Day2 - python数据类型:列表、元组、字典、集合、文件、编码与解码
本节内容
- 列表、元组操作
- 字符串操作
- 字典操作
- 集合操作
- 文件操作
- 字符编码与转码
1. 列表、元组操作
列表是我们最以后最常用的数据类型之一,通过列表可以对数据实现最方便的存储、修改等操作
定义列表
name_list = ['alex', 'seven', 'eric'] 或 name_list = list(['alex', 'seven', 'eric'])
通过下标访问列表中的元素,下标从0开始计数
1 >>> names[0] #0 表示列表从左边开始第一位 2 'Alex' 3 >>> names[2] 4 'Eric' 5 >>> names[-1] #-1 表示列表从左边开始最后一位,或者从右边开始第一位 6 'Eric' 7 >>> names[-2] #还可以倒着取 8 'Tenglan'
切片:取多个元素

>>> names = ["Alex","Tenglan","Eric","Rain","Tom","Amy"] >>> names[1:4] #取下标1至下标4之间的数字,包括1,不包括4 ['Tenglan', 'Eric', 'Rain'] >>> names[1:-1] #取下标1至-1的值,不包括-1 ['Tenglan', 'Eric', 'Rain', 'Tom'] >>> names[0:3] ['Alex', 'Tenglan', 'Eric'] >>> names[:3] #如果是从头开始取,0可以忽略,跟上句效果一样 ['Alex', 'Tenglan', 'Eric'] >>> names[3:] #如果想取最后一个,必须不能写-1,只能这么写 ['Rain', 'Tom', 'Amy'] >>> names[3:-1] #这样-1就不会被包含了 ['Rain', 'Tom'] >>> names[0::2] #后面的2是表示,每隔一个元素,就取一个 ['Alex', 'Eric', 'Tom'] >>> names[::2] #和上句效果一样 ['Alex', 'Eric', 'Tom']
追加

>>> names=['Alex', 'Tenglan', 'Eric', 'Rain', 'Tom', 'Amy'] >>> names.append("我是新来的") >>> print(names) ['Alex', 'Tenglan', 'Eric', 'Rain', 'Tom', 'Amy', '我是新来的']
插入

>>> names ['Alex', 'Tenglan', 'Eric', 'Rain', 'Tom', 'Amy', '我是新来的'] >>> names.insert(2,"强行从Eric前面插入") >>> names ['Alex', 'Tenglan', '强行从Eric前面插入', 'Eric', 'Rain', 'Tom', 'Amy', '我是新来的'] >>> names.insert(5,"从eric后面插入试试新姿势") >>> names ['Alex', 'Tenglan', '强行从Eric前面插入', 'Eric', 'Rain', '从eric后面插入试试新姿势', 'Tom', 'Amy', '我是新来的']
修改

>>> names ['Alex', 'Tenglan', '强行从Eric前面插入', 'Eric', 'Rain', '从eric后面插入试试新姿势', 'Tom', 'Amy', '我是新来的'] >>> names[2] = "该换人了" >>> names ['Alex', 'Tenglan', '该换人了', 'Eric', 'Rain', '从eric后面插入试试新姿势', 'Tom', 'Amy', '我是新来的']
删除

>>> del names[2] >>> names ['Alex', 'Tenglan', 'Eric', 'Rain', '从eric后面插入试试新姿势', 'Tom', 'Amy', '我是新来的'] >>> del names[4] >>> names ['Alex', 'Tenglan', 'Eric', 'Rain', 'Tom', 'Amy', '我是新来的'] >>> >>> names.remove("Eric") #删除指定元素 >>> names ['Alex', 'Tenglan', 'Rain', 'Tom', 'Amy', '我是新来的'] >>> names.pop() #删除列表最后一个值 '我是新来的' >>> names ['Alex', 'Tenglan', 'Rain', 'Tom', 'Amy']
扩展

>>> names ['Alex', 'Tenglan', 'Rain', 'Tom', 'Amy'] >>> b = [1,2,3] >>> names.extend(b) >>> names ['Alex', 'Tenglan', 'Rain', 'Tom', 'Amy', 1, 2, 3]
拷贝(注意浅拷贝与深拷贝的区别)

>>> names ['Alex', 'Tenglan', 'Rain', 'Tom', 'Amy', 1, 2, 3] >>> name_copy = names.copy() >>> name_copy ['Alex', 'Tenglan', 'Rain', 'Tom', 'Amy', 1, 2, 3]

