Shiro笔记
Shiro 实战
1. 权限管理
1.1 什么是权限管理
- 基本.上涉及到用户参与的系统都要进行权限管理,权限管理属于系统安全的范畴,权限管理实现对用户访问系统的控制,按照安全规则或者安全策略控制用户可以访问而且只能访问自己被授权的资源。
- 权限管理包括用户身份认证和授权两部分,简称认证授权。对于需要访问控制的资源用户首先经过身份认证,认证通过后用户具有该资源的访问权限方可访问。|
1.2 什么是身份认证
- 身份认证,就是判断一个用户是否为合法用户的处理过程。最常用的简单身份认证方式是系统通过核对用户输入的用户名和口令,看其是否与系统中存储的该用户的用户名和口令-致,来判断用户身份是否正确。对于采用指纹等系统,则出示指纹;对于硬件Key等刷卡系统,则需要刷卡。
1.3 什么是授权
- 授权,即访问控制,控制谁能访问哪些资源。主体进行身份认证后需要分配权限方可访问系统的资源,对于某些资源没有权限是无法访问的
2. 什么式 Shiro
Apache Shiro™ is a powerful and easy-to-use Java security framework that performs
authentication, authorization, cryptography, and session management. With Shiro’s
easy-to-understand API, you can quickly and easily secure any application – from the
smallest mobile applications to the largest web and enterprise applications.
Apache Shiro是一个功能强大且易于使用的Java安全框架,用于执行身份验证、授权、加密和会话管
理。
通过Shiro易于理解的API,您可以快速、轻松地保护任何应用程序,从最小的移动应用程序到最大的web
和企业应用程序。
Shiro 是 apache旗下的一个开源框架,它将软件系统的安全认证相关的功能抽取出来,实现用户身份认证,权限授权,加密,会话管理,组成了一个通用的安全认证框架
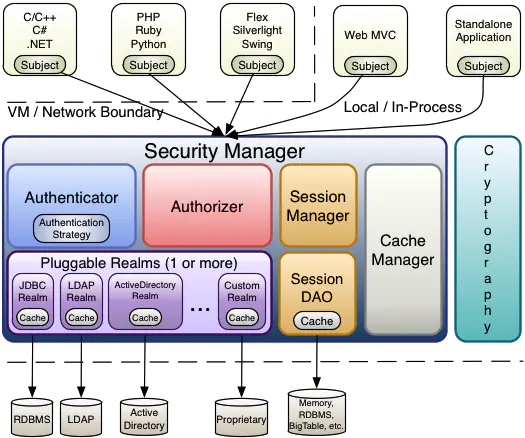
3. Shiro 的核心架构
3.1 Subject
- Subject即主体,外部应用与subject进行交互, subject记录 了当前操作用户,将用户的概念理解为当前操作的主体,可能是一个通过浏览器请求的用户,也可能是-个运行的程序。Subject在shiro中是一 个接口, 接口中定义了很多认证授相关的方法,外部程序通过subject进行认证授,而subject是 通过SecurityManager安全管理器进行认证授权
3.2 SecurityManager
- SecurityManager即安全管理器,对全部的subject进行安全管理, 它是shiro的核心, 负责对所有的subject进行安全管理。通过SecurityManager可以完成subject的认证、授权等,实质上SecurityManager是通过Authenticator进行认证,通过Authorizer进行授权,通过SessionManager进行会话管理等 。
- SecurityManager是一个接口, 继承了Authenticator, Authorizer, SessionManager这三个接口。
3.3 Authenticator
- Authenticator即认证器,对用户身份进行认证, Authenticator是一 个接口, shiro提供ModularRealmAuthenticator实现类,通过ModularRealmAuthenticator基本 上可以满足大多数需求,也可以自定义认证器。
3.4 Authorizer
- Authorizer即授权器, 用户通过认证器认证通过,在访问功能时需要通过授权器判断用户是否有此功能的操作权
3.5 Realm
- Realm即领域,相当于datasource数据源,securityManager进行安全认证需 要通过Realm获取用户权限数据,比如:如果
用户身份数据在数据库那么realm就需要从数据库获取用户身份信息。 - 注意:不要把realm理解成只是从数据源取数据,在realm中还有认证授权校验的相关的代码。
3.6 SessionManager
- sessionManager即会话管理,shiro框架定 义了一套会话管理, 它不依赖web容 器的session,所以shiro可以使用在非web应用上,也可以将分布式应用的会话集中在一点管理,此特性可使它实现单点登录。
3.7 SessionDAO
- SessionDAO即会话dao,是对session会话操作的一套接口,比如要将session存储到数据库,可以通过jdbc将会话存储到数据库。.
3.8 CacheManager
- CacheManager即缓存管理,将用户权限数据存储在缓存,这样可以提高性能。
3.9 Crytography
- Cryptography即密码管理,shiro提供了- 套加密/解密的组件, 方便开发。比如提供常用的散列、加/解密等功能。
4. Shiro中的认证
4.1 认证
- 身份认证,就是判断- -个用户是否为合法用户的处理过程。最常用的简单身份认证方式是系统通过核对用户输入的用户名和口令,看其是否与系统中存储的该用户的用户名和口令-致,来判断用户身份是否正确。
4.2 shiro 中认证的关键对象
- subject:主体
访问系统的用户,主体可以是用户,程序等,进行认证的都成为主题。 - principal:身份信息
是主体(subject)进行身份认证的标识,标识具有唯一性,如用户名,手机号,邮箱地址等,一个主体可以有多个身份,但是必须有一个主身份(primary principal) - credential:凭证信息
只有主体自己知道的安全信息,加密,证书等。
4.3 认证流程

4.4 认证开发
4.4.1 创建项目并引入依赖
<!--引入 shiro核心依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-core</artifactId>
<version>1.7.0</version>
</dependency>
4.4.2 引入 shiro配置文件并加入如下配置
- shiro配置文件以 ini结尾的配置文件;ini配置文件,用来学习 shiro书写我们系统中相关权限的数据
[users]
admi=1234
zhangsan=1234
lisi=1234
4.4.3 开发认证代码
public class TestAuthenticator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 创建安全管理器对象
// SecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultSecurityManager();
DefaultSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultSecurityManager();
//2. 给安全管理器设置 realm
securityManager.setRealm(new IniRealm("classpath:shiro.ini"));
//3. SecurityUtils 给全局安全工具类设置安全管理器
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
//4. 关键对象 subject (当前登陆的主体对象)主体
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
try {
//5. 创建令牌
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("admin", "123");
//认证状态
System.out.println("认证之前状态" + subject.isAuthenticated());
subject.login(token);// 用户认证
System.out.println("认证时候状态:" + subject.isAuthenticated());
} catch (UnknownAccountException e) {
System.out.println("认证失败,用户名不存在");
e.printStackTrace();//UnknownAccountException
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e) {
System.out.println("认证失败,密码错误");
e.printStackTrace();//IncorrectCredentialsException
}
}
}
- 认证:
- 最终执行用户名比较是在:SimpleAccountRealm类,执行
AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals)方法完成用户名校验。- 最终执行密码校验是在:AuthenticatingRealm类,执行
void assertCredentialsMatch(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info) throws AuthenticationException 方法完成密码校验
4.5 自定义 Realm
- 上边的程序使用的是 Shiro自带的 IniRealm,IniRealm从 ini配置文件中读取用户信息,大部分情况下需要从系统的数据库中读取用户信息,所以需要自定义 realm
1. shiro 提供的 realm
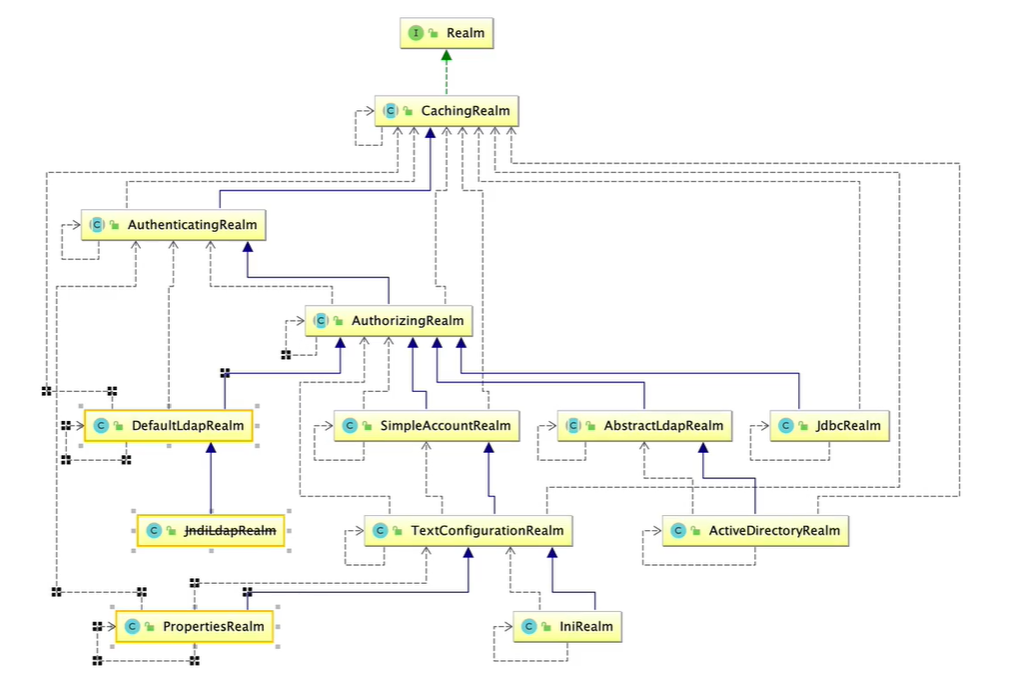
2. 根据认证源码认证使用的是 SimpleAccountRealm
public interface Realm
public abstract class CachingRealm implements Realm, Nameable, CacheManagerAware, LogoutAware
public abstract class AuthenticatingRealm extends CachingRealm implements Initializable
public abstract class AuthorizingRealm extends AuthenticatingRealm implements Authorizer, Initializable, PermissionResolverAware, RolePermissionResolverAware
public class SimpleAccountRealm extends AuthorizingRealm
- SimpleAccountRealm 的部分源码中有两个方法一个是认证一个是授权
ackage org.apache.shiro.realm;
public class SimpleAccountRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
//认证
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
UsernamePasswordToken upToken = (UsernamePasswordToken)token;
SimpleAccount account = this.getUser(upToken.getUsername());
if (account != null) {
if (account.isLocked()) {
throw new LockedAccountException("Account [" + account + "] is locked.");
}
if (account.isCredentialsExpired()) {
String msg = "The credentials for account [" + account + "] are expired";
throw new ExpiredCredentialsException(msg);
}
}
return account;
}
//授权
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
String username = this.getUsername(principals);
this.USERS_LOCK.readLock().lock();
AuthorizationInfo var3;
try {
var3 = (AuthorizationInfo)this.users.get(username);
} finally {
this.USERS_LOCK.readLock().unlock();
}
return var3;
}
}
总结
- AuthenticatingRealm 认证realm doGetAuthenticationInfo方法
- AuthorizingRealm 授权realm doGetAuthorizationInfo方法
3. 自定义 realm
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.SimpleAuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection;
/**
* 自定义 realm实现,目的:将认证/授权 数据的来源转为数据库的实现
*/
public class CustomerRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
//授权的
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection collection) {
return null;
}
//认证的
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
//在 token中获取用户名
String username = (String) token.getPrincipal();
System.out.println("principal = " + username);
//根据身份信息使用 jdbc mybatis查询相关数据库
if ("admin".equals(username)) {
//SimpleAuthenticationInfo(Object principal, Object credentials, String realmName)
//SimpleAuthenticationInfo(返回数据库中的正确用户名,返回数据库中的正确密码,提供当前 realm的名字【直接调用父类的就可】)
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo("admin", "1234", this.getName());
}
return null;
}
}
4. 使用自定义 realm认证
