第七周作业-N67044-张铭扬
1. 说明自动化运维的路径,原理,实践方法.
所谓自动化运维是指通过将日常IT运维中大量的重复性工作(小到简单的日常检查、配置变更和软件安装,大到整个变更流程的组织调度)由过去的手工执行转为标准化、流程化和自动化操作。
企业实际应用场景分析
Dev开发环境
使用者:程序员
功能:程序员个人的办公电脑或项目的开发测试环境,部署开发软件,测试个人或项目整体的BUG的环 境
管理者:程序员
测试环境
使用者:QA测试工程师
功能:测试经过Dev环境测试通过的软件的功能和性能,判断是否达到项目的预期目标,生成测试报告
管理者:运维
说明:测试环境往往有多套,测试环境满足测试功能即可,不宜过多;测试人员希望测试环境有多套,公司的产品多产品线并发,即多个版本,意味着多个版本同步测试;通常测试环境有多少套和产品线数量保持一样
预发布环境
使用者:运维
功能:使用和生产环境一样的数据库,缓存服务等配置,测试是否正常
发布环境
包括代码发布机,有些公司为堡垒机(安全屏障)
使用者:运维
功能:发布代码至生产环境
管理者:运维(有经验)
发布机:往往需要有2台(主备)
生产环境
使用者:运维,少数情况开放权限给核心开发人员,极少数公司将权限完全开放给开发人员并其维护
功能:对用户提供公司产品的服务
管理者:只能是运维
生产环境服务器数量:一般比较多,且应用非常重要。往往需要自动工具协助部署配置应用
灰度环境
属于生产环境的一部分
使用者:运维
功能:在全量发布代码前将代码的功能面向少量精准用户发布的环境,可基于主机或用户执行灰度发布
案例:共100台生产服务器,先发布其中的10台服务器,这10台服务器就是灰度服务器
管理者:运维
灰度环境:往往该版本功能变更较大,为保险起见特意先让一部分用户优化体验该功能,待这部分用户 使用没有重大问题的时候,再全量发布至所有服务器
2. 搭建pxe集群
节点1:10.0.0.156;节点2:10.0.0.157;节点3:10.0.0.158
#节点1 [root@centos7 ~]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/pxc.repo [percona] name=percona_repo baseurl = https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/percona/release/$releasever/RPMS/$basearch enabled = 1 gpgcheck = 0 [root@centos7 ~]#scp /etc/yum.repos.d/pxc.repo 10.0.0.157:/etc/yum.repos.d [root@centos7 ~]#scp /etc/yum.repos.d/pxc.repo 10.0.0.158:/etc/yum.repos.d
#在三个节点安装PXC
[root@centos7 ~]# yum install Percona-XtraDB-Cluster-57 -y
[root@centos7 ~]# yum install Percona-XtraDB-Cluster-57 -y
[root@centos7 ~]# yum install Percona-XtraDB-Cluster-57 -y
#修改配置
[root@centos7 ~]# vim /etc/percona-xtradb-cluster.conf.d/wsrep.cnf
[mysqld]
# Path to Galera library
wsrep_provider=/usr/lib64/galera3/libgalera_smm.so
# Cluster connection URL contains IPs of nodes
#If no IP is found, this implies that a new cluster needs to be created,
#in order to do that you need to bootstrap this node
wsrep_cluster_address=gcomm://10.0.0.156,10.0.0.157,10.0.0.158
# In order for Galera to work correctly binlog format should be ROW
binlog_format=ROW
# MyISAM storage engine has only experimental support
default_storage_engine=InnoDB
# Slave thread to use
wsrep_slave_threads= 8
wsrep_log_conflicts
# This changes how InnoDB autoincrement locks are managed and is a requirement for Galera
innodb_autoinc_lock_mode=2
# Node IP address
wsrep_node_address=10.0.0.156
# Cluster name
wsrep_cluster_name=pxc-cluster-zmy
#If wsrep_node_name is not specified, then system hostname will be used
wsrep_node_name=pxc-cluster-node-1
#pxc_strict_mode allowed values: DISABLED,PERMISSIVE,ENFORCING,MASTER
pxc_strict_mode=ENFORCING
# SST method
wsrep_sst_method=xtrabackup-v2
#Authentication for SST method
wsrep_sst_auth="sstuser:s3cretPass"
#标黄需要修改
#其余两个节点相同操作
启动第一个节点
[root@centos7 ~]# systemctl start mysql@bootstrap.service [root@centos7 ~]# grep "temporary password" /var/log/mysqld.log 2022-08-20T08:52:35.405492Z 1 [Note] A temporary password is generated for root@localhost: njQVMfRt;4wB [root@centos7 ~]# mysql -uroot -p'njQVMfRt;4wB' ysql> alter user 'root'@'localhost' identified by '123456'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> create user 'sstuser'@'localhost' identified by 's3cretPass'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> grant reload,lock tables,process,replication client on *.* to 'sstuser'@'localhost'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
启动其余两个节点
[root@centos7 ~]# systemctl start mysql [root@centos7 ~]# systemctl start mysql 节点一 mysql> show status like 'wsrep%'\G; *************************** 66. row *************************** Variable_name: wsrep_cluster_size Value: 3
已连接
测试
#节点三 mysql> create database db158; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) #其余节点查看是否成功 mysql> show databases;#节点一 +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | information_schema | | db1 | | db158 | | mysql | | performance_schema | | sys | +--------------------+ 6 rows in set (0.00 sec) #节点二 mysql> show databases; +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | information_schema | | db1 | | db158 | | mysql | | performance_schema | | sys | +--------------------+ 6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
冲突测试
#节点二 mysql> use db158; Database changed mysql> create table t1(id int); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) #节点一 mysql> create table t1(id int); ERROR 1046 (3D000): No database selected #节点三 mysql> create table t1(id int); ERROR 1046 (3D000): No database selected
3. playbook常用模块总结;一个简单的playbook完成安装httpd服务。
主机清单
[root@centos7 ~]# grep -v '^#' /etc/ansible/hosts [local] 10.0.0.156 ansible_connection=local [websrvs] 10.0.0.157 10.0.0.159 [dbsrvs] 10.0.0.159 10.0.0.158 [appsrvs] 10.0.0.156 10.0.0.157 10.0.0.158
Ansible模块:
shell模块:在远程主机执行命令,用shell执行命令,支持各种符号,比如:*,$, >
[root@centos7 ~]# ansible websrvs -m shell -a "echo $HOSTNAME" 10.0.0.157 | CHANGED | rc=0 >> centos7.linux.org 10.0.0.159 | CHANGED | rc=0 >> centos7.linux.org
Copy 模块:从ansible服务器主控端复制文件到远程主机。src=file 如果是没指明路径,则为当前目录或当前目录下的files目录下的file文件
ansible websrvs -m copy -a "src=/etc dest=/backup"
File 模块:设置文件属性,创建软链接等
ansible all -m file -a 'path=/data/test.txt state=touch' ansible all -m file -a 'path=/data/test.txt state=absent'
Yum 和 Apt 模块:yum 管理软件包,只支持RHEL,CentOS,fedora,不支持Ubuntu其它版本;apt 模块管理 Debian 相关版本的软件包
ansible websrvs -m yum -a 'name=httpd state=present' #安装 ansible websrvs -m yum -a 'name=nginx state=present enablerepo=epel' #启用epel源 进行安装 ansible websrvs -m yum -a 'name=* state=lastest exclude=kernel*,foo*' #升级除 kernel和foo开头以外的所有包
playbook完成安装httpd
[root@centos7 ~]# cat httpd.yml --- - hosts: websrvs remote_user: root gather_facts: no tasks: - name: install httpd yum: name=httpd state=present - name: copy html copy: src=/data/index.html /var/www/html/index.html - name: start httpd service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
4. httpd协议的工作过程。
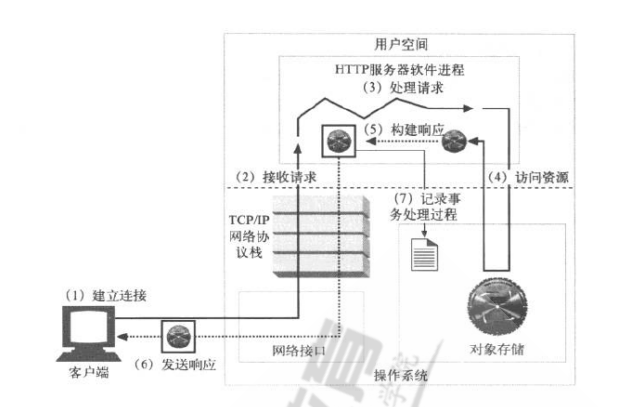
1、建立连接:接收或拒绝连接请求
2、接收请求:接收客户端请求报文中对某资源的一次请求的过程
3、处理请求:服务器对请求报文进行解析,并获取请求的资源及请求方法等相关信息,根据方法,资 源,首部和可选的主体部分对请求进行处理 常用请求Method: GET、POST、HEAD、PUT、DELETE、TRACE、OPTIONS
4、访问资源: 服务器获取请求报文中请求的资源web服务器,即存放了web资源的服务器,负责向请求者提供对方 请求的静态资源,或动态运行后生成的资源
5、构建响应报文: 一旦Web服务器识别除了资源,就执行请求方法中描述的动作,并返回响应报文。响应报文中 包含 有响应状态码、响应首部,如果生成了响应主体的话,还包括响应主体
1)响应实体:如果事务处理产生了响应主体,就将内容放在响应报文中回送过去。响应报文中通常包括:
描述了响应主体MIME类型的Content-Type首部
描述了响应主体长度的Content-Length
实际报文的主体内容
2)URL重定向:web服务构建的响应并非客户端请求的资源,而是资源另外一个访问路径
3)MIME类型: Web服务器要负责确定响应主体的MIME类型。多种配置服务器的方法可将MIME类型 与资源管理起来
魔法分类:Apache web服务器可以扫描每个资源的内容,并将其与一个已知模式表(被称为魔法文 件)进行匹配,以决定每个文件的MIME类型。这样做可能比较慢,但很方便,尤其是文件没有标准 扩展名时
显式分类:可以对Web服务器进行配置,使其不考虑文件的扩展名或内容,强制特定文件或目录内 容拥有某个MIME类型
类型协商: 有些Web服务器经过配置,可以以多种文档格式来存储资源。在这种情况下,可以配 置Web服务器,使其可以通过与用户的协商来决定使用哪种格式(及相关的MIME类型)"最好"
6、发送响应报文
Web服务器通过连接发送数据时也会面临与接收数据一样的问题。服务器可能有很多条到各个客户 端的连接,有些是空闲的,有些在向服务器发送数据,还有一些在向客户端回送响应数据。服务器要记 录连接的状态,还要特别注意对持久连接的处理。对非持久连接而言,服务器应该在发送了整条报文之 后,关闭自己这一端的连接。对持久连接来说,连接可能仍保持打开状态,在这种情况下,服务器要正 确地计算Content-Length首部,不然客户端就无法知道响应什么时候结束
7、记录日志 最后,当事务结束时,Web服务器会在日志文件中添加一个条目,来描述已执行的事务
5. 以apache/lamp架构,借助ansible实现自动化运维小案例。
ansible:10.0.0.156 ;
mysql:10.0.0.152;
apache、php:10.0.0.153
[root@ansible ~]# mkdir /data/ansible [root@ansible ~]# cd /data/ansible [root@ansible ansible]# vim hosts [root@ansible ansible]# cat /data/ansible/hosts [mysql] 10.0.0.152 [AP] 10.0.0.153 root@ansible ansible]# mkdir roles root@ansible ansible]# cp /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg ./ [root@ansible ansible]# vim ansible.cfg [root@ansible ansible]# grep -v '^#' ansible.cfg inventory = /data/ansible/hosts roles_path = /data/ansible/roles remote_user = root [root@ansible ansible]# ansible all -m ping -k SSH password: 10.0.0.152 | SUCCESS => { "ansible_facts": { "discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python" }, "changed": false, "ping": "pong" } 10.0.0.153 | SUCCESS => { "ansible_facts": { "discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python" }, "changed": false, "ping": "pong" }
[root@ansible ansible]# cd roles [root@ansible roles]# ansible-galaxy init apache - Role apache was created successfully [root@ansible roles]# ansible-galaxy init php - Role php was created successfully [root@ansible roles]# ansible-galaxy init mysql - Role mysql was created successfully #httpd [root@ansible roles]# cd apache [root@ansible apache]# vim files/httpd.conf [root@ansible apache]# cat files/httpd.conf DirectoryIndex index.php ProxyRequests Off ProxyPassMatch ^/(.*\.php)$ fcgi://10.0.0.153/data/html/$1 ProxyPassMatch ^/(fpm_status|ping) fcgi://10.0.0.153 [root@ansible apache]# cat tasks/main.yml --- # tasks file for apache - name: install yum: name=httpd state=present - name: copy config copy: src=httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf.d/ - name: start service service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes #php-fpm [root@ansible php]# cat files/www.conf user apache group apache pm.status_path = /fpm_status ping.path = /ping [root@ansible php]# vim tasks/main.yml [root@ansible php]# cat tasks/main.yml --- # tasks file for php - name: install php yum: name=php-fpm state=present - name: install php2 yum: name=php-json state=present - name: copy config copy: src=www.conf dest=/etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf - name: mkdir file: path=/var/www/html state=directory owner=apache group=apache - name: copy phpinfo copy: src=info.php dest=/data/html/info.php owner=apache group=apache - name: start service service: name=php-fpm state=started enabled=yes #mysql [root@ansible mysql]# vim tasks/main.yml [root@ansible mysql]# cat tasks/main.yml --- # tasks file for mysql - name: install mariadb yum: name=mariadb-server state=present - name: start mariadb service: name=mariadb state=started enabled=yes - name: change password shell: mysql -uroot -e " alter user root@'localhost' identified by '123456';"
[root@ansible ansible]# vim lamp.yml [root@ansible ansible]# cat lamp.yml - name: apache hosts: AP roles: - apache - name: php hosts: AP roles: - php - name: mysql hosts: mysql roles: - mysql