1 import copy 2 3 a = [1, 2, 3, 4, ['a', 'b']] # 原始对象 4 5 b = a # 赋值,传对象的引用 6 c = copy.copy(a) # 浅拷贝 7 d = copy.deepcopy(a) # 深拷贝 8 9 a.append(5) # 修改对象a 10 a[4].append('c') # 修改对象a中的['a', 'b']数组对象 11 12 print ('a = ', a) 13 print ('b = ', b) 14 print ('c = ', c) 15 print ('d = ', d) 16 17 输出: 18 a = [1, 2, 3, 4, ['a', 'b', 'c'], 5] 19 b = [1, 2, 3, 4, ['a', 'b', 'c'], 5] #b是a的内存地址的引用,所以最后b的值也改变了,像列表、元组、字典都是这样,字符串、数字就不会 20 c = [1, 2, 3, 4, ['a', 'b', 'c']] #浅拷贝,只拷贝第一层,即拷贝子列表的内存地址,所以a改变子列表c也会一起改变 21 d = [1, 2, 3, 4, ['a', 'b']] #深拷贝,拷贝到最里层,a的改变对d没有影响,d是一个独立的内存地址,不是a的内存地址的引用
统计

>>> names ['Alex', 'Tenglan', 'Amy', 'Tom', 'Amy', 1, 2, 3] >>> names.count("Amy") 2
排序&翻转

>>> names ['Alex', 'Tenglan', 'Amy', 'Tom', 'Amy', 1, 2, 3] >>> names.sort() #排序 Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> TypeError: unorderable types: int() < str() #3.0里不同数据类型不能放在一起排序了,擦 >>> names[-3] = '1' >>> names[-2] = '2' >>> names[-1] = '3' >>> names ['Alex', 'Amy', 'Amy', 'Tenglan', 'Tom', '1', '2', '3'] >>> names.sort() >>> names ['1', '2', '3', 'Alex', 'Amy', 'Amy', 'Tenglan', 'Tom'] >>> names.reverse() #反转 >>> names ['Tom', 'Tenglan', 'Amy', 'Amy', 'Alex', '3', '2', '1']
获取下标

>>> names ['Tom', 'Tenglan', 'Amy', 'Amy', 'Alex', '3', '2', '1'] >>> names.index("Amy") 2 #只返回找到的第一个下标
元组(只读列表)
元组其实跟列表差不多,也是存一组数,只不是它一旦创建,便不能再修改,所以又叫只读列表
创建元组
1 ages = (11, 22, 33, 44, 55) 2 或 3 ages = tuple((11, 22, 33, 44, 55))
元组只有2个方法,一个是count,一个是index。
程序练习
程序:购物车程序
需求:
- 启动程序后,让用户输入工资,然后打印商品列表
- 允许用户根据商品编号购买商品
- 用户选择商品后,检测余额是否够,够就直接扣款,不够就提醒
- 可随时退出,退出时,打印已购买商品和余额
2. 字符串操作
特性:不可修改

