django缓存优化(二)
一、缓存目的:
1、减小过载
2、避免重复计算
3、提高系统性能
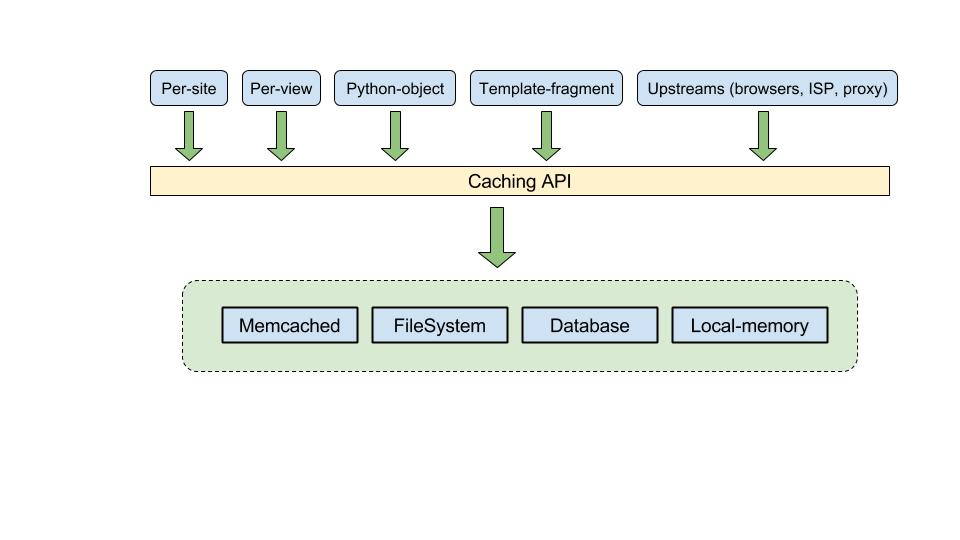
二、如何进行缓存

三、缓存类型

四、缓存粒度分类

五、缓存的设置与使用
示例一:
CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.memcached.MemcachedCache',
'LOCATION': '127.0.0.1:11211',
}
}
示例二:
CACHES = { 'default': { 'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.memcached.MemcachedCache',
'LOCATION': 'unix:/tmp/memcached.sock', } }
示例三:
CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.memcached.MemcachedCache',
'LOCATION': [
'172.19.26.240:11211',
'172.19.26.242:11211',
]
}
}
示例四:
CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.memcached.MemcachedCache',
'LOCATION': [
'172.19.26.240:11211',
'172.19.26.242:11212',
'172.19.26.244:11213',
]
}
}
访问缓存:
>>>from django.core.cache import caches >>>cache1 = caches[‘myalias’] >>>cache2 = caches[‘myalias’] >>>cache1 is cache2 True >>>from django.core.cache import cache >>>cache.set(‘my_key’, ‘hello, world’, 30) >>>cache.get(‘my_key’) ‘hello, world!’ >>>cache.get(‘my_key’) None >>>cache.get(‘my_key’,‘has expired’) ‘has expired’
六、缓存原理
明月装饰了你的窗子,你装饰了他的梦。


