Java Set集合
1 Set集合
一个不包含重复元素的 collection。更确切地讲,set 不包含满足 e1.equals(e2) 的元素对 e1 和 e2,并且最多包含一个 null 元素。正如其名称所暗示的,此接口模仿了数学上的 set 抽象。
public interface Set<E> extends Collection<E>
特点:无序、无下标、元素不可重复
方法:全部继承自Collection中的方法
2 常用方法
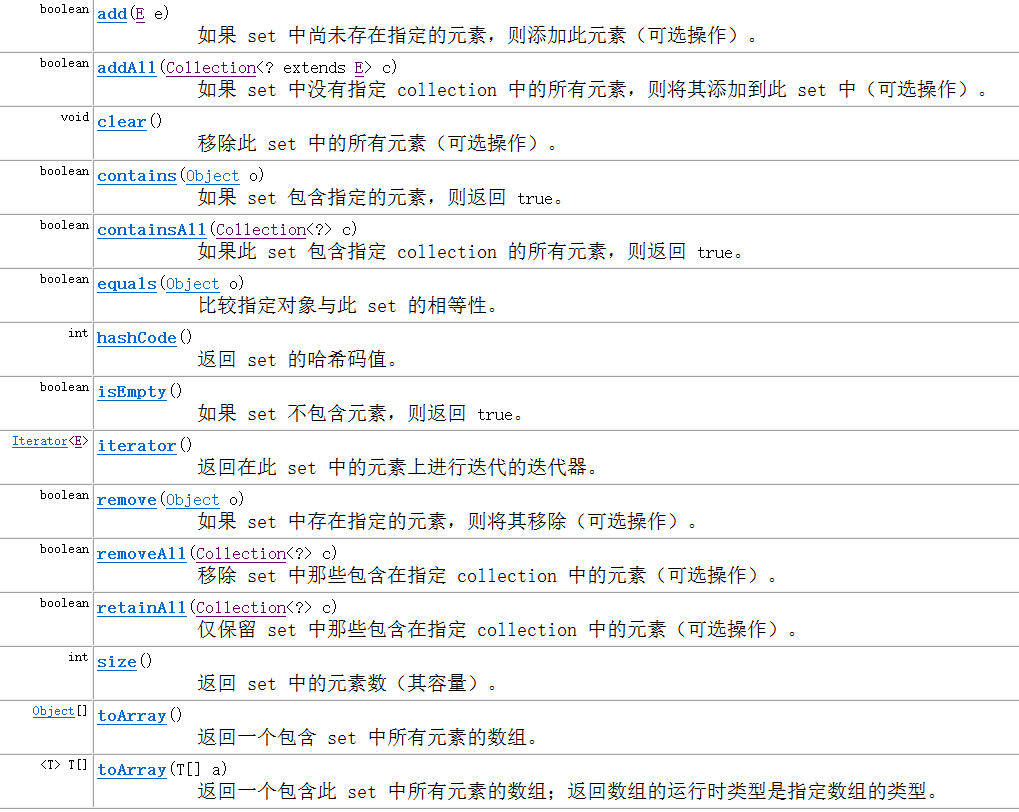
3 实现类
3.1 HashSet[重点]
- 基于HashCode、equals实现元素不重复
- 当存入元素的哈希码相同时,会调用equals进行确认,如结果为true,则拒绝后者存入
- 存入的元素要重写hashCode和equals方法
基本用法
/**
* HashSet的使用
* 存储结构:哈希表(数组+链表+红黑树)
*/
public class Set1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
Set<String> stringSet = new HashSet<>();
//添加元素
stringSet.add("小米");
stringSet.add("华为");
stringSet.add("苹果");
stringSet.add("苹果");//只能保存一个相同的元素
stringSet.add(null);
stringSet.add(null);//可以存放一个null
System.out.println(stringSet);//打印无序
//删除
stringSet.remove("苹果");
System.out.println(stringSet);
/**
* 遍历
*/
System.out.println("****增强for****");
for (String s : stringSet) {
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("****迭代器****");
Iterator<String> stringIterator = stringSet.iterator();
while (stringIterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(stringIterator.next());
}
//判断
boolean containsXiaoMi = stringSet.contains("小米");
System.out.println(containsXiaoMi);
System.out.println("集合大小:"+stringSet.size());
}
}
运行结果
[null, 苹果, 华为, 小米]
[null, 华为, 小米]
****增强for****
null
华为
小米
****迭代器****
null
华为
小米
true
集合大小:3
存放对象
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
//getter、setter、构造器、toString
/**
* 重写hashCode和equals方法
*/
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Person person = (Person) o;
return age == person.age &&
Objects.equals(name, person.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age);
}
}
/**
* HashSet的使用
* 存储结构:哈希表(数组+链表+红黑树)
* 存储过程:
* 1、根据hashCode计算保存的位置,如果此位置为空,则直接保存,如果不为空执行第二步
* 2、再执行equals方法,如果equals方法为true,则认为时重复,否则,形成链表
*/
public class Set2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<Person> personHashSet = new HashSet<>();
Person p1 = new Person("婉儿",18);
Person p2 = new Person("公孙离",18);
Person p3 = new Person("妲己",18);
personHashSet.add(p1);
personHashSet.add(p2);
personHashSet.add(p3);
personHashSet.add(null);
/**
* 因为Person重写了hashCode和equals方法,不能再重复添加了
*
*/
personHashSet.add(new Person("妲己",18));
System.out.println(personHashSet);
}
}
运行结果:
[null, Person{name='婉儿', age=18}, Person{name='妲己', age=18}, Person{name='公孙离', age=18}]
3.2 TreeSet
- 基于排列顺序实现元素不重复
- 实现了SortedSet接口,对集合元素自动排序
- 元素对象的类型必须实现Comparable接口,指定排序规则
- 通过CompareTo方法确定是否为重复元素
基本用法
/**
* TreeSet的使用:
* 存储结构:红黑树
* 要求:元素必须实现Comparable接口,compareTo()方法返回值为0,认为是重复元素
*/
