Spring Boot 9. 与缓存
JSR-107,Spring缓存抽象,整合 Redis
Spring Boot高级内容概要
9、Spring Boot与缓存
10、Spring Boot与消息
11、Spring Boot与检索
12、Spring Boot与任务
13、Spring Boot与安全
14、Spring Boot与分布式
15、Spring Boot与监控管理
17、Spring Boot与部署
一、JSR107
- Javax Caching定义了5个核心接口,分别是CachingProvider, CacheManager, Cache, Entry 和 Expiry。
- CachingProvider定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个CacheManager。一个应用可以在运行期访问多个CachingProvider。
- CacheManager定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个唯一命名的Cache,这些Cache存在于CacheManager的上下文中。一个CacheManager仅被一个CachingProvider所拥有。
- Cache是一个类似Map的数据结构并临时存储以Key为索引的值。一个Cache仅被一个CacheManager所拥有。
- Entry是一个存储在Cache中的key-value对。
- Expiry 每一个存储在Cache中的条目有一个定义的有效期。一旦超过这个时间,条目为过期的状态。一旦过期,条目将不可访问、更新和删除。缓存有效期可以通过ExpiryPolicy设置。

二、Spring缓存抽象
-
Spring从3.1开始定义了
org.springframework.cache.Cache
和org.springframework.cache.CacheManager接口来统一不同的缓存技术;
并支持使用JCache(JSR-107)注解简化我们开发; -
Cache接口为缓存的组件规范定义,包含缓存的各种操作集合;
-
Cache接口下Spring提供了各种xxxCache的实现;如RedisCache,EhCacheCache , ConcurrentMapCache等;
-
每次调用需要缓存功能的方法时,Spring会检查检查指定参数的指定的目标方法是否已经被调用过;如果有就直接从缓存中获取方法调用后的结果,如果没有就调用方法并缓存结果后返回给用户。下次调用直接从缓存中获取。
-
使用Spring缓存抽象时我们需要关注以下两点;
- 确定方法需要被缓存以及他们的缓存策略
- 从缓存中读取之前缓存存储的数据
三、几个重要概念&缓存注解
| Cache(接口) | 缓存接口,定义缓存操作。实现有:RedisCache、EhCacheCache,ConcurrentMapCache等。 |
|---|---|
| CacheManager(接口) | 缓存管理器,管理各种缓存(Cache)组件 |
| @Cacheable | 主要针对方法配置,能够根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存 |
| @CacheEvict | 清空缓存 |
| @CachePut | (更新缓存)保证方法被调用,有希望结果被缓存 |
| @EnableCaching | 开启基于注解的缓存 |
| keyGenerator | 缓存数据时key生成策略 |
| serialize | (需要实现 serializable)缓存数据时value序列化策略 |
1. @Cacheable/@CachePut/@CacheEvict 主要的参数
- CacheManager管理多个Cache组件的,对缓存的真正CRUD操作在Cache组件中,每一个缓存组件有自己唯一一个名字;
| 参数 | 描述 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| cacheNames/value | 缓存的名称,在 spring 配置文件中定义,必须指定至少一个 | @Cacheable(value="mycache") 或者 @Cacheable(value= |
| key | 缓存的 key,可以为空,如果指定要按照 SpEL 表达式编写,如果不指定,则缺省按照方法的所有参数进行组合 | @Cacheable(value= "testcache" ,key= "#userName" ) |
| condition | 缓存的条件,可以为空,使用 SpEL 编写,返回 true 或者 false,只有为 true 才进行缓存/清除缓存,在调用方法之前之后都能判断 | @Cacheable(value= "testcache" ,condition= "#userName.length()>2" ) |
| allEntries | 是否清空所有缓存内容,缺省为 false,如果指定为 true,则方法调用后将立即清空所有缓存 | @CachEvict(value= "testcache" ,allEntries=true) |
| beforeInvocation | 是否在方法执行前就清空,缺省为 false,如果指定为 true,则在方法还没有执行的时候就清空缓存,缺省情况下,如果方法执行抛出异常,则不会清空缓存 | @CachEvict(value= "testcache" ,beforeInvocation=true) |
| unless{@CachePut} | 用于否决缓存的,不像condition,该表达式只在方法执行之后判断,此时可以拿到返回值result进行判断 条件为true不会缓存,fasle才缓存 | @Cacheable(value= "testcache" ,unless= "#result == null" ) |
1.1 @Cacheable 属性
- cacheNames/value:指定缓存组件的名字;将方法的返回结果放在哪个缓存中,是数组的方式,可以指定多个缓存;
- key:缓存数据使用的key;可以用它来指定。默认是使用方法参数的值 如果k=1(v=方法的返回值)
编写SpEL; #id;参数id的值:#a0 ,#p0 , #root.args[0]getEmp[2]
@Cacheable(value = {"emp"} ,key = "#root.methodName'['+#id+']'") - keyGenerator:key的生成器;可以自己指定key的生成器的组件id
key/keyGenerator:二选一使用;@Configuration public class MyCacheConfig { @Bean("myKeyGenerator") public KeyGenerator keyGenerator(){ return new KeyGenerator(){ @Override public Object generate(Object target, Method method, Object... params) { return method.getName()+"["+ Arrays.asList(params).toString()+"]"; } }; } } @Cacheable(value = {"emp"},keyGenerator = "myKeyGenerator") - cacheManager:指定缓存管理器;或者cacheResolver指定获取解析器
- condition:指定符合条件的情况下才缓存;
condition = "#id>0"
condition = "#a0>1":第一个参数的值 大于 1的时候才进行缓存@Cacheable(value = {"emp"},keyGenerator = "myKeyGenerator",condition = "#a0>1")
- unless:否定缓存;当unless指定的条件为true,方法的返回值就不会被缓存;可以获取到结果进行判断
unless = "#result == null":如果结果为null不缓存
unless = "#a0==2":如果第一个参数的值是2,结果不缓存;@Cacheable(value = {"emp"},keyGenerator = "myKeyGenerator",condition = "#a0>1",unless = "#a0==2")
- sync:是否使用异步模式
1.2 @CachePut
- 方法运行以后给缓存中放入数据的
- 即调用方法,又更新缓存数据,同步更新缓存;修改了数据库的某个数据,同时更新缓存。
- 运行时机:
- 先调用目标方法
- 将目标方法的结果缓存起来
- 测试步骤
- 查询1号员工;查到的结果会放在缓存中;
key:1 value:lastName:张三 - 以后查询还是之前的结果
- 更新1号员工;【lastName:zhangsan;gender:0】
将方法的返回值也放进缓存了;
key:传入的employee对象 值:返回的employee对象; - 查询1号员工?