import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.IncorrectCredentialsException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UnknownAccountException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken;
import org.apache.shiro.mgt.DefaultSecurityManager;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject;
/**
* 使用自定义 realm
*/
public class TestCustomerRealmAuthenticator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 创建安全管理器对象
DefaultSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultSecurityManager();
//2. 给安全管理器设置 realm
securityManager.setRealm(new CustomerRealm());
//3. SecurityUtils 给全局安全工具类设置安全管理器
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
//4. 关键对象 subject (当前登陆的主体对象)主体
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
try {
//5. 创建令牌 token
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("admin", "1234");
//6. 用户认证
subject.login(token);
//状态
System.out.println(subject.isAuthenticated());
} catch (UnknownAccountException e) {
System.out.println("认证失败,用户名不存在");
e.printStackTrace();//UnknownAccountException
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e) {
System.out.println("认证失败,密码错误");
e.printStackTrace();//IncorrectCredentialsException
}
}
}
4.6使用 MD5 和 Salt
- md5 算法
作用:一般用来加密 或者 签名(校验)
特点:md5算法不可逆,无论相同内容执行多少次 md5生成的结果始终是一致的。
生成结果:始终是一个16进制32位长度字符串 - salt【随机盐】
- 实际应用是将盐和散列后的值存在数据库中,自动 realm从数据库取出盐和加密后的值由 shiro完成密码校验。
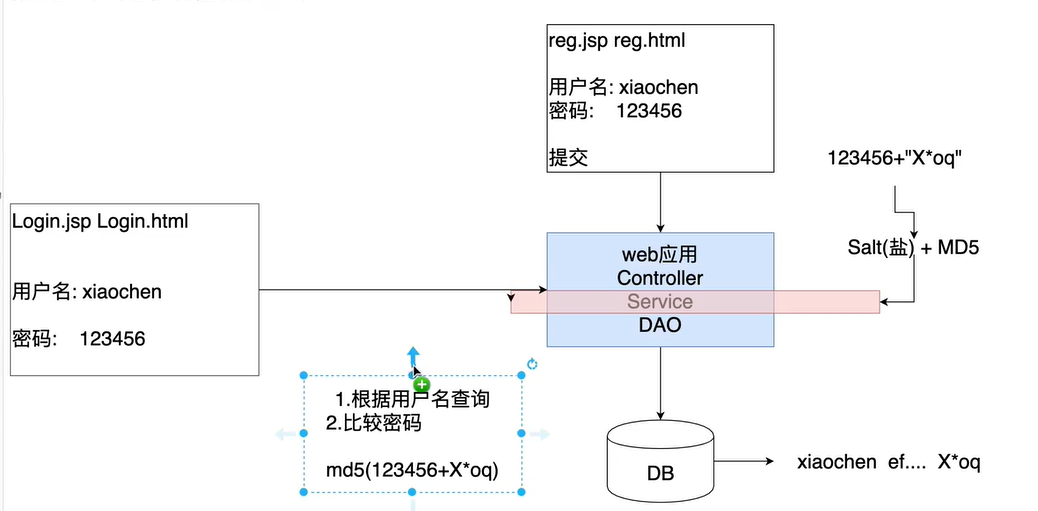
public class TestShiroMD5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建 md5算法
Md5Hash md5Hash = new Md5Hash();
md5Hash.setBytes("1234".getBytes());
System.out.println(md5Hash.toHex());//31323334
//使用 md5
System.out.println(new Md5Hash("1234").toHex());
//81dc9bdb52d04dc20036dbd8313ed055
//使用 md5 + salt处理
System.out.println(new Md5Hash("1234", "X0*7ps").toHex());
//6029a2a0be49f2d4f21941c8ae2cea0c
//使用 md5 + salt + hash散列
System.out.println(new Md5Hash("1234", "X0*7ps", 1024).toHex());
//67cdf0cac7bdd508f560ef7965e8934c
}
}
1.自定义 md5 的 realm
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.SimpleAuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection;
public class CustomerMd5Realm extends AuthorizingRealm {
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
return null;
}
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
//1. 获取身份信息
String username = (String) token.getPrincipal();
//2. 根据用户名查询数据库
if ("admin".equals(username)) {
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(username, "81dc9bdb52d04dc20036dbd8313ed055", this.getName());
}
return null;
}
}
2. 使用 md5 认证
import com.cianiao.realm.CustomerMd5Realm;
import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.*;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.credential.HashedCredentialsMatcher;
import org.apache.shiro.mgt.DefaultSecurityManager;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject;
public class TestCustomerMd5Realm {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 创建安全管理器对象
DefaultSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultSecurityManager();
//2. 给安全管理器设置 realm
CustomerMd5Realm realm = new CustomerMd5Realm();
//设置 realm使用 hash凭证匹配器
realm.setCredentialsMatcher(new HashedCredentialsMatcher("md5"));
securityManager.setRealm(realm);
//3. SecurityUtils 给全局安全工具类设置安全管理器
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
//4. 通过安全工具类获取关键对象 subject (当前登陆的主体对象)主体
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//5. 创建令牌 token
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("admin", "1234");
try {
//6. 用户认证
subject.login(token);
//状态
if (subject.isAuthenticated()) {
System.out.println("登陆成功!");
}
} catch (UnknownAccountException e) {
System.out.println("认证失败,用户名不存在");
e.printStackTrace();//UnknownAccountException
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e) {
System.out.println("认证失败,密码错误");
e.printStackTrace();//IncorrectCredentialsException
}
}
}
3. 使用 MD5+salt 认证
public class CustomerMd5Realm extends AuthorizingRealm {
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
return null;
}
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
//1. 获取身份信息
String username = (String) token.getPrincipal();
//2. 根据用户名查询数据库
if ("admin".equals(username)) {
//添加随机盐
//参数:数据库用户名,数据库 md5+salt加密的密码,注册时的随机盐,realm的名字
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(
username,
"6029a2a0be49f2d4f21941c8ae2cea0c",
ByteSource.Util.bytes("X0*7ps"),
this.getName());
}
return null;
}
}
- 这里 realm已经把 随机盐给了,所以 shiro就自动加上 盐去处理。
4.自定义 md5+salt+hash 的 realm
略:同上代码一样
5. 使用 md5+salt+hash 认证
public class TestCustomerMd5Realm {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 创建安全管理器对象
DefaultSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultSecurityManager();
//2. 给安全管理器设置 realm
CustomerMd5Realm realm = new CustomerMd5Realm();
//设置 realm使用 hash凭证匹配器
HashedCredentialsMatcher matcher =
//设置加密方式【使用的算法】
new HashedCredentialsMatcher("md5");
//设置 hash散列了多少此
matcher.setHashIterations(1024);
realm.setCredentialsMatcher(matcher);
securityManager.setRealm(realm);
//3. SecurityUtils 给全局安全工具类设置安全管理器
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
//4. 通过安全工具类获取关键对象 subject (当前登陆的主体对象)主体
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//5. 创建令牌 token
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("admin", "1234");
try {
//6. 用户认证
subject.login(token);
//状态
if (subject.isAuthenticated()) {
System.out.println("登陆成功!");
}
} catch (UnknownAccountException e) {
System.out.println("认证失败,用户名不存在");
e.printStackTrace();//UnknownAccountException
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e) {
System.out.println("认证失败,密码错误");
e.printStackTrace();//IncorrectCredentialsException
}
}
5. shiro 中的授权
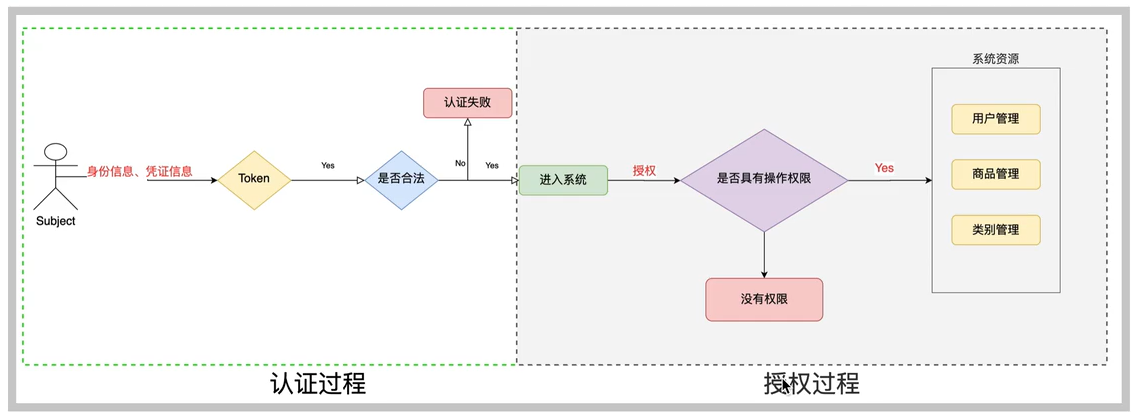
5.1 授权
- 授权,即访问控制,控制谁能访问那些资源,主体进行身份认证后需要分配权限方可访问系统的资源,对于某些资源没有权限是无法访问的。
5.2 关键对象
- 授权可简单理解为 who对 what(which)进行 how操作:
who,即主体(Subject),主体需要访问系统中的资源。what,即资源(Resource),如系统菜单,页面,按钮,类方法,系统商品信息等,资源包括资源类型和资源实例,比如商品信息为资源类型,类型为 t01的商品为资源实例,编号 001的商品信息也属于资源实例。how,权限/许可(Permission),
5.3 授权流程
5.4 授权方式
- 基于角色的访问控制
rbac基于角色的访问控制(role based access control)是以角色为中心进行访问控制if(subject.hasRole("admin")){ //具体操作什么资源 } - 基于资源的访问控制
rbac基于资源的访问控制(resource based access control)是以资源为中心访问控制if(subject.isPermission("user:*create")){//谁 对那些资源 有甚麽样的权限 //控制 user这一类的所有用户的创建权限 } if(subject.isPermission("user:update:01")){//资源实例 //对01用户进行修改 } if(subject.isPermission("user:update:*")){//资源类型 //对01用户进行修改 }
5.5 权限字符串
- 权限字符串的规则是:资源标识符:操作:资源实例标识符,意思是对哪个资源的哪个实例具有什么操作,“.”是资源/操作/实例的分割符,权限字符串也可以使用*通配符。
- 例子
- 用户创建权限:user:create 或 user:create:*
- 用户修改实例001:user:update:001
- 用户实例001的所有权限:user:*:001
5.6 shiro 中授权编程实现方式
编程式:
Subject subject =SecurityUtils.getSubject();
if(subject.hasRole("admin")){
//有权限
}else{
//无权限
}
注解式:
@RecuresRoles("admin")
public void hello(){
//有权限
}
标签式:
jsp/gsp 标签:在jsp、gsp页面通过相应的标签完成
<shiro:hasRole name="admin"
<!--有权限-->
</shiro:hasRole>
注意:thymeleaf 中使用shiro需要额外集成!!!
