@Aspect
一、简介
依赖:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-test</artifactId> <version>4.1.9.RELEASE</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.12</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId> <version>4.1.9.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId> <version>4.1.9.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId> <version>4.1.9.RELEASE</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.3</version> <configuration> <source>1.8</source> <target>1.8</target> <encoding>UTF-8</encoding> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build>
拦截器:
@Aspect @Component public class SomeInterceptor {
将拦截器注册到工厂:
<context:component-scan base-package="yourpackage"></context:component-scan>
开启代理(false 对应 jdk 动态代理,true 对应 cglib 动态代理):
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="false"></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
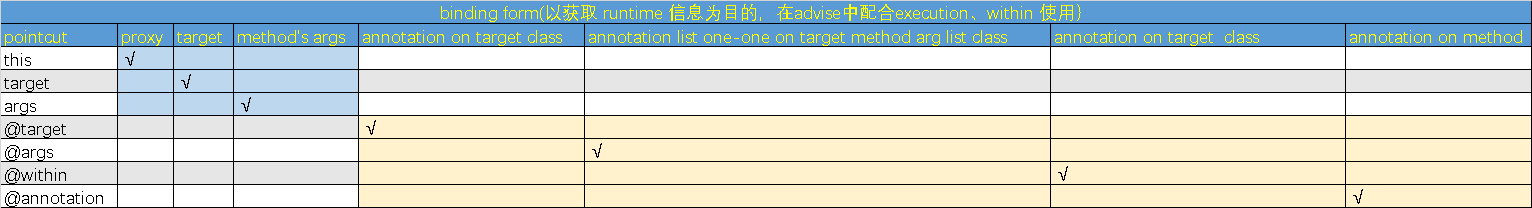
二、pointcut
execution - for matching method execution join points, this is the primary pointcut designator you will use when working with Spring AOP ①
within - limits matching to join points within certain types (simply the execution of a method declared within a matching type when using Spring AOP) ①
this - limits matching to join points (the execution of methods when using Spring AOP) where the bean reference (Spring AOP proxy) is an instance of the given type ②
target - limits matching to join points (the execution of methods when using Spring AOP) where the target object (application object being proxied) is an instance of the given type ②
args - limits matching to join points (the execution of methods when using Spring AOP) where the arguments are instances of the given types ②
@target - limits matching to join points (the execution of methods when using Spring AOP) where the class of the executing object has an annotation of the given type ②
@args - limits matching to join points (the execution of methods when using Spring AOP) where the runtime type of the actual arguments passed have annotations of the given type(s) ②
@within - limits matching to join points within types that have the given annotation (the execution of methods declared in types with the given annotation when using Spring AOP) ②
@annotation - limits matching to join points where the subject of the join point (method being executed in Spring AOP) has the given annotation ②
- ① 是最主要切面工具,excution 针对方法签名,within 针对类名
- ②是在①的前提下辅助获取特定信息,比如代理对象(this)、被代理对象(target)、入参(args)、类注解(@within)、方法注解(@annotation)、入参注解(@args)
- 当然只有②时相当于①是所有方法
- 见最后对各个概念的理解
1. execution
syntax:
execution(modifiers-pattern? ret-type-pattern declaring-type-pattern?name-pattern(param-pattern) throws-pattern?)
