pandas百题笔记
Pandas百题笔记
1.导入 Pandas:
import pandas as pd
2.查看 Pandas 版本信息:
print(pd.__version__) ==>1.0.1
Pandas 的数据结构:Pandas 主要有 Series(一维数组),DataFrame(二维数组),Panel(三维数组),Panel4D(四维数组),PanelND(更多维数组)等数据结构。其中 Series 和 DataFrame 应用的最为广泛。
#Series 是一维带标签的数组,它可以包含任何数据类型。包括整数,字符串,浮点数,Python 对象等。Series 可以通过标签来定位。 #DataFrame 是二维的带标签的数据结构。我们可以通过标签来定位数据。这是 NumPy 所没有的。
创建 Series 数据类型
创建 Series 语法:s = pd.Series(data, index=index),可以通过多种方式进行创建,以下介绍了 3 个常用方法。
3.从列表创建 Series:
arr = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4] s1 = pd.Series(arr) # 如果不指定索引,则默认从 0 开始 s1 ==> 0 0 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 dtype: int64
4.从 Ndarray 创建 Series:
import numpy as np n = np.random.randn(5) # 创建一个随机 Ndarray 数组 index = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'] s2 = pd.Series(n, index=index) s2 ==> a -0.766282 b 0.134975 c 0.175090 d 0.298047 e 0.171916 dtype: float64
5.从字典创建 Series:
d = {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3, 'd': 4, 'e': 5} # 定义示例字典
s3 = pd.Series(d)
s3
==>
a 1
b 2
c 3
d 4
e 5
dtype: int64
Series 基本操作
6.修改 Series 索引:
print(s1) # 以 s1 为例 s1.index = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E'] # 修改后的索引 s1 ==> 0 0 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 dtype: int64 A 0 B 1 C 2 D 3 E 4 dtype: int64
7.Series 纵向拼接:
s4 = s3.append(s1) # 将 s1 拼接到 s3 s4 ==> a 1 b 2 c 3 d 4 e 5 A 0 B 1 C 2 D 3 E 4 dtype: int64
8.Series 按指定索引删除元素:
print(s4)
s4 = s4.drop('e') # 删除索引为 e 的值
s4
==>
a 1
b 2
c 3
d 4
e 5
A 0
B 1
C 2
D 3
E 4
dtype: int64
a 1
b 2
c 3
d 4
A 0
B 1
C 2
D 3
E 4
dtype: int64
9.Series 修改指定索引元素:
s4['A'] = 6 # 修改索引为 A 的值 = 6 s4 ==> a 1 b 2 c 3 d 4 A 6 B 1 C 2 D 3 E 4 dtype: int64
10.Series 按指定索引查找元素:
s4['B'] ==> 1
11.Series 切片操作:
例如对s4的前 3 个数据访问
s4[:3] ==> a 1 b 2 c 3 dtype: int64
Series 运算
12.Series 加法运算:
Series 的加法运算是按照索引计算,如果索引不同则填充为 NaN(空值)。
s4.add(s3) ==> A NaN B NaN C NaN D NaN E NaN a 2.0 b 4.0 c 6.0 d 8.0 e NaN dtype: float64
13.Series 减法运算:
Series的减法运算是按照索引对应计算,如果不同则填充为 NaN(空值)。
s4.sub(s3) ==> A NaN B NaN C NaN D NaN E NaN a 0.0 b 0.0 c 0.0 d 0.0 e NaN dtype: float64
14.Series 乘法运算:
Series 的乘法运算是按照索引对应计算,如果索引不同则填充为 NaN(空值)。
s4.mul(s3) ==> A NaN B NaN C NaN D NaN E NaN a 1.0 b 4.0 c 9.0 d 16.0 e NaN dtype: float64
15.Series 除法运算:
Series 的除法运算是按照索引对应计算,如果索引不同则填充为 NaN(空值)。
s4.div(s3) ==> A NaN B NaN C NaN D NaN E NaN a 1.0 b 1.0 c 1.0 d 1.0 e NaN dtype: float64
16.Series 求中位数:
s4.median() ==> 3.0
17.Series 求和:
s4.sum() ==> 26
18.Series 求最大值:
s4.max() ==> 6
19.Series 求最小值:
s4.min() ==> 1
创建 DataFrame 数据类型
与 Sereis 不同,DataFrame 可以存在多列数据。一般情况下,DataFrame 也更加常用。
20.通过 NumPy 数组创建 DataFrame:
dates = pd.date_range('today', periods=6) # 定义时间序列作为 index
num_arr = np.random.randn(6, 4) # 传入 numpy 随机数组
columns = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'] # 将列表作为列名
df1 = pd.DataFrame(num_arr, index=dates, columns=columns)
df1
==>
A B C D
2020-07-05 13:58:34.723797 -0.820141 0.205872 -0.928024 -1.828410
2020-07-06 13:58:34.723797 0.750014 -0.340494 1.190786 -0.204266
2020-07-07 13:58:34.723797 -2.062106 -1.520711 1.414341 1.057326
2020-07-08 13:58:34.723797 -0.821653 0.564271 -1.274913 2.340385
2020-07-09 13:58:34.723797 -1.936687 0.447897 -0.108420 0.133166
2020-07-10 13:58:34.723797 0.707222 -1.251812 -0.235982 0.340147
21.通过字典数组创建 DataFrame:
data = {'animal': ['cat', 'cat', 'snake', 'dog', 'dog', 'cat', 'snake', 'cat', 'dog', 'dog'],
'age': [2.5, 3, 0.5, np.nan, 5, 2, 4.5, np.nan, 7, 3],
'visits': [1, 3, 2, 3, 2, 3, 1, 1, 2, 1],
'priority': ['yes', 'yes', 'no', 'yes', 'no', 'no', 'no', 'yes', 'no', 'no']}
labels = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j']
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data, index=labels)
df2
==>
animal age visits priority