5.7 开发授权
1. realm 的实现
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.SimpleAuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.SimpleAuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection;
import org.apache.shiro.util.ByteSource;
public class CustomerMd5Realm extends AuthorizingRealm {
//授权 PrincipalCollection:身份集合
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
System.out.println("============");
//根据身份集合获取主身份信息
String principal = (String) principalCollection.getPrimaryPrincipal();
System.out.println("身份信息(用户名) = " + principal);//admin
//根据用户名查询数据库,查看该用户的角色信息,以及权限信息
//返回一个权限信息
SimpleAuthorizationInfo authorizationInfo = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
//将数据库中查询校色信息赋值给权限对象
authorizationInfo.addRole("admin");
authorizationInfo.addRole("user");
//将数据库中查询权限信息赋值给权限对象
authorizationInfo.addStringPermission("admin:*:01");
return authorizationInfo;
}
//验证
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
//1. 获取身份信息
String username = (String) token.getPrincipal();
//2. 根据用户名查询数据库
if ("admin".equals(username)) {
//添加随机盐
//参数:数据库用户名,数据库 md5+salt加密的密码,注册时的随机盐,realm的名字
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(
username,
"67cdf0cac7bdd508f560ef7965e8934c",
ByteSource.Util.bytes("X0*7ps"),
this.getName());
}
return null;
}
}
2. 授权
import com.cianiao.realm.CustomerMd5Realm;
import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.*;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.credential.HashedCredentialsMatcher;
import org.apache.shiro.mgt.DefaultSecurityManager;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class TestCustomerMd5Realm {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 创建安全管理器对象
DefaultSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultSecurityManager();
//2. 给安全管理器设置 realm
CustomerMd5Realm realm = new CustomerMd5Realm();
//设置 realm使用 hash凭证匹配器
HashedCredentialsMatcher matcher =
//设置加密方式【使用的算法】
new HashedCredentialsMatcher("md5");
//设置 hash散列了多少此
matcher.setHashIterations(1024);
realm.setCredentialsMatcher(matcher);
securityManager.setRealm(realm);
//3. SecurityUtils 给全局安全工具类设置安全管理器
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
//4. 通过安全工具类获取关键对象 subject (当前登陆的主体对象)主体
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//5. 创建令牌 token
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("admin", "1234");
try {
//6. 用户认证
subject.login(token);
//状态
if (subject.isAuthenticated()) {
System.out.println("登陆成功!");
}
} catch (UnknownAccountException e) {
System.out.println("认证失败,用户名不存在");
e.printStackTrace();//UnknownAccountException
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e) {
System.out.println("认证失败,密码错误");
e.printStackTrace();//IncorrectCredentialsException
}
//7. 认证用户进行授权
if (subject.isAuthenticated()) {
//1. 基于(单)角色权限控制
//boolean hasRole(String roleIdentifier)
System.out.println("1~~~~~~~~~~~~~~");
System.out.println(subject.hasRole("admin"));//true
//2. 基于(多)角色权限控制
//boolean hasAllRoles(Collection<String> roleIdentifiers)
System.out.println("2~~~~~~~~~~~~~~");
System.out.println(subject.hasAllRoles(Arrays.asList("admin", "zhangsan")));//false
//3. 是否具有其中一个角色
//boolean[] hasRoles(List<String> roleIdentifiers)
System.out.println("3~~~~~~~~~~~~~~");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(subject.hasRoles(Arrays.asList("admin", "user"))));//[true, true]
//4. 基于权限字符串的访问控制【资源标识符:操作:资源类型】
//boolean isPermitted(String permission)
System.out.println("4~~~~~~~~~~~~~~");
System.out.println(subject.isPermitted("admin:*:*"));//false
System.out.println(subject.isPermitted("admin:*:01"));//true
System.out.println(subject.isPermitted("admin:update:01"));//true
//5. 分别具有那些权限
//boolean[] isPermitted(String... permissions)
//boolean[] isPermitted(List<Permission> permissions)
System.out.println("5~~~~~~~~~~~~~~");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(subject.isPermitted("admin:*:01", "admin:*:*")));//[true, false]
//6. 同时具有那些权限
//boolean isPermittedAll(String... permissions)
//boolean isPermittedAll(Collection<Permission> permissions)
System.out.println("6~~~~~~~~~~~~~~");
System.out.println(subject.isPermittedAll("admin:*:01", "admin:*:*"));//false
}
}
}
6. 整合 spring boot项目实战
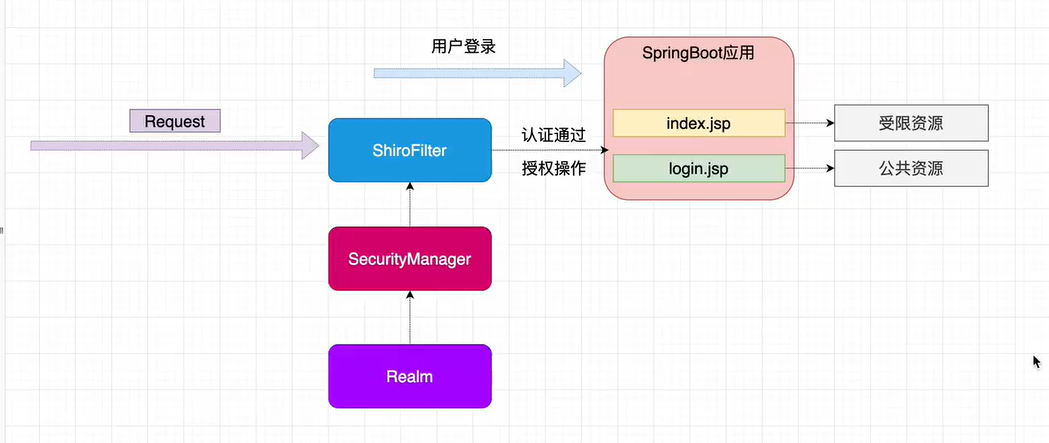
6.1 整合 spring boot 项目
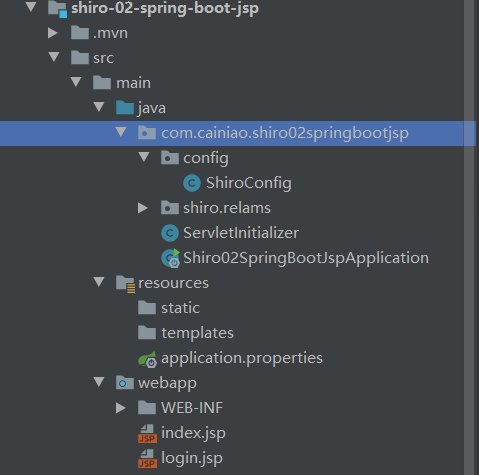
6.2 引入 shiro依赖
<!--引入 shiro依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.7.0</version>
</dependency>
<!--引入 tomcat解析 jsp依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--jstl-->
<dependency>
<groupId>jstl</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
6.3 application.properties配置
spring.application.name=shiro
server.port=8080
#server.servlet.context-path=/shiro
#设置模板为 jsp
spring.mvc.view.prefix=/
spring.mvc.view.suffix=.jsp
6.4 配置 shiro环境
1. ShiroConfig 配置类
mport com.cainiao.shiro02springbootjsp.shiro.relams.CustomerRealms;
import org.apache.shiro.realm.Realm;
import org.apache.shiro.spring.web.ShiroFilterFactoryBean;
import org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author shkstart
* 用来整合 shiro框架相关的配置类
*/
@Configuration
public class ShiroConfig {
//1. 创建 shiroFilter;负责拦截所有请求【设置对应的过滤条件和跳转条件】
@Bean
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean getShiroFilterFactoryBean(DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager) {
ShiroFilterFactoryBean filter = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
//1. 给 filter设置安全管理器
filter.setSecurityManager(defaultWebSecurityManager);
//2. 配置系统受限资源
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
//k:资源路径 , v:受限的权限
/*
* 这里忘记添加后缀了导致耽误许久
* */
map.put("/index.jsp", "authc"); //authc 请去这个资源需要认证和授权
filter.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(map);
//默认认证界面路径
filter.setLoginUrl("/login.jsp");
//3. 配置系统公共资源
return filter;
}
//2. 创建安全管理器【权限管理,配置主要是Realm的管理认证】
@Bean
public DefaultWebSecurityManager getDefaultWebSecurityManager(Realm realm) {
DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
//给安全管理器设置 realm
securityManager.setRealm(realm);
return securityManager;
}
//3. 创建自定义 realm【将自己的验证方式加入容器】
@Bean(name = "realm") //设立需要指定一下创建 bean的别名,否则上面报错
public Realm getRealm() {
return new CustomerRealms();
}
}
2. CustomerRealms relams类
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection;
/**
* @author shkstart
* 自定义 realm
*/
public class CustomerRealms extends AuthorizingRealm {
//授权
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
return null;
}
//验证
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {
return null;
}
}
3. jsp 页面
index.jsp,内容略
login.jsp,内容略
4. 重启项目
- 此时项目范围 localhost:index.jsp,此时跳转到login.jsp
6.4 常见过滤器
- 注意:shiro提供和多个默认的过滤器,我们可以用这些过滤器来配置控制指定的url的权限
| 配置缩写 | 对应的过滤器 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| anon | AnonymousFilter | 指定url可以匿名访问 |
| authc | BasicHttpAuthenticationFilter | 指定url需要form表单登录,默认会从请求中获取 username,password,remembrMe等参数并尝试登录,如果登录不了就会跳转到 loginUrl配置的路径。我们可以用这个过滤器做默认的登录逻辑,但是一般都是我们自己在控制器写登录逻辑的,自己写的话出错返回的信息都可以定制 |
| authcBasic | BasicHttpAuthenicationFilter | 指定url需要basic登录 |
| logout | LogoutFilter | 登出过滤器,配置指定url就可以是心啊推出功能,非常方便 |
| noSessionCreation | NoSessionCreationFilter | 禁止创建会话 |
| perms | PermissionsAuthorizationFilter | 需要指定权限才能访问 |
| port | PortFilter | 需要指定端口才能访问 |
| roles | RolesAuthorizationFilter | 需要指定角色才能访问 |
| ssl | SslFilter | 需要https请求才能访问 |
| user | UserFilter | 需要已登录或者“记住我”的用户才能访问 |
6.5 简单实现认证和退出
添加UserController类
@Controller
@RequestMapping("user")
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("logout")
public String logout() {
