runtime-compiler 和 runtime-only的区别
一.看图,查看代码区别
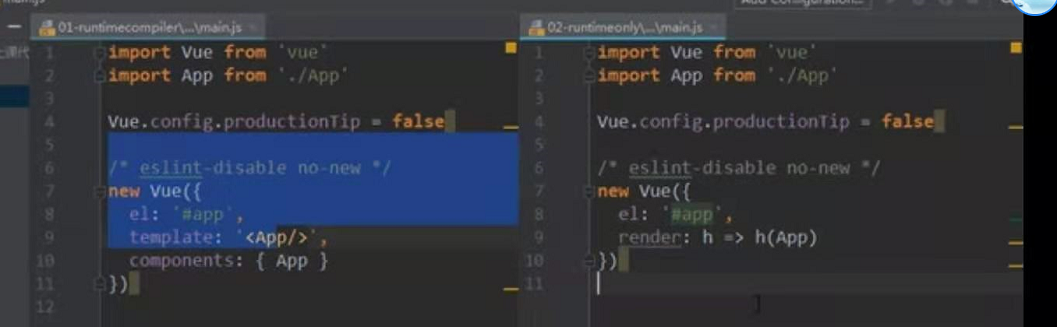
二.如图,进行分析
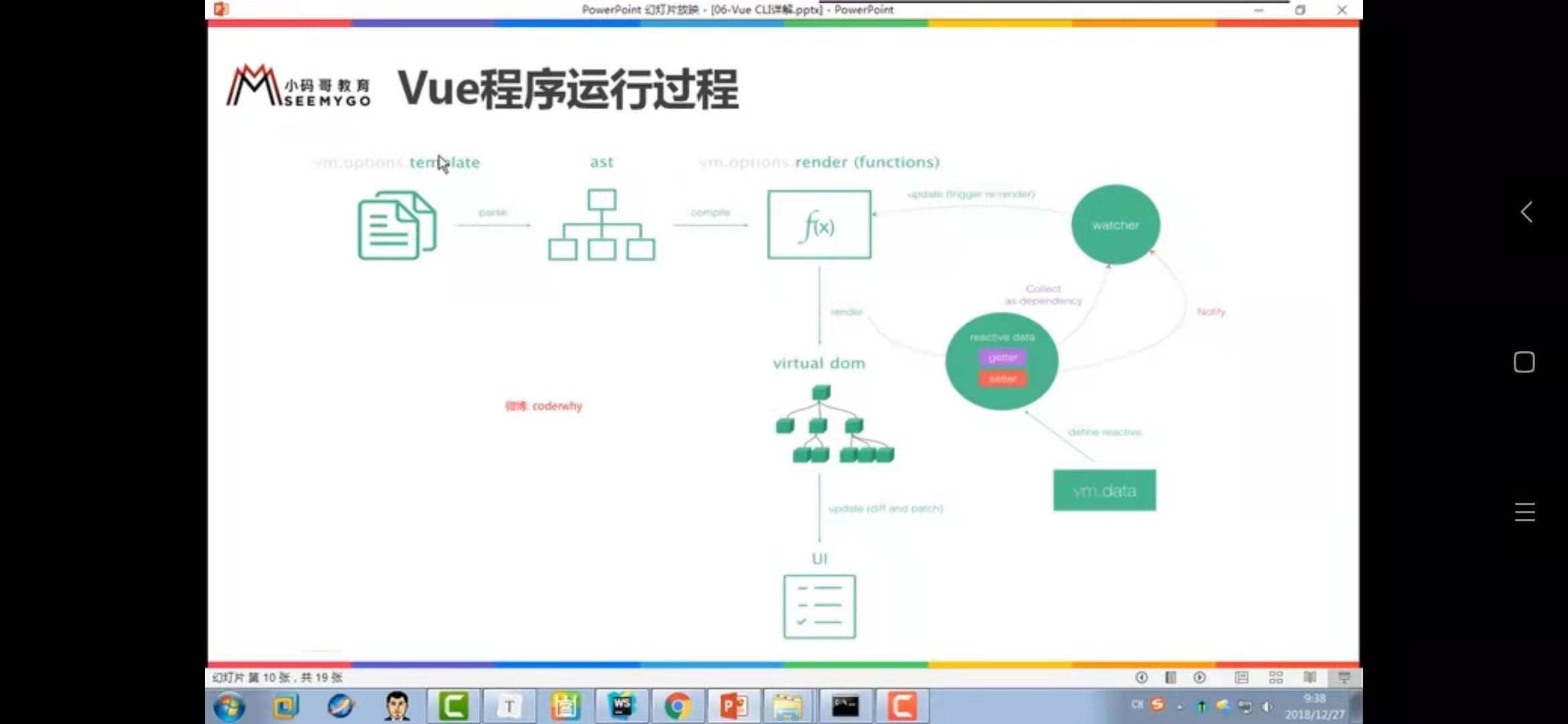
(1)runtime-compiler和runtime-only的执行步骤
runtime-compiler: teplate -> ast -> render ->vdom ->UI
runtime-only : render ->vdom -> UI
结论: runtime-only 1.性能更多 2. 代码量更多
推荐:以后工作在创建 vue项目时都要选 runtime-only这个模式
语言描述: template 解构为 ast(抽象语法树) 编译为 render函数 形成为 虚拟dom 最后转为 UI
三.通过修改runtime-compiler模式下的 main.js 来理解
main.js修改前
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | import Vue from 'vue'import App from './App'import router from './router'Vue.config.productionTip = false/* eslint-disable no-new */new Vue({ el: '#app', router, components: { App }, template: '<App/>'}) |
main.js修改后
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 | // The Vue build version to load with the `import` command// (runtime-only or standalone) has been set in webpack.base.conf with an alias.import Vue from "vue";import App from "./App";import router from "./router";Vue.config.productionTip = false;console.log(App) //zmztyaconst cpn = { template: "<div>我是组件</div>", data() { return { message: "测试" }; }};/* eslint-disable no-new */new Vue({ el: "#app", // router, // components: { App }, // template: '<App/>' //这里的template的 App组件是会替换 <div id="#app"></div> 这个标签 render: function(createElement) { //有另一种名字为 h //第一种:普通用法 //1.createElement('标签',{标签的属性},[标签的内容]) //标签属性这个部分是可以不用写的 //return createElement("h2", { class: "box" }, ["这是测试内容"]); //这里的内容会替换 el:#app即index.html 中 <div id="#app"></div>这个标签 被替换为 h2 // return createElement("h2", ["h2内容", createElement("button", ["点击"])]); //h2内部多了一个按钮内容 //第二种:这里还可以使用组件 return createElement(cpn); //分析:render函数是没有使用template的 思考:为什么App中有template,cpn有template,这里面明明有template,为什么说是没有使用呢? 因为这里的template是在编译的时候就已经渲染成了render函数,如何去查看呢? 在该文件中 标注了 //zmztya的地方打印出来,是一个对象,这个对象有render,而不是 template }}); |

扩展: :
1. .vue文件中的template 是由谁处理的呢?
是由 vue-template-compiler处理的




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 25岁的心里话
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 按钮权限的设计及实现