通过前面两篇文章, 我们已经解决了在手写笔迹中的平滑问题. 本篇将讲解如何让手写笔迹能够有笔锋效果.
想要让笔迹能够有笔锋的效果, 那么整个笔迹肯定不可能是等宽的.也就是说, 要让我们绘制出来的笔迹线条必须要有一定的粗细变化.
所有人都能够很自然的想到 粗细变化的原理: 运动快的地方肯定线条应该更细, 运动慢的的地方细条应该更粗.是的, 这是最基本的原理, 这个想法完全正确.
说点题外话, 最近在看机器学习, 神经网络模型里面有一个叫:激活函数的东西, 它的作用就是为了让神经网络具有分层的非线性映射学习的能力,
如果完全是线性的, 在处理某些复杂情况时,得到的结果会很糟糕.
同样, 我们在处理手写笔迹的时候, 线条的粗细也不应该完全和速度是一种线性的变化关系,.
事实上, 如果完全按照一种线性的变化关系, 绘制出来的线条会看起来非常奇怪(亲测完全如此).
所以, 在计算线条粗细的时候, 在遵循"速度越快的地方,线条更细; 速度慢的地方,线条更粗" 这一条基本准则的前提下,
也应该根据一些具体情况, 让线条的粗细变化具有"非线性"的能力.
下面我基于手写的实际情况,提出一些问题, 大家可以稍微思考一下:
1) 假设我们的计算线条笔宽的函数就是: W_current = k * s, 其中s为当前线段笔迹点移动的速度, k为将速度映射为笔宽的一个固定系数.
用户移动时, 得到了3个相邻的点依次分别为:a,b,c, 在ab线段, 移动速度接近无限大, 而在bc段移动的速度无限接近0,
事实上, 在手写笔迹的时候,完全有可能 前一段移动速度非常快, 到下一段距离的时候, 移动速度就立刻变得非常慢了.
我只是把可能遇到的情况进行了夸张, 那么, 在这种情况下,我们应该如何处理线条的粗细呢?
2) 同样假设3个点, 两条线段ab, bc, cd, 并且假设ab, bc有足够的长度, 使得我们计算出来的宽度变化看起来也是比较合理的, 这样说可能不太容易理解.
举个栗子: ab, bc的线段长度都为100个像素, 计算出ab线段线条的宽度应该是5, bc线段的线条宽度该是10,
从真实手写的情况来看, 200个像素长度的笔迹, 只有5个像素的宽度变化,这是完全合理的.
那么,如果我们用宽度5来绘制线段ab, 然后用宽度10来绘制线段bc, 我们绘制出来的笔迹是什么样子的? (发挥一下想象力)
3) 在真实手写的情况下, 文字的笔迹的笔锋主要体现在文字的哪些部位?
下面我们分别讨论这3个问题.
问题一:
如果完全按照线性函数W_current = k * s 来计算宽度, 相邻两端线条的笔宽变化有可能非常大, 大到超出了我们可以的接受范围.
所以我们考虑通过某种方式来限制这种突然的变化, 让线条宽度的变化看起来更自然.
下面是我修正以后的计算线条宽度的函数:
W_current =
W_previous + min( abs(k*s - W_previous), distance * K_width_unit_change) (k * s-W_previous) >= 0
W_previous - min( abs(k*s - W_previous), distance * K_width_unit_change) (k * s-W_previous) < 0
W_current 当前线段的宽度
W_previous 与当前线条相邻的前一条线段的宽度
distance 当前线条的长度
w_k 设定的一个固定阈值,表示:单位距离内, 笔迹的线条宽度可以变化的最大量.
distance * w_k 即为当前线段的长度内, 笔宽可以相对于前一条线段笔宽的基础上, 最多能够变宽或者可以变窄多少.
这个函数多引入了2个变量(前一条线段的宽度, 还有当前的线段的距离), 在计算线条宽度时, 考虑了更多的可能性.
还增加了一种非线性的变化机制, min.这个min就是我们的"激活函数".让我们的线宽不再只具有线性的变化了.
现在, 这个计算线宽的函数,看起来已经比较完美了.