//获取主体对象
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//退出
subject.logout();
return "redirect:/login.jsp";
}
/**
* 处理身份认证
*
* @param username
* @param password
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("login")
public String login(String username, String password) {
//获取主体对象
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
try {
//用户认证
subject.login(new UsernamePasswordToken(username, password));
return "redirect:/index.jsp";
} catch (UnknownAccountException e) {
e.printStackTrace();//UnknownAccountException
System.out.println("认证失败,用户名不存在");
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e) {
e.printStackTrace();//IncorrectCredentialsException
System.out.println("认证失败,密码错误");
}
return "redirect:/login.jsp";
}
}
修改 ShiroConfig类【整合 shiro框架相关的配置类】
//1. 创建 shiroFilter;负责拦截所有请求【设置对应的过滤条件和跳转条件】
@Bean
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean getShiroFilterFactoryBean(DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager) {
ShiroFilterFactoryBean filter = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
//1. 给 filter设置安全管理器
filter.setSecurityManager(defaultWebSecurityManager);
//2. 配置系统受限资源
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
//k:资源路径 , v:受限的权限
/*
* 这里忘记添加后缀了导致耽误许久
* */
// map.put("/index.jsp", "authc"); //authc 请去这个资源需要认证和授权
/*
* 不受限的资源放在上面,受限的放在下面
* */
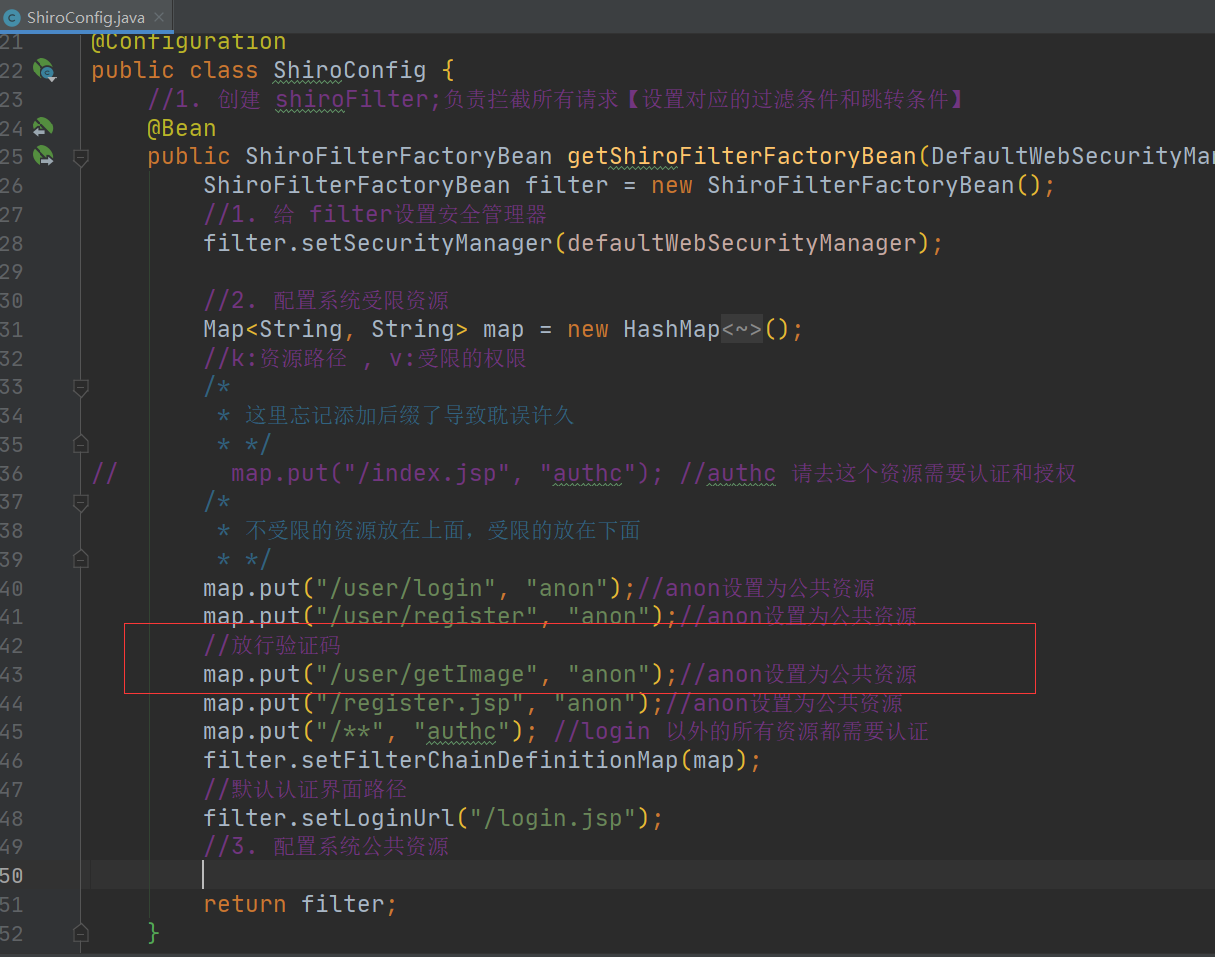
map.put("/user/login", "anon");//anon设置为公共资源
map.put("/**", "authc"); //login 以外的所有资源都需要认证
filter.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(map);
//默认认证界面路径
filter.setLoginUrl("/login.jsp");
//3. 配置系统公共资源
return filter;
}
修改 CustomerRealms类【自定义的 realm】
//验证
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
//1. 获取身份信息
String username = (String) token.getPrincipal();
//2. 根据用户名查询数据库
if ("admin".equals(username)) {
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(username, "1234", this.getName());
}
return null;
}
index.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>首页</h2>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/user/logout">退出</a>
<h2>受限资源</h2>
</body>
</html>
login.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>登陆页面</h2>
<h2>公共资源</h2>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/user/login" method="post">
用户名<input type="text" name="username"><br>
密码<input type="password" name="password"><br>
<input type="submit" value="登录">
</form>
</body>
</html>
6.6 实现 md5+salt注册和认证功能
注册功能
- 开发注册页面 register.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>注册页面</h2>
<h2>公共资源</h2>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/user/register" method="post">
用户名<input type="text" name="username"><br>
密码<input type="password" name="password"><br>
<input type="submit" value="注册">
</form>
</body>
</html>
- 创建数据库表结构
CREATE TABLE `test`.`t_user`(
`id` INT(6) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`username` VARCHAR(40),
`password` VARCHAR(40),
`salt` VARCHAR(255),
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
);
- 项目引入依赖
<!--mybatis 相关依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.2.0</version>
</dependency>
<!--mysql-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- druid 依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.19</version>
</dependency>
- 配置 application.properties配置文件
spring.application.name=shiro
server.port=8080
#server.servlet.context-path=/shiro
#设置模板为 jsp
spring.mvc.view.prefix=/
spring.mvc.view.suffix=.jsp
#配置数据源相关的配置
spring.datasource.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
#spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver #mysql 8的配置
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?characterEncoding=utf-8
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
#mybatis整合相关
mybatis.type-aliases-package=com.cainiao.shiro02springbootjsp.entity
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:com.cainiao.mapper/*.xml
#查看日志
#logging.level.root=debug
#logging.level.com.cainiao.shiro02springbootjsp.dao=debug
- 创建 entity【实体类】
@Data
@Accessors(chain = true)//链式调用
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ToString
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String salt;
}
- 创建 dao接口
@Repository
public interface UserDao {
void save(User user);
}
- 开发 mapper 文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.cainiao.shiro02springbootjsp.dao.UserDao">
<insert id="save" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id"
parameterType="com.cainiao.shiro02springbootjsp.entity.User">
insert into t_user values (#{id},#{username},#{password},#{salt})
</insert>
</mapper>
- 开发service接口
public interface UserService {
//注册用户方法
void register(User user);
}
- 创建 salt工具类
public class SaltUtils {
/**
* 生成 salt 的静态方法
*
* @return
*/
public static String getSalt(int n) {
char[] chars = "abcdefghigklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIGKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ1234567890~!@#$%^&*()-=_{}|';<>/?,.".toCharArray();
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
str.append(chars[(int) (Math.random() * chars.length )]);
}
return str.toString();
}
}
- 开发 service实现类
@Service
@Transactional
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
@Override
public void register(User user) {
//处理业务调用dao
//生成随机盐
String salt = SaltUtils.getSalt(8);
//将随机盐保存到数据
user.setSalt(salt);
//明文密码进行 md5 + salt + hash 散列
Md5Hash md5Hash = new Md5Hash(user.getPassword(), salt, 1024);
user.setPassword(md5Hash.toHex());//将密码加密
userDao.save(user);//将 user保存到数据库
}
}
- 开发 controller
@Controller
@RequestMapping("user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
/**
* 用户注册
*
* @param user
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("register")
public String register(User user) {
try {
userService.register(user);
return "redirect:/login.jsp";
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return "redirect:/register.jsp";
}
}
}
- 修改 ShiroConfig 配置类
@Configuration
public class ShiroConfig {
//1. 创建 shiroFilter;负责拦截所有请求【设置对应的过滤条件和跳转条件】
@Bean
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean getShiroFilterFactoryBean(DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager) {
ShiroFilterFactoryBean filter = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
//1. 给 filter设置安全管理器
filter.setSecurityManager(defaultWebSecurityManager);
//2. 配置系统受限资源
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
//k:资源路径 , v:受限的权限
/*
* 这里忘记添加后缀了导致耽误许久
* */
// map.put("/index.jsp", "authc"); //authc 请去这个资源需要认证和授权
/*
* 不受限的资源放在上面,受限的放在下面
* */
map.put("/user/login", "anon");//anon设置为公共资源
map.put("/user/register", "anon");//anon设置为公共资源【主要这里做修改】
map.put("/register.jsp", "anon");//anon设置为公共资源【主要这里做修改】
map.put("/**", "authc"); //login 以外的所有资源都需要认证
filter.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(map);
//默认认证界面路径
filter.setLoginUrl("/login.jsp");
//3. 配置系统公共资源
return filter;
}
}
- main入口修改
@MapperScan("com.cainiao.shiro02springbootjsp.dao") //添加这个就好
- 启动项目注册
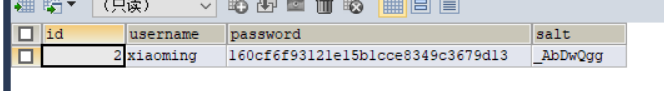
认证
- UserDao 新增方法
User findUserByName(String name);
- mapper 新增查询
<select id="findUserByName" parameterType="string"
resultType="com.cainiao.shiro02springbootjsp.entity.User">
select id,username,password,salt from
t_user where username=#{username}
</select>
- service接口新增方法
//根据用户名查询 user
User findUserByName(String name);
- service接口方法实现
@Override
public User findUserByName(String name) {
try {
return userDao.findUserByName(name);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
