Acwing 第二章 数据结构
单链表

#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int M = 1e5+10;
int val[M],ne[M],idx,head;
int m;
void add_head(int x)
{
val[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = head;
head = idx;
idx++;
}
void add(int k,int x)
{
val[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = ne[k];
ne[k] = idx;
idx++;
}
void del(int k)
{
ne[k] = ne[ne[k]];
}
int main()
{
memset(ne,-1,sizeof ne);
idx = 1,head = -1;
cin>>m;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
char op;
int k,x;
cin>>op;
switch(op)
{
case 'H':
{
cin>>x;
add_head(x);
break;
}
case 'D':
{
cin>>k;
if(k==0) head = ne[head];
del(k);
break;
}
case 'I':
{
cin>>k>>x;
add(k,x);
break;
}
default:break;
}
}
for(int i=head;i!=-1;i = ne[i])
{
cout<<val[i]<<" ";
}
return 0;
}
双链表

//: # (打卡模板,上面预览按钮可以展示预览效果 ^^)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int M=1e5+10;
int l[M],r[M],e[M],cur;
void init()
{
r[0]=1;
l[1]=0;
cur=2;//注意索引结点的设置
}
void insert_r(int k,int x)
{
e[cur]=x;
l[cur]=k;
r[cur]=r[k];
l[r[k]]=cur;//注意:顺序不能反
r[k]=cur;
cur++;//注意:更新索引结点
}
void insert_l(int k,int x)
{
insert_r(l[k],x);
}
void remove(int k)
{
r[l[k]]=r[k];
l[r[k]]=l[k];
}
int main()
{
init();
int M,x,k;
cin>>M;
while(M--)
{
string op;
cin>>op;
if(op=="L")
{
cin>>x;
insert_r(0,x);
}
if(op=="R")
{
cin>>x;
insert_l(1,x);
}
if(op=="D")
{
cin>>k;
remove(k+1);
}
if(op=="IL")
{
cin>>k>>x;
insert_l(k+1,x);
}
if(op=="IR")
{
cin>>k>>x;
insert_r(k+1,x);
}
}
for(int i=r[0];i!=1;i=r[i])
{
cout<<e[i]<<" ";
}
return 0;
}
表达式求值