a cat 2.5 1 yes
b cat 3.0 3 yes
c snake 0.5 2 no
d dog NaN 3 yes
e dog 5.0 2 no
f cat 2.0 3 no
g snake 4.5 1 no
h cat NaN 1 yes
i dog 7.0 2 no
j dog 3.0 1 no
#字典中的键值直接变为列名
22.查看 DataFrame 的数据类型:
df2.dtypes ==> animal object age float64 visits int64 priority object dtype: object
DataFrame 基本操作
23.预览 DataFrame 的前 5 行数据:
此方法对快速了解陌生数据集结构十分有用。
df2.head() # 默认为显示 5 行,可根据需要在括号中填入希望预览的行数
==>
animal age visits priority
a cat 2.5 1 yes
b cat 3.0 3 yes
c snake 0.5 2 no
d dog NaN 3 yes
e dog 5.0 2 no
24.查看 DataFrame 的后 3 行数据:
df2.tail(3)
==>
animal age visits priority
h cat NaN 1 yes
i dog 7.0 2 no
j dog 3.0 1 no
25.查看 DataFrame 的索引:
df2.index ==> Index(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j'], dtype='object')
26.查看 DataFrame 的列名:
df2.columns ==>Index(['animal', 'age', 'visits', 'priority'], dtype='object')
27.查看 DataFrame 的数值:
df2.values
==>
array([['cat', 2.5, 1, 'yes'],
['cat', 3.0, 3, 'yes'],
['snake', 0.5, 2, 'no'],
['dog', nan, 3, 'yes'],
['dog', 5.0, 2, 'no'],
['cat', 2.0, 3, 'no'],
['snake', 4.5, 1, 'no'],
['cat', nan, 1, 'yes'],
['dog', 7.0, 2, 'no'],
['dog', 3.0, 1, 'no']], dtype=object)
28.查看 DataFrame 的统计数据:
df2.describe()
==>
age visits
count 8.000000 10.000000
mean 3.437500 1.900000
std 2.007797 0.875595
min 0.500000 1.000000
25% 2.375000 1.000000
50% 3.000000 2.000000
75% 4.625000 2.750000
max 7.000000 3.000000
29.DataFrame 转置操作:
df2.T
==>
a b c d e f g h i j
animal cat cat snake dog dog cat snake cat dog dog
age 2.5 3 0.5 NaN 5 2 4.5 NaN 7 3
visits 1 3 2 3 2 3 1 1 2 1
priority yes yes no yes no no no yes no no
30.对 DataFrame 进行按列排序:
df2.sort_values(by='age') # 按 age 升序排列
==>
animal age visits priority
c snake 0.5 2 no
f cat 2.0 3 no
a cat 2.5 1 yes
b cat 3.0 3 yes
j dog 3.0 1 no
g snake 4.5 1 no
e dog 5.0 2 no
i dog 7.0 2 no
d dog NaN 3 yes
h cat NaN 1 yes
31.对 DataFrame 数据切片:
df2[1:3]
==>
animal age visits priority
b cat 3.0 3 yes
c snake 0.5 2 no
32.对 DataFrame 通过标签查询(单列):
df2['age'] ==> a 2.5 b 3.0 c 0.5 d NaN e 5.0 f 2.0 g 4.5 h NaN i 7.0 j 3.0 Name: age, dtype: float64 df2.age # 等价于 df2['age']
33.对 DataFrame 通过标签查询(多列):
df2[['age', 'animal']] # 传入一个列名组成的列表 ==> age animal a 2.5 cat b 3.0 cat c 0.5 snake d NaN dog e 5.0 dog f 2.0 cat g 4.5 snake h NaN cat i 7.0 dog j 3.0 dog
34.对 DataFrame 通过位置查询:
df2.iloc[1:3] # 查询 2,3 行
==>
animal age visits priority
b cat 3.0 3 yes
c snake 0.5 2 no
35.DataFrame 副本拷贝:
生成 DataFrame 副本,方便数据集被多个不同流程使用
df3 = df2.copy() df3 ==> animal age visits priority a cat 2.5 1 yes b cat 3.0 3 yes c snake 0.5 2 no d dog NaN 3 yes e dog 5.0 2 no f cat 2.0 3 no g snake 4.5 1 no h cat NaN 1 yes i dog 7.0 2 no j dog 3.0 1 no
36.判断 DataFrame 元素是否为空:
df3.isnull() # 如果为空则返回为 True
==>
animal age visits priority
a False False False False
b False False False False
c False False False False
d False True False False
e False False False False
f False False False False
g False False False False
h False True False False
i False False False False
j False False False False
37.添加列数据:
num = pd.Series([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9], index=df3.index) df3['No.'] = num # 添加以 'No.' 为列名的新数据列 df3 ==> animal age visits priority No. a cat 2.5 1 yes 0 b cat 3.0 3 yes 1 c snake 0.5 2 no 2 d dog NaN 3 yes 3 e dog 5.0 2 no 4 f cat 2.0 3 no 5 g snake 4.5 1 no 6 h cat NaN 1 yes 7 i dog 7.0 2 no 8 j dog 3.0 1 no 9
38.根据 DataFrame 的下标值进行更改:
修改第 2 行与第 2 列对应的值 3.0 → 2.0
df3.iat[1, 1] = 2 # 索引序号从 0 开始,这里为 1, 1 df3 ==> animal age visits priority No. a cat 2.5 1 yes 0 b cat 2.0 3 yes 1 c snake 0.5 2 no 2 d dog NaN 3 yes 3 e dog 5.0 2 no 4 f cat 2.0 3 no 5 g snake 4.5 1 no 6 h cat NaN 1 yes 7 i dog 7.0 2 no 8 j dog 3.0 1 no 9
39.根据 DataFrame 的标签对数据进行修改:
df3.loc['f', 'age'] = 1.5
df3
==>
animal age visits priority No.