- 开发在工厂中获取 bean对象的工具类
@Component
public class ApplicationContextUtils implements ApplicationContextAware {
private static ApplicationContext context;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.context = applicationContext;
}
//根据 bean名字获取工程中指定 bean对象
public static Object getBean(String beanName) {
return context.getBean(beanName);
}
}
- 修改自定义 realm
public class CustomerRealms extends AuthorizingRealm {
//授权
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
return null;
}
//验证
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
//1. 获取身份信息
String username = (String) token.getPrincipal();
//2. 根据用户名查询数据库
//在工程中获取 service对象 【默认类型小写】
UserService userService = (UserService) ApplicationContextUtils.getBean("userServiceImpl");
User user = userService.findUserByName(username);
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(user)) {
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(
user.getUsername(), user.getPassword(),
ByteSource.Util.bytes(user.getSalt()), this.getName());
}
return null;
}
}
- 修改 ShiroConfig配置类的 realm使用凭证匹配器以及hash散列
//3. 创建自定义 realm【将自己的验证方式加入容器】
@Bean(name = "realm") //设立需要指定一下创建 bean的别名,否则上面报错
public Realm getRealm() {
CustomerRealms realms = new CustomerRealms();
//修改 凭证校验匹配器
HashedCredentialsMatcher credentialsMatcher = new HashedCredentialsMatcher();
//设置加密算法为 md5
credentialsMatcher.setHashAlgorithmName("MD5");
//设置散列次数
credentialsMatcher.setHashIterations(1024);
//设置凭证校验匹配器
realms.setCredentialsMatcher(credentialsMatcher);
return realms;
}
6.7 授权实现
6.7.1 没有数据库
1. 页面资源授权
- 自定义的CustomerRealms类
//授权
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
//获取身份信息
String principal = (String) principalCollection.getPrimaryPrincipal();
System.out.println("调用授权验证" + principal);
//根据主身份信息获取角色信息 和 权限信息
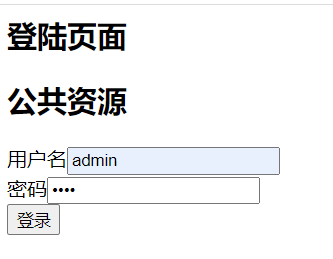
if ("admin".equals(principal)) {
SimpleAuthorizationInfo authorizationInfo = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
authorizationInfo.addRole("admin");// 如果admin登录的话它是一个管理员角色
authorizationInfo.addRole("user");// 如果admin登录的话它是一个管理员角色
authorizationInfo.addStringPermission("user:*:*");//增加权限字符串【资源标识符:操作:资源类型资源实例】
return authorizationInfo;
}
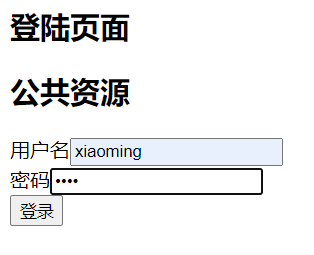
if ("xiaoming".equals(principal)) {
SimpleAuthorizationInfo authorizationInfo = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
authorizationInfo.addRole("user");// 如果admin登录的话它是一个管理员角色
authorizationInfo.addStringPermission("user:update:*");//增加权限字符串【资源标识符:操作:资源类型资源实例】
authorizationInfo.addStringPermission("user:query:*");//增加权限字符串【资源标识符:操作:资源类型资源实例】
return authorizationInfo;
}
return null;
}
- index.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@taglib prefix="shiro" uri="http://shiro.apache.org/tags" %>
<%--引入shiro标签库--%>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>首页</h2>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/user/logout">退出</a>
<h2>受限资源</h2>
<ul>
<shiro:hasAnyRoles name="user,admin">
<li>用户管理</li>
<ul>
<shiro:hasPermission name="user:add:*">
<li><a href="#">添加用户</a></li>
</shiro:hasPermission>
<shiro:hasPermission name="user:update:*">
<li><a href="#">修改用户</a></li>
</shiro:hasPermission>
<shiro:hasPermission name="user:delete:*">
<li><a href="#">删除用户</a></li>
</shiro:hasPermission>
<shiro:hasPermission name="order:query:*">
<li><a href="#">查询用户</a></li>
</shiro:hasPermission>
</ul>
</shiro:hasAnyRoles>
<shiro:hasRole name="admin">
<li>商品管理</li>
<li>订单管理</li>
<li>物理管理</li>
</shiro:hasRole>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
2. 代码方式授权
@Controller
@RequestMapping("order")
public class OrderController {
@RequestMapping("save")
public String save() {
//获取主体对象
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//代码方式授权
if (subject.hasRole("admin")) {
System.out.println("保存订单");
} else {
System.out.println("无权限访问");
}
return "redirect:/index.jsp";
}
}
3. 方法(注解)调用授权
@Controller
@RequestMapping("order")
public class OrderController {
@RequestMapping("save")
// @RequiresRoles("admin")//基于角色进行授权
// @RequiresRoles({"admin", "user"})//同时具有相同角色 【同时具有 admin和user权限】
@RequiresPermissions("user:update:01") //基于权限进行授权
public String save() {
System.out.println("进入方法");
return "redirect:/index.jsp";
}
}
6.7.2 连接数据库
1. 授权数据持久化

/*
SQLyog Ultimate v10.00 Beta1
MySQL - 5.5.49 : Database - test
*********************************************************************
*/
/*!40101 SET NAMES utf8 */;
/*!40101 SET SQL_MODE=''*/;
CREATE DATABASE /*!32312 IF NOT EXISTS*/`test`
USE `test`;
/*Table structure for table `t_pers` */
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_pers`;
CREATE TABLE `t_pers` (
`id` int(6) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(80) DEFAULT NULL,
`url` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=4 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
/*Data for the table `t_pers` */
insert into `t_pers`(`id`,`name`,`url`) values (1,'user:*:*',NULL),(2,'product:*:01',NULL),(3,'order:*:*',NULL);
/*Table structure for table `t_role` */
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_role`;
CREATE TABLE `t_role` (
`id` int(6) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(60) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=4 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
/*Data for the table `t_role` */
insert into `t_role`(`id`,`name`) values (1,'admin'),(2,'user'),(3,'product');
/*Table structure for table `t_user` */
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_user`;
CREATE TABLE `t_user` (
`id` int(6) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`username` varchar(40) DEFAULT NULL,
`password` varchar(40) DEFAULT NULL,
`salt` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=3 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
/*Data for the table `t_user` */
insert into `t_user`(`id`,`username`,`password`,`salt`) values (1,'admin','f4aa059ebf4268292ead6706a03c9754','|aA!Hx,X'),(2,'xiaoming','cd888f135685219643187c207b470d91','zIivni;9');
/*Table structure for table `t_user_role` */
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_user_role`;
CREATE TABLE `t_user_role` (
`id` int(6) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`userid` int(6) DEFAULT NULL,
`roleid` int(6) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=4 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
/*Data for the table `t_user_role` */
insert into `t_user_role`(`id`,`userid`,`roleid`) values (1,1,1),(2,2,2),(3,2,3);
2. 创建实体类
// 用户
@Data
@Accessors(chain = true)//链式调用
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ToString
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String salt;
//定义角色集合
private List<Role> roles;
}
// 权限信息
@Data
@Accessors(chain = true)//链式调用
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ToString
public class Perms {
private String id;
private String name;
private String url;
}
// 角色信息
@Data
@Accessors(chain = true)//链式调用
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ToString
public class Role {
private Integer id;
private String name;
//定义权限的集合
private List<Perms> perms;
}
3. 创建 dao方法
/*
* 在dao接口使用 @mapper注解
* 或者在main程序入口使用注解
* @MapperScan("com.xxx.xxx.dao"})
* */
//@Mapper
@Repository
public interface UserDao {
//根据用户名查询所有角色集合
User findRolesByUserName(String name);
//根据角色id查询 权限信息集合
List<Perms> findPermsByRoleId(Integer id);
}
4. mapper实现
<mapper namespace="com.cainiao.shiro02springbootjsp.dao.UserDao">
<!--封装 resultMap -->
<resultMap id="userType" type="com.cainiao.shiro02springbootjsp.entity.User">