如下图,execution 匹配的是方法签名,是最基础的匹配方式
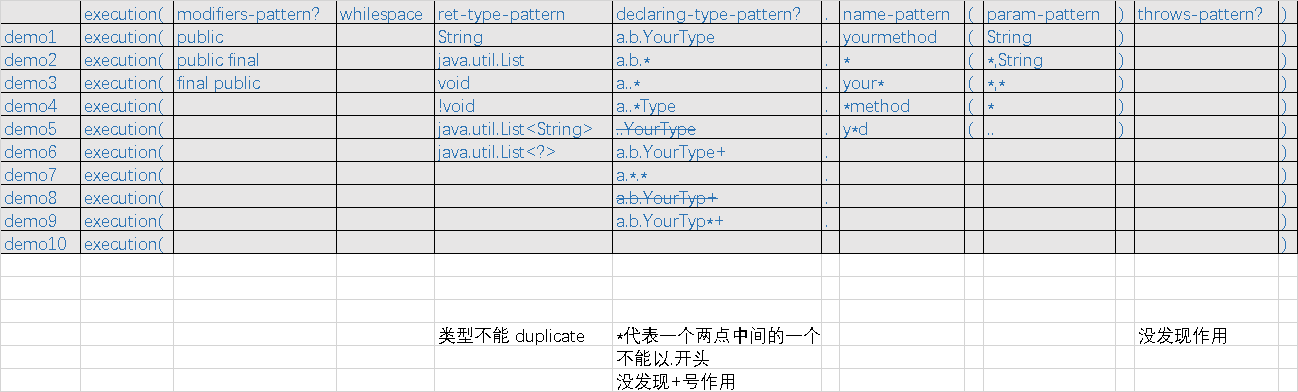
示意:
modifiers-pattern: 方法修饰符
ret-type-pattern: 返回值类型
declaring-type-pattern: 方法所在类
name-pattern: 方法名
param-pattern: 参数类型列表
throws-pattern: 异常
简版:
execution(ret-type-pattern name-pattern(param-pattern))
详细:
All parts except the returning type pattern (ret-type-pattern in the snippet above), name pattern, and parameters pattern are optional. The returning type pattern determines what the return type of the method must be in order for a join point to be matched. Most frequently you will use * as the returning type pattern, which matches any return type. A fully-qualified type name will match only when the method returns the given type. The name pattern matches the method name. You can use the * wildcard as all or part of a name pattern. If specifying a declaring type pattern then include a trailing . to join it to the name pattern component. The parameters pattern is slightly more complex: () matches a method that takes no parameters, whereas (..) matches any number of parameters (zero or more). The pattern (*) matches a method taking one parameter of any type, (*,String) matches a method taking two parameters, the first can be of any type, the second must be a String.
示例:
@Aspect @Component public class SomeInterceptor { @Pointcut("execution(* doTask*(..))") public void methodsToBeProfiled() { } @Around("methodsToBeProfiled()") public void profile(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable { System.out.println(pjp.getSignature().getName()); } }
2. within
syntax:
with(declaring-type-pattern)
如下图,with 是匹配类的全限定名,不是匹配方法
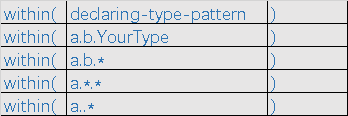
示例:
@Aspect @Component public class SomeInterceptor { @Pointcut("within(cn.zno..*)") public void methodsToBeProfiled() { } @Around("methodsToBeProfiled()") public void profile(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable { System.out.println(pjp.getSignature().getName()); } }
3. this
syntax:
this(advice-method's-arg-ref-of-target's-proxy-type)
这个是匹配目标类的代理对象
示例:
@Aspect @Component public class SomeInterceptor { @Before("execution(* doTaskA(..)) && this(s)") public void validateAccount(SomeClass s) { System.out.println(s.getClass()); } // class cn.zno.testaspect.SomeClass$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$5c6bdbdc }
4. target
syntax:
target(advice-method's-arg-ref-of-target-type)
这个是匹配目标类的实例,即被代理对象
示例:
@Aspect @Component public class SomeInterceptor { @Before("execution(* doTaskA(..)) && target(s)") public void validateAccount(SomeClass s) { System.out.println(s.getClass()); } // class cn.zno.testaspect.SomeClass }
5. args
syntax:
args(advise-method's-arg-ref-list-of-target-current-method's-arg-type-list)
获取目标对象的正在执行方法的入参列表
示例:
@Aspect @Component public class SomeInterceptor { @Before("execution(* doTaskA(..)) && args(s,i)") public void validateAccount(String s,Integer i) { System.out.println(s); System.out.println(i); } // abc // 123 }
6. @target
syntax:
@target(advise-method's-arg-ref-of-annotation-type-on-target-class)
获取目标类的注解
示例:
@Aspect @Component public class SomeInterceptor { @Before("execution(* doTaskA(..)) && @target(s)") public void validateAccount(SomeAnnotation s) { System.out.println(s.value()); } // 123 }
@Component @SomeAnnotation("123") public class SomeClass { public void doTaskA(String s1,Integer i1) { } }
7. @args
syntax:
@args(advise-method's-arg-ref-list-of-target's-current-method's-arg's-type's-annotation-type-list)
one-one (第一个入参类有第一个注解类,第二个入参类有第二个注解类,以此类推)