问题二:
我们直接看一个我故意做得比较不好的示范图:
虽然这个效果大致看起来看还行, 作为一名追求完美的程序员, 始终觉得什么地方不对劲.
那么我们再把这个问题放大到一种极端的情况:
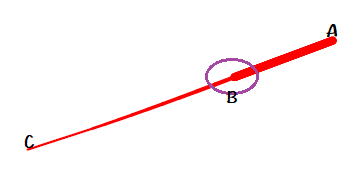
这样问题就很明显了.
我解决这个问题的方式是:利用微分的思想, 把线段再次细分成多条子线段, 宽度的变化均匀的分布在这些细分的子线段上.
这样, 我们的线条宽度变化看起来就更加自然了.
问题三:
在平时的书写过程中, 笔锋主要体现在笔画的起始位置, 转角位置, 和笔画结束的位置.
在笔迹转角的位置体现出笔锋看起来比较困难, 但是在笔迹开始和结束的地方做一些文章还是比较容易.
我的具体做法是这样, 在笔迹开始的前5个点(这个'5', 是我随便想出来的, 也可4,6,7,8), 让笔迹的宽细变化更加明显
在笔迹的结束位置, 不管之前的线段宽度是多少, 都让其在最后位置收缩为最小笔宽.
更好的理由我也说不出来为什么,应该是属于程序员的第七感吧, 感觉这样做会比较好. 而且事实证明效果的确不错.
其实这里也体现了"非线性"变化的思想, 因为我觉得这一点比较重要, 所以单独提出来.
解决以上3个问题, 离这个算法的成功, 就还差一些细节的问题了.(虽然是细节问题, 但是以下这几个需要注意的细节非常非常非常重要, 说三遍!!!!!!!)
下面我就不买关子, 直接告诉大家需要注意的地方:
1) 在实际的情况中, 移动 定位设备(鼠标,手写笔,或者触摸屏)时, 设备发送给我们的mouse_move消息会非常的多, 需要设立一个
时间阈值, 比如前一次消息到这一次消息的间隔时间小于30毫秒, 就把这个点废弃掉. 否则, 点太多, 每个都处理, 基本上都是多余的计算..
2) 在实际情况中, 需要设立一个距离阈值, 当本次得到的点, 到上一个点的距离小于这个阈值时, 把这个点舍弃掉, 距离太近, 也是多余的计算.
以上内容, 差不多就是手写笔迹算法中所有技术难点和需要注意的细节了.
下面把C++实现的源代码分享给大家, 其中z_math.h, z_math.c使用纯c实现,除了c标准库,没有其它任何依赖,可以毫无压力的移植到各个支持c/c++语言的任何平台.
z_math是算法的核心实现部分:
1 /* 2 ===================================================================================== 3 * Filename: z_math.h 4 * Description: 5 * Version: 2.0 6 * Created: 06/23/2016 14:53:43 7 * Revision: none 8 * Compiler: gcc 9 * Author: zl(88911562@qq.com), 10 * Organization: 11 * ===================================================================================== 12 */ 13 //_________________________________ 14 // stl on mac location is: 15 // /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Toolchains/XcodeDefault.xctoolchain/usr/include/c++/v1 16 // Mac OS X 10.9+ no longer uses GCC/libstdc++ but uses libc++ and Clang. 17 //--------------------------------- 18 //td c++ (STL, streams, ...) : Modified libstdc++ headers for use with ctags 19 //use ctags for c++(stl,streams....) 20 //www.vim.org/scripts/script.php?script_id=2358 21 //ctags -R --c++-kinds=+p --fields=+ias --extra=+q --language-force=c++ cpp_src 22 //sudo ctags -R --c++-kinds=+p --fields=+ias --extra=+q --language-force=c++ ./ 23 //================================= */ 24 #ifndef z_math_h_ 25 #define z_math_h_ 26 27 #ifdef __cplusplus 28 extern "C" { 29 #endif 30 31 #include <stdint.h> 32 33 typedef struct z_point_s z_point; 34 typedef struct z_fpoint_s z_fpoint; 35 typedef struct z_ipoint_s z_ipoint; 36 typedef struct z_fpoint_array_s z_fpoint_array; 37 typedef struct z_fpoint_arraylist_node_s z_fpoint_arraylist_node; 38 typedef struct z_fpoint_arraylist_s z_fpoint_arraylist; 39 40 struct z_point_s { 41 float x, y; 42 }; 43 44 struct z_fpoint_s{ 45 z_point p; 46 float w; 47 }; 48 49 struct z_ipoint_s { 50 z_point p; 51 int64_t t; 52 }; 53 54 struct z_fpoint_array_s { 55 z_fpoint *point; 56 float maxwidth; 57 float minwidth; 58 int ref; 59 int len; 60 int cap; 61 62 z_point last_point; 63 float last_width; 64 int64_t last_ms; 65 }; 66 67 struct