猴子拆房 题解
题目描述
输入
输出
样例输入
【样例输入1】 2 2 3 4 5 【样例输入2】 3 2 4 2 5 1 3 【样例输入3】 6 3 5 3 4 1 7 1 7 4 2 4 1 样例输出
【样例输出1】 3 【样例输出2】 0 【样例输出3】 10 数据范围限制
提示
这个是我的,是我的QWQ,我没有转载,只是把以前的博客搬运过来了。
然后就是因为markdown丢了,所以我截图:



不过代码还在OJ上存着,你们放心:
#include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #define ll long long #define INF 1e12 using namespace std; ll n; struct node{ friend bool operator <(const node &x,const node &y){ // 懒得改了 return x.v<y.v; } friend bool operator >(const node &x,const node &y){ return x.v>y.v; } ll h,v; // 小根堆 大根堆 } a[200010],b[200010],t1[200010],t2[200010]; ll num[200010]; ll cnt1,cnt2; ll big,sum,mn=INF; ll spend[200010]; ll s[200010]; // 下面是手写堆 // 下面的肯定对了! void insert1(node k){ t1[++cnt1]=k; ll x=cnt1; while(x>1 && t1[x/2]>t1[x]){ swap(t1[x/2],t1[x]); x/=2; } } void pop1(){ swap(t1[1],t1[cnt1]); cnt1--; ll x=1; while(2*x<=cnt1&&((2*x+1<=cnt1 && t1[x*2+1]<t1[x]) || t1[x*2]<t1[x])){ if(2*x+1>cnt1){ swap(t1[x*2],t1[x]); x*=2; } else if(t1[x*2+1]<t1[x*2]){ swap(t1[x*2+1],t1[x]); x=x*2+1; } else{ swap(t1[x*2],t1[x]); x*=2; } } } void insert2(node k){ t2[++cnt2]=k; ll x = cnt2; while(x>1 && t2[x/2]<t2[x]){ swap(t2[x/2],t2[x]); x/=2; } } void pop2(){ swap(t2[1],t2[cnt2]); cnt2--; ll x=1; while(2*x<=cnt2&&((2*x+1<=cnt2 && t2[x*2+1]>t2[x]) || t2[x*2]>t2[x])){ if(2*x+1>cnt2){ swap(t2[x*2],t2[x]); x*=2; } else if(t2[x*2+1]>t2[x*2]){ swap(t2[x*2+1],t2[x]); x=x*2+1; } else{ swap(t2[x*2],t2[x]); x*=2; } } } void solve(ll l,ll r){ if(l==r) return; ll mid=(l+r)>>1; solve(l,mid); solve(mid+1,r); ll pos1=l,pos2=mid+1; for(ll i=l;i<=r;i++){ if(pos2>r||(pos1<=mid && a[pos1].h<a[pos2].h)){ b[i]=a[pos1++]; } else if(pos2<=r){ b[i]=a[pos2++]; } } for(ll i=l;i<=r;i++){ a[i]=b[i]; } } // 上面的肯定对了! // 代码主要部分 void run(ll h){ ll k=(n-s[h])-(num[h]-1); // 最少拆多少个房子 while(k<cnt2 && cnt2){ // 多了 insert1(t2[1]); sum-=t2[1].v; pop2(); } while(cnt2<k){ // 不够 if(!cnt1){ return; } insert2(t1[1]); sum+=t1[1].v; pop1(); } big-=spend[h]; mn=min(mn,sum+big); } int main(){ freopen("house.in","r",stdin); freopen("house.out","w",stdout); scanf("%lld",&n); for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++){ scanf("%lld %lld",&a[i].h,&a[i].v); num[a[i].h]++; spend[a[i].h]+=a[i].v; } solve(1,n); for(ll i=100000;i>=1;i--){ s[i]=s[i+1]+num[i]; big+=spend[i]; } ll i=1; for(ll h=1;h<=100000;h++){ if(num[h]){ while(i<=n){ if(a[i].h>=h) break; insert2(a[i]); sum+=a[i].v; insert1(t2[1]); sum-=t2[1].v; pop2(); i++; } run(h); } } printf("%lld",mn); }
另外再贴HLY大佬的题解一篇(单堆,不理解我的可以试着理解他的):

虽然格式有点……但是思路很新奇。
代码帮你们从OJ上copy过来了,码风和我的不太一样:
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int n,b[100001],t[100001],tt[100001],cnt,sum,h=1,p[1000001],f[100001],k[100001],g,ans=23407234; struct st{ int h; int c; }a[100001]; void up(long long x) { p[++cnt]=x; long long wz=cnt; while(wz>1&&p[wz]>p[wz/2]) { swap(p[wz],p[wz/2]); wz/=2; } } long long down() { long long maxn=p[1],wz=1; p[1]=p[cnt--]; while(wz*2<=cnt&&p[wz]<p[wz*2] ||wz*2+1<=cnt&&p[wz]<p[wz*2+1]) { long long mx=p[wz*2],k=wz*2; if(wz*2+1<=cnt&&p[wz*2]<p[wz*2+1]) { mx=p[wz*2+1],k=wz*2+1; } swap(p[wz],p[k]); wz=k; } return maxn; } void hb(int x,int y,int p,int q) { int i=x,j=p,k=x; st b[200001]; while(i<=y&&j<=q) { if(a[i].h<a[j].h) b[k].c=a[i].c,b[k++].h=a[i++].h; else b[k].c=a[j].c,b[k++].h=a[j++].h; } while(i<=y) b[k].c=a[i].c,b[k++].h=a[i++].h; while(j<=q) b[k].c=a[j].c,b[k++].h=a[j++].h; for(int l=x;l<=q;l++) { a[l].h=b[l].h,a[l].c=b[l].c; } } void gb(int l,int r) { if(l==r) return; int mid=(l+r)/2; gb(l,mid); gb(mid+1,r); hb(l,mid,mid+1,r); } int main() { freopen("house.in","r",stdin); freopen("house.out","w",stdout); scanf("%d",&n); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { scanf("%d%d",&a[i].h,&a[i].c); } gb(1,n); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { if(t[a[i].h]==0) { b[++b[0]]=a[i].h; } t[a[i].h]++; tt[a[i].h]+=a[i].c; sum+=a[i].c; } for(int i=1;i<=b[0];i++) { int uu=b[i],g1=0; sum-=tt[uu]; f[i]=sum; while(a[h].h<uu) g+=a[h].c,up(a[h++].c); if(t[uu]<=cnt) { for(int j=1;j<=t[uu]-1;j++) { k[++k[0]]=down(); g1+=k[k[0]]; } f[i]+=g-g1; for(int j=1;j<=k[0];j++) { up(k[j]); } k[0]=0; } ans=min(ans,f[i]); } printf("%d",ans); }
另外手动膜拜HLY大佬,这里贴上他的博客



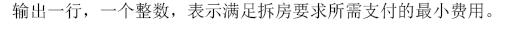
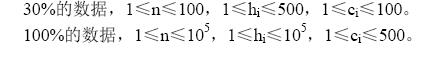





· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 使用C#创建一个MCP客户端
· ollama系列1:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 按钮权限的设计及实现