java 8 Stream 分页、list转map
public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> list = Lists.asList("1,2", new String[] { "3,4" }); List<String> collect = null; // map 是对各个元素依次做处理 collect = list.stream().map(s -> s + "_").collect(Collectors.toList()); System.out.println("a:" + collect); // 分页 collect = list.stream().skip(1).limit(1).collect(Collectors.toList()); System.out.println("b:" + collect); // 过滤 collect = list.stream().filter(e -> e.equals("2")).collect(Collectors.toList()); System.out.println("c:" + collect); // list 转 map Map<String, String> map = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(e -> e + ":", e -> e)); System.out.println("d:" + map); // 求和 long count = list.stream().count(); System.out.println("e:" + count); // flatMap collect = list.stream().flatMap(e -> Arrays.asList(e.split(",")).stream()).collect(Collectors.toList()); System.out.println("f:" + collect); collect = list.stream().flatMap(e -> Arrays.stream(e.split(","))).collect(Collectors.toList()); System.out.println("g:" + collect); collect = list.stream().flatMap(e -> Stream.of(e.split(","))).collect(Collectors.toList()); System.out.println("h:" + collect); collect.forEach(System.out::println); // 非缩略写法 Stream<String> s0 = list.stream(); Stream<String> s2 = s0.flatMap(e -> { Stream<String> s1 = Stream.of(e.split(",")); return s1; }); s2.forEach(System.out::println); }
java.util.function.Function<T, R> 代表函数,java8的一大特性就是可以把函数当参数,这类参数重要的两点:T 入参,R 返回
执行结果:
a:[1,2_, 3,4_]
b:[3,4]
c:[]
d:{1,2:=1,2, 3,4:=3,4}
e:2
f:[1, 2, 3, 4]
g:[1, 2, 3, 4]
h:[1, 2, 3, 4]
1
2
3
4
1
2
3
4
类似应用:数据库查询对象列表,转换为ID列表
List<Date> dateList = new ArrayList<>(); dateList.add(new Date()); List<Long> timestampList = dateList.stream().map(date->date.getTime()).collect(Collectors.toList()); System.out.println(timestampList);
java.util.stream.Stream<T> 元素序列,可以串行或并行进行合计处理
主要应用:
- list 内存分页;
- list 转 map;
- bean list 提取单字段list
注意:java.util.stream.Stream.map(Function<? super T, ? extends R>)
java.util.stream.Stream.flatMap(Function<? super T, ? extends Stream<? extends R>>)
均产生新的stream,不会影响原来的数据。
flatMap 目的是把原stream每个元素依次转为原stream泛型相同的stream,最终合并成一个stream
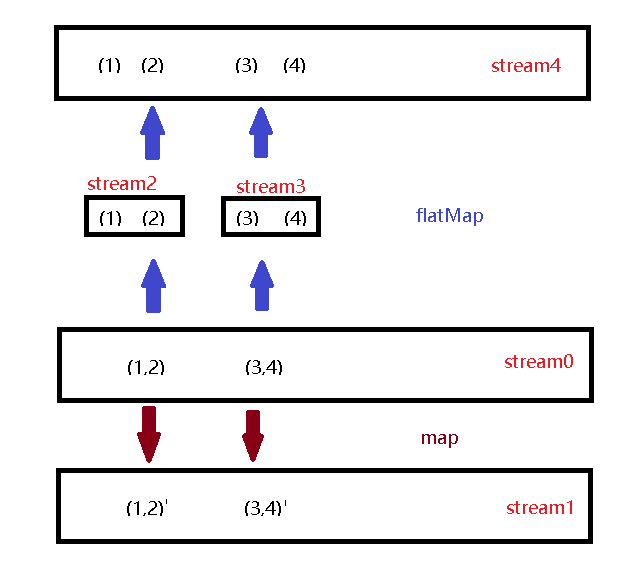
注意:e->e 是缩写;非简写第一部分是入参,第二部分是返回的statement,举例: (e) -> {/* TODO do something */ return e;}
注意:
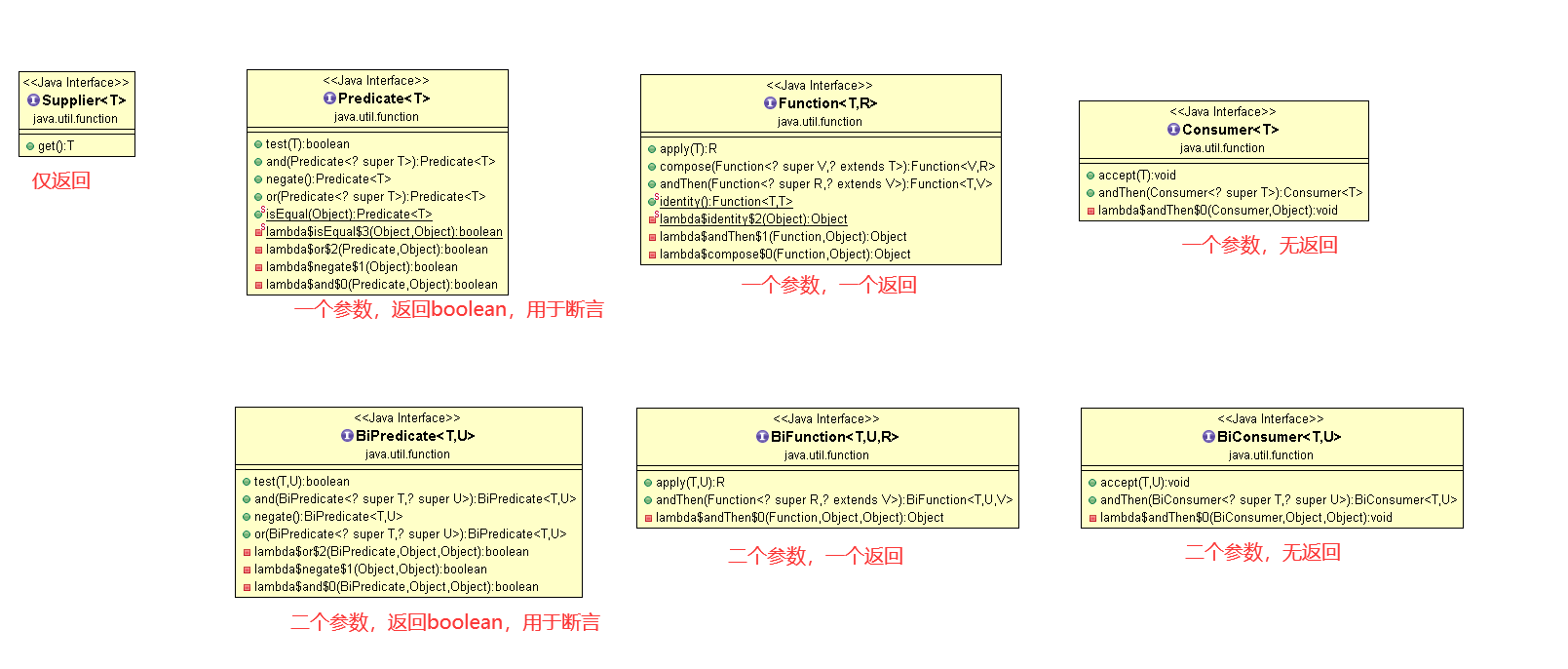
函数答题分类如下
- java.util.function.Supplier<T>
- java.util.function.Predicate<T>
- java.util.function.Function<T, R>
- java.util.function.Consumer<T>
注意:bi- 是英文词根,表示two,twice,比如bicycle 二轮自行车,binary 二进制
实际应用:
public static void main(String[] args) { // 引静态方法 Supplier<Calendar> s1 = Calendar::getInstance; Calendar c = s1.get(); System.out.println(c); // 引实例方法 Supplier<Date> s2 = c::getTime; System.out.println(s2.get()); // 自定义函数 Supplier<String> s3 = ()->"1"; System.out.println(s3.get()); }
public static void main(String[] args) { // 匿名类自定义函数 Predicate<String> p1 = new Predicate<String>() { @Override public boolean apply(String input) { return input.equals("1"); } }; System.out.println(p1.apply("1")); // lambda 自定义函数 Predicate<String> p2 = (e)->e.equals("1"); System.out.println(p2.apply("1")); }
public static void main(String[] args) { // 自定义function函数,自定义消费函数 Stream.of("1").map(e->e+")").forEach(e->System.out.println(e)); // forEach 引用消费函数 Stream.of("1").map(e->e+")").forEach(System.out::println); Stream.of("1").mapToInt(e->Integer.valueOf(e)).forEach(System.out::println); }
实际应用2:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号