Smith Number
题目
Given a number n, the task is to find out whether this number is a Smith number or not. A Smith number is a composite number whose sum of digits is equal to the sum of digits of its prime factors.
Example 1:
Input: n = 4 Output: 1 Explanation: The sum of the digits of 4 is 4, and the sum of the digits of its prime factors is 2 + 2 = 4.
Example 2:
Input: n = 378 Output: 1 Explanation: 378 = 21*33*71 is a Smith number since 3+7+8 = 2*1+3*3+7*1.
Your Task:
You don't need to read input or print anything. Your task is to complete the function smithNum() which takes an Integer n as input and returns the answer.
Expected Time Complexity: O(n * log(n))
Expected Auxiliary Space: O(n)
Constraints:
解题过程
class Solution: primes = [2, 3, 5, 7] def primeFactors(self, n): assert n >= 2 result = {} for i in self.primes: while n % i == 0: n = n // i result[i] = result.get(i, 0) + 1 if n == 1: return result # update primes, only function when `n > self.primes[-1]` candidate = self.primes[-1] + 2 while True: if all(candidate % i != 0 for i in self.primes): # not prime self.primes.append(candidate) while n % candidate == 0: n = n // candidate result[candidate] = result.get(candidate, 0) + 1 if n == 1: return result candidate += 2 def smithNum(self, n): if n <= 1: return 0 prime_factors = self.primeFactors(n) if n in self.primes: return 0 # it is a prime, so not smithNum sum_digits = lambda k: sum(int(i) for i in str(k)) v1 = sum_digits(n) v2 = sum(v * sum_digits(k) for k, v in prime_factors.items()) return int(v1 == v2)
我刚开始使用的方法是,用一个列表进行缓存,需要判断的数字比缓存的最大质数还大时,就找下一个质数(通过加2的形式)。
这个思路来自于一个“找第N个质数”的题目。
但是这个超时了,数字特别大时,这个会很耗时,因为每次加2只保证了不会装上2的倍数,对新的数字需要与所有已知的质数进行整除判断。
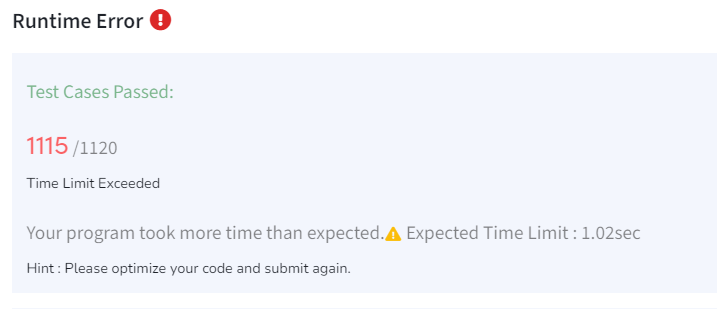
然后我就想到,有一个可以找到0-N内所有质数的算法。
但是这道题目里,没有指定范围,每次范围超出已知质数时,从0开始找也不太好。
于是我就改成了,如果数字大于缓存列表最大质数时,找到最大质数到这个数字之间的所有质数。相当于两个方法结合在一起,尽可能用到质数时再计算。
import numpy as np class Solution: def __init__(self): # initial primes self.primes = [2, 3, 5, 7] self.last_num = self.primes[-1] def primeFactors(self, n): result = {} if n <= 1: return result # try to simplify n with known primes for i in self.primes: while n % i == 0: n = n // i result[i] = result.get(i, 0) + 1 if n == 1: return result # update primes ranging from start to n start = self.last_num + 1 candidates = np.ones(n + 1) # 0 to n for p in self.primes: k = int(np.ceil(start / p) * p) while k < candidates.size: candidates[k] = 0 k += p new_primes = [] for idx, v in enumerate(candidates[start:]): if v: p = idx + start new_primes.append(p) k = 2 * p while k < candidates.size: candidates[k] = 0 k += p self.primes.extend(new_primes) self.last_num = n # using new primes to simplify n for i in new_primes: while n % i == 0: n = n // i result[i] = result.get(i, 0) + 1 if n == 1: return result def smithNum(self, n): if n <= 1: return 0 prime_factors = self.primeFactors(n) if n in self.primes: return 0 # it is a prime, so not smithNum sum_digits = lambda k: sum(int(i) for i in str(k)) v1 = sum_digits(n) v2 = sum(v * sum_digits(k) for k, v in prime_factors.items()) return int(v1 == v2)
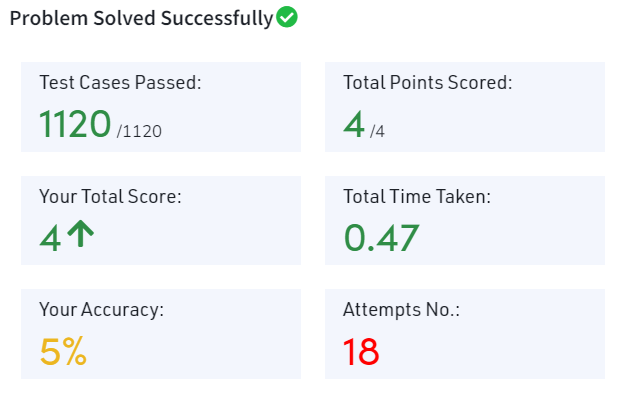
答案
看了看答案,思路是是先算出来一定范围内的所有质数,然后用这个表去计算。
和我的第二个思路比较像,不过我的第二个思路里,只有在需要时才计算新的质数,这个刚开始就找到所有质数。感觉见仁见智吧。
下面是根据答案改出来的可以提交的代码(默默吐槽一下,根本不是 Python 的代码风格……)。
不过,这个最后也超时了!我不知道是系统的原因还是Python语言的原因……
import math MAX = 10000 primes = [] # utility function for sieve of sundaram def sieveSundaram(): #In general Sieve of Sundaram, produces primes smaller # than (2*x + 2) for a number given number x. Since # we want primes smaller than MAX, we reduce MAX to half # This array is used to separate numbers of the form # i+j+2ij from others where 1 <= i <= j marked = [0] * int((MAX/2)+100) # Main logic of Sundaram. Mark all numbers which # do not generate prime number by doing 2*i+1 i = 1 while i <= ((math.sqrt (MAX)-1)/2) : j = (i* (i+1)) << 1 while j <= MAX/2 : marked[j] = 1 j = j+ 2 * i + 1 i = i + 1 # Since 2 is a prime number primes.append (2) # Print other primes. Remaining primes are of the # form 2*i + 1 such that marked[i] is false. i=1 while i <= MAX /2 : if marked[i] == 0 : primes.append( 2* i + 1) i=i+1 class Solution: def __init__(self): sieveSundaram() def smithNum(self, n): original_no = n #Find sum the digits of prime factors of n pDigitSum = 0; i=0 while (primes[i] <= n/2 ) : while n % primes[i] == 0 : #If primes[i] is a prime factor , # add its digits to pDigitSum. p = primes[i] n = n/p while p > 0 : pDigitSum += (p % 10) p = p/10 i=i+1 # If n!=1 then one prime factor still to be # summed up if not n == 1 and not n == original_no : while n > 0 : pDigitSum = pDigitSum + n%10 n=n/10 # All prime factors digits summed up # Now sum the original number digits sumDigits = 0 while original_no > 0 : sumDigits = sumDigits + original_no % 10 original_no = original_no/10 #If sum of digits in prime factors and sum # of digits in original number are same, then # return true. Else return false. return int(pDigitSum == sumDigits)
更多参考资料
Smith Number -- from Wolfram MathWorld
质数(素数)计算器 - 判断一个数是否为质数/素数
素数筛法算法及其原理 - kentle - 博客园




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人