#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
stack<int>nums;
stack<char>op;
void eval()//作用:分别取出数字栈顶两个数和运算符栈顶的一个数进行运算,并将结果入栈
{
auto b=nums.top();nums.pop();//注意b a的顺序(先进后出)
auto a=nums.top();nums.pop();
auto c=op.top();op.pop();
int x;
if(c=='+') x=a+b;
else if(c=='-') x=a-b;
else if(c=='*') x=a*b;
else x=a/b;
nums.push(x);
}
int main()
{
unordered_map<char,int>pr{{'+',1},{'-',1},{'*',2},{'/',2}};//定义四则运算符的优先级
string str;
cin>>str;
for(int i=0;i<str.size();i++)
{
if(isdigit(str[i]))//字符为数字,就要继续往后走,将连续的数字字符转化为完整的数字(如123 28)
{
int x=0,j=i;
while(j<str.size()&&isdigit(str[j]))
{
x=x*10+str[j]-'0';
j++;
}//循环结束后str[j]刚好不是数字字符
nums.push(x);//转化后的数字要入栈
i=j-1;//注意更新i的位置,考虑到for循环在每次循环结束后i自加,故i为j-1,而不是j
}
else if(str[i]=='(') op.push(str[i]);//遇到左括号:入栈
else if(str[i]==')')//遇到右括号,根据优先级一定要先计算括号里面的表达式
{
while(op.top()!='(') eval();
op.pop();//括号内表达式运算结束后弹出 )
}
else//遇到其他字符(+,-,*,/)
{
while(op.size()&&pr[op.top()]>=pr[str[i]])//若运算符栈的栈顶优先级大于当前str[i]字符
{
eval();//先取栈顶运算
}
op.push(str[i]);//再将该字符入栈
}
}
while(op.size()) eval();//处理栈中剩余运算
cout<<nums.top()<<endl;//最终输出数字栈顶,即为答案
return 0;
}
单调栈
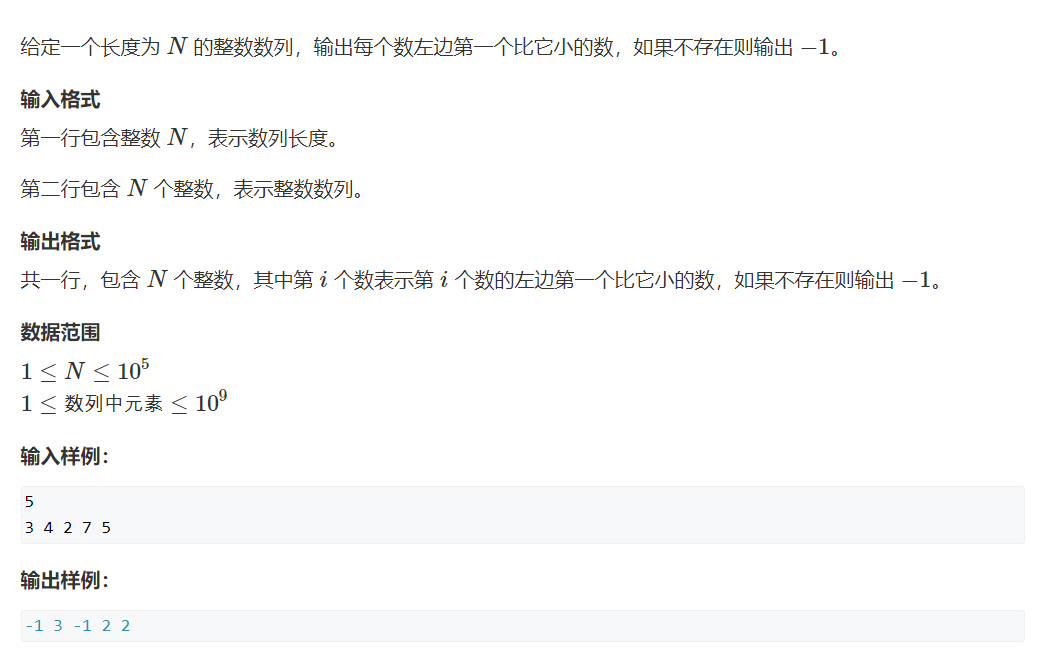
//: # (打卡模板,上面预览按钮可以展示预览效果 ^^)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int M=1e5+10;
int a[M],N,s[M],top=0;
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&N);
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
while(top&&s[top]>=a[i]) top--;//注意是>=
if(top) printf("%d ",s[top]);
else cout<<"-1 ";
s[++top]=a[i];
}
return 0;
}
单调队列
154. 滑动窗口
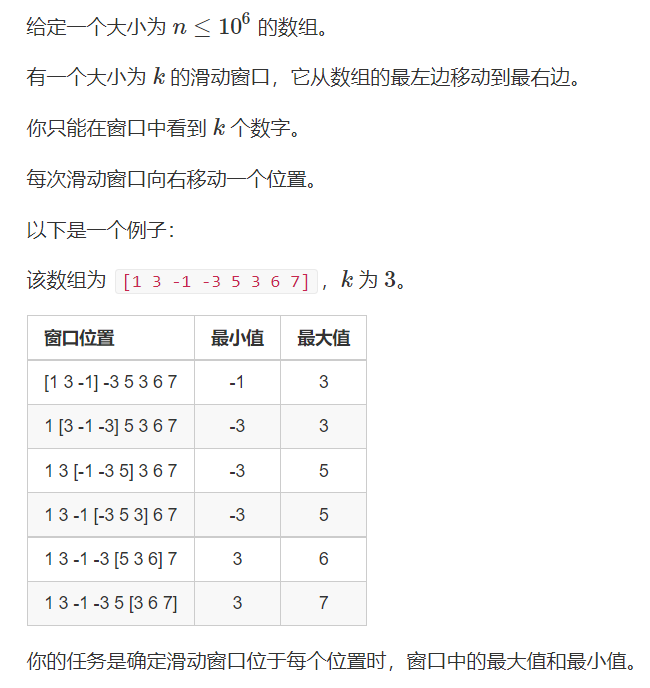
用一个队列维护窗口里面的所有值
当即将入队的队列比队尾元素小时,就让队尾元素出队,循环直到大于等于队尾元素时,停止,因为没有用

