Oracle 多表 连接 顺序 与 性能关系 测试
一. 创建表并insert 数据
create table ta (id number,name varchar2(10));
create table tb(id number,job varchar2(10));
begin
for i in 1..1000000 loop
begin
insert into ta values(i,'dave');
commit;
end;
end loop;
end;
begin
for i in 1..1000000 loop
begin
if i<10 then
insert into tb values(i,'boy');
elsif i<20 and i>10 then
insert into tb values(i,'girl');
commit;
end if;
end;
end loop;
end;
二.在没有索引的情况关联ta 和 tb 查询
相关链接:
Oracle Optimizer CBO RBO
http://blog.csdn.net/tianlesoftware/archive/2010/08/19/5824886.aspx
多表连接的三种方式详解 HASH JOIN MERGE JOIN NESTED LOOP
http://blog.csdn.net/tianlesoftware/archive/2010/08/21/5826546.aspx
Oracle Hint
http://blog.csdn.net/tianlesoftware/archive/2010/08/23/5833020.aspx
2.1 optimizer选择 CBO(10g 默认)
--ta 在前
select ta.id, ta.name,tb.job from ta,tb where ta.id=tb.id;

--tb 在前
select ta.id, ta.name,tb.job from tb,ta where ta.id=tb.id;
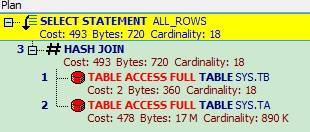
总结:
两条SQL 执行计划是一样的, ta和tb 的顺序没有影响。
因为ta和tb 的记录相差较大,ta是100万,tb 只有20条。 所以这里CBO 选择使用Hash Join。
CBO 选择2个表中记录较小的表tb,将其数据放入内存,对Join key构造hash 表,然后去扫描大表ta。 找出与散列表匹配的行。
2.2 对ta和tb 的ID 建b-tree 索引后在查看
--建索引
create index idx_ta_id on ta(id);
create index idx_tb_id on tb(id);
--tb 在前
select ta.id, ta.name,tb.job from tb,ta where ta.id=tb.id;

--ta 在前
select ta.id, ta.name,tb.job from ta,tb where ta.id=tb.id;
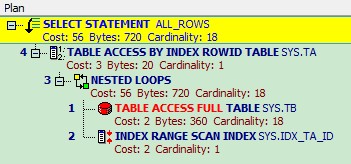
总结:
执行计划还是一样,不同的是表之间的关联模式发生的改变,从Hash Join 变成了Nested Loops。
Nested loop一般用在连接的表中有索引,并且索引选择性较好的时候. 在我们这个示例中,CBO 选择把返回结果集较小的表tb 作为outer table,CBO 下,默认把outer table 作为驱动表,然后用outer table 的每一行与inner table(我们这里是ta)进行Join,去匹配结果集。 由此可见,在tb(inner table) 有索引的情况,这种匹配就非常快。
这种情况下整个SQL的cost:
cost = outer access cost + (inner access cost * outer cardinality)
从某种角度上看,可以把Nested loop 看成2层for 循环。
2.3 使用RBO 查看
在10g里,optimizer 默认已经使用CBO了,如果我们想使用RBO, 只能通过Hint 来实现。
-- ta 在前
select /*+rule*/ta.id, ta.name,tb.job from ta,tb where ta.id=tb.id;
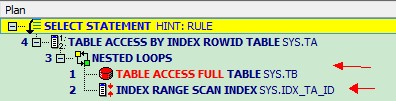
SYS@anqing2(rac2)> select /*+rule*/ta.id, ta.name,tb.job from ta,tb where ta.id<100 and ta.id=tb.id;
Elapsed: 00:00:00.00
-- 注意这个SQL里,我们加了ta.id<100 的条件
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 3943212106
---------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name |
---------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | |
| 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID | TB |
| 2 | NESTED LOOPS | |
| 3 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| TA |
|* 4 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | IDX_TA_ID |
|* 5 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | IDX_TB_ID |
---------------------------------------------------
-- 当我们加上条件之后,就先走ta了,而不是tb。 因为先走ta,用ta的限制条件过滤掉一部分结果,这样剩下的匹配工作就会减少。
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
4 - access("TA"."ID"<100)
5 - access("TA"."ID"="TB"."ID")
Note
-----
- rule based optimizer used (consider using cbo)
--tb 在前
select /*+rule*/ta.id, ta.name,tb.job from tb,ta where ta.id=tb.id;