a cat 2.5 1 yes 0
b cat 2.0 3 yes 1
c snake 0.5 2 no 2
d dog NaN 3 yes 3
e dog 5.0 2 no 4
f cat 1.5 3 no 5
g snake 4.5 1 no 6
h cat NaN 1 yes 7
i dog 7.0 2 no 8
j dog 3.0 1 no 9
40.DataFrame 求平均值操作:
df3.mean() ==> age 3.25 visits 1.90 No. 4.50 dtype: float64
41.对 DataFrame 中任意列做求和操作:
df3['visits'].sum() ==> 19
字符串操作
42.将字符串转化为小写字母:
string = pd.Series(['A', 'B', 'C', 'Aaba', 'Baca',
np.nan, 'CABA', 'dog', 'cat'])
print(string)
string.str.lower()
==>
0 A
1 B
2 C
3 Aaba
4 Baca
5 NaN
6 CABA
7 dog
8 cat
dtype: object
0 a
1 b
2 c
3 aaba
4 baca
5 NaN
6 caba
7 dog
8 cat
dtype: object
43.将字符串转化为大写字母:
string.str.upper() ==> 0 A 1 B 2 C 3 AABA 4 BACA 5 NaN 6 CABA 7 DOG 8 CAT dtype: object
DataFrame 缺失值操作
44.对缺失值进行填充:
df4 = df3.copy()
print(df4)
df4.fillna(value=3)
==>
animal age visits priority No.
a cat 2.5 1 yes 0
b cat 2.0 3 yes 1
c snake 0.5 2 no 2
d dog NaN 3 yes 3
e dog 5.0 2 no 4
f cat 1.5 3 no 5
g snake 4.5 1 no 6
h cat NaN 1 yes 7
i dog 7.0 2 no 8
j dog 3.0 1 no 9
animal age visits priority No.
a cat 2.5 1 yes 0
b cat 2.0 3 yes 1
c snake 0.5 2 no 2
d dog 3.0 3 yes 3
e dog 5.0 2 no 4
f cat 1.5 3 no 5
g snake 4.5 1 no 6
h cat 3.0 1 yes 7
i dog 7.0 2 no 8
j dog 3.0 1 no 9
45.删除存在缺失值的行:
df5 = df3.copy()
print(df5)
df5.dropna(how='any') # 任何存在 NaN 的行都将被删除
==>
animal age visits priority No.
a cat 2.5 1 yes 0
b cat 2.0 3 yes 1
c snake 0.5 2 no 2
d dog NaN 3 yes 3
e dog 5.0 2 no 4
f cat 1.5 3 no 5
g snake 4.5 1 no 6
h cat NaN 1 yes 7
i dog 7.0 2 no 8
j dog 3.0 1 no 9
animal age visits priority No.
a cat 2.5 1 yes 0
b cat 2.0 3 yes 1
c snake 0.5 2 no 2
e dog 5.0 2 no 4
f cat 1.5 3 no 5
g snake 4.5 1 no 6
i dog 7.0 2 no 8
j dog 3.0 1 no 9
46.DataFrame 按指定列对齐:
left = pd.DataFrame({'key': ['foo1', 'foo2'], 'one': [1, 2]})
right = pd.DataFrame({'key': ['foo2', 'foo3'], 'two': [4, 5]})
print(left)
print(right)
按照 key 列对齐连接,只存在 foo2 相同,所以最后变成一行
pd.merge(left, right, on='key')
==>
key one
0 foo1 1
1 foo2 2
key two
0 foo2 4
1 foo3 5
key one two
0 foo2 2 4
DataFrame 文件操作
47.CSV 文件写入:
df3.to_csv('animal.csv')
print("写入成功.")
==> 写入成功.
48.CSV 文件读取:
df_animal = pd.read_csv('animal.csv')
df_animal
==>
Unnamed: 0 animal age visits priority No.
0 a cat 2.5 1 yes 0
1 b cat 2.0 3 yes 1
2 c snake 0.5 2 no 2
3 d dog NaN 3 yes 3
4 e dog 5.0 2 no 4
5 f cat 1.5 3 no 5
6 g snake 4.5 1 no 6
7 h cat NaN 1 yes 7
8 i dog 7.0 2 no 8
9 j dog 3.0 1 no 9
49.Excel 写入操作:
df3.to_excel('animal.xlsx', sheet_name='Sheet1')
print("写入成功.")
==> 写入成功.
50.Excel 读取操作:
pd.read_excel('animal.xlsx', 'Sheet1', index_col=None, na_values=['NA'])
==>
Unnamed: 0 animal age visits priority No.