应该是更新后的员工;
key = "#employee.id":使用传入的参数的员工id;
key = "#result.id":使用返回后的id
@Cacheable的key是不能用#result,一个是方法运行之前,一个是之后
为什么是没更新前的?【1号员工没有在缓存中更新】
- 查询1号员工;查到的结果会放在缓存中;
1.3 @CacheEvict
- 缓存清除
- value/cache/Names:缓存的名称,在 spring配置文件中定义,必须指定至少一个。
- key:缓存的 key,可以为空。如果指定,则按照 SpEL表达式编写;如果不指定,则默认按照方法的所有参数进行组合。
- condition:缓存的条件,可以为空,使用 SpEL表达式编写,返回 true或者false,只有返回 true才清空缓存。unless 属性与 condition属性相反,满足条件则不进行缓存。
- allEntries = true:指定清除这个缓存中所有的数据
- beforeInvocation = false:默认 false,缓存的清除是否在方法之前执行
默认代表缓存清除操作是在方法执行之后执行;如果出现异常缓存就不会清除 - beforeInvocation = true:
true 代表清除缓存操作是在方法运行之前执行,无论方法是否出现异常,缓存都清除
1.4 @Caching
- 定义复杂的缓存规则
@Caching(
//cacheable 指定规则
cacheable = {
@Cacheable(value = "emp", key = "#lastName")
},
//put 规则
put = {
@CachePut(value = "emp", key = "#result.id"),
@CachePut(value = "emp", key = "#result.email")
}
)
public Employee getEmpByLastName(String lastName) {
return employeeMapper.getEmpByLastName(lastName);
}
1.5 @CacheConfig
- @Caching是一个组注解,可以为一个方法定义提供基于 @Cacheable,@CacheEvict或者 @CachePut注解的数组。
- 标识在类上抽取缓存的公共配置
//源码
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface CacheConfig {
String[] cacheNames() default {};
String keyGenerator() default "";
String cacheManager() default "";
String cacheResolver() default "";
}
2. Cache SpEL available metadata
| 名字 | 位置 | 描述 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| methodName | root object | 当前被调用的方法名 | #root.methodName |
| method | root object | 当前被调用的方法 | #root.method.name |
| target | root object | 当前被掉用的目标对象 | #root.target |
| targetClass | root object | 当前被调用的目标对象类 | #root.targetClass |
| args | root object | 当前被调用的方法的参数列表 | #root.args[0] |
| caches | root object | 当前方法调用使用的缓存列表(如@Cacheable(value={"cache1","cache2"})),则有两个cache | #root.caches[0].name |
| argument name | evaluation context | 方法参数的名字,可以直接 #参数名,也可以使用 #p0或者#a0的形式,0代表参数的索引 | #iban、#a0、#p0 |
| result | evaluation context | 方法执行后的返回值(仅当方法执行之后的判断有效,如 "unless","cache put"的表达式"cache evict"的表达式beforeInvocation=false) | #result |
四、缓存使用
1. pom
<dependencies>
<!--缓存-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--引入web模块 spring-boot-starter :springboot场景启动器,帮我们导入了web模块正常运行所依赖的 jar包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--jdbc-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--mysql-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--mybatis 与springboot整合-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.2.0</version>
</dependency>
<!--单元测试-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--导入配置文件处理器,配置文件进行绑定就会有提示-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2. application.properties
# mysql数据源
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
# 开启mybatis的驼峰命名
mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case=true
