4. 现代 javascript class 专题 和 异步专题
class 专题
定义 class
//es5 类的定义 属性定义在 function 上, 方法定义在原型链上
function foobar(){
this.foo_ = 'foo';
this.bar_ = 'bar';
}
foobar.prototype.sayHello = function(){ console.log('hello') }
const fb = new foobar();
fb.sayHello();
// es6 class 语法
class foobar2{
constructor(){
this.foo_ = 'foo';
this.bar_ = 'bar';
}
sayHello(){ console.log('hello') }
}
const fb2 = new foobar2();
fb2.sayHello();
继承
class father {
sayHi(){ console.log('Hi') }
}
class son extends father{
constructor () {
super();
this.me='son'
}
sayHello(){ console.log('hello') }
}
const son1 = new son();
// 调用 father 类的 sayHi 方法时 找自己的原型 son.prototype 是否含有这个 方法
// 通过查看父类的原型判断 是否调用的父类的方法 其中 son.prototype.__proto__=father.prototype
// 通过 类名.hasOwnProperty('方法的名称') 判断是否含有该方法
son1.sayHi();
异步专题
javascript 中的事件循环 (不限制时间)
物理线程的事件循环是有事件限制的
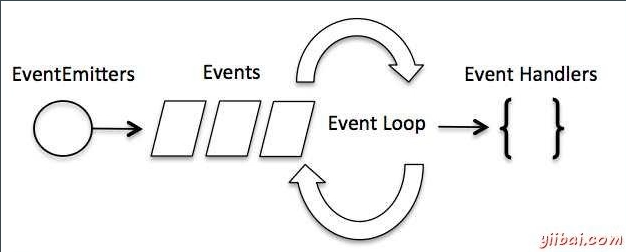
用事件提交器 将 事件 推入事件 队列 然后 通过事件循环 处理到当前 事件时 然后处理 事件处理函数 (回调函数)
Promise 语法糖 使用
把多重的 函数 嵌套请求 写得更简单
链式调用
eg:多次 发起 fetch 请求
window.fetch('//xx.com/1').then(data=>{
window.fetch('//xx.com/2');
}).then(data=>{
window.fetch('//xx.com/3');
}).then(_=>{
console.log('ok');
})
eg: 异步 多次 发起 延时3s 执行函数
function fn (){
console.log(Date.now())
}
function delay3sPromise( fn ){
return new Promise( (resolve, reject) =>{
// resolve 通知 promise 业务代码 成果 并 返回结果
// reject 函数执行失败 并返回错误
setTimeout(_ => {
try{
const ret = fn();
resolve(ret);
}catch(err){
reject(err); //发生了错误
}
}, 3000)
} )
}
// 调用
delay3sPromise(fn).then(_=>{
return delay3sPromise(fn);
}).then(_=>{
return delay3sPromise(fn);
}).catch(err => {
console.log(err);
})
eg: 同步 请求 处理
function delaySame(fn){
return new Promise(_ => {
try{
return Promise.resolve(data)
}catch(err){
return Promise.reject(err)
}
})
}
//调用
dedelaySame(fn).then(data=>{
console.log(data);
}).catch(err){
console.log(err);
}
要点
Promise 一旦创建是 一定会执行的
创建一个 Promise 只能调用一次
Promise的 三个状态: pending (执行代码前)-> fulfilled(执行成功) | rejected(执行失败)
try/catch 不能捕获 Promise 中的 异常(是使用 Promise 后的 catch 方法进行捕获)
