24. Swap Nodes in Pairs
Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head.
For example,
Given 1->2->3->4, you should return the list as 2->1->4->3.
Your algorithm should use only constant space. You may not modify the values in the list, only nodes itself can be changed.
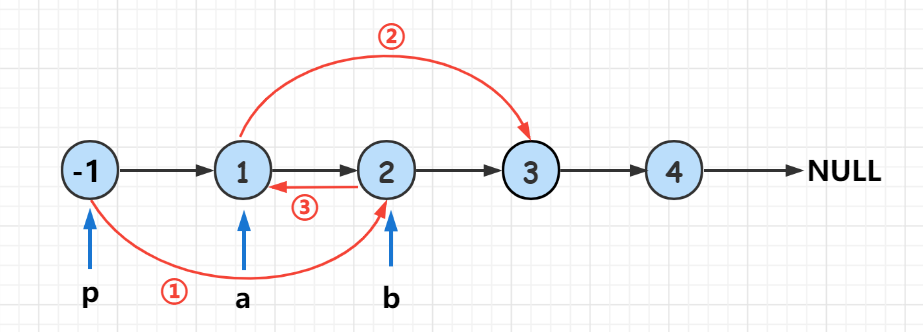
# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None): # self.val = val # self.next = next class Solution: def swapPairs(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]: def reverse(head,end): pre = None cur = head while cur != end: nxt = cur.next cur.next = pre pre = cur cur = nxt return pre if head == None: return end = head for i in range(2): if end == None: return head end = end.next new = reverse(head,end) head.next = self.swapPairs(end) return new
# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None): # self.val = val # self.next = next class Solution: def swapPairs(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]: def reverse(a,b): if a==b: return a pre = None cur = a while cur != b: nn = cur.next cur.next = pre pre = cur cur = nn #print(pre) return pre if head == None or head.next == None: return head h1 = head h2 = head.next h3 = head.next.next last = reverse(h1,h2.next) h1.next = self.swapPairs(h3) return last
class Solution { public: ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) { ListNode* fakehead = new ListNode(0); fakehead->next = head; ListNode* pos = fakehead; while(pos->next!=nullptr && pos->next->next != nullptr) { ListNode* a = pos->next; ListNode* b = a->next; a->next = b->next; b->next = a; pos->next = b; pos = a; } return fakehead->next; } };
1 class Solution { 2 public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) { 3 ListNode fakehead = new ListNode(0); 4 fakehead.next = head; 5 ListNode pre = fakehead; 6 ListNode cur = head; 7 while(cur !=null && cur.next != null){ 8 ListNode next = cur.next; 9 pre.next = next; 10 cur.next = next.next; 11 next.next = cur; 12 pre = cur; 13 cur = pre.next; 14 } 15 return fakehead.next; 16 } 17 }