# 打印 sql语句
logging.level.ink.sunflowerk.cache.mapper=debug
3. 创建数据库,创建 JavaBean 实现 serializable接口
CREATE TABLE `department` (
`id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`departmentName` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
CREATE TABLE `employee` (
`id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`lastName` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`email` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`gender` INT(2) DEFAULT NULL,
`d_id` INT(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
// 省略 set get tostring 方法
public class Department implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String departmentName;
}
public class Employee implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String lastName;
private String email;
private Integer gender; //性别 1男 0女
private Integer dId;
}
4. 整合 mybatis操作数据库
- 配置数据源(上面)
- 使用注解版的 mybatis
- 使用 @MapperScan 指定需要扫描 mapper接口所在的包
//在 main方法上使用 @MapperScan("ink.sunflowerk.cache.mapper")- 接口使用 @Mapper表明这是一个 mybatis的 mapper类
@Mapper //显示的声明这是一个 mybatis的mapper类 public interface DepartmentMapper { @Select("SELECT * FROM department WHERE id = #{id}") Department getDeptById(Integer id); } @Mapper //显示的声明这是一个 mybatis的mapper类 public interface EmployeeMapper { @Select("SELECT * FROM employee WHERE id = #{id}") public Employee getEmpById(Integer id); @Update("UPDATE employee SET lastName=#{lastName},email=#{email},gender=#{gender},d_id=#{dId} WHERE id=#{id}") public void updateEmp(Employee employee); @Delete("DELETE FROM employee WHERE id=#{id}") public void deleteEmpById(Integer id); @Insert("INSERT INTO employee(lastName,email,gender,d_id) VALUES(#{lastName},#{email},#{gender},#{dId})") public void insertEmployee(Employee employee); @Select("SELECT * FROM employee WHERE lastName = #{lastName}") Employee getEmpByLastName(String lastName); }
5. @EnableCaching开启缓存
//在 main方法上使用
@EnableCaching //开启基于注解的缓存
6. service 使用缓存注解
@CacheConfig(cacheNames="emp"/*,cacheManager = "employeeCacheManager"*/) //抽取缓存的公共配置
@Service
public class EmployeeService {
@Autowired
EmployeeMapper employeeMapper;
/**
* 将方法的运行结果进行缓存;以后再要相同的数据,直接从缓存中获取,不用调用方法;
* CacheManager管理多个Cache组件的,对缓存的真正CRUD操作在Cache组件中,每一个缓存组件有自己唯一一个名字;
*
*
* 原理:
* 1、自动配置类;CacheAutoConfiguration
* 2、缓存的配置类
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.GenericCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.JCacheCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.EhCacheCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.HazelcastCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.InfinispanCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CouchbaseCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CaffeineCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.GuavaCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.SimpleCacheConfiguration【默认】
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.NoOpCacheConfiguration
* 3、哪个配置类默认生效:SimpleCacheConfiguration;
*
* 4、给容器中注册了一个CacheManager:ConcurrentMapCacheManager
* 5、可以获取和创建ConcurrentMapCache类型的缓存组件;他的作用将数据保存在ConcurrentMap中;
*
* 运行流程:
* @Cacheable:
* 1、方法运行之前,先去查询Cache(缓存组件),按照cacheNames指定的名字获取;
* (CacheManager先获取相应的缓存),第一次获取缓存如果没有Cache组件会自动创建。
* 2、去Cache中查找缓存的内容,使用一个key,默认就是方法的参数;
* key是按照某种策略生成的;默认是使用keyGenerator生成的,默认使用SimpleKeyGenerator生成key;
* SimpleKeyGenerator生成key的默认策略;
* 如果没有参数;key=new SimpleKey();
* 如果有一个参数:key=参数的值
* 如果有多个参数:key=new SimpleKey(params);
* 3、没有查到缓存就调用目标方法;
* 4、将目标方法返回的结果,放进缓存中
*
* @Cacheable标注的方法执行之前先来检查缓存中有没有这个数据,默认按照参数的值作为key去查询缓存,
* 如果没有就运行方法并将结果放入缓存;以后再来调用就可以直接使用缓存中的数据;
*
* 核心:
* 1)、使用CacheManager【ConcurrentMapCacheManager】按照名字得到Cache【ConcurrentMapCache】组件
* 2)、key使用keyGenerator生成的,默认是SimpleKeyGenerator
*
*
* 几个属性:
* cacheNames/value:指定缓存组件的名字;将方法的返回结果放在哪个缓存中,是数组的方式,可以指定多个缓存;
*
* key:缓存数据使用的key;可以用它来指定。默认是使用方法参数的值 1-方法的返回值
* 编写SpEL; #i d;参数id的值 #a0 #p0 #root.args[0]
* getEmp[2]
*
* keyGenerator:key的生成器;可以自己指定key的生成器的组件id
* key/keyGenerator:二选一使用;
*
*
* cacheManager:指定缓存管理器;或者cacheResolver指定获取解析器
*
* condition:指定符合条件的情况下才缓存;
* ,condition = "#id>0"
* condition = "#a0>1":第一个参数的值》1的时候才进行缓存
*
* unless:否定缓存;当unless指定的条件为true,方法的返回值就不会被缓存;可以获取到结果进行判断
* unless = "#result == null"
* unless = "#a0==2":如果第一个参数的值是2,结果不缓存;
* sync:是否使用异步模式
* @param id
* @return
*
*/
@Cacheable(value = {"emp"}/*,keyGenerator = "myKeyGenerator",condition = "#a0>1",unless = "#a0==2"*/)
public Employee getEmp(Integer id){
System.out.println("查询"+id+"号员工");
Employee emp = employeeMapper.getEmpById(id);
return emp;
}
/**
* @CachePut:既调用方法,又更新缓存数据;同步更新缓存
* 修改了数据库的某个数据,同时更新缓存;
* 运行时机:
* 1、先调用目标方法
* 2、将目标方法的结果缓存起来
*
* 测试步骤:
* 1、查询1号员工;查到的结果会放在缓存中;
* key:1 value:lastName:张三
* 2、以后查询还是之前的结果
* 3、更新1号员工;【lastName:zhangsan;gender:0】
* 将方法的返回值也放进缓存了;
* key:传入的employee对象 值:返回的employee对象;
* 4、查询1号员工?
* 应该是更新后的员工;
* key = "#employee.id":使用传入的参数的员工id;
* key = "#result.id":使用返回后的id
* @Cacheable的key是不能用#result
* 为什么是没更新前的?【1号员工没有在缓存中更新】
*
*/
@CachePut(/*value = "emp",*/key = "#result.id")
public Employee updateEmp(Employee employee){
System.out.println("updateEmp:"+employee);
employeeMapper.updateEmp(employee);
return employee;
}
/**
* @CacheEvict:缓存清除
* key:指定要清除的数据
* allEntries = true:指定清除这个缓存中所有的数据
* beforeInvocation = false:缓存的清除是否在方法之前执行
* 默认代表缓存清除操作是在方法执行之后执行;如果出现异常缓存就不会清除
*
* beforeInvocation = true:
* 代表清除缓存操作是在方法运行之前执行,无论方法是否出现异常,缓存都清除
*
*
*/
@CacheEvict(value="emp",beforeInvocation = true/*key = "#id",*/)
