25. Reverse Nodes in k-Group(K 个一组,反转链表)
Given a linked list, reverse the nodes of a linked list k at a time and return its modified list.
k is a positive integer and is less than or equal to the length of the linked list. If the number of nodes is not a multiple of k then left-out nodes, in the end, should remain as it is.
You may not alter the values in the list's nodes, only nodes themselves may be changed.
Example 1:
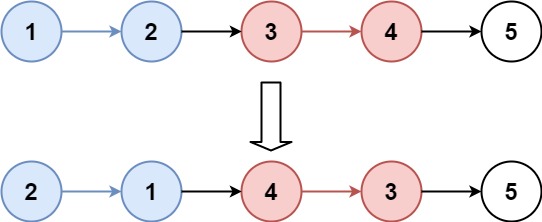
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 Output: [2,1,4,3,5]
Example 2:
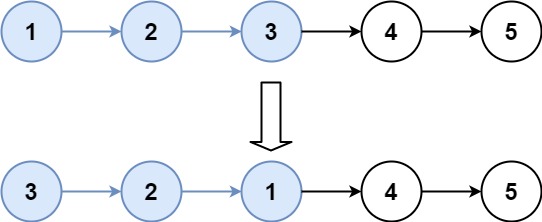
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3 Output: [3,2,1,4,5]
Example 3:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 1 Output: [1,2,3,4,5]
Example 4:
Input: head = [1], k = 1 Output: [1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
sz. 1 <= sz <= 50000 <= Node.val <= 10001 <= k <= sz
Follow-up: Can you solve the problem in O(1) extra memory space?
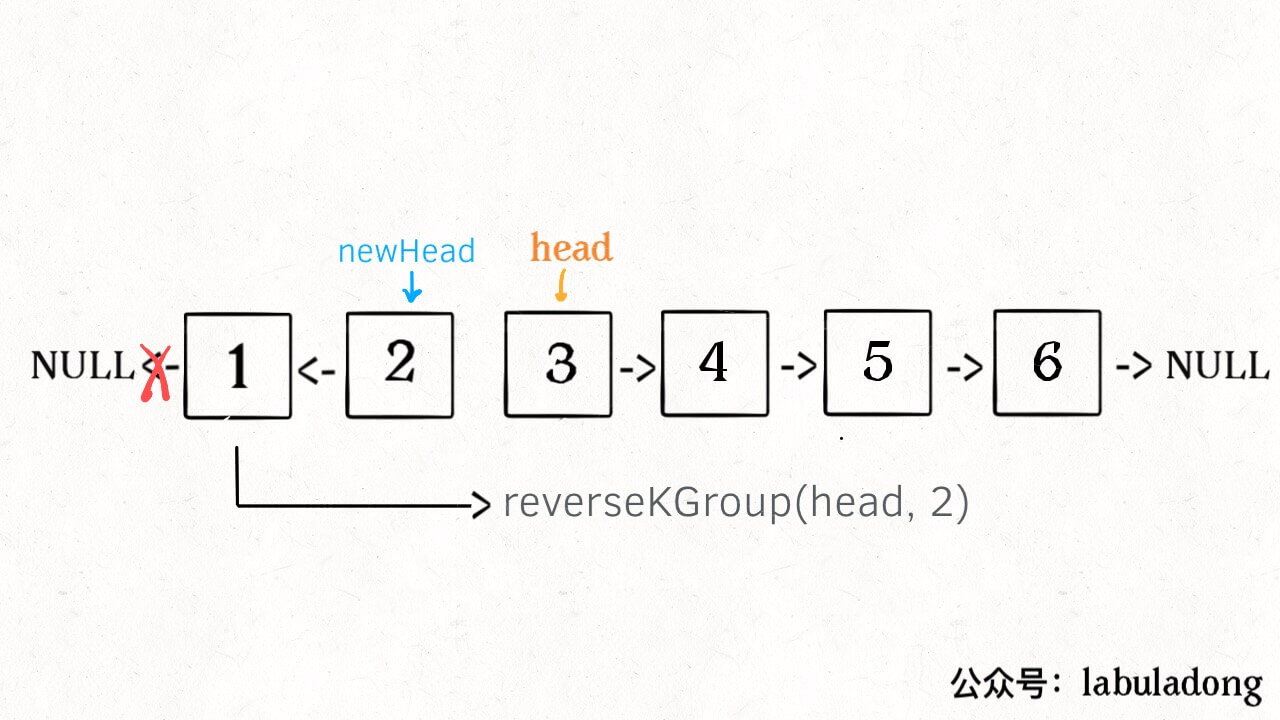
# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None): # self.val = val # self.next = next class Solution: def reverseKGroup(self, head: Optional[ListNode], k: int) -> Optional[ListNode]: def reverse(head,end): pre = None cur = head while cur != end: nxt = cur.next cur.next = pre pre = cur cur = nxt return pre if head == None: return end = head for i in range(k): if end == None: return head end = end.next new = reverse(head,end) head.next = self.reverseKGroup(end,k) return new
1 /** 2 * Definition for singly-linked list. 3 * struct ListNode { 4 * int val; 5 * ListNode *next; 6 * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {} 7 * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} 8 * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {} 9 * }; 10 */ 11 class Solution { 12 public: 13 ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head,ListNode* end) { 14 //[head,end) 15 if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return head; 16 ListNode* pre = nullptr; 17 ListNode* cur = head; 18 while(cur != end) { 19 ListNode* c_next = cur->next; 20 cur->next = pre; 21 pre = cur; 22 cur = c_next; 23 } 24 return pre; 25 } 26 ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) { 27 if (head == nullptr) return nullptr; 28 ListNode* end = head; 29 for(int i = 1; i <= k;i++) { 30 if (end == nullptr) return head; 31 end = end->next; 32 } 33 ListNode* newhead = reverseList(head,end); 34 head->next = reverseKGroup(end,k); 35 return newhead; 36 } 37 };

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) { 4 if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return head; 5 ListNode* pre = nullptr; 6 ListNode* cur = head; 7 while(cur != nullptr) { 8 ListNode* c_next = cur->next; 9 cur->next = pre; 10 pre = cur; 11 cur = c_next; 12 } 13 return pre; 14 } 15 ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) { 16 ListNode* fakehead = new ListNode(-1); 17 fakehead->next = head; 18 ListNode* pre =fakehead; 19 ListNode* cur = head; 20 while(cur != nullptr) { 21 for(int i = 1;i < k && cur != nullptr ;++i) { 22 cur = cur->next; 23 } 24 if(cur==nullptr) break; 25 26 ListNode* start = pre->next; 27 ListNode* c_next = cur->next; 28 29 cur->next = nullptr; 30 pre->next = reverseList(start); 31 start->next = c_next; 32 pre = start; 33 cur = pre->next; 34 } 35 return fakehead->next; 36 } 37 };