总结:
这2个就区别很明显。 因为Oracle对sql的解析是从后向前的。 那么当先遇到tb时,那么会对tb进行全表扫描,然后用这个结果匹配ta。因为ta有索引,所以通过索引去匹配。
如果先遇到ta,那么就会对ta进行全表扫描。 因为2个表的差距很大,所以全表扫描的成本也就很大。
所以在RBO 下,大表在前,小表在后。这样就会先遇到小表,后遇到大表。 如果有指定限定的where 条件,会先走限定条件的表。
2.4 drop 索引之后,在走RBO
drop index idx_ta_id;
drop index idx_tb_id;
--ta 在前
select /*+rule*/ta.id, ta.name,tb.job from ta,tb where ta.id=tb.id;

--tb 在前
select /*+rule*/ta.id, ta.name,tb.job from tb,ta where ta.id=tb.id;

总结:
这里选择了Sort Merge Join 来连接2张表。Sort Merge join 用在没有索引,并且数据已经排序的情况.
我们表中的记录是按照顺序插叙的,所以符合这个条件。 SQL 的解析还是按照从后往前,所以这里ta和tb 在前先扫描的顺序不一样,不过都是全表扫描。 效率都不高。
2.5 引深一个问题:使用 字段名 代替 *
* 能方便很多,但在ORACLE解析的过程中, 会通过查询数据字典,会将’*’ 依次转换成所有的列名,这就需要耗费更多的时间. 从而降低了效率。
SYS@anqing2(rac2)> set timing on
SYS@anqing2(rac2)> select * from ta where rownum=1;
ID NAME
---------- ----------
1 dave
Elapsed: 00:00:00.03
SYS@anqing2(rac2)> desc ta
Name Null? Type
----------------------------------------- -------- ----------------------------
ID NUMBER
NAME VARCHAR2(10)
SYS@anqing2(rac2)> select id,name from ta where rownum=1;
ID NAME
---------- ----------
1 dave
Elapsed: 00:00:00.02
时间已经缩短。 但不明显,用Toad 来查看一下:
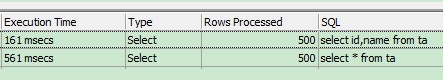
写全字段,执行时间是161 毫秒,用* 是561毫秒。 差距很明显。
查看一下他们的执行计划:
SYS@anqing2(rac2)> select * from ta where rownum=1;
Elapsed: 00:00:00.00
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 761731071
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
| id | operation | name | rows | bytes | cost (%cpu)| time |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | select statement | | 1 | 20 | 7 (72)| 00:00:01 |
|* 1 | count stopkey | | | | | |
| 2 | table access full| ta | 890k| 16m| 7 (72)| 00:00:01 |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
1 - filter(ROWNUM=1)
Note
-----
- dynamic sampling used for this statement
SYS@anqing2(rac2)> select id,name from ta where rownum=1;
Elapsed: 00:00:00.00
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 761731071
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
| id | operation | name | rows | bytes | cost (%cpu)| time |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | select statement | | 1 | 20 | 7 (72)| 00:00:01 |
|* 1 | count stopkey | | | | | |
| 2 | table access full| ta | 890k| 16m| 7 (72)| 00:00:01 |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
1 - filter(ROWNUM=1)
Note
-----
- dynamic sampling used for this statement
注意:
使用 * 和 写全字段名,他们的执行计划是一样的,但是执行时间不一样。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Blog: http://blog.csdn.net/tianlesoftware
Email: dvd.dba@gmail.com
DBA1 群:62697716(满); DBA2 群:62697977(满) DBA3 群:62697850(满)
DBA 超级群:63306533(满); DBA4 群: 83829929 DBA5群: 142216823
DBA6 群:158654907 聊天 群:40132017 聊天2群:69087192
--加群需要在备注说明Oracle表空间和数据文件的关系,否则拒绝申请




