437. Path Sum III(路径可以任意点开始,任意点结束 or. 前缀和)
You are given a binary tree in which each node contains an integer value.
Find the number of paths that sum to a given value.
The path does not need to start or end at the root or a leaf, but it must go downwards (traveling only from parent nodes to child nodes).
The tree has no more than 1,000 nodes and the values are in the range -1,000,000 to 1,000,000.
Example:
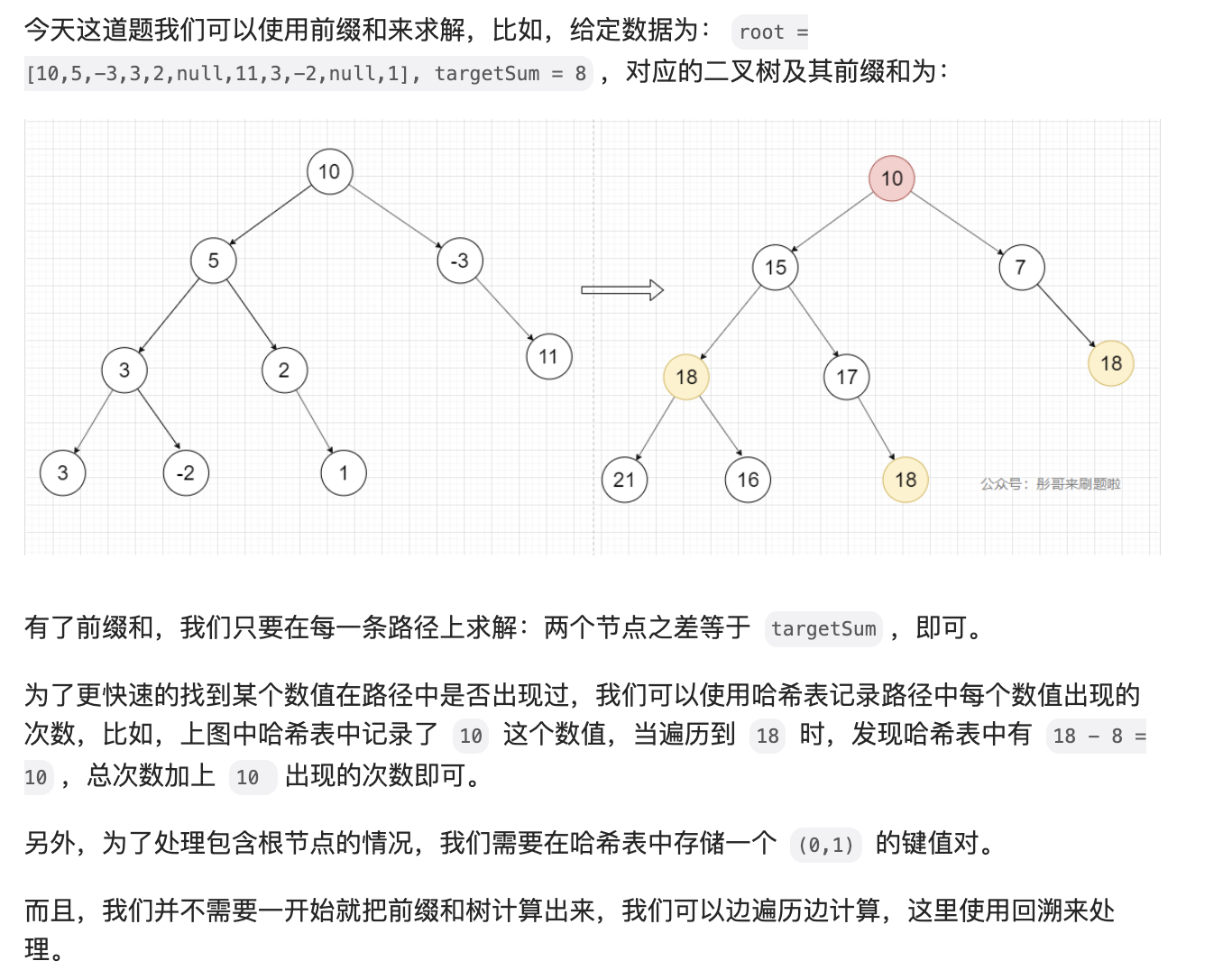
root = [10,5,-3,3,2,null,11,3,-2,null,1], sum = 8
10
/ \
5 -3
/ \ \
3 2 11
/ \ \
3 -2 1
Return 3. The paths that sum to 8 are:
1. 5 -> 3
2. 5 -> 2 -> 1
3. -3 -> 11

# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def pathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> int: def dfs(root,cur_sum): if root == None: return 0 cnt = 0 if cur_sum+root.val == targetSum: cnt = 1 l = dfs(root.left,cur_sum+root.val) r = dfs(root.right,cur_sum+root.val) return l + r + cnt if root == None: return 0 a = dfs(root,0) b = self.pathSum(root.left,targetSum) c = self.pathSum(root.right,targetSum) return a+b+c
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: long cnt = 0; void path_test(TreeNode* root, long targetSum) { if (root == nullptr) return; if (targetSum == root->val){ cnt++; } path_test(root->left,targetSum-root->val); path_test(root->right,targetSum-root->val); } void dfs(TreeNode* root,long targetSum) { if (root == nullptr) return ; path_test(root,targetSum); dfs(root->left,targetSum); dfs(root->right,targetSum); } int pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) { dfs(root,targetSum); return cnt; } };
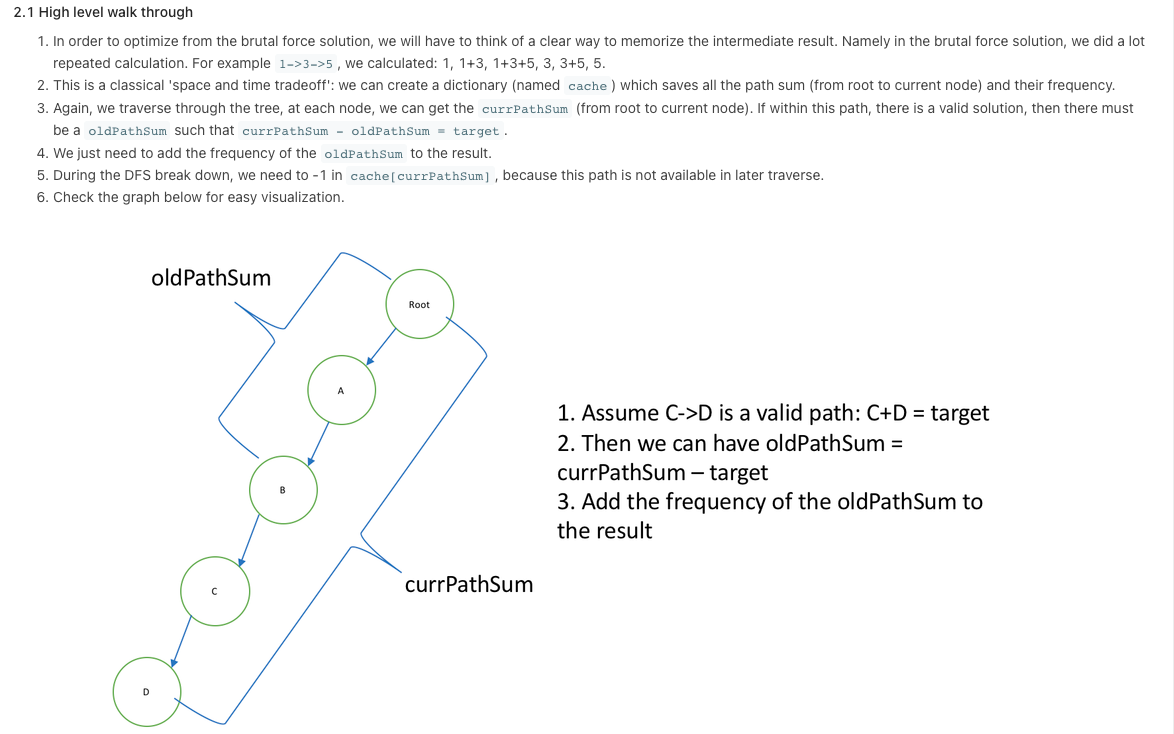
https://leetcode.com/problems/path-sum-iii/discuss/141424/Python-step-by-step-walk-through.-Easy-to-understand.-Two-solutions-comparison.-%3A-)
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def __init__(self): self.res = 0 self.tmap = {} def pathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> int: def dfs(root,cursum,target): if root == None: return cursum += root.val sum2 = cursum - target self.res += self.tmap.get(sum2,0) self.tmap[cursum] = self.tmap.get(cursum,0) + 1 dfs(root.left,cursum,target) dfs(root.right,cursum,target) self.tmap[cursum]-=1 self.tmap[0] = 1 dfs(root,0,targetSum) return self.res
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: long cnt = 0; unordered_map<long,int> map_cnt; //哈希表,快速找到满足以 cur 为「路径结尾」的、使得路径总和为 targetSum 的目标「路径起点」有多少个 void dfs(TreeNode* root,long targetSum, long root_cur_sum) { if (root == nullptr) return ; root_cur_sum += root->val; long old_sum = root_cur_sum - targetSum; cnt += map_cnt[old_sum]; map_cnt[root_cur_sum]++; dfs(root->left,targetSum,root_cur_sum); dfs(root->right,targetSum,root_cur_sum); map_cnt[root_cur_sum]--; } int pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) { map_cnt[0] = 1; dfs(root,targetSum,0); return cnt; } };
1 class Solution { 2 3 public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) { 4 if(root==null) return 0; 5 int res = path(root,sum)+pathSum(root.right,sum)+pathSum(root.left,sum); 6 return res; 7 8 } 9 10 private int path(TreeNode root, int sum) { 11 int res=0; 12 if(root==null) 13 return res ; 14 if(sum==root.val) 15 res+=1; 16 res+=path(root.left,sum-root.val); 17 res+=path(root.right,sum-root.val); 18 return res; 19 } 20 21 }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号