public class Set3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合 String类已经实现了Comparable接口,可以直接添加
Set<String> stringSet = new TreeSet<>();
stringSet.add("hello");
stringSet.add("abc");
stringSet.add("xyz");
stringSet.add("xyz");//重复元素不能添加
//stringSet.add(null); //发现不能存放null
System.out.println(stringSet);//发现集合已经排序了
//Person类需要实现Comparable接口,实现compareTo方法
Set<Person> personSet = new TreeSet<>();
Person p1 = new Person("x婉儿",18);
Person p2 = new Person("a公孙离",18);
Person p3 = new Person("d妲己",18);
Person p4 = new Person("d妲己",16);
personSet.add(p1);
personSet.add(p2);
personSet.add(p3);
personSet.add(p4);
System.out.println(personSet);
//查询某个元素是否存在
boolean b = personSet.contains(new Person("d妲己", 16));
System.out.println(b);
//集合大小
System.out.println("大小:"+personSet.size());
//删除某个元素 comparedTo方法的返回值相同就认为元素存在,就可以删除
System.out.println(personSet.remove(new Person("d妲己", 16)));
//清空集合
personSet.clear();
//遍历
//迭代器
//增强for
}
}
public class Person implements Comparable<Person>{
private String name;
private int age;
//getter、setter、构造器、toString
/**
* 定义排序规则:名字,年龄
*/
@Override
public int compareTo(Person o) {
int byName = this.name.compareTo(o.name);
int byAge = this.age - o.age;
return byName==0 ? byAge : byName;
}
}
运行结果
[abc, hello, xyz]
[Person{name='a公孙离', age=18}, Person{name='d妲己', age=16}, Person{name='d妲己', age=18}, Person{name='x婉儿', age=18}]
true
大小:4
true
也可以通过TreeSet的构造方法传入Comparator指定比较规则,这样元素就可以不用实现Comparable接口了
public class Set3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//通过TreeSet的构造方法传入Comparator指定比较规则
//使用匿名内部类
Set<Person> personSet2 = new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<Person>() {
@Override
public int compare(Person p1, Person p2) {
int byName = p1.getName().compareTo(p2.getName());
int byAge = p1.getAge()- p2.getAge();
return byName==0 ? byAge:byName;
}
});
//使用Lambda表达式
Set<Person> personSet = new TreeSet<>((p1,p2)->{
int byName = p1.getName().compareTo(p2.getName());
int byAge = p1.getAge()- p2.getAge();
return byName==0 ? byAge:byName;
});
Person p1 = new Person("x婉儿",18);
Person p2 = new Person("a公孙离",18);
Person p3 = new Person("d妲己",18);
Person p4 = new Person("d妲己",16);
personSet.add(p1);
personSet.add(p2);
personSet.add(p3);
personSet.add(p4);
System.out.println(personSet);
}
}
4 HashSet和TreeSet区别
HashSet
不能保证元素的排列顺序,顺序有可能发生变化
集合元素可以是null,但只能放入一个null
HashSet底层是采用HashMap实现的
HashSet底层是哈希表实现的
TreeSet
Treeset中的数据是排好序的,不允许放入null值。
TreeSet是通过TreeMap实现的,只不过Set用的只是Map的key。
TreeSet的底层实现是采用二叉树(红-黑树)的数据结构
---------------
我每一次回头,都感觉自己不够努力,所以我不再回头。
---------------