name.capitalize() 首字母大写 name.casefold() 大写全部变小写 name.center(50,"-") 输出 '---------------------Alex Li----------------------' name.count('lex') 统计 lex出现次数 name.encode() 将字符串编码成bytes格式 name.endswith("Li") 判断字符串是否以 Li结尾 "Alex\tLi".expandtabs(10) 输出'Alex Li', 将\t转换成指定的空格 name.find('A') 查找A,找到返回其索引, 找不到返回-1 #字符串格式化输出 format : >>> msg = "my name is {}, and age is {}" >>> msg.format("alex",22) 'my name is alex, and age is 22' >>> msg = "my name is {1}, and age is {0}" >>> msg.format("alex",22) 'my name is 22, and age is alex' >>> msg = "my name is {name}, and age is {age}" >>> msg.format(age=22,name="ale") 'my name is ale, and age is 22' format_map : >>> msg.format_map({'name':'alex','age':22}) 'my name is alex, and age is 22' %s(占位符) : >>>msg = "my name is %s, and age is %s"%("alex",22) 'my name is alex, and age is 22' #字符串拼接 #str1 + str2,效率低,不推荐使用 >>>"a"+"l"+"e"+"x" “alex” #str1,str2 >>>"a","l","e","x" “alex” #str1 str2,两个字符串中间有没有空格、空格多大都一样的效果 >>>"a""l" "e" "x" “alex” # % 连接字符串:"%s%s"%(str1,str2) >>>'%s %s' % ('Jim', 'Green') 'Jim Green' #字符串列表连接:str.join(some_list) >>>var_list = ['tom', 'david', 'john'] >>>a = "###" >>>a.join(var_list) 'tom###david###john' msg.index('a') 返回a所在字符串的索引 '9aA'.isalnum() True '9'.isdigit() 是否整数 name.isnumeric name.isprintable name.isspace name.istitle name.isupper "|".join(['alex','jack','rain']) 'alex|jack|rain' maketrans >>> intab = "aeiou" #This is the string having actual characters. >>> outtab = "12345" #This is the string having corresponding mapping character >>> trantab = str.maketrans(intab, outtab) >>> >>> str = "this is string example....wow!!!" >>> str.translate(trantab) 'th3s 3s str3ng 2x1mpl2....w4w!!!' msg.partition('is') 输出 ('my name ', 'is', ' {name}, and age is {age}') >>> "alex li, chinese name is lijie".replace("li","LI",1) 'alex LI, chinese name is lijie' msg.swapcase 大小写互换 >>> msg.zfill(40) 不够40位就填充满 '00000my name is {name}, and age is {age}' >>> n4.ljust(40,"-") 'Hello 2orld-----------------------------' >>> n4.rjust(40,"-") '-----------------------------Hello 2orld' >>> b="ddefdsdff_哈哈" >>> b.isidentifier() #检测一段字符串可否被当作标志符,即是否符合变量命名规则 True
3. 字典操作
字典一种key - value 的数据类型,使用就像我们上学用的字典,通过笔划、字母来查对应页的详细内容。
语法:
info = { 'stu1101': "TengLan Wu", 'stu1102': "LongZe Luola", 'stu1103': "XiaoZe Maliya", }
字典的特性:
- dict是无序的
- key必须是唯一的,so 天生去重
增加

>>> info["stu1104"] = "苍井空" >>> info {'stu1102': 'LongZe Luola', 'stu1104': '苍井空', 'stu1103': 'XiaoZe Maliya', 'stu1101': 'TengLan Wu'}
修改

>>> info['stu1101'] = "武藤兰" >>> info {'stu1102': 'LongZe Luola', 'stu1103': 'XiaoZe Maliya', 'stu1101': '武藤兰'}
删除

>>> info {'stu1102': 'LongZe Luola', 'stu1103': 'XiaoZe Maliya', 'stu1101': '武藤兰'} >>> info.pop("stu1101") #标准删除姿势 '武藤兰' >>> info {'stu1102': 'LongZe Luola', 'stu1103': 'XiaoZe Maliya'} >>> del info['stu1103'] #换个姿势删除 >>> info {'stu1102': 'LongZe Luola'} >>> >>> >>> info = {'stu1102': 'LongZe Luola', 'stu1103': 'XiaoZe Maliya'} >>> info {'stu1102': 'LongZe Luola', 'stu1103': 'XiaoZe Maliya'} #随机删除 >>> info.popitem() ('stu1102', 'LongZe Luola') >>> info {'stu1103': 'XiaoZe Maliya'}
查找

>>> info = {'stu1102': 'LongZe Luola', 'stu1103': 'XiaoZe Maliya'}
>>>
>>> "stu1102" in info #标准用法
True
>>> info.get("stu1102") #获取
'LongZe Luola'
>>> info["stu1102"] #同上,但是看下面
'LongZe Luola'
>>> info["stu1105"] #如果一个key不存在,就报错,get不会,不存在只返回None
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
KeyError: 'stu1105'
多级字典嵌套及操作

av_catalog = { "欧美":{ "www.youporn.com": ["很多免费的,世界最大的","质量一般"], "www.pornhub.com": ["很多免费的,也很大","质量比yourporn高点"], "letmedothistoyou.com": ["多是自拍,高质量图片很多","资源不多,更新慢"], "x-art.com":["质量很高,真的很高","全部收费,屌比请绕过"] }, "日韩":{ "tokyo-hot":["质量怎样不清楚,个人已经不喜欢日韩范了","听说是收费的"] }, "大陆":{ "1024":["全部免费,真好,好人一生平安","服务器在国外,慢"] } } av_catalog["大陆"]["1024"][1] += ",可以用爬虫爬下来" print(av_catalog["大陆"]["1024"]) #ouput ['全部免费,真好,好人一生平安', '服务器在国外,慢,可以用爬虫爬下来']
其它知识点