示例:
@SomeAnnotation("111")
public class Other {
}
@Component public class SomeClass { public void doTaskA(Other s1) { } }
@Aspect @Component public class SomeInterceptor { @Around("execution(* doTaskA(..)) && @args(s)") public void validateAccount(SomeAnnotation s) { System.out.println(s.value());// 111 } }
8. @within
syntax:
@within(advise-method's-arg-ref-of-annotation-type-on-target-class)
和@target 有区别(未做详细调查)
示例:
@Component @SomeAnnotation("1212") public class SomeClass { public void doTaskA(String s1) { } }
@Aspect @Component public class SomeInterceptor { @Around("execution(* doTask*(..)) && @within(s)") public void validateAccount(SomeAnnotation s) { System.out.println(s.value());// 1212 } }
9. @annotation
syntax:
@annotation(advise-method's-arg-ref-of-annotation-type-on-target-class-method)
示例:
@Component public class SomeClass { @SomeAnnotation("333") public void doTaskA(String s1) { } }
@Aspect @Component public class SomeInterceptor { @Around("@annotation(s)") public void validateAccount(SomeAnnotation s) { System.out.println(s.value());// 333 } }
10. combine ( and or not) : && || !
@Pointcut("execution()")
private void a() {}
@Pointcut("within()")
private void b() {}
@Pointcut("a() && b()")
private void ab() {}
或者
@Pointcut("execution() && within()")
private void ab() {}
三、advise(对切面的处理链路)
1. 切面是获取方法集合,advise 是对每一个方法的处理链路,即可以多个advise针对同一个方法。任何一个advise 方法都可以获取 JoinPoint
@Around("@annotation(s)")
public void validateAccount(JoinPoint jp) {
System.out.println(jp.getSignature());
}
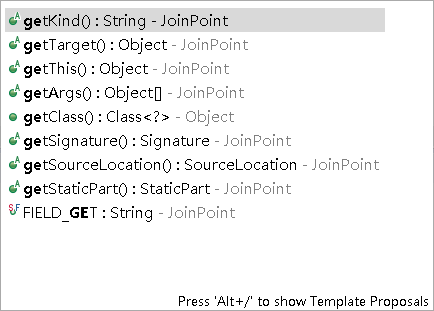
2. @Before
@Before(value="execution(* doTask*(..))") public void validateAccount(JoinPoint jp) { System.out.println(jp.getSignature()); }
@AfterReturning
public Integer doTaskA(String s1,String s2) { return new Integer("111"); }
@AfterReturning(value="execution(* doTask*(..))",returning="ret") public void validateAccount(JoinPoint jp,Object ret) { System.out.println(jp.getSignature()); System.out.println(ret.getClass()); }
输出:
Integer cn.zno.testaspect.SomeClass.doTaskA(String,String) class java.lang.Integer
@AfterThrowing
public Integer doTaskA(String s1,String s2) { if(1<2) throw new RuntimeException("eee"); return new Integer("111"); }
@AfterThrowing(value="execution(* doTask*(..))",throwing="e") public void validateAccount(JoinPoint jp,Exception e) { System.out.println(jp.getSignature()); System.out.println(e.getMessage()); }
输出:
Integer cn.zno.testaspect.SomeClass.doTaskA(String,String)
eee
问题:如何将异常处理,使其不再往外抛?需参考spring mvc
@After(finally)
public Integer doTaskA(String s1,String s2) { Integer integer; try { integer = new Integer("111"); }finally { System.out.println(123); } return integer; }
@After(value="execution(* doTask*(..))") public void validateAccount(JoinPoint jp) { System.out.println(jp.getSignature()); }
结果:
123 Integer cn.zno.testaspect.SomeClass.doTaskA(String,String)
确实在finally 块执行完毕之后才会拦截
@Around
public Integer doTaskA(String s1,String s2) { Integer integer; try { integer = new Integer("111"); }finally { System.out.println(123); } return integer; }
@Around(value="execution(* doTask*(..))") public void validateAccount(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) { System.out.println("before"); try { pjp.proceed(); } catch (Throwable e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("after"); }
结果:
before 123 after
四、辅助工具
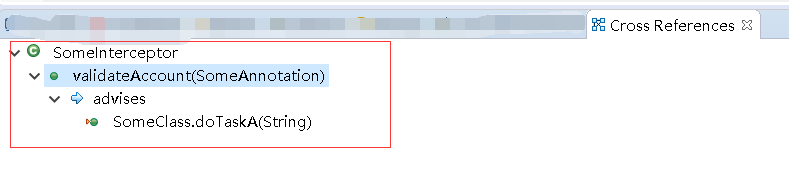
STS4 -> Window -> show view -> AspectJ-> Cross References
注意:需要运行一次单元测试,对应的advise 才会更新
1. 拦截器中有提示

2. 目标类中有提示

