ServletContext相关
简介
每个web工程都只有一个ServletContext对象。 说白了也就是不管在哪个servlet里面,获取到的这个类的对象都是同一个。
如何得到对象
//1. 获取对象
ServletContext context = getServletContext();有什么作用
- 获取全局配置参数
- 获取web工程中的资源
- 存取数据,servlet间共享数据 域对象
1、获取全局配置参数
web.xml中设置参数
<context-param>
<param-name>name</param-name>
<param-value>朱俊伟</param-value>
</context-param>
</web-app>创建Servlet并配置Servlet并读取相应的参数
package com.zhujunwei.servletContext;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
/**
*
* @author Administrator
* 创建ServletContext读取全局变量的值
*
*/
public class ServletContext01 extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//读取全局变量的值
ServletContext context = getServletContext();
String name = context.getInitParameter("name");
System.out.println(name);
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
}
}运行结果
朱俊伟2、获取web工程中的资源
如果在项目中存在配置文件想要读取(如config.properties),可采用如下三种方法:
config.properties文件所在目录
-WebContent
-file
-config.properties
-META-INF
-WEB-INFconfig.properties文件内容
name=zhujunwei读取的三种方法
package com.zhujunwei.servletContext;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
/**
*
* @author Administrator
* 读取工程文件的三种方法
*
*/
public class ServletContext02 extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
getProperty1();
getProperty2();
getProperty3();
}
/**
* 方法3:通过类加载器读取工程中的文件
* @throws IOException
*/
private void getProperty3() throws IOException {
// 1、创建属性对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
// 2、指定载入的数据源
InputStream inStream = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("../../file/config.properties");
properties.load(inStream);
// 3、获取name属性的值
String name = properties.getProperty("name");
System.out.println("getProperty3():name=" + name);
}
/**
* 方法2:通过ServletContext中的getResourceAsStream方法读取文件
* @throws IOException
*/
private void getProperty2() throws IOException {
// 获取ServletContext对象
ServletContext context = getServletContext();
// 1、创建属性对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
// 2、指定载入的数据源
InputStream inStream = context.getResourceAsStream("file/config.properties");
properties.load(inStream);
// 3、获取name属性的值
String name = properties.getProperty("name");
System.out.println("getProperty2():name=" + name);
}
/**
* 方法1:通过ServletContext中的getRealPath方法读取文件
* @throws FileNotFoundException
* @throws IOException
*/
private void getProperty1() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
// 获取ServletContext对象
ServletContext context = getServletContext();
// 获取给定的文件在服务器上面的绝对路径
String path = context.getRealPath("file/config.properties");
// 1、创建属性对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
// 2、指定载入的数据源
InputStream inStream = new FileInputStream(path);
properties.load(inStream);
// 3、获取name属性的值
String name = properties.getProperty("name");
System.out.println("getProperty1():name=" + name);
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
}
}
配置Servlet,执行得到结果
getProperty1():name=zhujunwei
getProperty2():name=zhujunwei
getProperty3():name=zhujunwei3、存取数据,servlet间共享数据 域对象
思路分析
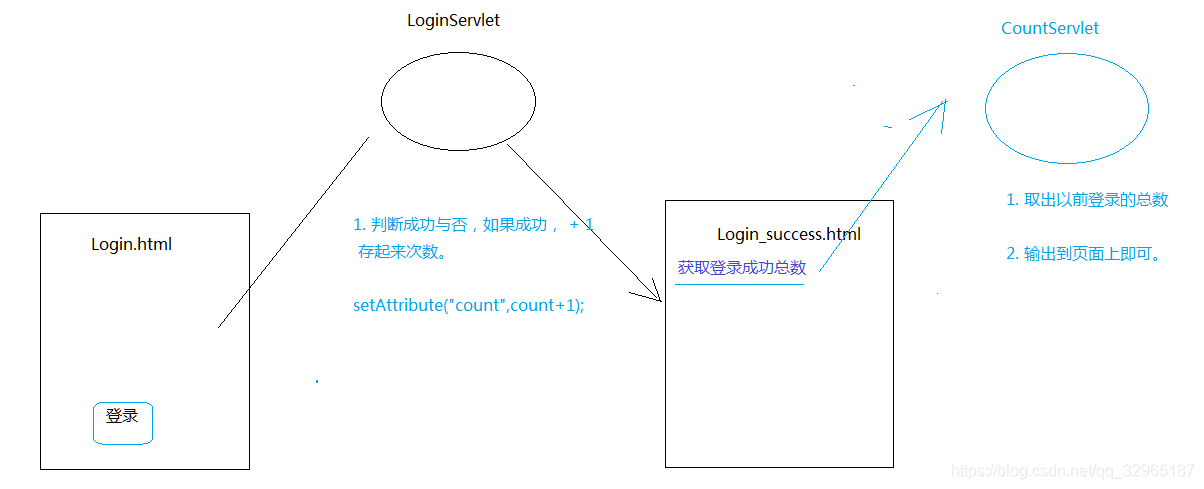
Login.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>请输入账号密码登录</h2>
<form action="LoginServlet" method="get">
账号:<input type="text" name="username"><br>
密码:<input type="text" name="password"><br>
<input type="submit" value="登录">
</form>
</body>
</html>LoginServlet
package com.zhujunwei.servletContext;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
/**
* 从客户端取得用户输入的账号和密码,经过校验后跳转到指定的页面
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//获取客户端输入的值
String username = request.getParameter("username");
String password = request.getParameter("password");
//对值进行校验并返回客户端
if("admin".equals(username)&&"123456".equals(password))
{
//1、成功次数的累加
//获取以前存的值,然后在旧的值基础上+1
Object obj = getServletContext().getAttribute("count");
//默认就是0次
int totalCount = 0;
if(obj!=null)
{
totalCount = (int) obj;
}
//给count赋新的值
getServletContext().setAttribute("count", totalCount+1);
//2、跳转到login_success.html
//设置状态码 :重新定位状态码
response.setStatus(302);
//定位跳转的位置是哪一个页面
response.setHeader("Location", "login_success.html");
}
else
{
PrintWriter pw = response.getWriter();
pw.write("login filed...");
}
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
}
}
login_success.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>登录成功</h2>
<a href="ServletContext04">查看网页登录成功的次数。</a>
</body>
</html>CountServlet
package com.zhujunwei.servletContext;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class CountServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//取值
int count = (int) getServletContext().getAttribute("count");
//输出到界面
response.getWriter().write("Login Success Count:"+count);
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
}
}
运行结果



ServlerContext的生命周期
服务器启动的时候,会为托管的每一个web应用程序,创建一个ServletContext对象
从服务器移除托管,或者是关闭服务器。
ServletContext 的作用范围
只要在这个项目里面,都可以取。 只要同一个项目。 A项目存,在B项目取,是取不到的,因为ServletContext对象不同。
---------------
我每一次回头,都感觉自己不够努力,所以我不再回头。
---------------