0 a cat 2.5 1 yes 0
1 b cat 2.0 3 yes 1
2 c snake 0.5 2 no 2
3 d dog NaN 3 yes 3
4 e dog 5.0 2 no 4
5 f cat 1.5 3 no 5
6 g snake 4.5 1 no 6
7 h cat NaN 1 yes 7
8 i dog 7.0 2 no 8
9 j dog 3.0 1 no 9
进阶部分
时间序列索引
51.建立一个以 2018 年每一天为索引,值为随机数的 Series:
dti = pd.date_range(start='2018-01-01', end='2018-12-31', freq='D')
s = pd.Series(np.random.rand(len(dti)), index=dti)
s
==>
2018-01-01 0.441330
2018-01-02 0.182571
2018-01-03 0.141348
2018-01-04 0.604700
2018-01-05 0.300351
...
2018-12-27 0.499318
2018-12-28 0.530867
2018-12-29 0.183895
2018-12-30 0.163899
2018-12-31 0.173812
Freq: D, Length: 365, dtype: float64
52.统计s 中每一个周三对应值的和:
周一从 0 开始
s[s.index.weekday == 2].sum() ==> 22.592391213957054
53.统计s中每个月值的平均值:
s.resample('M').mean()
==>
2018-01-31 0.441100
2018-02-28 0.506476
2018-03-31 0.501672
2018-04-30 0.510073
2018-05-31 0.416773
2018-06-30 0.525039
2018-07-31 0.433221
2018-08-31 0.472530
2018-09-30 0.388529
2018-10-31 0.550011
2018-11-30 0.486513
2018-12-31 0.443012
Freq: M, dtype: float64
54.将 Series 中的时间进行转换(秒转分钟):
s = pd.date_range('today', periods=100, freq='S')
ts = pd.Series(np.random.randint(0, 500, len(s)), index=s)
ts.resample('Min').sum()
==>
2020-07-05 14:48:00 15836
2020-07-05 14:49:00 9298
Freq: T, dtype: int64
55.UTC 世界时间标准:
s = pd.date_range('today', periods=1, freq='D') # 获取当前时间
ts = pd.Series(np.random.randn(len(s)), s) # 随机数值
ts_utc = ts.tz_localize('UTC') # 转换为 UTC 时间
ts_utc
==>
2020-07-05 14:48:38.609382+00:00 -0.348899
Freq: D, dtype: float64
56.转换为上海所在时区:
ts_utc.tz_convert('Asia/Shanghai')
==>
2020-07-05 22:48:38.609382+08:00 -0.348899
Freq: D, dtype: float64
57.不同时间表示方式的转换:
rng = pd.date_range('1/1/2018', periods=5, freq='M')
ts = pd.Series(np.random.randn(len(rng)), index=rng)
print(ts)
ps = ts.to_period()
print(ps)
ps.to_timestamp()
==>
2018-01-31 0.621688
2018-02-28 -1.937715
2018-03-31 0.081314
2018-04-30 -1.308769
2018-05-31 -0.075345
Freq: M, dtype: float64
2018-01 0.621688
2018-02 -1.937715
2018-03 0.081314
2018-04 -1.308769
2018-05 -0.075345
Freq: M, dtype: float64
2018-01-01 0.621688
2018-02-01 -1.937715
2018-03-01 0.081314
2018-04-01 -1.308769
2018-05-01 -0.075345
Freq: MS, dtype: float64
Series 多重索引
58.创建多重索引 Series:
构建一个 letters = ['A', 'B', 'C'] 和 numbers = list(range(10))为索引,值为随机数的多重索引 Series。
letters = ['A', 'B', 'C'] numbers = list(range(10)) mi = pd.MultiIndex.from_product([letters, numbers]) # 设置多重索引 s = pd.Series(np.random.rand(30), index=mi) # 随机数 s ==> A 0 0.698046 1 0.380276 2 0.873395 3 0.628864 4 0.528025 5 0.677856 6 0.194495 7 0.164484 8 0.018238 9 0.747468 B 0 0.623616 1 0.560504 2 0.731296 3 0.760307 4 0.807663 5 0.347980 6 0.005892 7 0.807262 8 0.650353 9 0.803976 C 0 0.387503 1 0.943305 2 0.215817 3 0.128086 4 0.252103 5 0.048908 6 0.779633 7 0.825234 8 0.624257 9 0.263373 dtype: float64
59.多重索引 Series 查询:
查询索引为 1,3,6 的值
s.loc[:, [1, 3, 6]] ==> A 1 0.380276 3 0.628864 6 0.194495 B 1 0.560504 3 0.760307 6 0.005892 C 1 0.943305 3 0.128086 6 0.779633 dtype: float64