public void deleteEmp(Integer id){
System.out.println("deleteEmp:"+id);
//employeeMapper.deleteEmpById(id);
int i = 10/0;
}
// @Caching 定义复杂的缓存规则
@Caching(
cacheable = {
@Cacheable(/*value="emp",*/key = "#lastName")
},
put = {
@CachePut(/*value="emp",*/key = "#result.id"),
@CachePut(/*value="emp",*/key = "#result.email")
}
)
public Employee getEmpByLastName(String lastName){
return employeeMapper.getEmpByLastName(lastName);
}
}
@Service
public class DeptService {
@Autowired
DepartmentMapper departmentMapper;
@Qualifier("deptCacheManager")
@Autowired
RedisCacheManager deptCacheManager;
/**
* 缓存的数据能存入redis;
* 第二次从缓存中查询就不能反序列化回来;
* 存的是dept的json数据;CacheManager默认使用RedisTemplate<Object, Employee>操作Redis
*
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
// @Cacheable(cacheNames = "dept",cacheManager = "deptCacheManager")
// public Department getDeptById(Integer id){
// System.out.println("查询部门"+id);
// Department department = departmentMapper.getDeptById(id);
// return department;
// }
// 使用缓存管理器得到缓存,进行api调用
public Department getDeptById(Integer id){
System.out.println("查询部门"+id);
Department department = departmentMapper.getDeptById(id);
//获取某个缓存
Cache dept = deptCacheManager.getCache("dept");
dept.put("dept:1",department);
return department;
}
}
7. Controller
@RestController
public class EmployeeController {
@Autowired
EmployeeService employeeService;
@GetMapping("/emp/{id}")
public Employee getEmployee(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
Employee employee = employeeService.getEmp(id);
return employee;
}
@GetMapping("/emp")
public Employee update(Employee employee){
Employee emp = employeeService.updateEmp(employee);
return emp;
}
@GetMapping("/delemp")
public String deleteEmp(Integer id){
employeeService.deleteEmp(id);
return "success";
}
@GetMapping("/emp/lastname/{lastName}")
public Employee getEmpByLastName(@PathVariable("lastName") String lastName){
return employeeService.getEmpByLastName(lastName);
}
}
@RestController
public class DeptController {
@Autowired
DeptService deptService;
@GetMapping("/dept/{id}")
public Department getDept(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
return deptService.getDeptById(id);
}
}
缓存工作原理@Cacheable运行流程
a.工作原理
1. 自动配置类;CacheAutoConfiguration
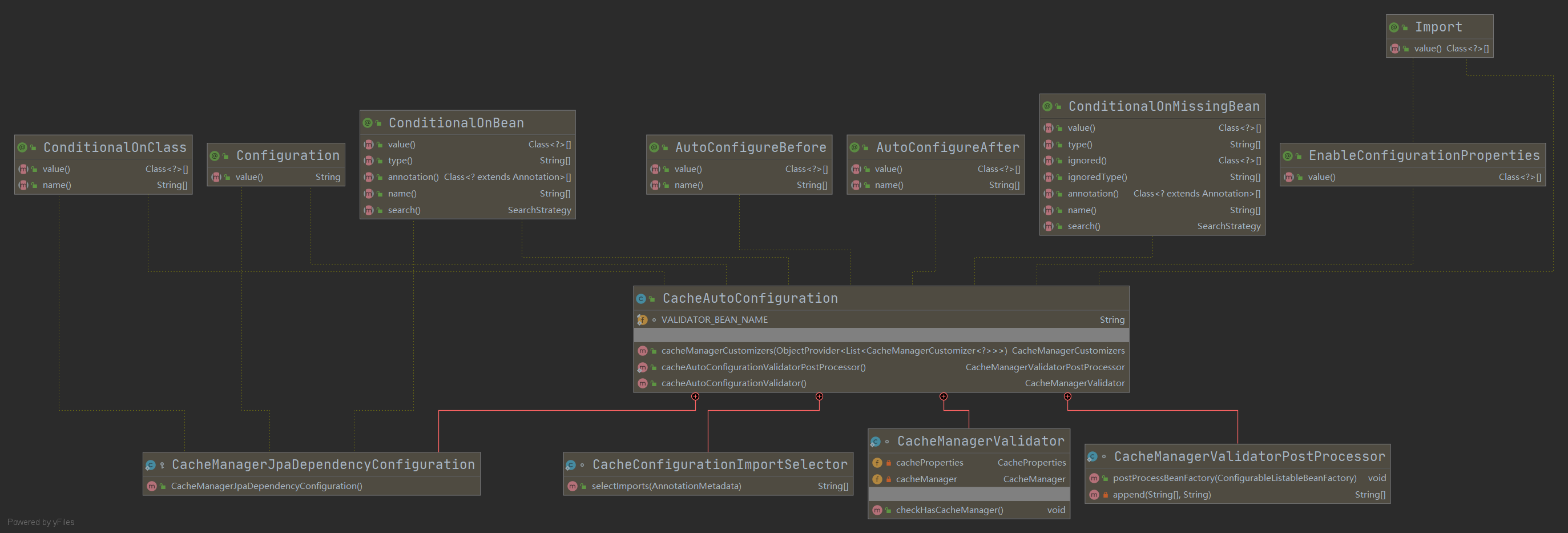
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(CacheManager.class)
@ConditionalOnBean(CacheAspectSupport.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = CacheManager.class, name = "cacheResolver")
@EnableConfigurationProperties(CacheProperties.class)
@AutoConfigureBefore(HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration.class)
@AutoConfigureAfter({ CouchbaseAutoConfiguration.class, HazelcastAutoConfiguration.class,
RedisAutoConfiguration.class })
@Import(CacheConfigurationImportSelector.class) //导入缓存要用到的组件
public class CacheAutoConfiguration {
}
2. 导入缓存要用到的组件(配置类),CacheConfigurationImportSelector.class
static class CacheConfigurationImportSelector implements ImportSelector {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
CacheType[] types = CacheType.values();
String[] imports = new String[types.length];
for (int i = 0; i < types.length; i++) {
imports[i] = CacheConfigurations.getConfigurationClass(types[i]);
}
return imports;//所有地缓存配置
}
}
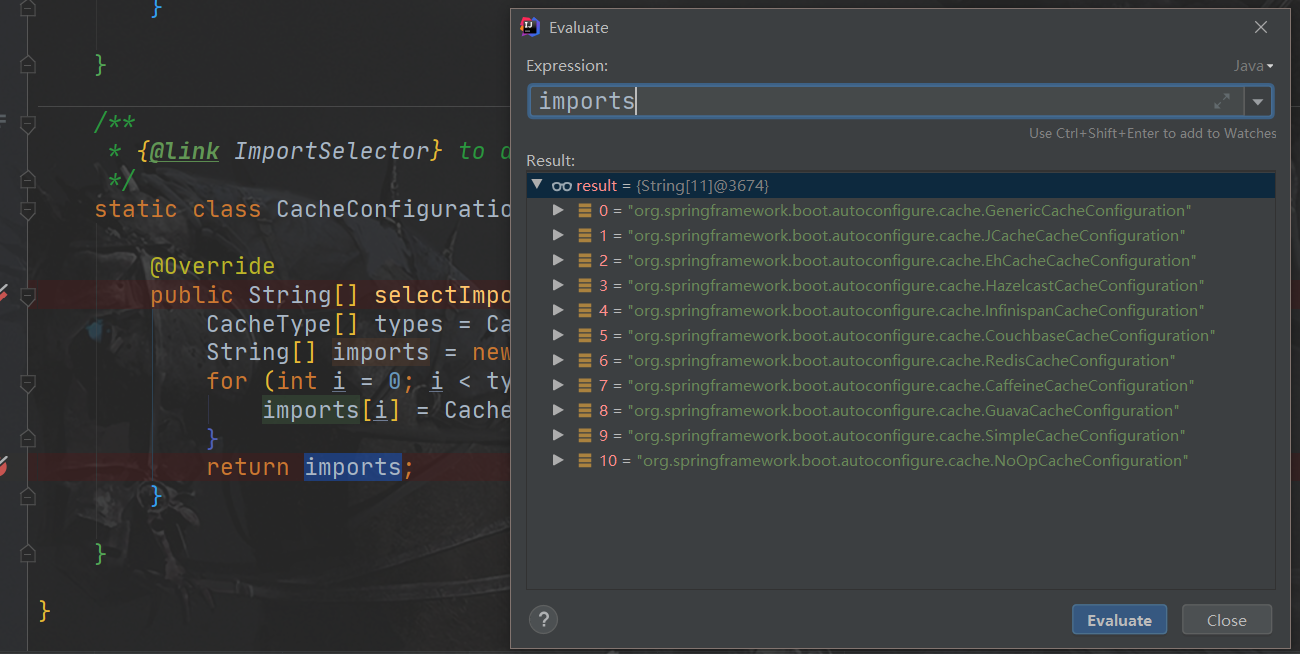
0 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.GenericCacheConfiguration"
1 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.JCacheCacheConfiguration"
2 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.EhCacheCacheConfiguration"
3 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.HazelcastCacheConfiguration"
4 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.InfinispanCacheConfiguration"
5 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CouchbaseCacheConfiguration"
6 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration"
7 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CaffeineCacheConfiguration"
8 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.GuavaCacheConfiguration"
9 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.SimpleCacheConfiguration"【默认】
10 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.NoOpCacheConfiguration"
3. 那个缓存的配置类默认生效
//我们可以这样查看
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnBean(Cache.class) //如果容器中有 cache这个组件
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(CacheManager.class) //如果容器中没有 cacheManager这个对象
@Conditional(CacheCondition.class)
class GenericCacheConfiguration {
}
- 我们可以使用 debug=true来查看那个默认生效
- 默认生效的组件是:SimpleCacheConfiguration

//实现了 CacheManager,CacheManager有一个方法 getCache按照一个名字得到一个缓存对象
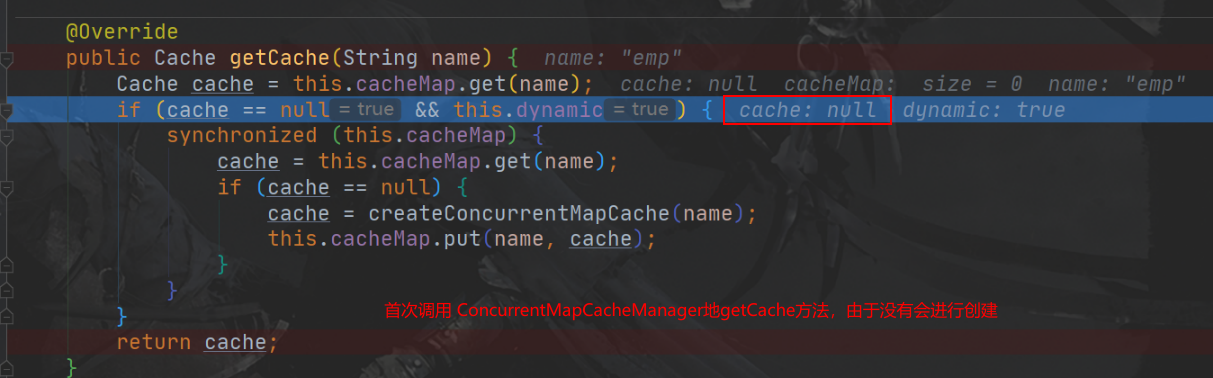
public class ConcurrentMapCacheManager implements CacheManager, BeanClassLoaderAware {
@Override
public Cache getCache(String name) {
//private final ConcurrentMap<String, Cache> cacheMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Cache>(16);
Cache cache = this.cacheMap.get(name);
//如果缓存的对象为空,进入同步方法进行创建
if (cache == null && this.dynamic) {
synchronized (this.cacheMap) {
cache = this.cacheMap.get(name);
if (cache == null) {
cache = createConcurrentMapCache(name);
this.cacheMap.put(name, cache);
}
}
}
return cache;
}
//为指定的缓存名创建一个 ConcurrentMapCache对象
protected Cache createConcurrentMapCache(String name) {
SerializationDelegate actualSerialization = (isStoreByValue() ? this.serialization : null);