求最大值与该思想类似
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int n,k;
int a[N];
int q[N];//队列存储的是下标
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &k);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
cin>>a[i];
}
int hh = 0,tt = -1;
for (int i=0;i<n;i++) //单调队列处理最小值
{
if(hh<=tt && i - q[hh] + 1 > k) hh++; //维护当前窗口元素个数与k一致
while(hh<=tt && a[i] <= a[q[tt]]) tt--; //删去冗余元素,注意是从队尾删除
q[++tt] = i; //新元素入队
if(i+1>=k) cout<<a[q[hh]]<<' '; //i要足够大才能输出最值
}
puts("");
hh = 0,tt = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) //单调队列处理最大值
{
if(hh<=tt && i - q[hh] + 1 > k) hh++;
while(hh<=tt && a[i] >= a[q[tt]]) tt--;
q[++tt] = i;
if(i+1>=k) cout<<a[q[hh]]<<' ';
}
return 0;
}
KMP

//: # (打卡模板,上面预览按钮可以展示预览效果 ^^)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e5+10,M=1e6+10;
int n,m,ne[M];
char s[M],p[N];
int main()
{
cin>>n>>p+1>>m>>s+1;
for(int i=2,j=0;i<=n;i++)//ne[]的推导过程,在子串P中推导
{
while(j&&p[i]!=p[j+1]) j=ne[j];
if(p[i]==p[j+1]) j++;
ne[i]=j;
}
for(int i=1,j=0;i<=m;i++)//kmp的匹配过程,在总串S中推导
{
while(j&&s[i]!=p[j+1]) j=ne[j];
if(s[i]==p[j+1]) j++;
if(j==n)
{
cout<<i-n<<" ";//注意本题从0开始计数,不需要+1
j=ne[j];
}
}
return 0;
}
字典树(Trie)
835. Trie字符串统计
Trie:高效的存储和查找字符串集合的数据结构

#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e4+10;
int son[N][26],idx;//son数组表示字典树,idx表示层数索引
int cnt[N];//以当前结点结尾的单词数量
char x[N];
char op[2];
void insert(char s[])
{
int cur = 0;//表示当前位于第几层
for(int i=0;s[i]!='\0';i++)
{
int t = s[i] - 'a';
if(!son[cur][t]) son[cur][t] = ++idx; //没有路径就创造路径,注意是++idx
//idx是下一字母的层数
cur = son[cur][t];
}
cnt[cur]++;//更新以该结点结尾的单词数量
}
int query(char s[])
{
int cur = 0;//表示当前位于第几层
for(int i=0;s[i]!='\0';i++)
{
int t = s[i] - 'a';
if(!son[cur][t]) return 0;//不存在路径,直接返回0
cur = son[cur][t];
}
return cnt[cur];
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
cin>>op>>x;
if(op[0] == 'I')
{
insert(x);
}
else cout<<query(x)<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
143.最大异或对

