C++-------Map
map简介
Map是STL的一个关联容器,它提供一对一(其中第一个可以称为关键字,每个关键字只能在map中出现一次,第二个可能称为该关键字的值)的数据处理能力,由于这个特性,它完成有可能在我们处理一对一数据的时候,在编程上提供快速通道。这里说下map内部数据的组织,map内部自建一颗红黑树(一 种非严格意义上的平衡二叉树),这颗树具有对数据自动排序的功能,所以在map内部所有的数据都是有序的,后边我们会见识到有序的好处。
map是一类关联式容器。它的特点是增加和删除节点对迭代器的影响很小,除了那个操作节点,对其他的节点都没有什么影响。对于迭代器来说,可以修改实值,而不能修改key。
map的特点(快速的查找、插入、删除)
1、自动建立Key - value的对应。key 和 value可以是任意你需要的类型。
2、根据key值快速查找记录,查找的复杂度基本是Log(N),如果有1000个记录,最多查找10次,1,000,000个记录,最多查找20次。
3、快速插入Key -Value 记录,快速删除记录。
4、根据Key 修改value记录。
5、遍历所有记录。
map的使用
include <map>
map<int,string> personnel
map->first和map->second
插入
// 插入单个键值对,并返回插入位置和成功标志,插入位置已经存在值时,插入失败 pair<iterator,bool> insert (const value_type& val); //在指定位置插入,在不同位置插入效率是不一样的,因为涉及到重排 iterator insert (const_iterator position, const value_type& val); // 插入多个 void insert (InputIterator first, InputIterator last); //c++11开始支持,使用列表插入多个
下面是具体代码
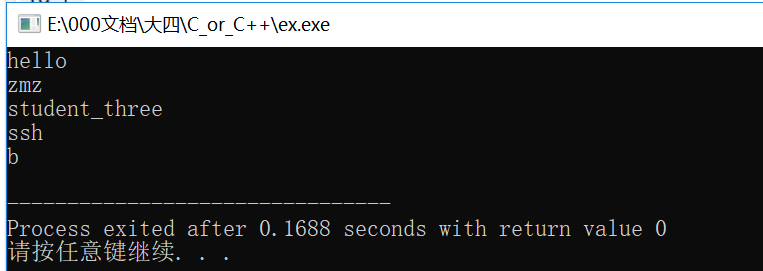
#include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<map> using namespace std; int main() { map<int,string> map_student; //构造函数 //1、用insert函数插入pair数据 map_student.insert(pair<int,string>(1,"hello")); //2、用insert函数插入value_type数据 map_student.insert(map<int, string>::value_type (3, "student_three")); //第三种:用数组方式插入数据 map<int,string> ans={{2,"zmz"},{4,"ssh"}}; map_student.insert(ans.begin(),ans.end()); //第四种方式,指定位子插入 map<int, string>::iterator it = map_student.begin(); map_student.insert(it, pair<int, string>(300,"b")); //效率更高 //取出 cout<<map_student.at(1)<<endl; cout<<map_student.at(2)<<endl; cout<<map_student.at(3)<<endl; cout<<map_student.at(4)<<endl; cout<<map_student.at(300)<<endl; return 0; }
结果
map_student.size()
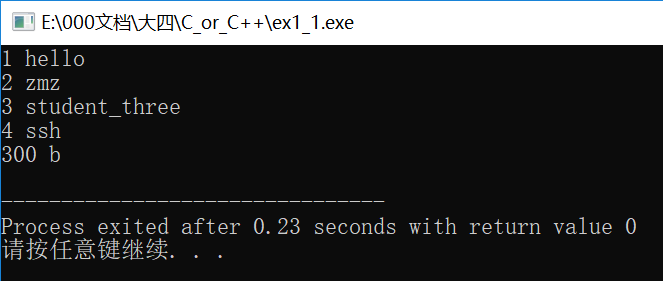
#include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<map> using namespace std; int main() { map<int,string> map_student; //构造函数 map_student.insert(pair<int,string>(1,"hello")); map_student.insert(map<int, string>::value_type (3, "student_three")); map<int,string> ans={{2,"zmz"},{4,"ssh"}}; map_student.insert(ans.begin(),ans.end()); map<int, string>::iterator it = map_student.begin(); map_student.insert(it, pair<int, string>(300,"b")); //效率更高 //第一种遍历方法 //遍历,注意iterator的定义,是map类型并且:: map<int,string>::iterator iter; for(iter=map_student.begin();iter!=map_student.end();iter++) cout<<iter->first<<" "<<iter->second<<endl; return 0; }
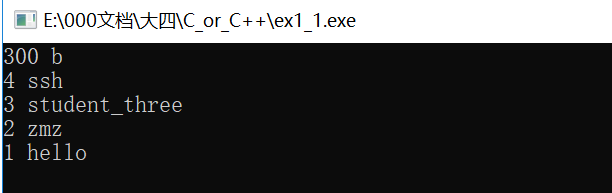
#include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<map> using namespace std; int main() { map<int,string> map_student; //构造函数 map_student.insert(pair<int,string>(1,"hello")); map_student.insert(map<int, string>::value_type (3, "student_three")); map<int,string> ans={{2,"zmz"},{4,"ssh"}}; map_student.insert(ans.begin(),ans.end()); map<int, string>::iterator it = map_student.begin(); map_student.insert(it, pair<int, string>(300,"b")); //效率更高 //第二种遍历方式,反向迭代器 (reverse_iterator,rbegin(),rend()) map<int,string>::reverse_iterator iter; for(iter=map_student.rbegin();iter!=map_student.rend();iter++) cout<<iter->first<<" "<<iter->second<<endl; return 0; }
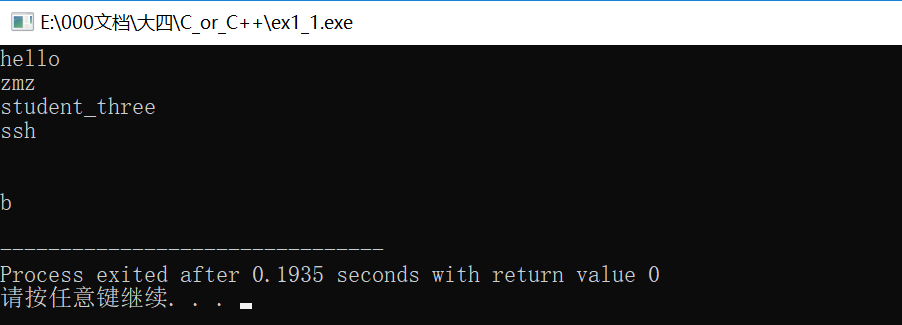
#include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<map> using namespace std; int main() { map<int,string> map_student; //构造函数 map_student.insert(pair<int,string>(1,"hello")); map_student.insert(map<int, string>::value_type (3, "student_three")); map<int,string> ans={{2,"zmz"},{4,"ssh"}}; map_student.insert(ans.begin(),ans.end()); map<int, string>::iterator it = map_student.begin(); map_student.insert(it, pair<int, string>(7,"b")); //效率更高 //第三种遍历方式,数组遍历,注意是从1开始,并且<=size() for(int i=1;i<=map_student.size();i++) cout<<map_student[i]<<endl; return 0; }
第一种:用count函数来判定关键字是否出现,其缺点是无法定位数据出现位置,由于map的特性,一对一的映射关系,就决定了count函数的返回值只有两个,要么是0,要么是1,出现的情况,当然是返回1了 。
第二种:用find函数来定位数据出现位置,它返回的一个迭代器,当数据出现时,它返回数据所在位置的迭代器,如果map中没有要查找的数据,它返回的迭代器等于end函数返回的迭代器。查找map中是否包含某个关键字条目用find()方法,传入的参数是要查找的key,在这里需要提到的是begin()和end()两个成员,
分别代表map对象中第一个条目和最后一个条目,这两个数据的类型是iterator.
补充:什么是迭代器
迭代器(iterator)是一种对象,它能够用来遍历标准模板库容器中的部分或全部元素,
#include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<map> using namespace std; int main() { map<int,string> map_student; //构造函数 map_student.insert(pair<int,string>(1,"hello")); map_student.insert(map<int, string>::value_type (3, "student_three")); map<int,string> ans={{2,"zmz"},{4,"ssh"}}; map_student.insert(ans.begin(),ans.end()); map<int, string>::iterator it = map_student.begin(); map_student.insert(it, pair<int, string>(7,"b")); //效率更高 //第一种数据查找count()函数 if(map_student.count(4)); cout<<"yes"<<endl; //第二种数据查找find()函数 map<int,string>::iterator iter; iter=map_student.find(3); if(iter!=map_student.end()) cout<<"yes "<<iter->first<<" "<<iter->second<<endl; return 0; }

/* 移除某个map中某个条目用erase() 该成员方法的定义如下: iterator erase(iterator it);//通过一个条目对象删除 iterator erase(iterator first,iterator last)//删除一个范围 size_type erase(const Key&key);//通过关键字删除 clear()就相当于enumMap.erase(enumMap.begin(),enumMap.end()); */ map<int,string>::iterator iter=map_student.find(2); map_student.erase(iter); map_student.erase(2); map_student.clear(); map_student.erase(map_student.begin(),map_student.end());
map中的swap不是一个容器中的元素交换,而是两个容器所有元素的交换。
排序 · map中的sort问题
map中的元素是自动按Key升序排序,所以不能对map用sort函数;