60.多重索引 Series 切片:
s.loc[pd.IndexSlice[:'B', 5:]]
==>
A 5 0.677856
6 0.194495
7 0.164484
8 0.018238
9 0.747468
B 5 0.347980
6 0.005892
7 0.807262
8 0.650353
9 0.803976
dtype: float64
DataFrame 多重索引
61.根据多重索引创建 DataFrame:
创建一个以 letters = ['A', 'B'] 和 numbers = list(range(6))为索引,值为随机数据的多重索引 DataFrame。
frame = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape(6, 2),
index=[list('AAABBB'), list('123123')],
columns=['hello', 'shiyanlou'])
frame
==>
hello shiyanlou
A 1 0 1
2 2 3
3 4 5
B 1 6 7
2 8 9
3 10 11
62.多重索引设置列名称:
frame.index.names = ['first', 'second']
frame
==>
hello shiyanlou
first second
A 1 0 1
2 2 3
3 4 5
B 1 6 7
2 8 9
3 10 11
63.DataFrame 多重索引分组求和:
frame.groupby('first').sum()
==>
hello shiyanlou
first
A 6 9
B 24 27
64.DataFrame 行列名称转换:
print(frame)
frame.stack()
==>
hello shiyanlou
first second
A 1 0 1
2 2 3
3 4 5
B 1 6 7
2 8 9
3 10 11
first second
A 1 hello 0
shiyanlou 1
2 hello 2
shiyanlou 3
3 hello 4
shiyanlou 5
B 1 hello 6
shiyanlou 7
2 hello 8
shiyanlou 9
3 hello 10
shiyanlou 11
dtype: int64
65.DataFrame 索引转换:
print(frame)
frame.unstack()
==>
hello shiyanlou
first second
A 1 0 1
2 2 3
3 4 5
B 1 6 7
2 8 9
3 10 11
hello shiyanlou
second 1 2 3 1 2 3
first
A 0 2 4 1 3 5
B 6 8 10 7 9 11
66.DataFrame 条件查找:
示例数据
data = {'animal': ['cat', 'cat', 'snake', 'dog', 'dog', 'cat', 'snake', 'cat', 'dog', 'dog'],
'age': [2.5, 3, 0.5, np.nan, 5, 2, 4.5, np.nan, 7, 3],
'visits': [1, 3, 2, 3, 2, 3, 1, 1, 2, 1],
'priority': ['yes', 'yes', 'no', 'yes', 'no', 'no', 'no', 'yes', 'no', 'no']}
labels = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j']
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=labels)
查找 age 大于 3 的全部信息
df[df['age'] > 3] ==> animal age visits priority e dog 5.0 2 no g snake 4.5 1 no i dog 7.0 2 no
67.根据行列索引切片:
df.iloc[2:4, 1:3]
==>
age visits
c 0.5 2
d NaN 3
68.DataFrame 多重条件查询:
查找 age<3 且为 cat 的全部数据。
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=labels) df[(df['animal'] == 'cat') & (df['age'] < 3)] ==> animal age visits priority a cat 2.5 1 yes f cat 2.0 3 no
69.DataFrame 按关键字查询:
df3[df3['animal'].isin(['cat', 'dog'])]
==>
animal age visits priority No.
a cat 2.5 1 yes 0
b cat 2.0 3 yes 1
d dog NaN 3 yes 3
e dog 5.0 2 no 4
f cat 1.5 3 no 5
h cat NaN 1 yes 7
i dog 7.0 2 no 8
j dog 3.0 1 no 9
70.DataFrame 按标签及列名查询:
df.loc[df2.index[[3, 4, 8]], ['animal', 'age']]
==>
animal age
d dog NaN
e dog 5.0
i dog 7.0
71.DataFrame 多条件排序:
按照 age 降序,visits 升序排列
df.sort_values(by=['age', 'visits'], ascending=[False, True])
==>
animal age visits priority
i dog 7.0 2 no
e dog 5.0 2 no
g snake 4.5 1 no
j dog 3.0 1 no
b cat 3.0 3 yes
a cat 2.5 1 yes
f cat 2.0 3 no
c snake 0.5 2 no
h cat NaN 1 yes
d dog NaN 3 yes
72.DataFrame 多值替换:
将 priority 列的 yes 值替换为 True,no 值替换为 False。
df['priority'].map({'yes': True, 'no': False})
==>
a True
b True
c False
d True
e False
f False
g False
h True
i False
j False
Name: priority, dtype: bool
73.DataFrame 分组求和:
df4.groupby('animal').sum()
==>
age visits No.