3. Cross References 有全部的!!(IMPORTANT!!)
五、补充知识点
1. 如何修改入参or返回结果
@Around("someAdvice()")
public Object someAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
// a. 获取目标方法入参列表
Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();
// b. 修改目标入参
...
// c. 传入修改后入参列表并 d.返回目标方法结果 (如果调用无参方法 proceed(); 则使用原有参数列表)
Object proceed = pjp.proceed(args);
// e. 修改目标方法返回结果
...
// f. 返回修改后的结果
return proceed;
}
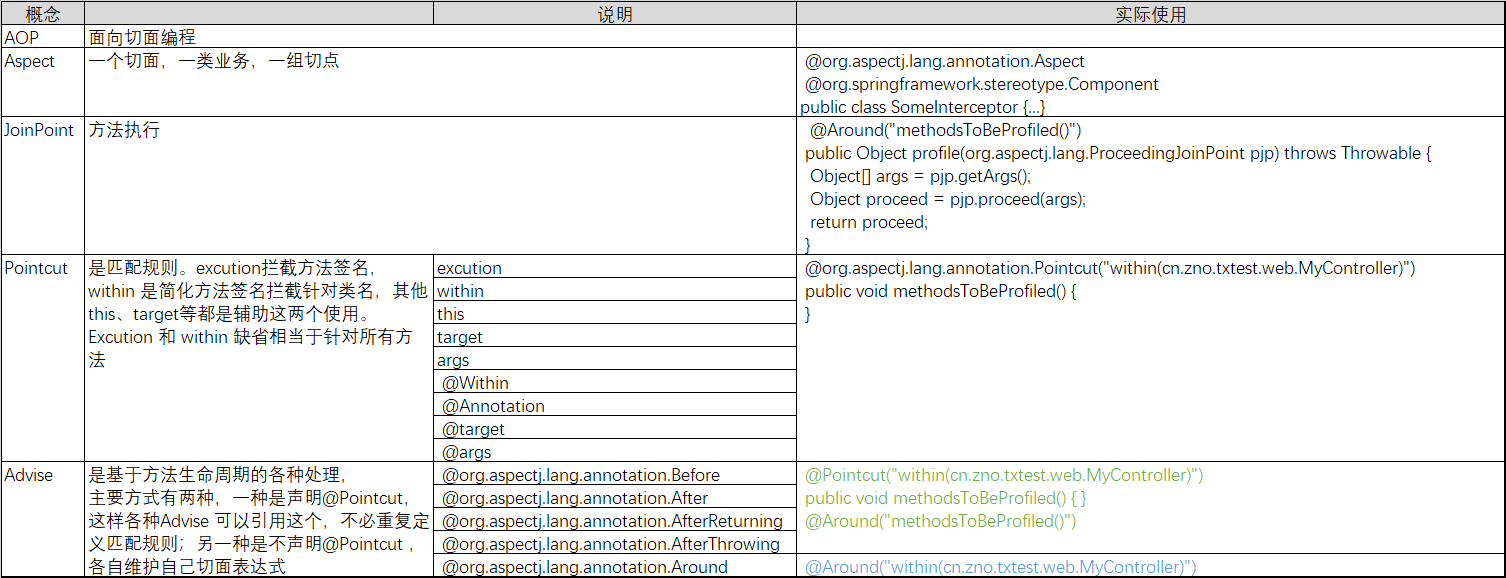
六、理解


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号