z_fpoint_arraylist_node_s { 68 z_fpoint_array *a; 69 z_fpoint_arraylist_node *n; 70 }; 71 72 struct z_fpoint_arraylist_s { 73 int ref; 74 z_fpoint_arraylist_node *first; 75 z_fpoint_arraylist_node *end; 76 z_fpoint_arraylist_node *cur; 77 }; 78 79 z_fpoint_array *z_keep_fpoint_array(z_fpoint_array *a); 80 void z_drop_fpoint_array(z_fpoint_array *a); 81 82 z_fpoint_arraylist* z_keep_fpoint_arraylist(z_fpoint_arraylist *l); 83 void z_drop_fpoint_arraylist(z_fpoint_arraylist *l); 84 85 z_fpoint_array *z_new_fpoint_array(int initsize, float maxwidth, float minwidth); 86 z_fpoint_array *z_resize_fpoints_array(z_fpoint_array* a, int size); 87 88 z_fpoint_arraylist *z_new_fpoint_arraylist(); 89 void z_fpoint_arraylist_append(z_fpoint_arraylist *l, z_fpoint_array *a); 90 // must be drop after used 91 z_fpoint_array *z_fpoint_arraylist_append_new(z_fpoint_arraylist *l, float maxwidth, float minwidth); 92 void z_fpoint_arraylist_removelast(z_fpoint_arraylist *l); 93 94 float z_movespeed(z_ipoint s, z_ipoint e); 95 float z_distance(z_point s, z_point e); 96 void z_fpoint_add_xyw(z_fpoint_array *a, float x, float y, float w); 97 void z_fpoint_add(z_fpoint_array *a, z_fpoint p); 98 void z_fpoint_differential_add(z_fpoint_array *a, z_fpoint p); 99 void z_square_bezier(z_fpoint_array *a, z_fpoint b, z_point c, z_fpoint e); 100 float z_linewidth(z_ipoint b, z_ipoint e, float w, float step); 101 102 float z_insert_point(z_fpoint_array *arr, z_point point); 103 void z_insert_last_point(z_fpoint_array *arr, z_point e); 104 105 106 typedef struct z_list_node_s z_list_node; 107 struct z_list_node_s { 108 void *data; 109 z_list_node *n; 110 z_list_node *p; 111 }; 112 typedef void*(*z_list_node_alloc_fun)(); 113 typedef void(*z_list_node_drop_fun) (void *data); 114 115 116 struct z_list_s { 117 z_list_node_alloc_fun alloc; 118 z_list_node_drop_fun drop; 119 z_list_node *first; 120 z_list_node *last; 121 }; 122 typedef struct z_list_s z_list; 123 124 z_list *z_list_new(z_list_node_alloc_fun allocfun, z_list_node_drop_fun dropfun); 125 void *z_list_append_new(z_list *zlist); 126 void *z_list_remove_last(z_list *zlist); 127 void z_list_clear(z_list *zlist); 128 void z_list_free(z_list *zlist); 129 130 /* digest must be 33 char size */ 131 // void z_text_md5(const char* str, char *digest); 132 133 #ifdef __cplusplus 134 } 135 #endif 136 137 #endif
1 /* 2 ===================================================================================== 3 * Filename: z_math.c 4 * Description: 5 * Version: 1.0 6 * Created: 06/23/2016 14:53:43 7 * Revision: none 8 * Compiler: gcc 9 * Author: zl(88911562@qq.com), 10 * Organization: 11 * ===================================================================================== 12 */ 13 #include <math.h> 14 #include <stdio.h> 15 #include <string.h> 16 #include <stdlib.h> 17 #include <time.h> 18 #include "z_math.h" 19 20 #define z_malloc_struct(t) (t*)calloc(1, sizeof(t)) 21 static void* z_malloc_array(unsigned int count, unsigned int size); 22 static void* z_resize_array(void *p, size_t count, size_t size); 23 24 static void z_fpoint_array_set_last_info(z_fpoint_array *arr, z_point last_point, float last_width); 25 26 /***************************** mac stdlib location: 27 Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/MacOSX.platform/Developer/SDKs/MacOSX10.11.sdk/usr/include/stdio.h 28 */ 29 static float z_square(float f){ return (float)f*f; }; 30 static float z_cubic_(float f){ return (float)powf(f, 3); }; 31 32 typedef struct z_bezier_factors_s { 33 float bezier_step; // must be divisible by 1.0f 34 float max_width_diff; // max width diff between two near lines 35 float max_move_speed; // 36 float max_linewith; 37 } z_bezier_factors ; 38 39 int z_point_equals(z_point *p1, z_point *p2) { 40 return (p1->x==p2->x&&p1->y==p2->y) ? 1 : 0; 41 } 42 43 z_fpoint_array *z_keep_fpoint_array(z_fpoint_array *a) { 44 if(a) a->ref++; 45 return a; 46 } 47 48 void z_drop_fpoint_array(z_fpoint_array *a) { 49 if(!a) return; 50 51 if( !(--(a->ref)) ) { 52 free(a); 53 } 54 } 55 56 z_fpoint_arraylist *z_keep_fpoint_arraylist(z_fpoint_arraylist *l) { 57 if(!l) return NULL; 58 l->ref++; 59 return l; 60 } 61 62 void z_drop_fpoint_arraylist(z_fpoint_arraylist *l) { 63 if(!l) return; 64 65 if( !(--(l->ref)) ) { 66 z_fpoint_arraylist_node *c = l->first; 67 z_fpoint_arraylist_node *n; 68 while(c) { 69 z_drop_fpoint_array(c->a); 70 n = c->n; 71 free(c); 72 c = n; 73 } 74 } 75 } 76 77 static const float defualt_max_width = 5.0f; 78 static const float default_min_width = 1.0f; 79 80 z_fpoint_array *z_new_fpoint_array(int initsize, float maxwidth, float minwidth) { 81 if(initsize<=0) return NULL; 82 z_fpoint_array *a = malloc(sizeof(z_fpoint_array)); 83 a->point = z_malloc_array(initsize, sizeof(z_fpoint)); 84 a->ref = 1; 85 a->len = 0; 86 87 if(maxwidth<0 || minwidth<0 || maxwidth<minwidth ){ 88 maxwidth = defualt_max_width; 89 minwidth = default_min_width; 90 } 91 92 a->maxwidth = maxwidth; 93 a->minwidth = minwidth; 94 95 a->cap = initsize; 96 return a; 97 } 98 99 z_fpoint_array *z_resize_fpoints_array(z_fpoint_array* a, int count){ 100 if(!a || count<=0) return NULL; 101 102 a->point = (z_fpoint*)z_resize_array(a->point, count, sizeof(z_fpoint)); 103 a->cap = count; 104 a->len = min(a->cap, a->len); 105 return a; 106 } 107 108 z_fpoint_arraylist *z_new_fpoint_arraylist() { 109 z_fpoint_arraylist *l = z_malloc_struct(z_fpoint_arraylist); 110 l->ref = 1; 111 l->first = l->end = NULL; 112 return l; 113 } 114 115 void z_fpoint_arraylist_append(z_fpoint_arraylist *l, z_fpoint_array *a) { 116 z_fpoint_arraylist_node *node = z_malloc_struct(z_fpoint_arraylist_node); 117 node->a = z_keep_fpoint_array(a); 118 node->n = NULL; 119 120 if(!l->first) { 121 l->first = node; 122 } 123 else { 124 l->end->n = node; 125 } 126 127 l->end = node; 128 } 129 130 z_fpoint_array *z_fpoint_arraylist_append_new(z_fpoint_arraylist *l, float max, float min) { 131 z_fpoint_array *a = z_new_fpoint_array(24, max, min); 132 z_fpoint_arraylist_append(l, a); 133 printf("append new points array\n"); 134 return a; 135 } 136 137 void z_fpoint_arraylist_removelast(z_fpoint_arraylist *l) { 138 139 z_fpoint_arraylist_node *c = l->first; 140 141 z_drop_fpoint_array(l->end->a); 142 free(l->end); 143 144 while(c->n != l->end) { c = c->n; } 145 146 c->n = NULL; 147 l->end = c; 148 } 149 150 z_fpoint_array *z_auto_increase_fpoints_array(z_fpoint_array *a) { 151 int cap = a->cap + (a->cap+3)/4; 152 return z_resize_fpoints_array(a, cap); 153 } 154 155 float z_movespeed(z_ipoint s, z_ipoint e) { 156 float d = z_distance(s.p, e.p); 157 return (0==d) ? 0 : d/(e.t-s.t); 158 } 159 160 float z_distance(z_point b, z_point e){ 161 return (float)sqrtf( z_square(e.x-b.x) + z_square(e.y-b.y) ); 162 } 163 164 void z_fpoint_add_xyw(z_fpoint_array *a, float x, float y, float w) { 165 if( !a || (a->point[a->len-1].p.x==x && a->point[a->len-1].p.y==y) ) return; 166 167 if(a->len==a->cap) 168 z_auto_increase_fpoints_array(a); 169 170 z_fpoint *p = a->point + (a->len++); 171 p->p.x = x; p->p.y = y; p->w = w; 172 } 173 174 void z_fpoint_add(z_fpoint_array *a, z_fpoint p) { 175 z_fpoint_add_xyw(a, p.p.x, p.p.y, p.w); 176 } 177 178 void z_fpoint_differential_add(z_fpoint_array *a, z_fpoint p) { 179 if(!a) return; 180 181 if( a->len==0 ) { 182 z_fpoint_add(a, p); 183 return; 184 } 185 186 // #define bad_show 187 #ifdef bad_show 188 z_fpoint_add(a, p); 189 return; 190 #endif 191 float max_diff = 0.1f; 192 z_fpoint *last = a->point + (a->len-1); 193 z_point sp = last->p; 194 float sw = last->w; 195 196 int n = (int)((fabsf(p.w - last->w) / max_diff) + 1); 197 float x_step = (p.p.x - sp.x) / n; 198 float y_step = (p.p.y - sp.y) / n; 199 float w_step = (p.w - sw) / n; 200 201 int i; 202 for(i=0; i<(n-1); i++ ){ 203 sp.x += x_step; 204 sp.y += y_step; 205 sw += w_step; 206 z_fpoint_add_xyw(a, sp.x, sp.y, sw); 207 } 208 z_fpoint_add(a, p); 209 } 210 211 void z_square_bezier(z_fpoint_array *a, z_fpoint b, z_point c, z_fpoint e){ 212 if(!a) return; 213 const float f = 0.1f; 214 for(float t=f; t<=1.0; t+=f ) { 215 float x1 = z_square(1-t)*b.p.x + 2*t*(1-t)*c.x + z_square(t)*e.p.x; 216 float y1 = z_square(1-t)*b.p.y + 2*t*(1-t)*c.y + z_square(t)*e.p.y; 217 float w = b.w + (t* (e.w-b.w)); 218 z_fpoint pw = { {x1, y1}, w}; 219 z_fpoint_differential_add(a, pw); 220 } 221 } 222 223 float z_linewidth(z_ipoint b, z_ipoint e, float bwidth, float step) { 224 const float max_speed = 2.0f; 225 float d = z_distance(b.p, e.p); 226 float s = d / (e.t - b.t); s = s > max_speed ? max_speed : s; 227 float w = (max_speed-s) / max_speed; 228 float max_dif = d * step; 229 if( w<0.05f ) w = 0.05f; 230 if( fabs( w-bwidth ) > max_dif ) { 231 if( w > bwidth ) 232 w = bwidth + max_dif; 233 else 234 w = bwidth - max_dif; 235 } 236 // printf("d:%.4f, time_diff:%lld, speed:%.4f, width:%.4f\n", d, e.t-b.t, s, w); 237 return w; 238 } 239 240 241 float z_insert_point(z_fpoint_array *arr, z_point point) { 242 243 if(!arr) return 0; 244 int len = arr->len; 245 246 z_point zp = {point.x, point.y}; 247 if( 0==len ){ 248 z_fpoint p = {zp, 0.4f}; 249 z_fpoint_add(arr, p); 250 z_fpoint_array_set_last_info(arr, point, p.w); 251 return p.w; 252 } 253 254 int64_t cur_ms = clock(); 255 float last_width = arr->last_width; 256 int64_t last_ms = arr->last_ms; 257 z_point last_point = arr->last_point; 258 259 printf("cur_ms - last_ms = 0x%llx\n", cur_ms - last_ms); 260 // 两次采样时间小于25毫秒, 或者距离小于2个像素, 不采样计算!!! 261 float distance = z_distance(point, last_point); 262 if( (cur_ms-last_ms) < 50 || distance < 3) { 263 return 0; 264 } 265 266 float step = arr->len > 4 ? 0.05f : 0.2f; 267 z_ipoint bt = { {last_point.x,last_point.y}, last_ms}; 268 z_ipoint et = { zp, cur_ms}; 269 float w = (z_linewidth(bt, et, last_width, step) + last_width) / 2; 270 z_fpoint_array *points = z_new_fpoint_array(51, arr->maxwidth, arr->minwidth); 271 z_fpoint tmppoint = arr->point[len-1]; 272 z_fpoint_add(points, tmppoint); 273 274 if( 1==len ) { 275 z_fpoint p = { {(bt.p.x + et.p.x + 1) / 2, (bt.p.y + et.p.y +1) / 2}, w}; 276 z_fpoint_differential_add(points, p); 277 w = p.w; 278 } 279 else { 280 z_fpoint bw = tmppoint; 281 z_point c = {last_point.x,last_point.y}; 282 z_fpoint ew = {{(last_point.x + point.x)/2, (last_point.y + point.y)/2}, w}; 283 z_square_bezier(points, bw, c, ew); 284 } 285 286 // escape the first point 287 int i; 288 for(i=1; i<points->len; i++) { 289 z_fpoint_add(arr, points->point[i]); 290 } 291 292 z_drop_fpoint_array(points); 293 z_fpoint_array_set_last_info(arr, point, w); 294 295 return w; 296 } 297 298 void z_insert_last_point(z_fpoint_array *arr, z_point e) { 299 if(!arr) return; 300 long len= arr->len; 301 if(len==0 ) return; 302 z_fpoint_array *points = z_new_fpoint_array(51, arr->maxwidth, arr->minwidth); 303 z_fpoint zb = arr->point[len-1]; 304 z_fpoint_add(points, zb); 305 306 z_fpoint ze = { {e.x, e.y}, 0.1f}; 307 z_fpoint_differential_add(points, ze); 308 int i; 309 for(i=1; i<points->len; i++) { 310 z_fpoint_add(arr, points->point[i]); 311 } 312 z_drop_fpoint_array(points); 313 } 314 315 z_list *z_list_new(z_list_node_alloc_fun allocfun, z_list_node_drop_fun dropfun) 316 { 317 z_list *l = NULL; 318 l = z_malloc_struct(z_list); 319 l->alloc = allocfun; 320 l->drop = dropfun; 321 l->first = l->last = NULL; 322 return l; 323 } 324 325 void *z_list_append_new(z_list *zlist) 326 { 327 z_list_node *node = NULL; 328 void *data = NULL; 329 330 if(!zlist->alloc || !zlist->drop) 331 return NULL; 332 333 node = z_malloc_struct(z_list_node); 334 node->data = zlist->alloc(); 335 node->n = NULL; 336 node->p = NULL; 337 338 if(node) { 339 if(!zlist->first) { 340 zlist->first = zlist->last = node; 341 } 342 else { 343 node->n = NULL; 344 node->p = zlist->last; 345 zlist->last->n = node; 346 zlist->last = node; 347 } 348 data = node->data; 349 } 350 351 return data; 352 } 353 void *z_list_remove_last(z_list *zlist) 354 { 355 void *data = NULL; 356 z_list_node *tmp = zlist->last; 357 if(zlist->last) { 358 tmp = zlist->last; 359 if(zlist->last==zlist->first){ 360 zlist->last = zlist->first = NULL; 361 } 362 else { 363 zlist->last = tmp->p; 364 zlist->last->n = NULL; 365 } 366 } 367 368 if(tmp) { 369 data = tmp->data; 370 free(tmp); 371 } 372 373 return data; 374 } 375 376 void z_list_clear(z_list *zlist) 377 { 378 while (zlist->first) 379 zlist->drop(z_list_remove_last(zlist)); 380 } 381 382 void z_list_free(z_list *zlist) 383 { 384 z_list_clear(zlist); 385 free(zlist); 386 } 387 388 /* digest must be 33 char size */ 389 // void 390 // z_text_md5(const char* str, char *digest) 391 // { 392 // int len = strlen(str); 393 // unsigned char d[16]; 394 // fz_md5 state; 395 // fz_md5_init(&state); 396 // fz_md5_update(&state, (const unsigned char*)str, len); 397 // fz_md5_final(&state, d); 398 // 399 // int i; 400 // for(i=0; i<(int)sizeof(d); i++) { 401 // sprintf(digest, "%02x", d[i]); 402 // digest+=2; 403 // } 404 // *digest = '\0'; 405 // } 406 407 void* z_malloc_array(unsigned int count, unsigned int size) { 408 unsigned int totalsize = count * size; 409 if (totalsize <= 0) return 0; 410 411 void *buffer = malloc(count * size); 412 if(buffer) memset(buffer, 0, count * size); 413 return buffer; 414 } 415 416 void* z_resize_array(void *p, size_t count, size_t size) { 417 void *np = 0; 418 size_t total_size = count * size; 419 420 if (total_size <= 0) 421 return np; 422 423 np = realloc(p, total_size); 424 425 return np; 426 } 427 428 void z_fpoint_array_set_last_info(z_fpoint_array *arr, z_point last_point, float last_width) { 429 if (!arr) return; 430 arr->last_point = last_point; 431 arr->last_ms = clock(); 432 arr->last_width = last_width; 433 printf("reset last ms to 0x%llx\n", arr->last_ms); 434 }
前几天有个公司让我优化一下我的算法, 我又优化了一下, 提供出了一个 :
快乐的时光总是过得那么快, 留下的总是无尽的唏嘘和感叹, 又到时间和朋友们讲拜拜了!!!
最后展示一张在解决这些问题时,留下的真迹:
手写笔迹这一个系列总算是写完了.在这几篇原创文章中, 我有很多地方没有办法完全把自己的想法表达清楚,这可能也是很多程序员攻城狮的通病, 表达能力不怎么样.
如果大家有什么不清楚或者我说得有问题的地方, 可以在留言区留言.我会尽量回答.
下面!!!!!!!!我不得不再次提起一件很让我气愤的事情!!!!!!!
无良公司老板拖欠两个月工资了, 穷得叮当响,我靠!!!!!!!!现在每天吃8块钱的蛋炒饭, 早上点一份,中午吃一半, 晚上吃一半, 日子真实苦啊..
大家如果大家觉得这篇文章对您有帮助, 又愿意打赏一些银两, 请拿起你的手机, 打开你的微信, 扫一扫下方二维码, 作为一个有骨气的程序员攻城狮, 我非常愿意接受大家的支助...哈哈哈!!!




