集合框架(一)
集合框架
Collection体系集合:
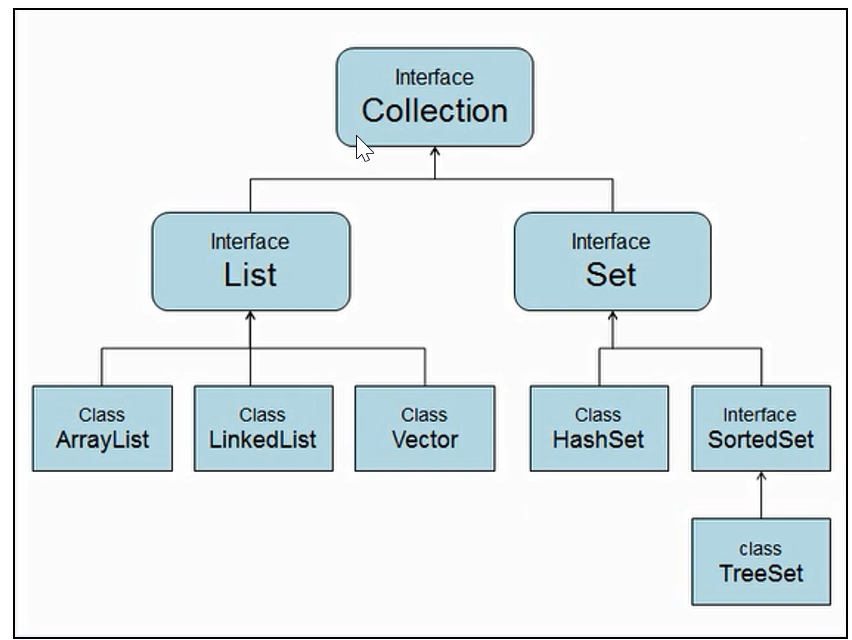
)
(一)对象的容器,实现了对对象常用的操作,类似数组的功能。
(二)集合和数组的区别:
- 数组长度固定,集合长度不固定
- 数组可以存储基本类型和引用类型,集合只能存储引用类型(装箱)
(三)位置:java.util.*;
1.Collection父接口
- 特点:代表一组任意类型的对象,无序、无下标、不能重复。
- 方法:
- boolean add(Object obj):添加一个对象。
- boolean addAll(Collection c):将一个集合中的所有对象添加到此集合中
- void clear():清除此集合中的所有对象
- boolean contains(Object o):检查此集合中是否包含o对象
- boolean equals(Object o):比较此集合是否与指定对象相等
- boolean isEmpty():判断此集合是否为空
- boolean remove(Object o):在此集合中移除o对象
- int size():返回此集合中的元素个数。
- Object[] toArray():将此集合转成数组。
注意迭代器(Iterator)的使用
package com.collection.demo01;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
/*
Collection 接口的使用
1.添加元素
2.删除元素
3.遍历元素
4.判断
*/
public class demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
//1.添加元素
collection.add("苹果");
collection.add("西瓜");
collection.add("榴莲");
System.out.println("元素个数:"+collection.size());
System.out.println(collection.toString());
//2.删除元素
//collection.remove("榴莲");
//collection.clear();
//System.out.println(collection.size());
//3.遍历元素[重点]
//3.1.使用增强for
System.out.println("=======================");
for (Object object : collection) {
System.out.println(object);
}
System.out.println("=======================");
//3.2.使用迭代器(迭代器专门用来遍历集合的一种方式)
//hasNext();有没有下一个元素
//next();获取下一个元素
//remove();删除当前元素
Iterator iterator = collection.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
String s = (String)iterator.next();
System.out.println(s);
//不能使用collection删除方法
//collection.remove(s);//ConcurrentModificationException 并发修改异常
//iterator.remove();
}
System.out.println("元素个数:"+collection.size());
System.out.println("=======================");
//4.判断
System.out.println(collection.contains("西瓜"));
System.out.println(collection.isEmpty());
}
}
例二:
package com.collection.demo01;
/*
学生类
*/
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
package com.collection.demo02;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/*
List的使用
*/
public class demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
List list = new ArrayList();
//1.添加数字数据(自动装箱)
list.add(20);
list.add(30);
list.add(40);
list.add(50);
list.add(60);
System.out.println("元素个数:"+list.size());
System.out.println(list.toString());
//2.删除操作
//list.remove(0);
//list.remove((Object)20);
list.remove(new Integer(20));
System.out.println("删除元素:"+list.size());
System.out.println(list.toString());
//3.补充方法subList:返回子集合,含头不含尾
List subList = list.subList(1,3);
System.out.println(subList.toString());
}
}
2.List集合(List子接口)
- 特点:有序、有下标、元素可以重复。
- 方法:
- void add(int index,Object o):在index位置插入对象o
- boolean addAll(int index,Collection c):将一个集合中的元素添加到此集合中的index位置。
- Object get(int index):返回集合中指定位置的元素
- List subList(int fromIndex,int toIndex):返回formIndex和toIndex之间的集合元素
List接口的使用:
package com.collection.demo02;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ListIterator;
/*
List子接口的使用
特点:有序、有下标、元素可以重复
*/
public class demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//先创建集合对象
List list = new ArrayList<>();
//1.添加元素
list.add("苹果");
list.add("小米");
list.add(0,"华为");
System.out.println("元素个数"+list.size());
System.out.println(list.toString());
//2.删除元素
//list.remove("苹果");
//list.remove(0);
//list.clear();
//System.out.println("删除之后"+list.size());
//System.out.println(list.toString());
System.out.println("===================");
//3.遍历
//3.1.使用for来遍历
for(int i = 0;i<list.size();i++){
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
System.out.println("===================");
//3.2.使用增强for
for (Object object : list) {
System.out.println(object);
}
System.out.println("===================");
//3.3.迭代器
Iterator it = list.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
//3.4.列表迭代器,和Iterator的区别,ListIterator可以向前或向后遍历,添加、删除、修改元素
ListIterator lit = list.listIterator();
System.out.println("========从前往后===========");
while(lit.hasNext()){
System.out.println(lit.nextIndex()+":"+lit.next());
}
System.out.println("========从后往前===========");
while(lit.hasPrevious()){
System.out.println(lit.previousIndex()+":"+lit.previous());
}
System.out.println("===================");
//4.判断
System.out.println(list.contains("苹果"));
System.out.println(list.isEmpty());
System.out.println("===================");
//5.获取位置
System.out.println(list.indexOf("华为"));
}
}
List接口的使用2:
package com.collection.demo02;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/*
List的使用
*/
public class demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
List list = new ArrayList();
//1.添加数字数据(自动装箱)
list.add(20);
list.add(30);
list.add(40);
list.add(50);
list.add(60);
System.out.println("元素个数:"+list.size());
System.out.println(list.toString());
//2.删除操作
//list.remove(0);
list.remove(new Integer(20));
System.out.println("删除元素:"+list.size());
System.out.println(list.toString());
//3.补充方法subList:返回子集合,含头不含尾
List subList = list.subList(1,3);
System.out.println(subList.toString());
}
}
1.List实现类
- ArrayList【重点】:
- 数组结构实现,查询块、增删慢;
- JDK1.2版本,运行效率块、线程不安全。
- Vector:
- 数组结构实现,查询块、增删慢;
- JDK1.0版本,运行效率慢、线程安全
- LinkedList:(双向链表)
- 链表结构实现,增删块,查询慢。
2.ArrayList的使用
package com.collection.demo02;
import com.collection.demo01.Student;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.ListIterator;
public class demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
Student s1 = new Student("刘德华", 20);
Student s2 = new Student("郭富城", 22);
Student s3 = new Student("梁朝伟", 24);
//添加元素
arrayList.add(s1);
arrayList.add(s2);
arrayList.add(s3);
System.out.println(arrayList.size());//个数
System.out.println(arrayList.toString());
//删除
System.out.println("==================");
arrayList.remove(s1);
//arrayList.remove(new Student("刘德华", 20));//要在Student重写equals
System.out.println(arrayList.size());
//遍历元素【重点】
System.out.println("==================");
//3.1使用迭代器
Iterator it = arrayList.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
Student s = (Student) it.next();
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
System.out.println("==================");
//3.2.列表迭代器
ListIterator lit = arrayList.listIterator();
while(lit.hasNext()) {
Student s = (Student) lit.next();
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
//3.3逆序
System.out.println("==================");
while(lit.hasPrevious()){
Student s = (Student) lit.previous();
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
//4.判断
System.out.println(arrayList.contains(s2));
System.out.println(arrayList.isEmpty());
//5.查找
System.out.println(arrayList.indexOf(s2));
}
}
ArrayList的源码分析:
DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; 默认容量
注意:如果没有向集合中添加任何元素时,容量为0。添加一个元素之后容量为10,每次扩容大小是原来的1.5倍
elementData 存放元素的数组
size 实际的元素个数
add() 添加元素
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
3.Vector的使用
其中创建、添加、删除、遍历、判断都和List一样
其中遍历可以使用枚举器:
package com.collection.demo03;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Vector;
/*
Vector集合的使用
*/
public class demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vector vector = new Vector();
vector.add("草莓");
vector.add("芒果");
vector.add("西瓜");
//遍历
//使用枚举器
Enumeration en = vector.elements();
while (en.hasMoreElements()){
String o =(String)en.nextElement();
System.out.println(o);
}
//其它方法
//firstElement、lastElement、elementAt
}
}
4.LinkedList的使用
创建、添加、删除、遍历、判断都和List一样
LinkedList的源码分析:
int size 集合大小
Node first 链表的头结点
Node last 链表的尾结点
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node<E> f = first;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
first = newNode;
if (f == null)
last = newNode;
else
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
ArrayList:必须开辟一个连续的空间
LinkedList:无需开辟连续的空间
3.泛型
- Java泛型是JDK1.5中引入的一个新特性,其本质是参数化类型,把类型作为参数传递。
- 常见形式有泛型类、泛型接口、泛型方法
- 语法:
- <T,...> T称为类型占位符,表示一种引用类型
- 好处:
- 提高代码的重用性
- 防止类型转换异常,提高代码的安全性
泛型类的使用
package com.generic.demo01;
/*
泛型类
语法:类名<T>
T是类型占位符,表示一种引用类型如果是编写多个使用逗号隔开
*/
public class demo01<T> {
//使用泛型 T
//1.创建变量
T t;
//2.泛型作为方法的参数
public void show(T t){
System.out.println(t);
}
//3.泛型作为方法的返回值
public T getT(){
return t;
}
}
//使用泛型类创建对象
//注意:1.泛型只能是使用引用类型,2.不同泛型类型对象之间不能相互赋值
demo01<String> myGeneric = new demo01<String>();
myGeneric.t = "hello";
myGeneric.show("大家好,加油");
String string = myGeneric.getT();
System.out.println(string);
demo01<Integer> myGeneric2 = new demo01<>();
myGeneric2.t = 100;
myGeneric2.show(200);
Integer integer = myGeneric2.getT();
System.out.println(integer);
泛型接口的使用
package com.generic.demo01;
/*
泛型接口
语法:接口名<T>
注意:不能建立泛型静态常量
*/
public interface MyInterface<T> {
String name = "张三";
T server(T t);
}
已经确定了类型
package com.generic.demo01;
public class MyInterfaceImpl implements MyInterface<String> {
@Override
public String server(String t) {
System.out.println(t);
return t;
}
}
不确定类型
package com.generic.demo01;
public class MyInterfaceImpl2<T> implements MyInterface<T> {
@Override
public T server(T t) {
System.out.println(t);
return t;
}
}
MyInterfaceImpl impl = new MyInterfaceImpl();
impl.server("xxxxx");
MyInterfaceImpl2<Integer> impl2 = new MyInterfaceImpl2<>();
impl2.server(1000);
泛型方法的使用
package com.generic.demo01;
/*
泛型方法
语法:<T> 返回值类型
*/
public class MyGenericMethod {
//泛型方法
public <T> T show(T t){
System.out.println("泛型方法"+t);
return t;
}
}
类型会由输入的内容自动转换类型
//泛型方法
MyGenericMethod myGenericMethod = new MyGenericMethod();
myGenericMethod.show("中国");
myGenericMethod.show(1000);
myGenericMethod.show(3.14);
泛型集合
- 概念:参数化类型、类型安全的集合,强制集合元素的类型必须一致。
- 特点:
- 编译时即可检查,而非运行时抛出异常
- 访问时,不必类型转换(拆箱)
- 不同泛型之间引用不能相互赋值,泛型不存在多态
package com.generic.demo01;
import com.collection.demo03.Student;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<String>();
arrayList.add("xxx");
arrayList.add("yyy");
for (String string : arrayList) {
System.out.println(string);
}
ArrayList<Student> arrayList2 = new ArrayList<>();
Student s1 = new Student("刘德华",20);
Student s2 = new Student("郭富城",22);
Student s3 = new Student("梁朝伟",24);
arrayList2.add(s1);
arrayList2.add(s2);
arrayList2.add(s3);
Iterator<Student> it = arrayList2.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Student s = it.next();
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
}
}





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· AI编程工具终极对决:字节Trae VS Cursor,谁才是开发者新宠?
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!