#values 以列表格式返回字典的值 >>> info.values() dict_values(['LongZe Luola', 'XiaoZe Maliya']) #keys 以列表格式返回字典的键 >>> info.keys() dict_keys(['stu1102', 'stu1103']) #items 以列表格式返回可遍历的(键, 值) 元组数组 info.items() dict_items([('stu1102', 'LongZe Luola'), ('stu1103', 'XiaoZe Maliya'),]) #setdefault 如果键在字典中,返回这个键所对应的值。如果键不在字典中,向字典 中插入这个键值对,并返回 键值对的值。 >>> info.setdefault("stu1106","Alex") 'Alex' >>> info {'stu1102': 'LongZe Luola', 'stu1103': 'XiaoZe Maliya', 'stu1106': 'Alex'} >>> info.setdefault("stu1102","龙泽萝拉") 'LongZe Luola' >>> info {'stu1102': 'LongZe Luola', 'stu1103': 'XiaoZe Maliya', 'stu1106': 'Alex'} #update 更新字典,添加新的键值对到字典里 >>> info {'stu1102': 'LongZe Luola', 'stu1103': 'XiaoZe Maliya', 'stu1106': 'Alex'} >>> b = {1:2,3:4, "stu1102":"龙泽萝拉"} >>> info.update(b) >>> info {'stu1102': '龙泽萝拉', 1: 2, 3: 4, 'stu1103': 'XiaoZe Maliya', 'stu1106': 'Alex'} #通过一个列表生成默认dict,有个没办法解释的坑,少用吧这个 >>> dict.fromkeys([1,2,3],'testd') {1: 'testd', 2: 'testd', 3: 'testd'}
循环dict
#方法1 for key in info: print(key,info[key]) #方法2 for k,v in info.items(): #会先把dict转成list,数据里大时莫用 print(k,v)
程序练习
程序: 三级菜单
要求:
- 打印省、市、县三级菜单
- 可返回上一级
- 可随时退出程序

1 menu = { 2 '北京':{ 3 '海淀':{ 4 '五道口':{ 5 'soho':{}, 6 '网易':{}, 7 'google':{} 8 }, 9 '中关村':{ 10 '爱奇艺':{}, 11 '汽车之家':{}, 12 'youku':{}, 13 }, 14 '上地':{ 15 '百度':{}, 16 }, 17 }, 18 '昌平':{ 19 '沙河':{ 20 '老男孩':{}, 21 '北航':{}, 22 }, 23 '天通苑':{}, 24 '回龙观':{}, 25 }, 26 '朝阳':{}, 27 '东城':{}, 28 }, 29 '上海':{ 30 '闵行':{ 31 "人民广场":{ 32 '炸鸡店':{} 33 } 34 }, 35 '闸北':{ 36 '火车战':{ 37 '携程':{} 38 } 39 }, 40 '浦东':{}, 41 }, 42 '山东':{}, 43 } 44 45 46 exit_flag = False 47 current_layer = menu 48 49 layers = [menu] 50 51 while not exit_flag: 52 for k in current_layer: 53 print(k) 54 choice = input(">>:").strip() 55 if choice == "b": 56 current_layer = layers[-1] 57 #print("change to laster", current_layer) 58 layers.pop() 59 elif choice not in current_layer:continue 60 else: 61 layers.append(current_layer) 62 current_layer = current_layer[choice]
4.集合操作
集合是一个无序的,不重复的数据组合,它的主要作用如下:
- 去重,把一个列表变成集合,就自动去重了
- 关系测试,测试两组数据之前的交集、差集、并集等关系
常用操作