return new ConcurrentMapCache(name, new ConcurrentHashMap<Object, Object>(256),
isAllowNullValues(), actualSerialization);
}
}
- ConcurrentMapCacheManager 作用:可以获取和创建 ConcurrentMapCache类型的组件,将数据保存在
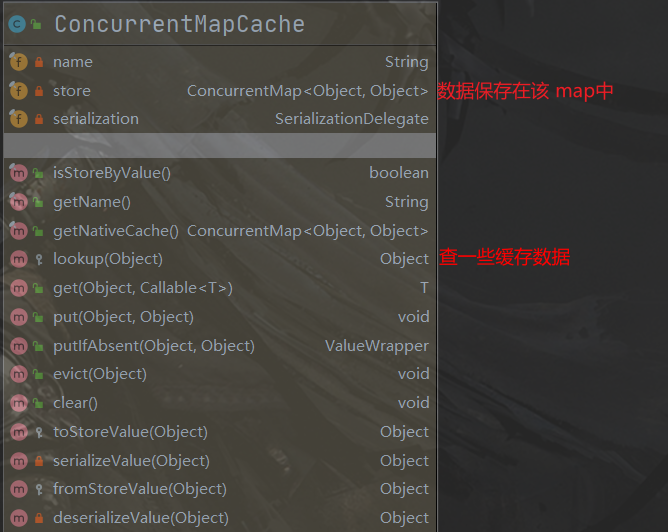
b. 运行流程
- 方法运行之前,先去查询 cache(缓存组件),按照 cacheName指定地名字获取
(CacheManager 先获取相应地缓存),第一次获取缓存如果没有 Cache组件会自动创建。
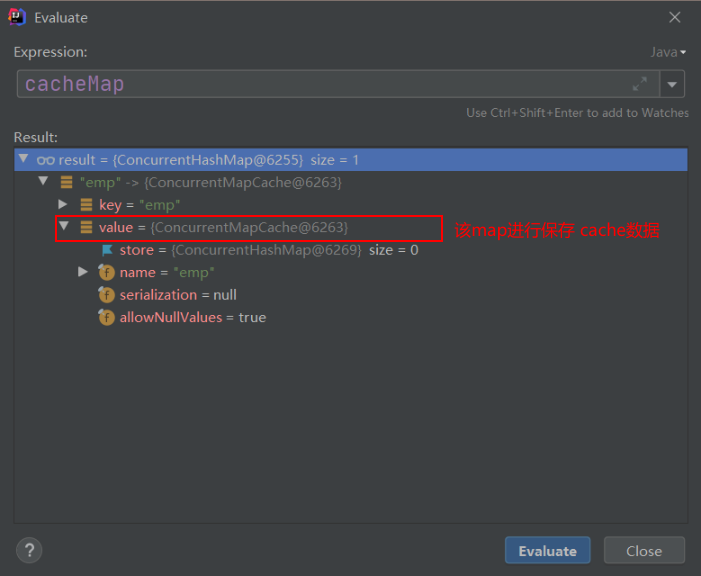
- 去 Cache中查找缓存地内容,使用一个 key,默认就是方法地参数。
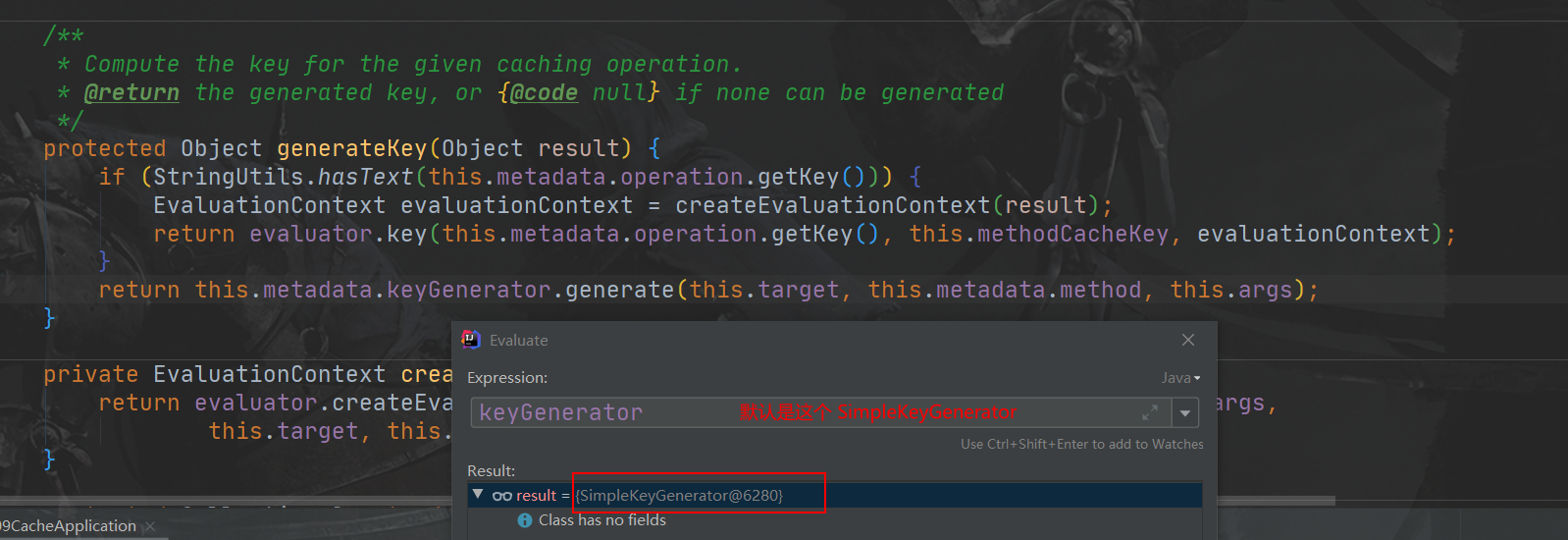
Object key = generateKey(context, result);key是按照某种策略生成地:默认是使用 keyGenerator生成地,默认使用地是 SimpleKeyGenerator生成 key
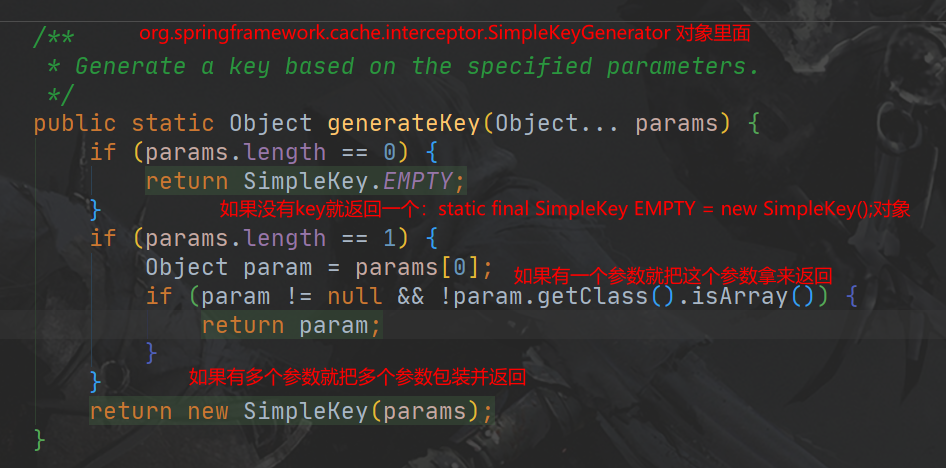
SimpleKeyGenerator生成 key的默认策略:如果没有参数:key = new SimpleKey(),如果有一个参数:key=参数的值,如果有多个参数:key=new SimpleKey(params)
- 没有查询到缓存就调用目标方法。
- 将目标方法返回的结果,放进缓存中
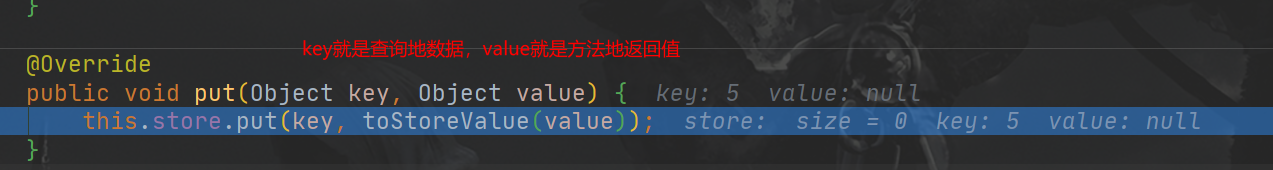
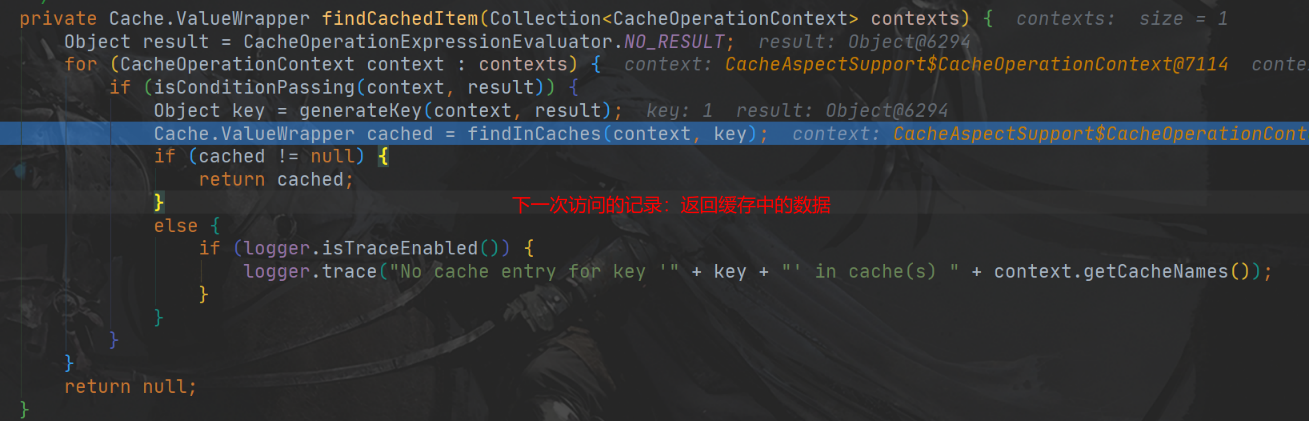
总结
- @Cacheable标注的方法执行之前先检查缓存中有没有这个数据,默认按照参数的值为 key去查询缓存,如果没有运行方法并将结果放入缓存,以后再来调用可以直接使用缓存中的数据。
- 核心:
- 使用 CacheManager【ConcurrentMapCacheManager】按照名字得到 Cache【ConcurrentMapCache】组件的。
- key 使用 keyGenerator生成的,默认是 SimpleKeyGenerator
五、整合 Redis实现缓存
Redis是一个开源的,内存中的数据结构存储系统,它可以作为数据库,缓存和消息中间件。
- 安装 redis:使用 docker
docker pull redis # docker 下载 redis docker images # 查看下载的 镜像 docker run -d -p 6379:6379 --name myredis redis # docker run运行 d后台运行 p暴露端口 name起一个自己的名字 运行的镜像名 docker ps #查看容器中运行的程序 - 引入spring-boot-starter-data-redis
<!--引入 redis的starter--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> </dependency> - application.yml配置redis连接地址
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration 配置了 redis的相关配置# redis配置 ,还有其他配置可以根据需求配置 spring.redis.host=localhost - 使用ReditTemplate操作redis
redisTemplate.opsForValue(); 操作字符串
redisTemplate.opsForHash(); 操作hash
redisTemplate.opsForList(); 操作list
redisTemplate.opsForSet(); 操作set
redisTemplate.opsForZSet(); 操作有序set
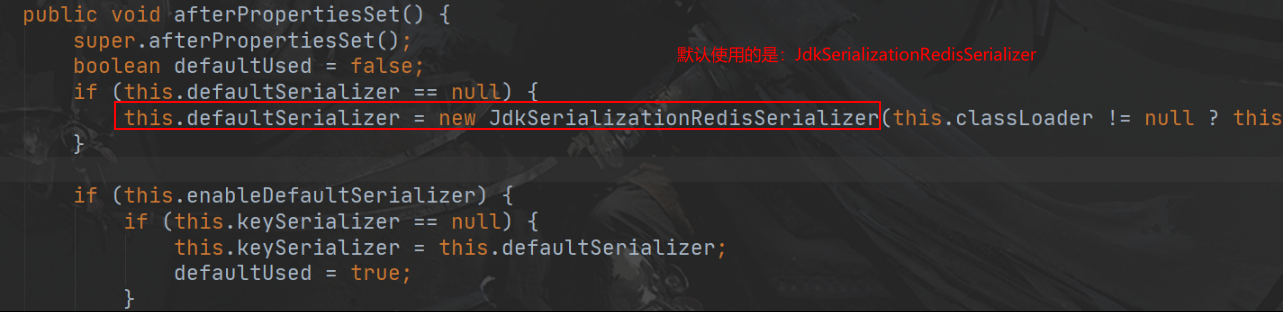
默认如果保存对象,使用 jdk序列化机制,序列化后的数据保存到 redis中//改变 redisTemplate的序列化规则为 json @Configuration public class MyRedisConfig { @Bean public RedisTemplate<Object, Employee> empRedisTemplate( RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) throws UnknownHostException { RedisTemplate<Object, Employee> template = new RedisTemplate<Object, Employee>(); template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory); //创建序列化器 json Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Employee> ser = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Employee>(Employee.class); template.setDefaultSerializer(ser); return template; } } - 配置缓存、CacheManagerCustomizers
- 原理:CacheManager==Cache 缓存组件来实际给缓存中存取数据
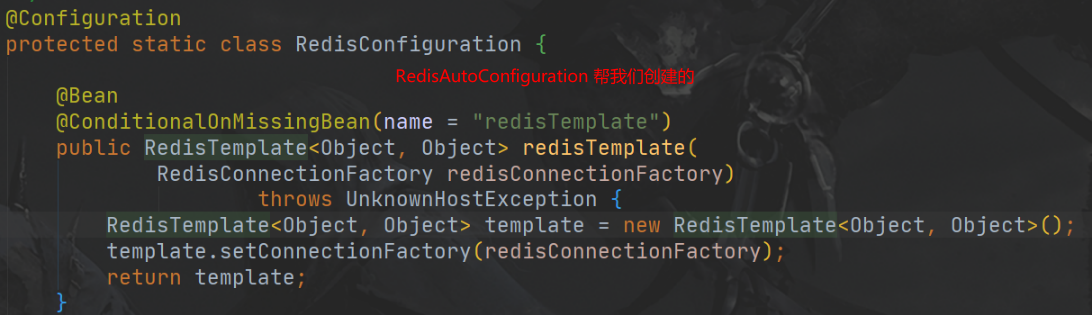
- 引入 redis的starter,容器中保存的是 RedisCacheManager
- RedisCacheManager帮我们创建缓存 RedisCache作为缓存组件。RedisCache通过操作 redis操作缓存数据的。
- 默认保存 k-v都是 object:利用序列化保存的;如何保存为 json?
- 引入了 redis的 start,cacheManager变为 RedisCacheManager
- 默认创建的 RedisCacheManager 操作 redis的时候使用的是
cacheManager(RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate)
- 自定义CacheManager
@Configuration public class MyRedisConfig { @Bean public RedisTemplate<Object, Employee> empRedisTemplate( RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) throws UnknownHostException { RedisTemplate<Object, Employee> template = new RedisTemplate<Object, Employee>(); template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory); //创建序列化器 json Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Employee> ser = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Employee>(Employee.class); template.setDefaultSerializer(ser); return template; } @Bean public RedisTemplate<Object, Department> deptRedisTemplate( RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) throws UnknownHostException { RedisTemplate<Object, Department> template = new RedisTemplate<Object, Department>(); template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory); //创建序列化器 json Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Department> ser = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Department>(Department.class); template.setDefaultSerializer(ser); return template; } //CacheManagerCustomizers可以来定制缓存的一些规则 @Primary //多个的情况下一定要标识:将某个缓存管理器作为默认的 @Bean public RedisCacheManager employeeCacheManager(RedisTemplate<Object, Employee> empRedisTemplate){ RedisCacheManager cacheManager = new RedisCacheManager(empRedisTemplate); //key多了一个前缀 //使用前缀,默认会将CacheName作为key的前缀 cacheManager.setUsePrefix(true); return cacheManager; } @Bean public RedisCacheManager deptCacheManager(RedisTemplate<Object, Department> deptRedisTemplate){ RedisCacheManager cacheManager = new RedisCacheManager(deptRedisTemplate); //key多了一个前缀 //使用前缀,默认会将CacheName作为key的前缀 cacheManager.setUsePrefix(true); return cacheManager; } } - 原理:CacheManager==Cache 缓存组件来实际给缓存中存取数据
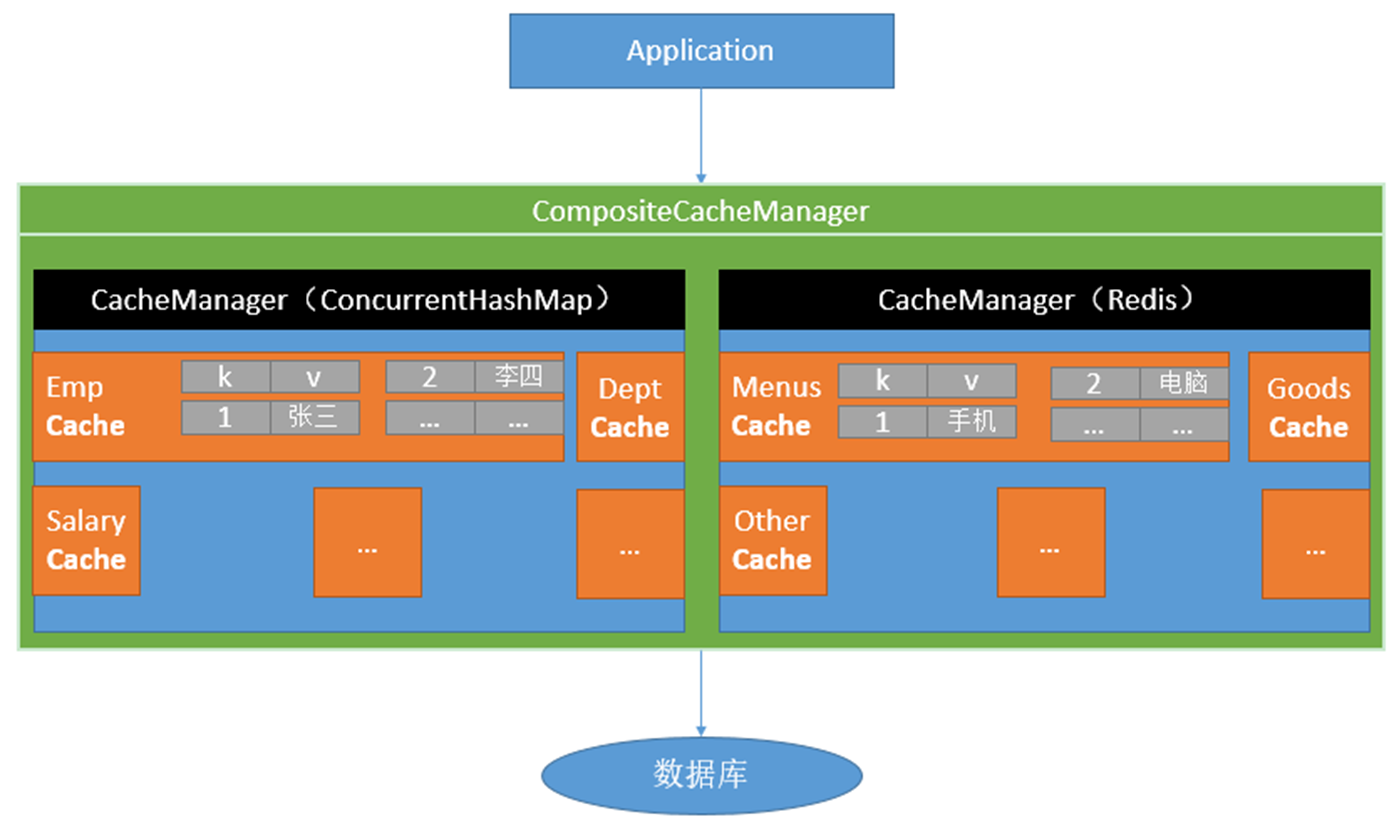
- 测试使用缓存、切换缓存、 CompositeCacheManager
//抽取缓存的公共配置,使用 employeeCacheManager的缓存管理器 //使用在类上 @CacheConfig(cacheNames="emp",cacheManager = "employeeCacheManager") //使用在方法上 @Cacheable(cacheNames = "dept",cacheManager = "deptCacheManager")















【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 一文读懂知识蒸馏
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下