eg: new Promise(fn).catch(err=>{ console.log(err) })
链式调用
三种异步
macro task 宏任务
micro task 微任务 (优先级 比 宏任务高)
物理线程
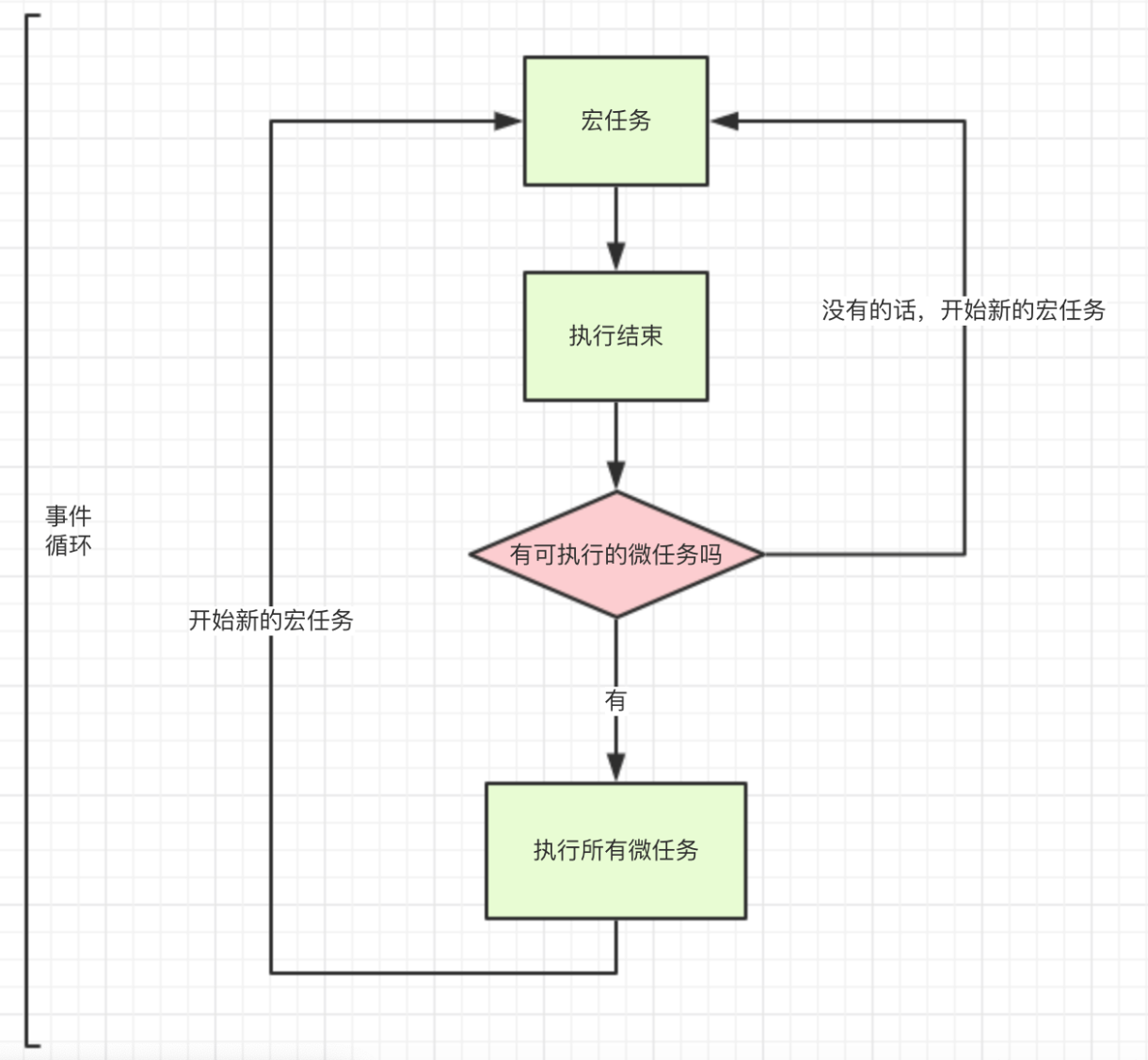
eg: 同步代码先执行 同步代码后的 异步代码先执行 后执行 异步代码
console.log(0)
setTimeout(_=> console.log(1)) // 异步代码 宏任务
new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{ // 该回调为 同步执行
console.log(2)
resolve()
console.log(3)
}).then(_=>{ // 异步代码 微任务
console.log(4)
}).then(_=>{ // 异步代码 微任务
console.log(5)
})
console.log(6)
结果: 0 2 3 6 4 5 1
async 和 await 用法
一种比 Promise 更好用的语法
Promise 语法
eg:
function copyFile(src, dst) {
return readFile(src).then(content => {
return writeFile(dst, content)
})}
copyFile('src', 'dst')
.then(_ => console.log('finished'))
.catch(err => console.error(err))
async 和 await 语法
1. async 函数 只有在 async 函数内使用
2. wait 是 .then 的 语法糖
3. async await 函数内 能使用 try catch
async function copyFile (src, dst) {
const content = await readFile(src) // await 等同于使用 .then
writeFile(dst, content)
}
async function writeFile(dst, content){
console.log(dst, content);
}
async function readFile(src){
console.log(src);
return 'readFile content'
}
async function main () {
try {
await copyFile('src', 'dst')
console.log('finished')
} catch (err) {
console.error(err)
}
}
console.log(1);
main();
console.log2;
结果: 1 src 2 (src readFile content) finishd
// 解析 main 函数 内的 copyFile 会 先解析成 一个 Promise 的 同步代码 然后拼接成 .then 的 异步代码 所以会有 1 后 先输出 src 再输出 2 Promise 代码 在上面
拓展
callback 转 promise
eg:
function ajax(url, callback){ //... } // callback
function ajaxPromise(url){ // promise
return new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
ajax(url, (err, content)=>{
if(err){ reject(err); return }
resolve(content)
})
})
}
ajaxPromise('xxx.com').then((content)=>{
// 调用成功 处理
}).catch((err)=>{
// 调用失败 处理
})
promise 转 async
sync function main(){
try{
const content = await ajaxPromise('xxx.com');
}catch(err){
console.log(err);
}
}
callback 转 async



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号