animal
cat 6.0 8 13
dog 15.0 8 24
snake 5.0 3 8
74.使用列表拼接多个 DataFrame:
temp_df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(5, 4)) # 生成由随机数组成的 DataFrame 1
temp_df2 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(5, 4)) # 生成由随机数组成的 DataFrame 2
temp_df3 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(5, 4)) # 生成由随机数组成的 DataFrame 3
print(temp_df1)
print(temp_df2)
print(temp_df3)
pieces = [temp_df1, temp_df2, temp_df3]
pd.concat(pieces)
==>
0 1 2 3
0 1.061349 0.927805 -0.270724 0.232218
1 -2.049875 -0.896899 -0.738298 0.547709
2 0.084709 -1.801844 0.610220 -1.304246
3 1.384591 0.872657 -0.829547 -0.332316
4 -0.255004 2.177881 0.615079 0.767592
0 1 2 3
0 0.009016 1.181569 -1.403829 -0.745604
1 -0.270313 -0.258377 -1.067346 1.465726
2 -1.619676 -0.324374 -0.433600 0.211323
3 0.163223 0.144191 0.717129 -0.555298
4 -0.718321 1.688866 -0.607994 1.731248
0 1 2 3
0 -1.178622 0.415409 0.496004 1.368869
1 0.724433 -0.262059 0.514689 -1.666051
2 -0.325606 0.013015 1.010961 2.075196
3 2.212960 -0.132432 -1.603347 -1.182487
4 0.102536 1.384535 0.411434 -0.175592
0 1 2 3
0 1.061349 0.927805 -0.270724 0.232218
1 -2.049875 -0.896899 -0.738298 0.547709
2 0.084709 -1.801844 0.610220 -1.304246
3 1.384591 0.872657 -0.829547 -0.332316
4 -0.255004 2.177881 0.615079 0.767592
0 0.009016 1.181569 -1.403829 -0.745604
1 -0.270313 -0.258377 -1.067346 1.465726
2 -1.619676 -0.324374 -0.433600 0.211323
3 0.163223 0.144191 0.717129 -0.555298
4 -0.718321 1.688866 -0.607994 1.731248
0 -1.178622 0.415409 0.496004 1.368869
1 0.724433 -0.262059 0.514689 -1.666051
2 -0.325606 0.013015 1.010961 2.075196
3 2.212960 -0.132432 -1.603347 -1.182487
4 0.102536 1.384535 0.411434 -0.175592
75.找出 DataFrame 表中和最小的列:
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.random(size=(5, 10)), columns=list('abcdefghij'))
print(df)
df.sum().idxmin() # idxmax(), idxmin() 为 Series 函数返回最大最小值的索引值
==>
a b c d e f g \
0 0.931149 0.641776 0.758608 0.630512 0.170375 0.211306 0.973363
1 0.730186 0.682949 0.554609 0.356089 0.399012 0.939087 0.908047
2 0.261405 0.434525 0.490395 0.368307 0.832568 0.571115 0.936016
3 0.161993 0.132176 0.852158 0.140710 0.165902 0.564976 0.656718
4 0.810233 0.385639 0.127849 0.166585 0.302643 0.947498 0.164274
h i j
0 0.223378 0.115285 0.161207
1 0.765946 0.206518 0.951096
2 0.891956 0.430530 0.045640
3 0.955571 0.962989 0.123037
4 0.391810 0.696404 0.561719
'd'
76.DataFrame 中每个元素减去每一行的平均值:
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.random(size=(5, 3)))
print(df)
df.sub(df.mean(axis=1), axis=0)
==>
0 1 2
0 0.028539 0.555065 0.166588
1 0.781335 0.086089 0.616780
2 0.022462 0.047383 0.476410
3 0.796853 0.850955 0.765398
4 0.208298 0.858031 0.264920
0 1 2
0 -0.221525 0.305001 -0.083476
1 0.286600 -0.408646 0.122046
2 -0.159623 -0.134702 0.294325
3 -0.007549 0.046553 -0.039004
4 -0.235452 0.414281 -0.178830
77.DataFrame 分组,并得到每一组中最大三个数之和:
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': list('aaabbcaabcccbbc'),
'B': [12, 345, 3, 1, 45, 14, 4, 52, 54, 23, 235, 21, 57, 3, 87]})
print(df)
df.groupby('A')['B'].nlargest(3).sum(level=0)
==>
A B
0 a 12
1 a 345
2 a 3
3 b 1
4 b 45
5 c 14
6 a 4
7 a 52
8 b 54
9 c 23
10 c 235
11 c 21
12 b 57
13 b 3
14 c 87
A
a 409
b 156
c 345
Name: B, dtype: int64
透视表
当分析庞大的数据时,为了更好的发掘数据特征之间的关系,且不破坏原数据,就可以利用透视表 pivot_table 进行操作。
78.透视表的创建:
新建表将 A, B, C 列作为索引进行聚合。
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': ['one', 'one', 'two', 'three'] * 3,
'B': ['A', 'B', 'C'] * 4,
'C': ['foo', 'foo', 'foo', 'bar', 'bar', 'bar'] * 2,
'D': np.random.randn(12),
'E': np.random.randn(12)})
print(df)
print(pd.pivot_table(df, index=['A', 'B']))
==>
A B C D E
0 one A foo -2.718717 1.749056
1 one B foo -0.710776 0.442023
2 two C foo -0.824951 2.244523
3 three A bar 0.300916 1.709200
4 one B bar -2.590790 0.292709
5 one C bar 0.908543 -0.598258
6 two A foo -0.521278 0.204491