<id column="uid" property="id"/>
<result column="username" property="username"/>
<!--角色信息[集合]-->
<collection property="roles" javaType="list" ofType="com.cainiao.shiro02springbootjsp.entity.Role">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="rname" property="name"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="findRolesByUserName" parameterType="string"
resultMap="userType">
SELECT u.`id` uid,u.`username`,r.`id`,r.`name` rname
FROM t_user u
LEFT JOIN t_user_role ur
ON u.`id`=ur.`userid`
LEFT JOIN t_role r
ON r.`id`=ur.`roleid`
WHERE u.`username`=#{username};
</select>
<select id="findPermsByRoleId" parameterType="integer" resultType="com.cainiao.shiro02springbootjsp.entity.Perms">
SELECT p.id,p.name,p.url,r.name
FROM t_role r
LEFT JOIN t_role_pers rp
ON r.id=rp.roleid
LEFT JOIN t_pers p
ON rp.persid=p.id
WHERE r.id =#{id};
</select>
</mapper>
5.Service接口
public interface UserService {
// //根据用户名查询所有角色
User findRoleByUsername(String username);
//根据角色 id查询权限集合
List<Perms> findPermsByRoleId(Integer id);
}
6.Service实现
@Service
@Transactional
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
/*
* @Autowired
* private UserDao userDao;
* 等同于
* private final UserDao userDao;
* public UserServiceImpl(UserDao userDao) {
* this.userDao = userDao;
* }
* */
private final UserDao userDao;
public UserServiceImpl(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
@Override
public User findRoleByUsername(String username) {
return userDao.findRolesByUserName(username);
}
@Override
public List<Perms> findPermsByRoleId(Integer id) {
return userDao.findPermsByRoleId(id);
}
}
7.修改自定义realm
public class CustomerRealms extends AuthorizingRealm {
//授权
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
//获取身份信息
String principal = (String) principalCollection.getPrimaryPrincipal();
System.out.println("调用授权验证" + principal);
//根据主身份信息获取角色信息 和 权限信息
UserService userService = (UserService) ApplicationContextUtils.getBean("userServiceImpl");
User user = userService.findRoleByUsername(principal);
System.out.println(user);
//授权角色信息
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(user.getRoles())) {
SimpleAuthorizationInfo authorizationInfo = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
user.getRoles().forEach(role -> {
System.out.println("添加角色信息:" + role.getName());
authorizationInfo.addRole(role.getName());
//授权权限信息
List<Perms> perms = userService.findPermsByRoleId(role.getId());
System.out.println(perms);
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(perms)) {
perms.forEach(p -> {
System.out.println("添加权限信息" + p.getName());
authorizationInfo.addStringPermission(p.getName());
});
}
});
return authorizationInfo;
}
return null;
}
}
8.向数据库添加信息
- 略,sql里面有
9.启动测试


6.7 使用 CacheManager
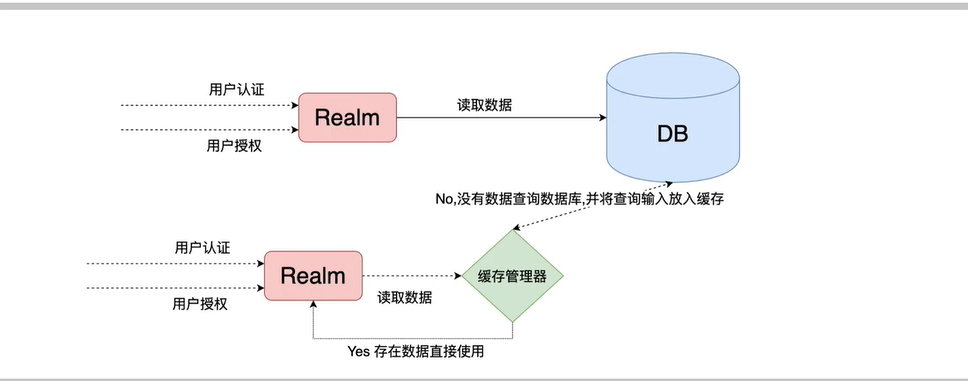
6.7.1 Cache作用
- Cache 缓存:计算机内存中一段数据
- 作用:用来减轻 db的访问压力,从而提高系统的查询效率
- 流程
6.7.2 使用 Shiro中默认 EhCache实现缓存
1. 引入依赖
<!--引入 shiro和 ehcache整合-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-ehcache</artifactId>
<version>1.7.0</version>
</dependency>
2. 开启缓存【在 ShiroConfig类中】
/**
* @author shkstart
* 用来整合 shiro框架相关的配置类
*/
@Configuration
public class ShiroConfig {
//3. 创建自定义 realm【将自己的验证方式加入容器】
@Bean(name = "realm") //设立需要指定一下创建 bean的别名,否则上面报错
public Realm getRealm() {
//创建
CustomerRealms realms = new CustomerRealms();
//修改 凭证校验匹配器
HashedCredentialsMatcher credentialsMatcher = new HashedCredentialsMatcher();
//设置加密算法为 md5
credentialsMatcher.setHashAlgorithmName("MD5");
//设置散列次数
credentialsMatcher.setHashIterations(1024);
//设置凭证校验匹配器
realms.setCredentialsMatcher(credentialsMatcher);
/*
* 开启缓存管理
* */
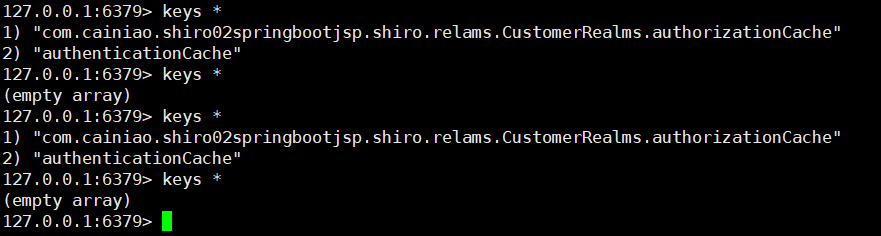
realms.setCacheManager(new RedisCacheManager());
realms.setCachingEnabled(true);//开启全局缓存管理
realms.setAuthenticationCachingEnabled(true);//开启身份的缓存
realms.setAuthenticationCacheName("authenticationCache");//给缓存在内存中起一个名字
realms.setAuthorizationCachingEnabled(true); //开启授权的缓存
realms.setAuthorizationCacheName("authorizationCache");//起一个别名
return realms;
}
}
6.7.3 Shiro中使用 Redis作为缓存实现
1. 引入 readis依赖
<!--redis 整合springboot-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
2. 配置 redis连接
# 整合 redis
spring.redis.port=6379
spring.redis.host=192.168.200.130
spring.redis.database=0
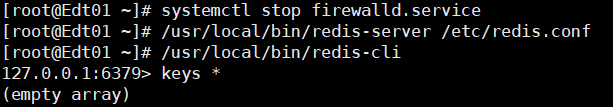
3. 启动 redis服务
4. 开发 RedisCacheManager
/**
* @author shkstart
* 自定义 shiro缓存管理器
* 实现 shiro的 CacheManager
*/
public class RedisCacheManager implements CacheManager {
/**
* @param cacheName 参数,认证或者是授权缓存的统一名称
* @param <K>
* @param <V>
* @return
* @throws CacheException
*/
@Override
public <K, V> Cache<K, V> getCache(String cacheName) throws CacheException {
System.out.println("自定义的 RedisCacheManager");
System.out.println(cacheName);//authorizationCache.2
//com.cainiao.shiro02springbootjsp.shiro.relams.CustomerRealms.authorizationCache
return new RedisCache<K, V>(cacheName);
}
}
5. 开 RedisCache实现
/**
* @author shkstart
* 自定义 redis缓存的实现
*/
public class RedisCache<K, V> implements Cache<K, V> {
private String cacheName;
public RedisCache() {
}
public RedisCache(String cacheName) {
this.cacheName = cacheName;
}
// 从 redis中获取缓存
@Override
public V get(K k) throws CacheException {
System.out.println("get k = " + k);
//把指定的的 k v 放进 redis做实现就可以了,
// 通过RedisTemplate【通过工厂工具类获取】 放入缓存中
return (V) getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().get(this.cacheName, k.toString());//获取key键对应的值
}
//把查询数据库的数据放进缓存
@Override
public V put(K k, V v) throws CacheException {
System.out.println("put k = " + k);
System.out.println("put v = " + v);
//把指定的的 k v 放进 redis做实现就可以了,
// 通过RedisTemplate【通过工厂工具类获取】 放入缓存中
getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().put(cacheName, k.toString(), v);//结构:字段名、用户名、认证/授权对象
return null;
}
//清空指定的缓存
@Override
public V remove(K k) throws CacheException {
System.out.println("---remove---");
return (V) getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().delete(cacheName, k.toString());
}
@Override
public void clear() throws CacheException {
System.out.println("---clear---");
getRedisTemplate().delete(cacheName);
}
@Override
public int size() {
return getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().size(cacheName).intValue();
}
//获取所有的 k
@Override
public Set<K> keys() {
return getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().keys(cacheName);
}
//获取所有的 v
@Override
public Collection<V> values() {
return getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().values(cacheName);
}
private RedisTemplate getRedisTemplate() {
// 通过RedisTemplate【通过工厂工具类获取】 放入缓存中
RedisTemplate redisTemplate = (RedisTemplate) ApplicationContextUtils.getBean("redisTemplate");
//这是k的序列化方式改为 string的序列化方式
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
//Map<String,Map<String,Object>> 设置了外部的String的序列化方式还要设置内部的序列化方式
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
return redisTemplate;
}
}
6. 关于序列化错误
- Failed to serialize object using defaultSerializer;nested exception is java.io.NotSerializableException: org.apache.shiro.util.SimpleByteSource
- 错误解释:由于 Shiro中提供的 simpleByteSource没有实现序列化,所以在认证时出现错误
- 解决方案:需要自动 sqlt实现序列化【SimpleByteSource类的所有属性,方法复制一下构造方法替换一下,写一个无参构造,然后实现 Serializable即可】
//自定义 salt实现序列化接口 public class MyByteSource implements ByteSource, Serializable { private byte[] bytes; private String cachedHex; private String cachedBase64; ////加入无参数构造方法实现序列化和反序列化 public MyByteSource() { } public MyByteSource(byte[] bytes) { this.bytes = bytes; } public MyByteSource(char[] chars) { this.bytes = CodecSupport.toBytes(chars); } public MyByteSource(String string) { this.bytes = CodecSupport.toBytes(string); } public MyByteSource(ByteSource source) { this.bytes = source.getBytes(); } public MyByteSource(File file) { this.bytes = (new MyByteSource.BytesHelper()).getBytes(file); } public MyByteSource(InputStream stream) { this.bytes = (new BytesHelper()).getBytes(stream); } public static boolean isCompatible(Object o) { return o instanceof byte[] || o instanceof char[] || o instanceof String || o instanceof ByteSource || o instanceof File || o instanceof InputStream; } public byte[] getBytes() { return this.bytes; } public boolean isEmpty() { return this.bytes == null || this.bytes.length == 0; } public String toHex() { if (this.cachedHex == null) { this.cachedHex = Hex.encodeToString(this.getBytes()); } return this.cachedHex; } public String toBase64() { if (this.cachedBase64 == null) { this.cachedBase64 = Base64.encodeToString(this.getBytes()); } return this.cachedBase64; } public String toString() { return this.toBase64(); } public int hashCode() { return this.bytes != null && this.bytes.length != 0 ? Arrays.hashCode(this.bytes) : 0; } public boolean equals(Object o) { if (o == this) { return true; } else if (o instanceof ByteSource) { ByteSource bs = (ByteSource) o; return Arrays.equals(this.getBytes(), bs.getBytes()); } else { return false; } } private static final class BytesHelper extends CodecSupport { private BytesHelper() { } public byte[] getBytes(File file) { return this.toBytes(file); } public byte[] getBytes(InputStream stream) { return this.toBytes(stream); } } }- 自定义的 realm CustomerRealms修改
//验证 @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { //1. 获取身份信息 String username = (String) token.getPrincipal(); //2. 根据用户名查询数据库 //在工程中获取 service对象 【默认类型小写】【使用 @Autowired 也行】 UserService userService = (UserService) ApplicationContextUtils.getBean("userServiceImpl"); User user = userService.findUserByName(username); if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(user)) { return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo( user.getUsername(), user.getPassword(), //ByteSource.Util.bytes(user.getSalt()) //这里的util没有实现序列化 new MyByteSource(user.getSalt()), this.getName()); } return null; }
7. 关于 ClassCastException异常
- java.lang.ClassCastException: org.apache.shiro.authc.SimpleAuthenticationInfo cannot be cast to org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo
- (该地址解决问题,大致是我写错为了)[https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44967580/article/details/116743018]
6.7.4 加入验证码
1. 验证码工具类
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.geom.AffineTransform;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
/**
*@创建人 cx
*@创建时间 2018/11/27 17:36
*@描述 验证码生成
*/
public class VerifyCodeUtils{
//使用到Algerian字体,系统里没有的话需要安装字体,字体只显示大写,去掉了1,0,i,o几个容易混淆的字符
public static final String VERIFY_CODES = "23456789ABCDEFGHJKLMNPQRSTUVWXYZ";
private static Random random = new Random();
/**
* 使用系统默认字符源生成验证码
* @param verifySize 验证码长度
* @return
*/
public static String generateVerifyCode(int verifySize){
return generateVerifyCode(verifySize, VERIFY_CODES);
}
/**
* 使用指定源生成验证码
* @param verifySize 验证码长度
* @param sources 验证码字符源
* @return
*/
public static String generateVerifyCode(int verifySize, String sources){
if(sources == null || sources.length() == 0){
sources = VERIFY_CODES;
}
int codesLen = sources.length();
Random rand = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
StringBuilder verifyCode = new StringBuilder(verifySize);
for(int i = 0; i < verifySize; i++){
verifyCode.append(sources.charAt(rand.nextInt(codesLen-1)));
}
return verifyCode.toString();
}
/**
* 生成随机验证码文件,并返回验证码值
* @param w
* @param h
* @param outputFile
* @param verifySize
* @return
* @throws IOException
*/
public static String outputVerifyImage(int w, int h, File outputFile, int verifySize) throws IOException{
String verifyCode = generateVerifyCode(verifySize);
outputImage(w, h, outputFile, verifyCode);
return verifyCode;
}
/**
* 输出随机验证码图片流,并返回验证码值
* @param w
* @param h
* @param os
* @param verifySize
* @return
* @throws IOException
*/
public static String outputVerifyImage(int w, int h, OutputStream os, int verifySize) throws IOException{
String verifyCode = generateVerifyCode(verifySize);
outputImage(w, h, os, verifyCode);
return verifyCode;
}
/**
* 生成指定验证码图像文件
* @param w
* @param h
* @param outputFile
* @param code
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void outputImage(int w, int h, File outputFile, String code) throws IOException{
if(outputFile == null){
return;
}
File dir = outputFile.getParentFile();
if(!dir.exists()){
dir.mkdirs();
}
try{
outputFile.createNewFile();
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(outputFile);
outputImage(w, h, fos, code);
fos.close();
} catch(IOException e){
throw e;
}
}
/**
* 输出指定验证码图片流
* @param w
* @param h
* @param os
* @param code
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void outputImage(int w, int h, OutputStream os, String code) throws IOException{
int verifySize = code.length();
BufferedImage image = new BufferedImage(w, h, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
Random rand = new Random();
Graphics2D g2 = image.createGraphics();
g2.setRenderingHint(RenderingHints.KEY_ANTIALIASING,RenderingHints.VALUE_ANTIALIAS_ON);
Color[] colors = new Color[5];
Color[] colorSpaces = new Color[] { Color.WHITE, Color.CYAN,
Color.GRAY, Color.LIGHT_GRAY, Color.MAGENTA, Color.ORANGE,
Color.PINK, Color.YELLOW };
float[] fractions = new float[colors.length];
for(int i = 0; i < colors.length; i++){
colors[i] = colorSpaces[rand.nextInt(colorSpaces.length)];
fractions[i] = rand.nextFloat();
}
Arrays.sort(fractions);
g2.setColor(Color.GRAY);// 设置边框色
g2.fillRect(0, 0, w, h);
Color c = getRandColor(200, 250);
g2.setColor(c);// 设置背景色
g2.fillRect(0, 2, w, h-4);
//绘制干扰线
Random random = new Random();
g2.setColor(getRandColor(160, 200));// 设置线条的颜色
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
int x = random.nextInt(w - 1);
int y = random.nextInt(h - 1);
int xl = random.nextInt(6) + 1;
int yl = random.nextInt(12) + 1;
g2.drawLine(x, y, x + xl + 40, y + yl + 20);
}
// 添加噪点
float yawpRate = 0.05f;// 噪声率
int area = (int) (yawpRate * w * h);
for (int i = 0; i < area; i++) {
int x = random.nextInt(w);
int y = random.nextInt(h);
int rgb = getRandomIntColor();
image.setRGB(x, y, rgb);
}
shear(g2, w, h, c);// 使图片扭曲
g2.setColor(getRandColor(100, 160));
int fontSize = h-4;
Font font = new Font("Algerian", Font.ITALIC, fontSize);
g2.setFont(font);
char[] chars = code.toCharArray();
for(int i = 0; i < verifySize; i++){
AffineTransform affine = new AffineTransform();
affine.setToRotation(Math.PI / 4 * rand.nextDouble() * (rand.nextBoolean() ? 1 : -1), (w / verifySize) * i + fontSize/2, h/2);
g2.setTransform(affine);
g2.drawChars(chars, i, 1, ((w-10) / verifySize) * i + 5, h/2 + fontSize/2 - 10);
}
g2.dispose();
ImageIO.write(image, "jpg", os);
}
private static Color getRandColor(int fc, int bc) {
if (fc > 255)
fc = 255;
if (bc > 255)
bc = 255;
int r = fc + random.nextInt(bc - fc);
int g = fc + random.nextInt(bc - fc);
int b = fc + random.nextInt(bc - fc);
return new Color(r, g, b);
}
private static int getRandomIntColor() {
int[] rgb = getRandomRgb();
int color = 0;
for (int c : rgb) {
color = color << 8;
color = color | c;
}
return color;
}
private static int[] getRandomRgb() {
int[] rgb = new int[3];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
rgb[i] = random.nextInt(255);
}
return rgb;
}
private static void shear(Graphics g, int w1, int h1, Color color) {
shearX(g, w1, h1, color);
shearY(g, w1, h1, color);
}
private static void shearX(Graphics g, int w1, int h1, Color color) {
int period = random.nextInt(2);
boolean borderGap = true;
int frames = 1;
int phase = random.nextInt(2);
for (int i = 0; i < h1; i++) {
double d = (double) (period >> 1)
* Math.sin((double) i / (double) period
+ (6.2831853071795862D * (double) phase)
/ (double) frames);
g.copyArea(0, i, w1, 1, (int) d, 0);
if (borderGap) {
g.setColor(color);
g.drawLine((int) d, i, 0, i);
g.drawLine((int) d + w1, i, w1, i);
}
}
}
private static void shearY(Graphics g, int w1, int h1, Color color) {
int period = random.nextInt(40) + 10; // 50;
boolean borderGap = true;
int frames = 20;
int phase = 7;
for (int i = 0; i < w1; i++) {
double d = (double) (period >> 1)
* Math.sin((double) i / (double) period
+ (6.2831853071795862D * (double) phase)
/ (double) frames);
g.copyArea(i, 0, 1, h1, 0, (int) d);
if (borderGap) {
g.setColor(color);
g.drawLine(i, (int) d, i, 0);
g.drawLine(i, (int) d + h1, i, h1);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//获取验证码
String s = generateVerifyCode(4);
//将验证码放入图片中
outputImage(260,60,new File("/Users/chenyannan/Desktop/安工资料/aa.jpg"),s);
System.out.println(s);
}
}
2. 开发页面加入验证码
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>登陆页面</h2>
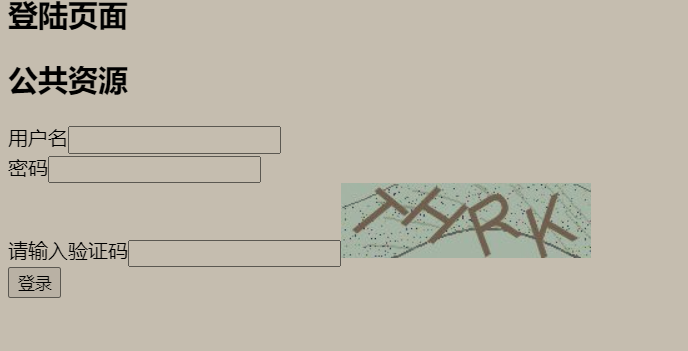
<h2>公共资源</h2>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/user/login" method="post">
用户名<input type="text" name="username"><br>
密码<input type="password" name="password"><br>
请输入验证码<input type="text" name="code"><img src="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/user/getImage" alt=""> <br>
<input type="submit" value="登录">
</form>
</body>
</html>
3. 开发控制器
/**
* 验证码方法
*/
@RequestMapping("/getImage")
public void getImage(HttpSession session, HttpServletResponse response) {
//生成验证码
String code = VerifyCodeUtils.generateVerifyCode(4);
//验z证码放入 session
session.setAttribute("code", code);
//验证码存入图片
try {
response.setContentType("image/png");
VerifyCodeUtils.outputImage(200, 60, response.getOutputStream(), code);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
4. 放行验证码
5. 修改认证流程
/**
* 用来处理身份认证
*
* @param username
* @param password
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("login")
public String login(String username, String password, String code, HttpSession session) {
//比较验证码
String captcha = (String) session.getAttribute("code");
try {
if (captcha.equalsIgnoreCase(code)) {
System.out.println(username + "," + password);
//获取主体对象
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//用户认证【在定义 realms】
subject.login(new UsernamePasswordToken(username, password));
return "redirect:/index.jsp";
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("验证码错误");
}
} catch (UnknownAccountException e) {
e.printStackTrace();//UnknownAccountException
System.out.println("认证失败,用户名不存在");
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e) {
e.printStackTrace();//IncorrectCredentialsException
System.out.println("认证失败,密码错误");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("验证码错误");
}
return "redirect:/login.jsp";
}
6. 修改 salt不能序列化的问题
- 略,上面已经修改了,加入无参构造,方便序列化使用
7. 启动测试
6.7.5 jsp中 Shiro常用标签
- jsp页面头部加上 shiro标签库
<%@taglib prefix="shiro" uri="http://shiro.apache.org/tags" %> - 常用 Shiro标签的介绍
- shiro:guest
用户没有 - shiro:user
用户已经经过认证/记住我登录后显示相应的信息 - shiro:authenticated
用户已经身份验证通过,即Subject.login登录成功,不是记住我登录的 - shiro:notAuthenticated
用户未进行身份验证,既没有调用 subject.login进行登录,包括记住我自定登录的也属于未进行身份验证 - shiro:pincipal
显示用户身份信息,默认调用 subject.getPrincipal() 获取,即 Primary Principal - shiro:hasRole
如果当前 subject有角色将显示body体内容 - shiro:hasAnyRoles
如果当前 subject有任意一个角色(或的关系)将显示body体内容 - Shiro:lacksRole
如果当前 subject没有角色将显示 body体内容 - shiro:hasPermission
如果当前 subject有权限将显示 body提内容 - shiro:lacksPermission
如果当前 subject没有权限将显示 body体内容
- shiro:guest
<!--验证当前用户是否拥有指定权限。 -->
<a shiro:hasPermission="user:add" href="#" >add用户</a><!-- 拥有权限 -->
<!--与hasPermission标签逻辑相反,当前用户没有制定权限时,验证通过。-->
<p shiro:lacksPermission="user:del"> 没有权限 </p>
<!--验证当前用户是否拥有以下所有权限。-->
<p shiro:hasAllPermissions="user:view, user:add"> 权限与判断 </p>
<!--验证当前用户是否拥有以下任意一个权限。-->
<p shiro:hasAnyPermissions="user:view, user:del"> 权限或判断 </p>
<!--验证当前用户是否属于该角色。-->
<a shiro:hasRole="admin" href="#">拥有该角色</a>
<!--与hasRole标签逻辑相反,当用户不属于该角色时验证通过。-->
<p shiro:lacksRole="developer"> 没有该角色 </p>
<!--验证当前用户是否属于以下所有角色。-->
<p shiro:hasAllRoles="developer, admin"> 角色与判断 </p>
<!--验证当前用户是否属于以下任意一个角色。-->
<p shiro:hasAnyRoles="admin, vip, developer"> 角色或判断 </p>
<!--验证当前用户是否为“访客”,即未认证(包含未记住)的用户。-->
<p shiro:guest="">访客 未认证</a></p>
<!--认证通过或已记住的用户-->
<p shiro:user=""> 认证通过或已记住的用户 </p>
<!--已认证通过的用户。不包含已记住的用户,这是与user标签的区别所在。-->
<p shiro:authenticated=""> <span shiro:principal=""></span> </p>
<!--输出当前用户信息,通常为登录帐号信息-->
<p> <shiro:principal/> </p>
<!--未认证通过用户,与authenticated标签相对应。-->
<!--与guest标签的区别是,该标签包含已记住用户。-->
<p shiro:notAuthenticated=""> 未认证通过用户 </p>
7. Shiro整合 SpringBoot值 thymelaf
7.1 引入依赖
<!--引入 thymeleaf 依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--引入 thymeleaf 整合 shiro-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.theborakompanioni</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-shiro</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0</version>
</dependency>
7.2 页面中引入命名空间
- 如果现在 thymeleaf中使用 shiro标签就要引入名称空间
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
xmlns:shiro="http://pollix.at/thymeleaf/shiro ">
7.3 常见权限控制标签使用
<!-- 验证当前用户是否为“访客”,即未认证(包含未记住)的用户。 -->
<p shiro:guest="">Please <a href="login.html">login</a></p>
<!-- 认证通过或已记住的用户。 -->
<p shiro:user="">
Welcome back John! Not John? Click <a href="login.html">here</a> to login.
</p>
<!-- 已认证通过的用户。不包含已记住的用户,这是与user标签的区别所在。 -->
<p shiro:authenticated="">
Hello, <span shiro:principal=""></span>, how are you today?
</p>
<a shiro:authenticated="" href="updateAccount.html">Update your contact information</a>
<!-- 输出当前用户信息,通常为登录帐号信息。 -->
<p>Hello, <shiro:principal/>, how are you today?</p>
<!-- 未认证通过用户,与authenticated标签相对应。与guest标签的区别是,该标签包含已记住用户。 -->
<p shiro:notAuthenticated="">
Please <a href="login.html">login</a> in order to update your credit card information.
</p>
<!-- 验证当前用户是否属于该角色。 -->
<a shiro:hasRole="admin" href="admin.html">Administer the system</a><!-- 拥有该角色 -->
<!-- 与hasRole标签逻辑相反,当用户不属于该角色时验证通过。 -->
<p shiro:lacksRole="developer"><!-- 没有该角色 -->
Sorry, you are not allowed to developer the system.
</p>
<!-- 验证当前用户是否属于以下所有角色。 -->
<p shiro:hasAllRoles="developer, 2"><!-- 角色与判断 -->
You are a developer and a admin.
</p>
<!-- 验证当前用户是否属于以下任意一个角色。 -->
<p shiro:hasAnyRoles="admin, vip, developer,1"><!-- 角色或判断 -->
You are a admin, vip, or developer.
</p>
<!--验证当前用户是否拥有指定权限。 -->
<a shiro:hasPermission="userInfo:add" href="createUser.html">添加用户</a><!-- 拥有权限 -->
<!-- 与hasPermission标签逻辑相反,当前用户没有制定权限时,验证通过。 -->
<p shiro:lacksPermission="userInfo:del"><!-- 没有权限 -->
Sorry, you are not allowed to delete user accounts.
</p>
<!-- 验证当前用户是否拥有以下所有角色。 -->
<p shiro:hasAllPermissions="userInfo:view, userInfo:add"><!-- 权限与判断 -->
You can see or add users.
</p>
<!-- 验证当前用户是否拥有以下任意一个权限。 -->
<p shiro:hasAnyPermissions="userInfo:view, userInfo:del"><!-- 权限或判断 -->
You can see or delete users.
</p>
<a shiro:hasPermission="pp" href="createUser.html">Create a new User</a>
7.4 加入 shiro的方言配置
- 页面标签没有作用加入方言
/**
* 配置 ShiroDialect(Shiro 方言) 对象
*/
@Bean(name = "shiroDialect")
public ShiroDialect shiroDialect() {
return new ShiroDialect();
}