Spring+Maven学习实验- Spring 中将值注入集合类型(三)
将值注入集合类型,包含以下四种主要的集合类型:
- List ——
- Set ——
- Map ——
- Properties ——

1.pom.xml
略
2.编写 Person.java && Customer.java
package com.shiyanlou.spring.collections; public class Person { private String name; private String address; private int age; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getAddress() { return address; } public void setAddress(String address) { this.address = address; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person [name=" + name + ", address=" + address + ", age=" + age + "]"; } }
package com.shiyanlou.spring.collections; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Properties; import java.util.Set; public class Customer { private List<Object> lists;//这里的lists要和Bean中的property标签的name一样 private Set<Object> sets; private Map<Object,Object> maps; private Properties pros; public List<Object> getLists() { return lists; } public void setLists(List<Object> lists) { this.lists = lists; } public Set<Object> getSets() { return sets; } public void setSets(Set<Object> sets) { this.sets = sets; } public Map<Object, Object> getMaps() { return maps; } public void setMaps(Map<Object, Object> maps) { this.maps = maps; } public Properties getPros() { return pros; } public void setPros(Properties pros) { this.pros = pros; } private Person person;//不要忘记写内部要引用的Bean public Customer(Person person){ this.person = person; } public Customer(){} public Person getPerson() { return person; } public void setPerson(Person person) { this.person = person; } @Override public String toString() { return "Customer [person=" + person + "]"; } }
注意: JavaBean 关于属性命名的特殊规范,spring 配置文件中 元素所指定的属性名和 Bean 实现类的 Setter 方法满足 Sun JavaBean 的属性命名规范: xxx 的属性对应 setXxx() 方法。一般情况下 Java 的属性变量名都以小写字母起头,如: maxSpeed 。但也存在特殊的情况,考虑到一些特定意义的大写英文缩略词(如: USA 、 XML ),JavaBean 也允许大写字母起头的属性变量名,不过必须满足: 变量的前两个字母要么全部大写,要么全部小写.如: iC 、 iCcard 、 iDcode 这些都不合法的。
3.编写 SpringCollections.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd"> <bean id="customerBean" class="com.shiyanlou.spring.collections.Customer"> <!-- java.util.List --> <property name="lists"> <list> <value>1</value> <!-- List 属性既可以通过 <value> 注入字符串,也可以通过 <ref> 注入容器中其他的 Bean--> <ref bean="personBean"/> <value>2</value> <bean class="com.shiyanlou.spring.collections.Person"> <property name="name" value="testList"/> <property name="address" value="Wuhan"/> <property name="age" value="18"/> </bean> </list> </property> <!-- java.util.Set --> <property name="sets"> <set> <value>1</value> <ref bean="personBean"/> <bean class="com.shiyanlou.spring.collections.Person"> <property name="name" value="testSet"/> <property name="address" value="Wuhan"/> <property name="age" value="18"/> </bean> </set> </property> <!-- java.util.Map --> <property name="maps"> <map> <entry key="Key 1" value="1"/> <!--一个 entry 就是一个 Map 元素--> <entry key="Key 2" value-ref="personBean"/> <entry key="key 3"> <bean class="com.shiyanlou.spring.collections.Person"> <property name="name" value="testMap"/> <property name="address" value="Wuhan"/> <property name="age" value="18"/> </bean> </entry> </map> </property> <property name="pros"> <props> <prop key="admin">admin@nospam.com</prop> <prop key="support">support@nospam.com</prop> </props> </property> </bean> <bean id="personBean" class="com.shiyanlou.spring.collections.Person"> <property name="name" value="shiyanlouPersonBean" /> <property name="address" value="chengdu" /> <property name="age" value="25" /> </bean> </beans>
4.编写测试类App.java
package com.shiyanlou.spring.collections;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class App {
private static ApplicationContext context;
public static void main(String[] args) {
context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("SpringCollections.xml");
/*
* 1.List的情况
*/
// Customer lists = (Customer)context.getBean("customerBean");
// System.out.println(lists.getLists().toString());
/*
* 2.Set的情况
*/
// Customer sets = (Customer) context.getBean("customerBean");
// System.out.println(sets.getSets().toString());
/*
* 3.Map的情况
*/
// Customer maps = (Customer) context.getBean("customerBean");
// System.out.println(maps.getMaps().toString());
/*
* 4.Property
*/
Customer pros = (Customer) context.getBean("customerBean");
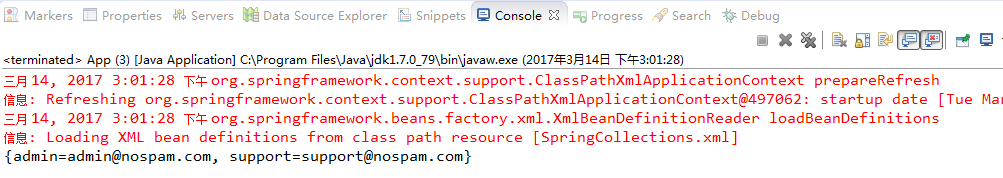
System.out.println(pros.getPros().toString());
}
}
运行结果:
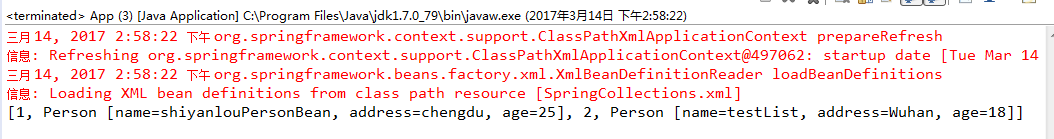
case1-List的情况:
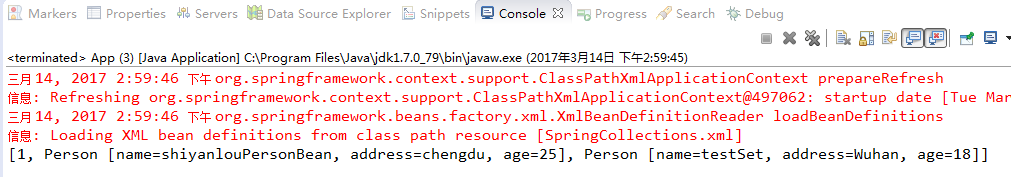
case2-Set的情况:
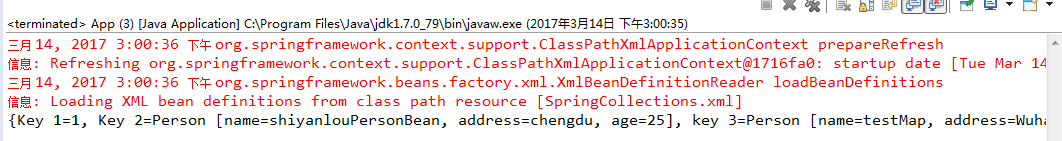
case3-Map的情况:
case4-Prop的情况: