Vue高级 - vuex通信,Router路由,localstorage、sessionstorage和cookie
一 vuex使用
1.1 概念
- vuex :状态管理器---> 存数据(变量)的地方,所有组件都可以操作
在Vue中实现集中式状态(数据)管理的一个Vue插件,对vue应用中多个组件的共享状态进行集中式的管理(读/写),也是一种组件间通信的方式,且适用于任意组件间通信 - 多个组件需要共享数据时,就需要使用vuex 了
- vuex只在当前会话中生效,只要刷新页面或者关闭页面,就会失效,恢复到原来的数据
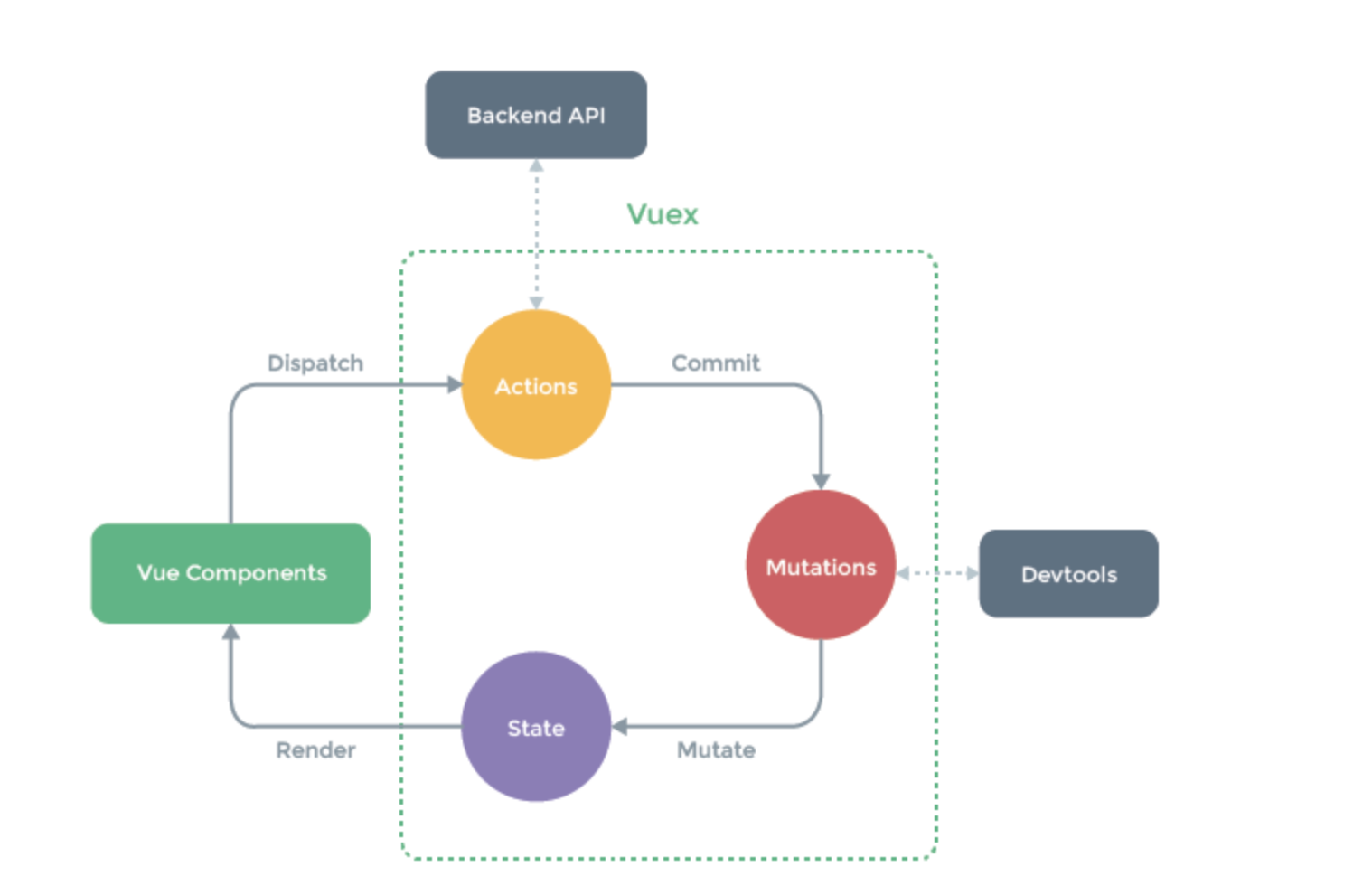
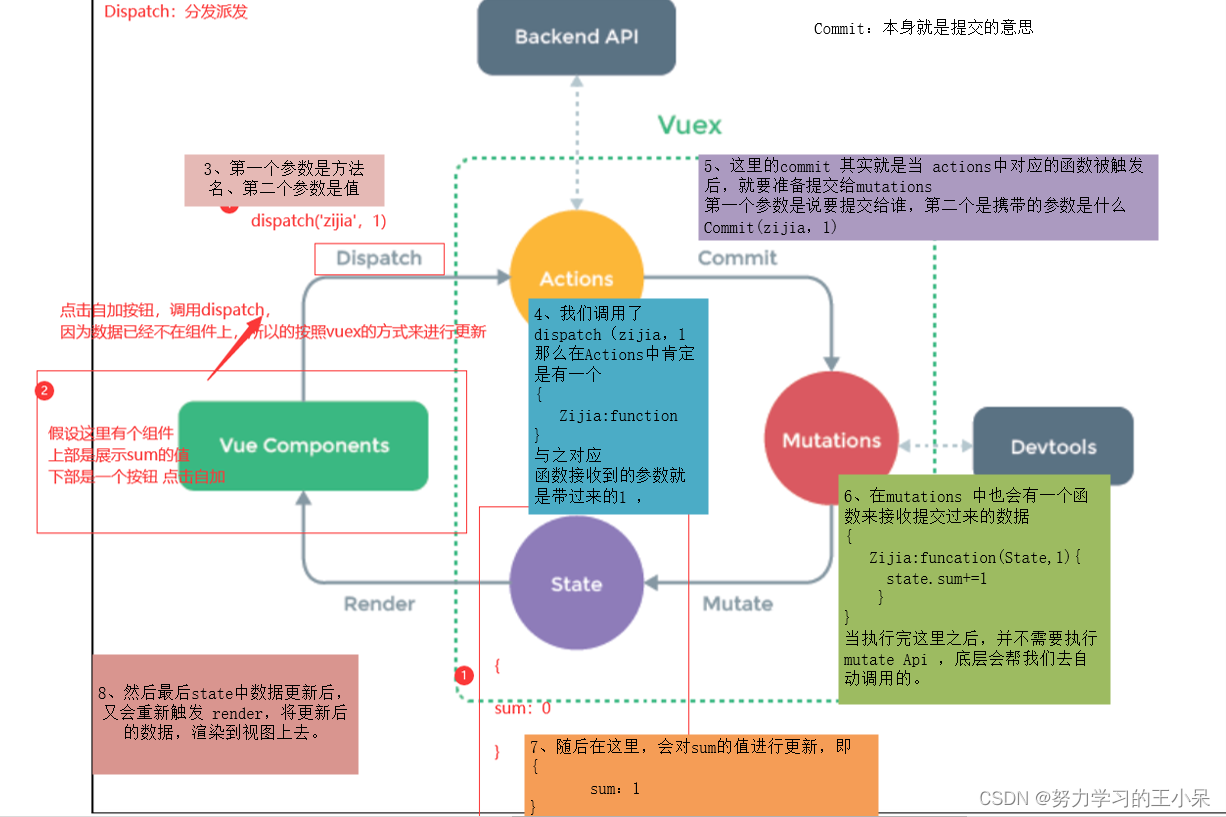
# 是可以越过步骤,直接去操作每一层。
# actions中可以去链接后端,让后端去完成操作数据库,完成数据的校验工作,或者像后端发起请求,让后端的数据库更改数据
# 安装vuex插件后自动创建store文件夹
组件间通信总结
1.父传子:自定义属性。子传父:自定义变量
2.ref属性,通过this.$refs可以获取到组件对象
3.vuex插件,集中管理数据
1.2 案例1:显示购物车商品数量
HomeView.vue
<template>
<div class="home">
<h1>1 vuex的使用 -基本使用(操作state的数据)</h1>
<!--这个是在main.js中导入,并在Vue对象中注册,所以使用this.$store就能获取到Vuex.Store对象-->
<!--其中的this可以不写-->
购物车商品数量:{{ $store.state.num }}
<br>
<button @click="handleAdd">点我加购物增1</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'HomeView',
methods: {
handleAdd() {
// 正统方式
// 1 通过dispatch触发actions
this.$store.dispatch('add', 2) //add 必须是action中得函数
},
}
}
</script>
src/store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
actions: {
// 2 axtions中有一个add函数,触发mutations中函数执行
// 默认传入一个参数,context上下文对象
// count才是真正传入的参数2
add(context, count) {
// console.log(context)
// console.log(count)
// 使用commit,触发mutations中得函数
context.commit('mAdd', count) // 会触发mutations中得mAdd的执行
},
},
mutations: {
// 3 mutations中有一个mAdd函数
// 也默认传入一个参数,是state对象
mAdd(state, count) {
// console.log(state)
// console.log(count)
state.num = state.num + count
// 这样一些,就修改了state中的num的值,这样页面中就显示新的值
}
},
state: {
num: 10,
},
})


1.3 直接操作每一层
1.页面组件中直接使用state中定义的数据
HomeView.vue
<template>
<div class="home">
<h1>1 vuex的使用 -基本使用(操作state的数据)</h1>
购物车商品数量:{{ $store.state.num }}
<br>
<button @click="handleAdd">点我加购物增1</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'HomeView',
methods: {
handleAdd() {
// 直接操作state中的数据
this.$store.state.num += 1
}
},
}
</script>
src/store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
actions: {},
mutations: {},
state: {
num: 10,
},
})
2.页面组件通过操作mutations来操作state中的数据
HomeView.vue
<template>
<div class="home">
<h1>1 vuex的使用 -基本使用(操作state的数据)</h1>
购物车商品数量:{{ $store.state.num }}
<br>
<button @click="handleAdd">点我加购物增1</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'HomeView',
methods: {
handleAdd() {
// 直接操作mutations
this.$store.commit('mAdd', 3)
}
},
}
</script>
src/store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
actions: {},
mutations: {
// mutations中有一个mAdd函数
// 也默认传入一个参数,是state对象
mAdd(state, count) {
// console.log(state)
// console.log(count)
state.num = state.num + count
// 这样一些,就修改了state中的num的值,这样页面中就显示新的值
},
},
state: {
num: 10
},
})

3.在actions中直接操作state的数据
HomeView.vue
<template>
<div class="home">
<h1>1 vuex的使用 -基本使用(操作state的数据)</h1>
购物车商品数量:{{ $store.state.num }}
<br>
<button @click="handleAdd">点我加购物增1</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'HomeView',
methods: {
handleAdd() {
// 通过dispatch触发actions
this.$store.dispatch('add', 2) //add 必须是action中得函数
}
},
}
</script>
src/store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
actions: {
// axtions中有一个add函数,触发mutations中函数执行
// 可以直接修改state中的数据
add(context, count) {
// console.log(context)
// console.log(count)
// 上下文对象中也有state,可以直接操作state的数据
// context.state.num = context.state.num + count
context.state.num = 66
},
},
mutations: {},
state: {
num: 10,
},
})

1.4 案例2:组件间通信
HomeView.vue
<template>
<div class="home">
<h1>vuex的组件间通信:父传子</h1>
<div>父传子,父组件中点击加号,子组件ShoppingCard中的列表就会加对应水果</div>
<ul>
<li>苹果
<button @click="Add('苹果')">+</button>
</li>
<li>桃子
<button @click="Add('桃子')">+</button>
</li>
<li>梨
<button @click="Add('梨')">+</button>
</li>
</ul>
<hr>
<ShoppingCard></ShoppingCard>
<hr>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import ShoppingCard from "@/components/ShoppingCard.vue";
export default {
name: 'HomeView',
methods: {
Add(name) {
// 1 直接操作
// this.$store.state.goods.push(name)
//2 正常套路
this.$store.dispatch('addShopping', name)
}
},
components: {
ShoppingCard
}
}
</script>
src/store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
actions: {
addShopping(context, name) {
// 这里可以跟后端交互,发起ajax请求,检查name库存够不够
// 假设库存不够,弹个不够的消息
// alert('库存不够了')
// return
// 库存充足,继续执行,else
context.commit('addShopping', name)
}
},
mutations: {
addShopping(state, name) { // 与actions中的方法名可以重复
state.goods.push(name)
}
},
state: {
goods: []
},
})
ShoppingCard.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>我是购物车小组件</h2>
购物车商品:{{ $store.state.goods }}
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "ShoppingCard"
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
1.5 案例3:两个组件间通信
HomeView.vue
<template>
<div class="home">
<h1>vuex的组件间通信:不同组件通信</h1>
<hr>
<Good></Good>
<hr>
<ShoppingCard></ShoppingCard>
<hr>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import ShoppingCard from "@/components/ShoppingCard.vue";
import Good from "@/components/Good.vue";
export default {
name: 'HomeView',
components: {
ShoppingCard,
Good
}
}
</script>
src/store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
actions: {
addShopping(context, name) {
context.commit('addShopping', name)
}
},
mutations: {
addShopping(state, name) {
state.goods.push(name)
}
},
state: {
goods: []
},
})
Good.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>商品组件</h2>
<ul>
<li>苹果
<button @click="Add('苹果')">+</button>
</li>
<li>桃子
<button @click="Add('桃子')">+</button>
</li>
<li>梨
<button @click="Add('梨')">+</button>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Good",
methods: {
Add(name) {
// 1 直接操作
// this.$store.state.goods.push(name)
//2 正常套路
this.$store.dispatch('addShopping', name)
}
}
}
</script>
ShoppingCard.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>我是购物车小组件</h2>
购物车商品:{{ $store.state.goods }}
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "ShoppingCard"
}
</script>

二 Router使用
2.1 说明
-
官方提供的用来实现SPA 的vue 插件
-
vue是单页面应用,可以借助于Router实现页面组件的跳转
-
下载:
npm install vue-router --save -
引入
router的index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
// 引入页面路由
import HomeView from '../views/HomeView.vue'
// 使用vue-router插件
Vue.use(VueRouter)
// 页面的一个个路由
const routes = [
{
path: '/', // 访问路径
name: 'home', // 路由别名,可以通过别名找到该路由
component: HomeView
},
{
path: '/about',
name: 'about',
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/AboutView.vue')
}
]
const router = new VueRouter({
mode: 'history',
base: process.env.BASE_URL,
routes
})
// 默认导出
export default router
main.js中注册路由
import router from './router'
new Vue({
router,
})
2.1.1 简单使用
# 1 简单使用
-浏览器中实现页面跳转(咱们之前学过了)
-写个页面组件
-在router--->index.js--->routes数组中加入一个路由即可
# 2 组件中实现页面跳转
-两种方式
-方式一:使用 router-link 标签,to 地址
<router-link to="/about"></router-link>
-方式二:js控制
this.$router.push('/about')
# 3 to值的不同类型
-可以是个字符串,写路径地址后缀
<router-link to="/about"></router-link>
-使用属性指令
<router-link :to="url"></router-link>
export default {
data(){
return {
url: '/about'
}}}
-可以使用对象,属性指令才能写js变量,就可以使用对象了
<router-link :to="{name:'about'}"></router-link>
2.1.2 路由跳转时,使用对象
-1 通过对象跳转路由,name形式:
<router-link :to="{name:'about'}"></router-link>
-2 通过对象跳转路由,path形式:
<router-link :to="{path:'/about'}"></router-link>
-3 对象中可以有query属性,是个对象类型,会把里面的key-value拼到路径后面
<router-link :to="{path: '/about', query: {id: 1, name: 'kevin'}}"></router-link>
# http://localhost:8080/about?id=1&name=kevin
-4 在另一个页面中取出地址栏中数据:
console.log(this.$route.query)
-5 这种传递方式和 3 一样
<router-link to="/about?name=lqz&age=19">
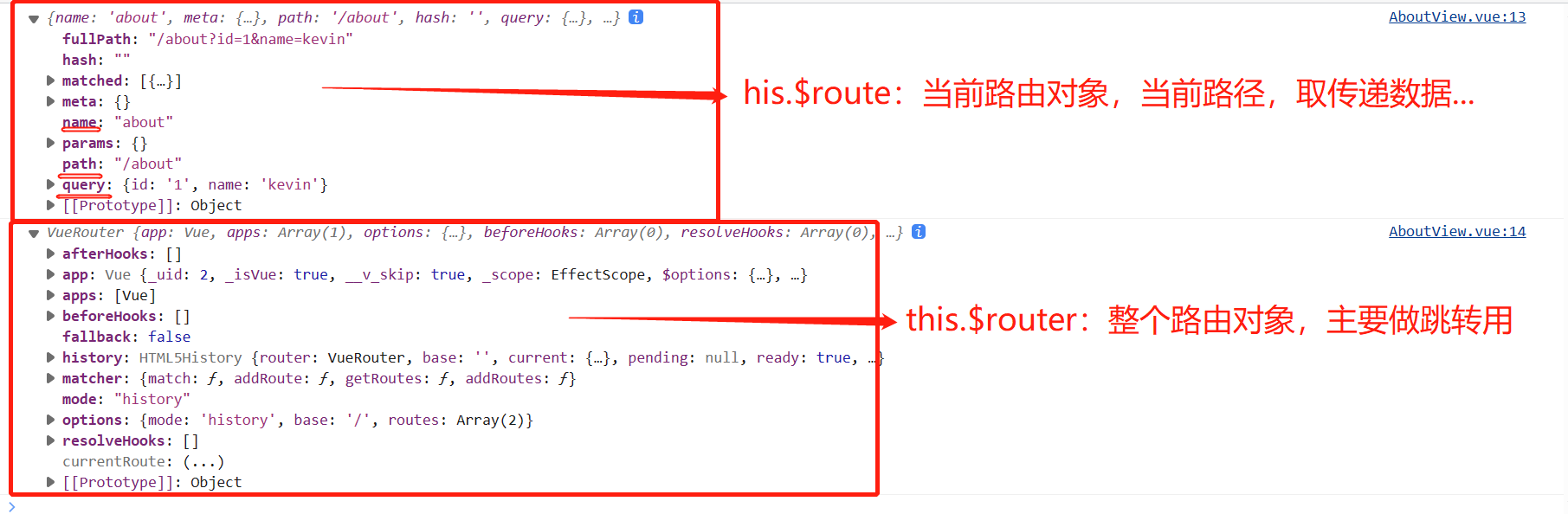
-6 注意区分:
this.$route:当前路由对象,当前路径地址,别名,携带的query参数,传递数据...
this.$router:(index.js中new出来的VueRouter对象)整个路由对象,主要做跳转、后退使用
-7 路径中分割出 参数
-配置:
{
path: '/detail/:pk', # 变量pk,一定要加冒号
name: 'detail',
component: DetailView
},
-在路由中取:
this.$route.params.pk
-8 路由跳转时,使用 7 的样子
-this.$router.push({name: 'detail', params: {pk: 999}})
-<router-link :to="{name:'detail',params:{pk:88}}">
2.1.3 this.router 的一些方法
this.$router.push(path): 相当于点击路由链接(可以返回到当前路由界面)
this.$router.replace(path): 用新路由替换当前路由(不可以返回到当前路由界面)
this.$router.back(): 请求(返回)上一个记录路由
this.$router.go(-1): 请求(返回)上一个记录路由
this.$router.go(1): 请求下一个记录路由
2.2 多级路由
# 使用步骤:
- 1 新建一个页面组件(LqzView),配置路由(在router的index.js中)
{
path: '/lqz',
name: 'lqz',
component: LqzView,
},
-2 在页面中,想再显示页面组件,实现点击切换的效果
<h1>lqz页面</h1>
<router-link to="lqz01"> // 只写后缀就行,不要加前面的路径,也不要加/
<button>lqz-01</button>
</router-link>
<router-link to="lqz02">
<button>lqz-02</button>
</router-link>
<router-view>
# 以后这里变换页面组件,多级路由
</router-view>
-3 新建两个页面组件,Lqz01.vue,Lqz02.vue,配置路由children
{
path: '/lqz',
name: 'lqz',
component: LqzView,
children: [ //通过children配置子级路由
{
path: 'lqz01', //此处一定不要写:/lqz01
component: Lqz01
},
{
path: 'lqz02',//此处一定不要写:/lqz02
component: Lqz02
}
]
},
2.3 路由守卫
# 前置路由守卫,再进入路由之前做判断
# 写在router-index.js中,以后访问任意一个路由,都会执行这个代码
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
# to是前往的路由对象
# from是来的路由的对象,可以打印一下
console.log('前置路由守卫', to, from)
// 要是访问lqz01,都不能跳转
// 如果没有登录,不能访问
if (to.path == '/lqz/lqz01') {
alert('你没有权限')
} else {
next() # 继续访问
}
2.4 路由的两种工作模式
路由器的两种工作模式
1 对于一个url来说,什么是hash值 —— ?及其后面的内容就是hash值。
2 hash值不会包含在 HTTP 请求中,即:hash值不会带给服务器。
3 hash模式:
地址中永远带着#号,不美观 。
若以后将地址通过第三方手机app分享,若app校验严格,则地址会被标记为不合法。
兼容性较好。
4 history模式:
地址干净,美观 。
兼容性和hash模式相比略差。
应用部署上线时需要后端人员支持,解决刷新页面服务端404的问题
router的index.js中
const router = new VueRouter({
// mode修改路由的模式
mode: 'history',
// mode: 'hash',
base: process.env.BASE_URL,
routes
})
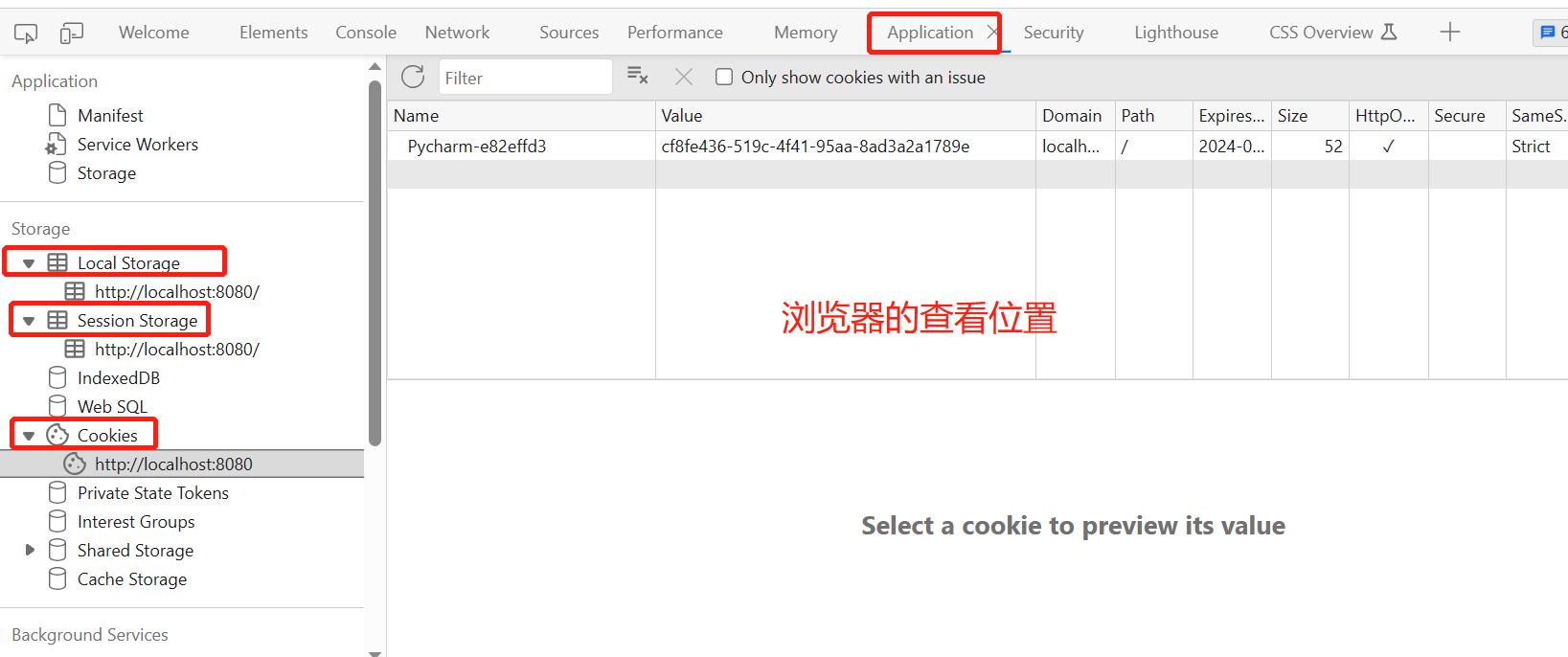
三 localstorage和sessionstorage,和cookie
# 前端存储数据
- 登录成功,有token,存本地
- 不登陆加购物车
# 前端可以存数据的位置:
localstorage:永久存储,除非你删除,关闭浏览器,再打开还会在
sessionstorage:只在当前会话生效,关闭浏览器,就没了
cookie:有过期时间,到了过期时间,自动删除
# 操作这三个位置
3.1 操作localstorage
<template>
<div class="home">
<h1>操作localstorage,永久存储</h1>
<button @click="addLocalstorage">增加</button>
<button @click="getLocalstorage">查</button>
<button @click="deleteLocalstorage">删除</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'HomeView',
methods: {
addLocalstorage() {
var userinfo = {name: 'lqz', age: 19}
localStorage.setItem('userinfo', JSON.stringify(userinfo)) // 需要转成字符串形式才能写入
},
getLocalstorage() {
var userinfo = localStorage.getItem('userinfo')
console.log(JSON.parse(userinfo).name)
},
deleteLocalstorage() {
localStorage.clear()
localStorage.removeItem('userinfo')
},
}
}
</script>
3.2 操作sessionstorage
<template>
<div class="home">
<h1>操作sessiostorage,当前会话,关闭浏览器</h1>
<button @click="addSessiostorage">增加</button>
<button @click="getSessiostorage">查</button>
<button @click="deleteSessiostorage">删除</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'HomeView',
methods: {
addSessiostorage() {
var userinfo = {name: '彭于晏', age: 19}
sessionStorage.setItem('userinfo', JSON.stringify(userinfo))
},
getSessiostorage() {
var userinfo = sessionStorage.getItem('userinfo')
console.log(JSON.parse(userinfo).name)
},
deleteSessiostorage() {
sessionStorage.clear()
sessionStorage.removeItem('userinfo')
},
}
}
</script>
3.3 操作cookie
使用:https://blog.csdn.net/z591102/article/details/117961384
<template>
<div class="home">
<h1>操作cookie,有过期时间</h1>
<button @click="addCookie">增加</button>
<button @click="getCookie">查</button>
<button @click="deleteCookie">删除</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'HomeView',
methods: {
addCookie() {
// 需要借助于第三方 vue-cookies
// cnpm install -S vue-cookies
this.$cookies.set('name', '刘亦菲', '300s')
},
getCookie() {
console.log(this.$cookies.get('name'))
},
deleteCookie() {
this.$cookies.remove('name')
},
}
}
</script>