s = set([3,5,9,10]) #创建一个数值集合 t = set("Hello") #创建一个唯一字符的集合 a = t | s # t 和 s的并集 b = t & s # t 和 s的交集 c = t – s # 求差集(项在t中,但不在s中) d = t ^ s # 对称差集(项在t或s中,但不会同时出现在二者中) 基本操作: t.add('x') # 添加一项 s.update([10,37,42]) # 在s中添加多项 使用remove()可以删除一项: t.remove('H') len(s) set 的长度 x in s 测试 x 是否是 s 的成员 x not in s 测试 x 是否不是 s 的成员 s.issubset(t) s <= t 测试是否 s 中的每一个元素都在 t 中 s.issuperset(t) s >= t 测试是否 t 中的每一个元素都在 s 中 s.union(t) s | t 返回一个新的 set 包含 s 和 t 中的每一个元素 s.intersection(t) s & t 返回一个新的 set 包含 s 和 t 中的公共元素 s.difference(t) s - t 返回一个新的 set 包含 s 中有但是 t 中没有的元素 s.symmetric_difference(t) s ^ t 返回一个新的 set 包含 s 和 t 中不重复的元素 s.copy() 返回 set “s”的一个浅复制
5. 文件操作
对文件操作流程
- 打开文件,得到文件句柄并赋值给一个变量
- 通过句柄对文件进行操作
- 关闭文件
基本操作
1 f = open('filename') #打开文件 2 first_line = f.readline() #读一行 3 print('first line:',first_line) 4 print('我是分隔线'.center(50,'-')) 5 data = f.read()# 读取所有内容,文件大时不要用 6 print(data) #打印文件 7 8 f.close() #关闭文件
打开文件的模式有:
- r,只读模式(默认)。
- w,只写模式。【不可读;不存在则创建;存在则删除内容;】
- a,追加模式。【可读; 不存在则创建;存在则只追加内容;】
"+" 表示可以同时读写某个文件
- r+,可读写文件。【可读;可写;可追加】
- w+,写读
- a+,同a
"U"表示在读取时,可以将 \r \n \r\n自动转换成 \n (与 r 或 r+ 模式同使用)
- rU
- r+U
"b"表示处理二进制文件(如:FTP发送上传ISO镜像文件,linux可忽略,windows处理二进制文件时需标注)
- rb
- wb
- ab
其它语法

def close(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ Close the file. A closed file cannot be used for further I/O operations. close() may be called more than once without error. """ pass def fileno(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return the underlying file descriptor (an integer). """ pass def isatty(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ True if the file is connected to a TTY device. """ pass def read(self, size=-1): # known case of _io.FileIO.read """ 注意,不一定能全读回来 Read at most size bytes, returned as bytes. Only makes one system call, so less data may be returned than requested. In non-blocking mode, returns None if no data is available. Return an empty bytes object at EOF. """ return "" def readable(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ True if file was opened in a read mode. """ pass def readall(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Read all data from the file, returned as bytes. In non-blocking mode, returns as much as is immediately available, or None if no data is available. Return an empty bytes object at EOF. """ pass def readinto(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ Same as RawIOBase.readinto(). """ pass #不要用,没人知道它是干嘛用的 def seek(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Move to new file position and return the file position. Argument offset is a byte count. Optional argument whence defaults to SEEK_SET or 0 (offset from start of file, offset should be >= 0); other values are SEEK_CUR or 1 (move relative to current position, positive or negative), and SEEK_END or 2 (move relative to end of file, usually negative, although many platforms allow seeking beyond the end of a file). Note that not all file objects are seekable. """ pass def seekable(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ True if file supports random-access. """ pass def tell(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Current file position. Can raise OSError for non seekable files. """ pass def truncate(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Truncate the file to at most size bytes and return the truncated size. Size defaults to the current file position, as returned by tell(). The current file position is changed to the value of size. """ pass def writable(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ True if file was opened in a write mode. """ pass def write(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Write bytes b to file, return number written. Only makes one system call, so not all of the data may be written. The number of bytes actually written is returned. In non-blocking mode, returns None if the write would block. """ pass
with语句
为了避免打开文件后忘记关闭,可以通过管理上下文,即:
1 with open('log','r') as f: 2 3 ...
如此方式,当with代码块执行完毕时,内部会自动关闭并释放文件资源。
在Python 2.7 后,with又支持同时对多个文件的上下文进行管理,即:
with open('log1') as obj1, open('log2') as obj2: pass
程序练习
程序1: 实现简单的shell sed替换功能
程序2:修改haproxy配置文件
需求:
 需求
需求 原配置文件
原配置文件
6. 字符编码与转码
详细文章:
http://www.cnblogs.com/yuanchenqi/articles/5956943.html
http://www.diveintopython3.net/strings.html
需知:
1.在python2默认编码是ASCII, python3里默认是unicode
2.unicode 分为 utf-32(占4个字节),utf-16(占两个字节),utf-8(占1-4个字节), so utf-16就是现在最常用的unicode版本, 不过在文件里存的还是utf-8,因为utf8省空间
3.在py3中encode,在转码的同时还会把string 变成bytes类型,decode在解码的同时还会把bytes变回string
先说python2
- py2里默认编码是ascii
- 文件开头那个编码声明是告诉解释这个代码的程序 以什么编码格式 把这段代码读入到内存,因为到了内存里,这段代码其实是以bytes二进制格式存的,不过即使是2进制流,也可以按不同的编码格式转成2进制流,你懂么?
- 如果在文件头声明了#_*_coding:utf-8*_,就可以写中文了, 不声明的话,python在处理这段代码时按ascii,显然会出错, 加了这个声明后,里面的代码就全是utf-8格式了
- 在有#_*_coding:utf-8*_的情况下,你在声明变量如果写成name=u"大保健",那这个字符就是unicode格式,不加这个u,那你声明的字符串就是utf-8格式
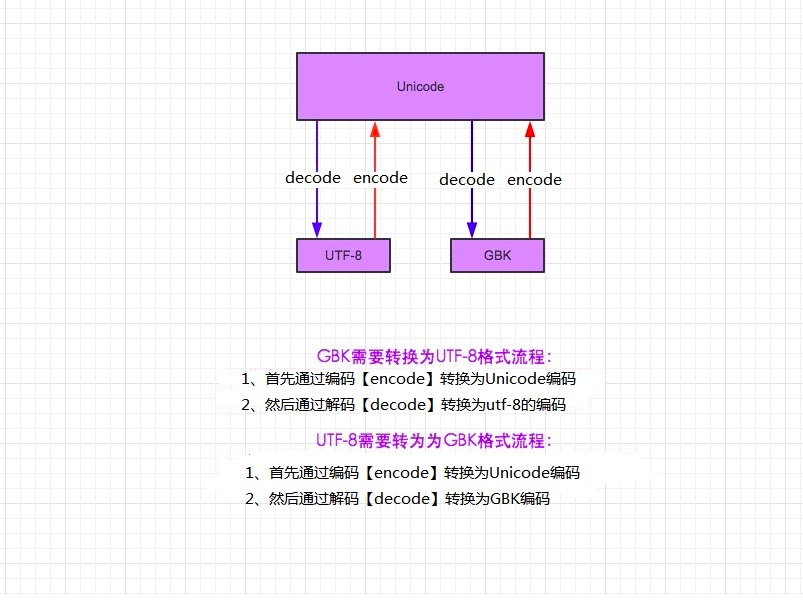
- utf-8 to gbk怎么转,utf8先encode成unicode,再decode成gbk
再说python3
- py3里默认文件编码就是utf-8,所以可以直接写中文,也不需要文件头声明编码了,干的漂亮
- 你声明的变量默认是unicode编码,不是utf-8, 因为默认即是unicode了(不像在py2里,你想直接声明成unicode还得在变量前加个u), 此时你想转成gbk的话,直接your_str.encode("gbk")即可以
- 但py3里,你在your_str.encode("gbk")时,感觉好像还加了一个动作,就是就是encode的数据变成了bytes里,我擦,这是怎么个情况,因为在py3里,str and bytes做了明确的区分,你可以理解为bytes就是2进制流,你会说,我看到的不是010101这样的2进制呀, 那是因为python为了让你能对数据进行操作而在内存级别又帮你做了一层封装,否则让你直接看到一堆2进制,你能看出哪个字符对应哪段2进制么?什么?自己换算,得了吧,你连超过2位数的数字加减运算都费劲,还还是省省心吧。
- 那你说,在py2里好像也有bytes呀,是的,不过py2里的bytes只是对str做了个别名(python2里的str就是bytes, py3里的str是unicode),没有像py3一样给你显示的多出来一层封装,但其实其内部还是封装了的。 这么讲吧, 无论是2还是三, 从硬盘到内存,数据格式都是 010101二进制到-->b'\xe4\xbd\xa0\xe5\xa5\xbd' bytes类型-->按照指定编码转成你能看懂的文字
编码应用比较多的场景应该是爬虫了,互联网上很多网站用的编码格式很杂,虽然整体趋向都变成utf-8,但现在还是很杂,所以爬网页时就需要你进行各种编码的转换,不过生活正在变美好,期待一个不需要转码的世界。
最后,编码is a piece of fucking shit, noboby likes it.