7 three B foo -3.302320 -1.762640
8 one C foo -1.311013 -0.722187
9 one A bar 0.785471 -0.231635
10 two B bar -1.758329 -0.031603
11 three C bar 1.236829 1.235032
D E
A B
one A -0.966623 0.758711
B -1.650783 0.367366
C -0.201235 -0.660222
three A 0.300916 1.709200
B -3.302320 -1.762640
C 1.236829 1.235032
two A -0.521278 0.204491
B -1.758329 -0.031603
C -0.824951 2.244523
79.透视表按指定行进行聚合:
将该 DataFrame 的 D 列聚合,按照 A,B 列为索引进行聚合,聚合的方式为默认求均值。
pd.pivot_table(df, values=['D'], index=['A', 'B'])
==>
D
A B
one A -0.966623
B -1.650783
C -0.201235
three A 0.300916
B -3.302320
C 1.236829
two A -0.521278
B -1.758329
C -0.824951
80.透视表聚合方式定义:
上一题中 D 列聚合时,采用默认求均值的方法,若想使用更多的方式可以在 aggfunc 中实现。
pd.pivot_table(df, values=['D'], index=['A', 'B'], aggfunc=[np.sum, len])
==>
sum len
D D
A B
one A -1.933246 2.0
B -3.301567 2.0
C -0.402470 2.0
three A 0.300916 1.0
B -3.302320 1.0
C 1.236829 1.0
two A -0.521278 1.0
B -1.758329 1.0
C -0.824951 1.0
81.透视表利用额外列进行辅助分割:
D 列按照 A,B 列进行聚合时,若关心 C 列对 D 列的影响,可以加入 columns 值进行分析。
pd.pivot_table(df, values=['D'], index=['A', 'B'],
columns=['C'], aggfunc=np.sum)
==>
D
C bar foo
A B
one A 0.785471 -2.718717
B -2.590790 -0.710776
C 0.908543 -1.311013
three A 0.300916 NaN
B NaN -3.302320
C 1.236829 NaN
two A NaN -0.521278
B -1.758329 NaN
C NaN -0.824951
82.透视表的缺省值处理:
在透视表中由于不同的聚合方式,相应缺少的组合将为缺省值,可以加入 fill_value 对缺省值处理。
pd.pivot_table(df, values=['D'], index=['A', 'B'],
columns=['C'], aggfunc=np.sum, fill_value=0)
==>
D
C bar foo
A B
one A 0.785471 -2.718717
B -2.590790 -0.710776
C 0.908543 -1.311013
three A 0.300916 0.000000
B 0.000000 -3.302320
C 1.236829 0.000000
two A 0.000000 -0.521278
B -1.758329 0.000000
C 0.000000 -0.824951
绝对类型¶
在数据的形式上主要包括数量型和性质型,数量型表示着数据可数范围可变,而性质型表示范围已经确定不可改变,绝对型数据就是性质型数据的一种。
83.绝对型数据定义:
df = pd.DataFrame({"id": [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], "raw_grade": [
'a', 'b', 'b', 'a', 'a', 'e']})
df["grade"] = df["raw_grade"].astype("category")
df
==>
id raw_grade grade
0 1 a a
1 2 b b
2 3 b b
3 4 a a
4 5 a a
5 6 e e
84.对绝对型数据重命名:
df["grade"].cat.categories = ["very good", "good", "very bad"]
df
==>
id raw_grade grade
0 1 a very good
1 2 b good
2 3 b good
3 4 a very good
4 5 a very good
5 6 e very bad
85.重新排列绝对型数据并补充相应的缺省值:
df["grade"] = df["grade"].cat.set_categories(
["very bad", "bad", "medium", "good", "very good"])
df
==>
id raw_grade grade
0 1 a very good
1 2 b good
2 3 b good
3 4 a very good
4 5 a very good
5 6 e very bad
86.对绝对型数据进行排序:
df.sort_values(by="grade")
==>
id raw_grade grade
5 6 e very bad
1 2 b good
2 3 b good
0 1 a very good
3 4 a very good
4 5 a very good
87.对绝对型数据进行分组:
df.groupby("grade").size()
==>
grade
very bad 1
bad 0
medium 0
good 2
very good 3
dtype: int64
数据清洗
常常我们得到的数据是不符合我们最终处理的数据要求,包括许多缺省值以及坏的数据,需要我们对数据进行清洗。
88.缺失值拟合:
在FilghtNumber中有数值缺失,其中数值为按 10 增长,补充相应的缺省值使得数据完整,并让数据为 int 类型。
df = pd.DataFrame({'From_To': ['LoNDon_paris', 'MAdrid_miLAN', 'londON_StockhOlm',
'Budapest_PaRis', 'Brussels_londOn'],
'FlightNumber': [10045, np.nan, 10065, np.nan, 10085],
'RecentDelays': [[23, 47], [], [24, 43, 87], [13], [67, 32]],
'Airline': ['KLM(!)', '<Air France> (12)', '(British Airways. )',
'12. Air France', '"Swiss Air"']})
df['FlightNumber'] = df['FlightNumber'].interpolate().astype(int)
df
==>
From_To FlightNumber RecentDelays Airline
0 LoNDon_paris 10045 [23, 47] KLM(!)
1 MAdrid_miLAN 10055 [] <Air France> (12)
2 londON_StockhOlm 10065 [24, 43, 87] (British Airways. )
3 Budapest_PaRis 10075 [13] 12. Air France
4 Brussels_londOn 10085 [67, 32] "Swiss Air"
89.数据列拆分:
其中From_to应该为两独立的两列From和To,将From_to依照_拆分为独立两列建立为一个新表。
temp = df.From_To.str.split('_', expand=True)
temp.columns = ['From', 'To']
temp
==>
From To
0 LoNDon paris
1 MAdrid miLAN
2 londON StockhOlm
3 Budapest PaRis
4 Brussels londOn
90.字符标准化:
其中注意到地点的名字都不规范(如:londON应该为London)需要对数据进行标准化处理。
temp['From'] = temp['From'].str.capitalize() temp['To'] = temp['To'].str.capitalize()
91.删除坏数据加入整理好的数据:
将最开始的 From_to 列删除,加入整理好的 From 和 to 列。
df = df.drop('From_To', axis=1)
df = df.join(temp)
print(df)
==>
FlightNumber RecentDelays Airline From To
0 10045 [23, 47] KLM(!) London Paris
1 10055 [] <Air France> (12) Madrid Milan
2 10065 [24, 43, 87] (British Airways. ) London Stockholm
3 10075 [13] 12. Air France Budapest Paris
4 10085 [67, 32] "Swiss Air" Brussels London
92.去除多余字符:
如同 airline 列中许多数据有许多其他字符,会对后期的数据分析有较大影响,需要对这类数据进行修正。
df['Airline'] = df['Airline'].str.extract(
'([a-zA-Z\s]+)', expand=False).str.strip()
df
==>
FlightNumber Airline From To delay_1 delay_2 \
0 10045 KLM London Paris 23.0 47.0
1 10055 Air France Madrid Milan NaN NaN
2 10065 British Airways London Stockholm 24.0 43.0
3 10075 Air France Budapest Paris 13.0 NaN
4 10085 Swiss Air Brussels London 67.0 32.0
delay_3
0 NaN
1 NaN
2 87.0
3 NaN
4 NaN
93.格式规范:
在 RecentDelays 中记录的方式为列表类型,由于其长度不一,这会为后期数据分析造成很大麻烦。这里将 RecentDelays 的列表拆开,取出列表中的相同位置元素作为一列,若为空值即用 NaN 代替。
delays = df['RecentDelays'].apply(pd.Series)
delays.columns = ['delay_{}'.format(n)
for n in range(1, len(delays.columns)+1)]
df = df.drop('RecentDelays', axis=1).join(delays)
df
==>
FlightNumber Airline From To delay_1 delay_2 delay_3
0 10045 KLM London Paris 23.0 47.0 NaN
1 10055 Air France Madrid Milan NaN NaN NaN
2 10065 British Airways London Stockholm 24.0 43.0 87.0
3 10075 Air France Budapest Paris 13.0 NaN NaN
4 10085 Swiss Air Brussels London 67.0 32.0 NaN
数据预处理
94.信息区间划分:
班级一部分同学的数学成绩表,如下图所示
df=pd.DataFrame({'name':['Alice','Bob','Candy','Dany','Ella','Frank','Grace','Jenny'],
'grades':[58,83,79,65,93,45,61,88]})
但我们更加关心的是该同学是否及格,将该数学成绩按照是否>60来进行划分。
df = pd.DataFrame({'name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Candy', 'Dany', 'Ella',
'Frank', 'Grace', 'Jenny'],
'grades': [58, 83, 79, 65, 93, 45, 61, 88]})
def choice(x):
if x > 60:
return 1
else:
return 0
df.grades = pd.Series(map(lambda x: choice(x), df.grades))
df
==>
name grades
0 Alice 0
1 Bob 1
2 Candy 1
3 Dany 1
4 Ella 1
5 Frank 0
6 Grace 1
7 Jenny 1
95.数据去重:
一个列为A的 DataFrame 数据,如下图所示
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 7, 7]})
尝试将 A 列中连续重复的数据清除。
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 7, 7]})
df.loc[df['A'].shift() != df['A']]
==>
A
0 1
1 2
3 3
4 4
5 5
8 6
9 7
96.数据归一化:
有时候,DataFrame 中不同列之间的数据差距太大,需要对其进行归一化处理。 其中,Max-Min 归一化是简单而常见的一种方式,公式如下:
def normalization(df):
numerator = df.sub(df.min())
denominator = (df.max()).sub(df.min())
Y = numerator.div(denominator)
return Y
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.random(size=(5, 3)))
print(df)
normalization(df)
==>
0 1 2
0 0.923325 0.925392 0.203170
1 0.770389 0.050410 0.605788
2 0.146447 0.542584 0.056240
3 0.161917 0.841527 0.547914
4 0.948175 0.814426 0.980268
0 1 2
0 0.969004 1.000000 0.159009
1 0.778247 0.000000 0.594731
2 0.000000 0.562496 0.000000
3 0.019297 0.904153 0.532098
4 1.000000 0.873179 1.000000
Pandas 绘图操作
为了更好的了解数据包含的信息,最直观的方法就是将其绘制成图。
97.Series 可视化:
%matplotlib inline
ts = pd.Series(np.random.randn(100), index=pd.date_range('today', periods=100))
ts = ts.cumsum()
ts.plot()
==>输出图像:
98.DataFrame 折线图:
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(100, 4), index=ts.index,
columns=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'])
df = df.cumsum()
df.plot()
==>输出图像:
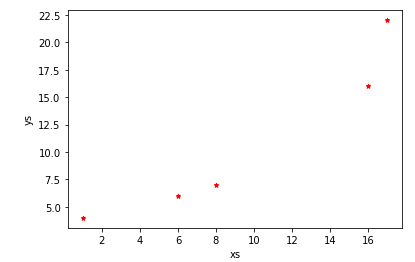
99.DataFrame 散点图:
df = pd.DataFrame({"xs": [1, 5, 2, 8, 1], "ys": [4, 2, 1, 9, 6]})
df = df.cumsum()
df.plot.scatter("xs", "ys", color='red', marker="*")
==>输出图像:
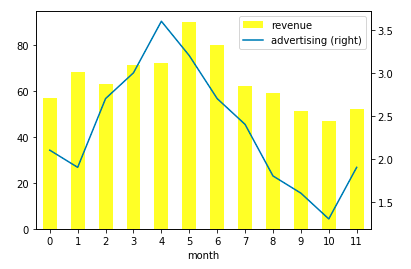
100.DataFrame 柱形图:
df = pd.DataFrame({"revenue": [57, 68, 63, 71, 72, 90, 80, 62, 59, 51, 47, 52],
"advertising": [2.1, 1.9, 2.7, 3.0, 3.6, 3.2, 2.7, 2.4, 1.8, 1.6, 1.3, 1.9],
"month": range(12)
})
ax = df.plot.bar("month", "revenue", color="yellow")
df.plot("month", "advertising", secondary_y=True, ax=ax)
==>输出图像: