真实存在服务器上的内容,是通过数据库或者其他服务拼凑成的数据
当用户发起http请求,请求会被Nginx处理,如果是静态资源请求Nginx则直接返回,如果是动态请求Nginx则通过uwsgi协议转交给后端的Python程序处理
2.uwsgi
- 因为nginx不支持wsgi协议,无法直接调用py开发的webApp。
- 在nginx+uWsgi+Django的框架里,nginx代理+webServer,uWsgi是wsgiServer,Django是webApp。
- nginx接收用户请求,并判定哪些转发到uWsgi,uWsgi再去调用pyWebApp。
3.uwsgi服务部署
# 查看端口
netstat -ntlp
kill +端口 杀死进程
tail -f /var/log/nginx/access.log
# 查看进程
ps -ef | grep xxx
1、创建用户
[root@web01 opt]# groupadd django -g 888
[root@web01 opt]# useradd django -u 888 -g 888 -r -M -s /bin/sh
2、安装依赖软件
[root@web01 opt]# yum install python3 libxml* python-devel gcc* pcre-devel openssl-devel python3-devel -y
3、安装Django和uwsgi
[root@web01 opt]# pip3 install django==1.11
[root@web01 opt]# pip3 install uwsgi
4、创建项目
[root@web01 opt]# cd /opt
[root@web01 opt]# django-admin startproject linux
[root@web01 opt]# cd linux
[root@web01 opt]# django-admin startapp app01
[root@web01 linux]# vim linux/settings.py
ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['*']
DATABASES = {}
# 启动测试
[root@web01 linux]# python3 manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8000
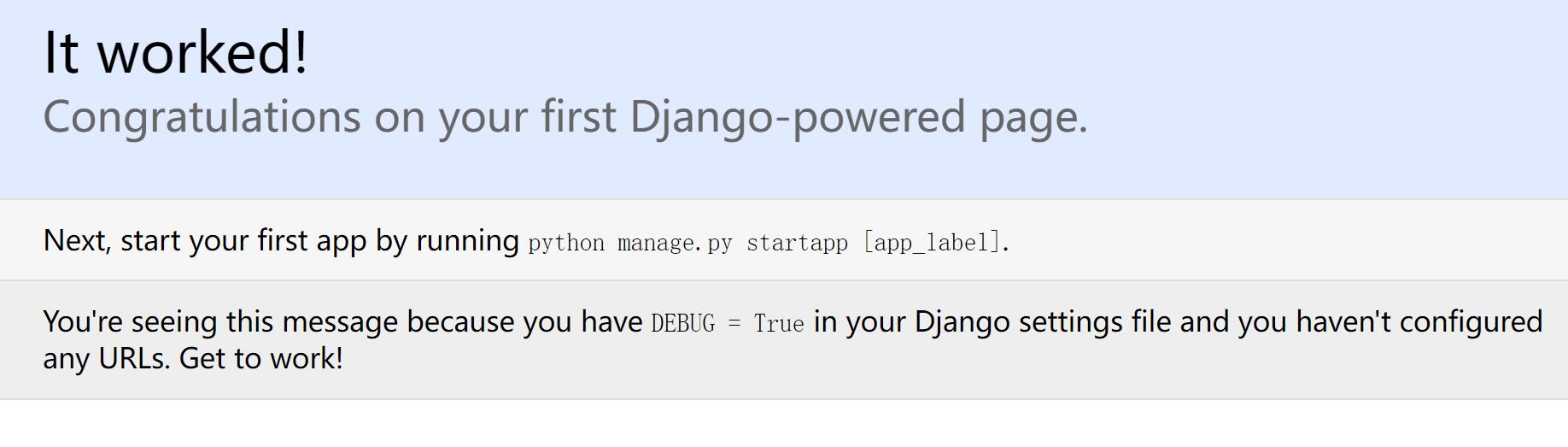
不同版本的django显示的图片不一样.
5、编辑项目配置文件
[root@localhost ~]# vim /opt/linux/myweb_uwsgi.ini
[uwsgi]
# 端口号
socket = :8000
# 指定项目的目录
chdir = /opt/linux
# wsgi文件路径
wsgi-file = linux/wsgi.py
# 模块wsgi路径
module = linux.wsgi
# 是否开启master进程
master = true
# 工作进程的最大数目
processes = 4
# 结束后是否清理文件
vacuum = true
6、启动uwsgi
[root@web01 linux]# uwsgi -d --ini myweb_uwsgi.ini --uid 666
-d : 以守护进程方式运行
--ini : 指定配置文件路径
--uid : 指定uid
7、编辑Nginx配置文件
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/python.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name py.test.com;
location / {
include uwsgi_params;
uwsgi_pass 127.0.0.1:8000;
uwsgi_read_timeout 2;
uwsgi_param UWSGI_SCRIPT linux.wsgi;
uwsgi_param UWSGI_CHDIR /opt/linux;
index index.html index.htm;
client_max_body_size 35m;
}
}
8、重启Nginx配置
systemctl restart nginx
在window里的hosts文件添加172.16.1.8 py.test.com
访问 py.test.com
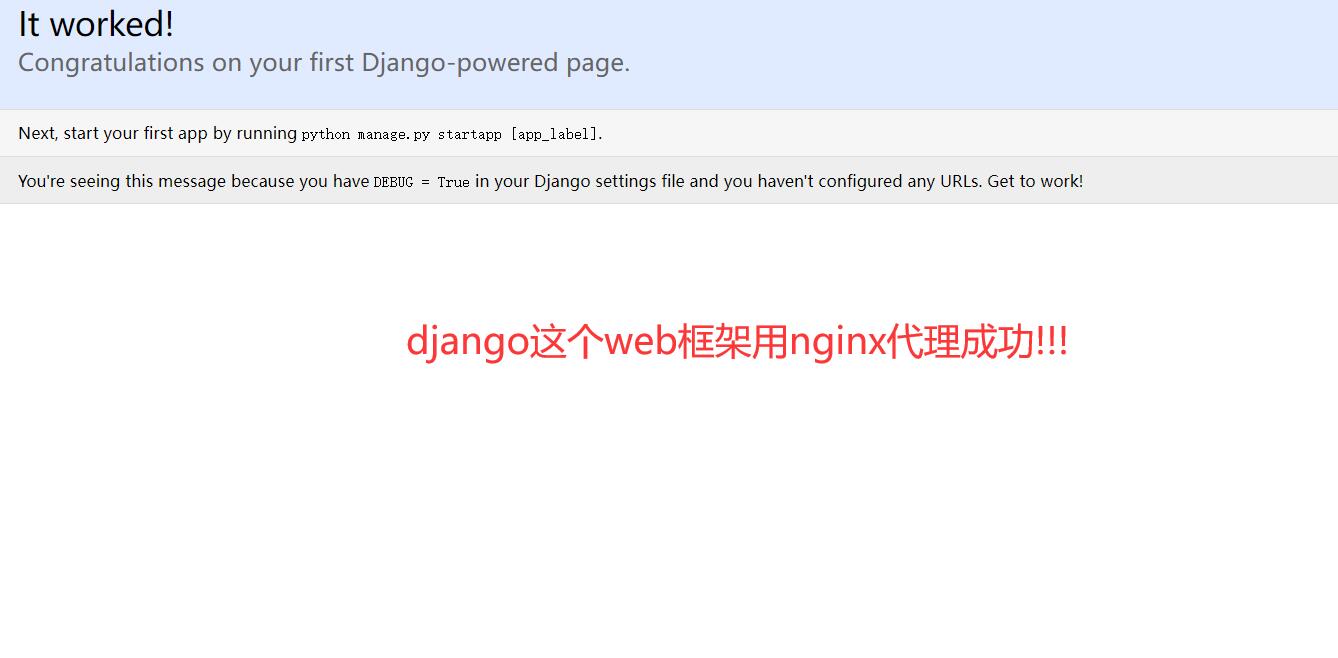
4.nginx代理python服务(压力测试)
[root@web01 linux]# python3 manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8001
[root@web02 conf.d]# vim py1.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name py1.test.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8001;
}
}
[root@web02 conf.d]# systemctl restart nginx
[root@web02 conf.d]# vim /etc/hosts
172.16.1.8 py.test.com py1.test.com
[root@web02 conf.d]# curl -I -H'Host: py.test.com' 172.16.1.8
[root@web02 conf.d]# curl -I -H'Host: py1.test.com' 172.16.1.8
# 开始压力测试
[root@web02 conf.d]# ab -n 10000 -c 10 http://py.test.com/
# 这是uwsgi代理 Time taken for tests: 6.958 seconds
[root@web02 conf.d]# ab -n 10000 -c 10 http://py1.test.com/
# 这是python代理 Time taken for tests: 20.714 seconds
由此可以看出uwsgi代理要比python要快很多.
部署BBS项目
在db01上
1、部署数据库
[root@db01 ~]# yum install mariadb* -y
2、启动数据库
[root@db01 ~]# systemctl start mariadb
# 运行数据库
[root@db01 ~]# mysql
3、远程连接MySQL数据
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'root'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY '123' WITH GRANT OPTION;FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
# 这里的用户名和密码根据自己设置
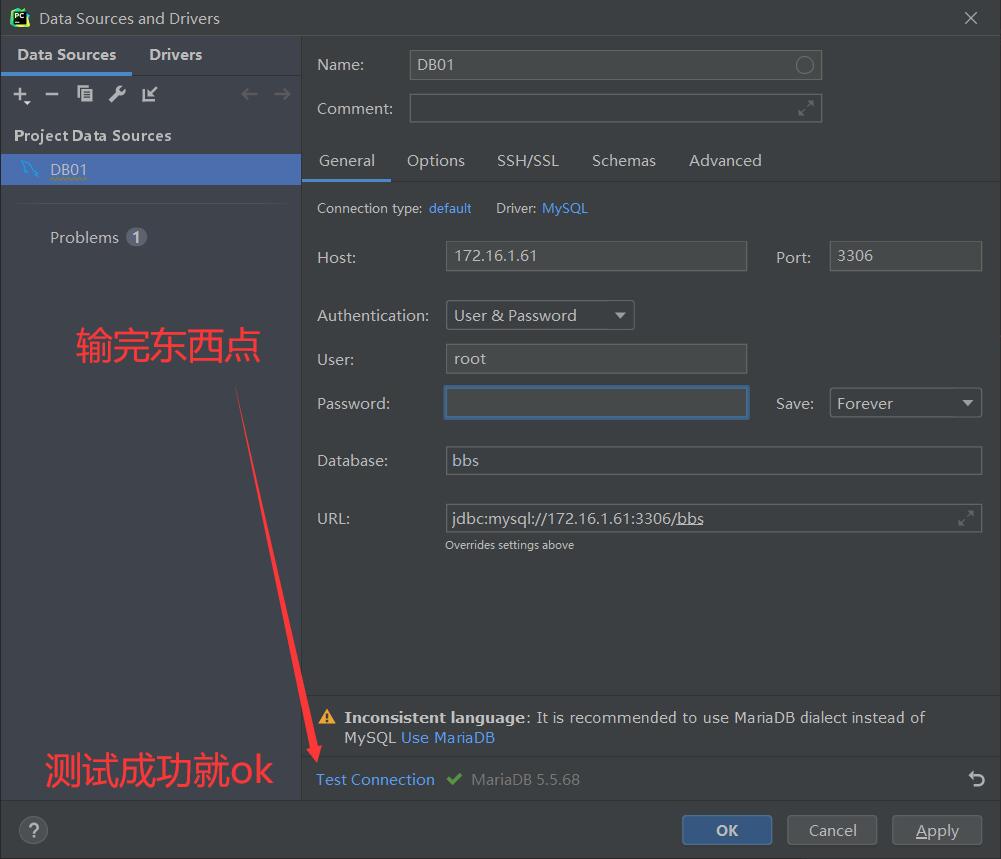
4.创建BBS数据库
CREATE DATABASE `bbs` DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci;
打开pycharm
在web01上
4.1、上传代码
[root@web01 ~]# unzip bbs.zip
[root@web01 ~]# mv bbs /opt/
4.2、数据库迁移
# 删除之前别人迁移好的数据库,只留一个_ _init_ _(新项目就不需要)
[root@web01 migrations]# cd /opt/bbs/app01/migrations
[root@web01 migrations]# rm -rf 00*
[root@web01 migrations]# rm -rf __pycache__/
[root@web01 migrations]# cd /opt/bbs/
# 安装MySQL数据库插件
[root@web01 bbs]# pip3 install pymysql
# 修改数据连接
[root@web01 bbs]# vim bbs/settings.py
ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['*']
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql',
'NAME': 'bbs',
'USER': 'root',
'PASSWORD': '123',
'HOST': '172.16.1.61',
'PORT': 3306,
'CHARSET': 'utf8'
}
}
# 创建数据库迁移文件
[root@web01 bbs]# python3 manage.py makemigrations
# 数据库迁移
[root@web01 bbs]# python3 manage.py migrate
4.3、配置UWSGI
[root@web01 bbs]# vim /opt/bbs/myweb_uwsgi.ini
[uwsgi]
# 端口号
socket = :8002
# 指定项目的目录
chdir = /opt/bbs
# wsgi文件路径
wsgi-file = bbs/wsgi.py
# 模块wsgi路径
module = bbs.wsgi
# 是否开启master进程
master = true
# 工作进程的最大数目
processes = 4
# 结束后是否清理文件
vacuum = true
# 测试UWSGI配置是否成功
[root@web01 bbs]# uwsgi -d --ini myweb_uwsgi.ini --uid 666
4.4、配置Nginx
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/python.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name bbs.test.com;
location / {
include uwsgi_params;
uwsgi_pass 127.0.0.1:8002;
uwsgi_read_timeout 2;
uwsgi_param UWSGI_SCRIPT bbs.wsgi;
uwsgi_param UWSGI_CHDIR /opt/bbs;
index index.html index.htm;
client_max_body_size 35m;
}
}
[root@web01 bbs]# systemctl restart nginx
把bbs.test.com加入window里的hosts配置文件里
打开bbs.test.com
问题排错
出现502一定是uwsgi出了问题
出现无法访问此网站一定是nginx出错了
404是匹配不到对应的location
403是匹配到对应的location,但是找不到文件


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号