#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int M = 1e5+10;
int n,a[M],son[31*M][2],idx,res;//son[]存字典树
void insert(int x)
{
int p=0;
for(int i=30;i>=0;i--)
{
int t=x>>i&1;//取第31-i位
if(!son[p][t]) son[p][t]=++idx;//若为0则说明不存在此节点,建立
p=son[p][t];//p走到下一层
}
}
int query(int x)
{
int p=0,re=0;//re用来以10进制的方式记录最大异或值
for(int i=30;i>=0;i--)
{
int t=x>>i&1;//取第31-i位
if(son[p][!t])//如果与第31-i位的互异数存在
{
p=son[p][!t];//走到互异的数那一层
re=re*2+!t;//计算最大异或值
}
else
{
p=son[p][t];//不存在只能走相同的数的层
re=re*2+t;//计算最大异或值
}
}
return re;
}
int main()
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
insert(a[i]);//先插入a[i]
int t=query(a[i]);//求出与a[i]最异的数
res = max(res,a[i]^t);//比较异或值
}
cout<<res;
return 0;
}
并查集
模板
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int M=1e5+10;
int n,m,p[M];//起初p[]表示每个结点的双亲结点,在find()操作后表示该节点的祖宗结点
int find(int x)//返回x的祖宗结点+路径压缩+递归
{
if(x!=p[x]) p[x]=find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
int main()
{
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) p[i]=i;//初始化每个集合,每个集合的祖宗结点是它数值本身
while(m--)
{
char op[2];
int a,b;
scanf("%s%d%d",op,&a,&b);
if(op[0]=='M')
{
p[find(b)]=find(a);//a的祖宗成为b的祖宗的双亲 or b的祖宗成为a的祖宗的双亲
}
else
{
if(find(a)==find(b)) cout<<"Yes"<<endl;//祖宗一样,证明是一个集合
else cout<<"No"<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
240. 食物链
带权并查集

#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 50005;
int n,k,c,x,y;
int p[N],d[N];
int ans;
int find(int x)
{
int t = p[x];
if(p[x]!=x)
{
p[x] = find(p[x]);
d[x] += d[t]; //维护距离,find前表示到父节点的距离,find后表示到祖宗结点的距离
}
return p[x];
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &k);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
p[i] = i;
}
while(k--)
{
cin>>c>>x>>y;
if(x>n||y>n)
{
++ans;
continue;
}
int px = find(x),py = find(y);
if(c==1) //同类,距离取余3为0
{
if(px == py && (d[x] - d[y]) % 3 != 0) ans++; //同一集合但距离mod3不为0,假话
else if(px!=py) //不同集合,则是真话,合并它们并用距离表示同类关系
{
p[px] = py;
d[px] = d[y] - d[x];
}
}
else //x吃y,距离取余3为1
{
if(px == py && (d[x] - d[y] - 1) % 3 !=0) ans++; //同一集合但距离mod3不为1,假话
else if(px != py) //不同集合,则是真话,合并它们并用距离表示捕食关系
{
p[px] = py;
d[px] = d[y] - d[x] + 1;
}
}
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
堆
838. 堆排序
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int M=1e5+10;
int h[M],cnt,n,m;
void down(int u)
{
int t=u;
if(2*u<=cnt&&h[2*u]<h[t]) t=2*u;//左儿子是否存在?左儿子是否小于父节点?
if(2*u+1<=cnt&&h[2*u+1]<h[t]) t=2*u+1;//右儿子是否存在?右儿子是否小于父节点或左儿子
if(t!=u)//最小值不是父节点
{
swap(h[t],h[u]);//交换
down(t);//必须最大限度的down到底
}
}
int main()
{
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&h[i]);
cnt++;
}
for(int i=n/2;i;i--)//无序插入不符合小根堆的性质,必须从n/2到堆顶进行down操作
down(i);
while(m--)//输出堆顶,删除堆顶
{
cout<<h[1]<<" ";
h[1]=h[cnt--];
down(1);
}
return 0;
}
839. 模拟堆

#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int h[N], ph[N], hp[N], cnt;
void heap_swap(int a, int b)
{
swap(ph[hp[a]],ph[hp[b]]);
swap(hp[a], hp[b]);
swap(h[a], h[b]);
}
void down(int u)
{
int t = u;
if (u * 2 <= cnt && h[u * 2] < h[t]) t = u * 2;
if (u * 2 + 1 <= cnt && h[u * 2 + 1] < h[t]) t = u * 2 + 1;
if (u != t)
{
heap_swap(u, t);
down(t);
}
}
void up(int u)
{
while (u / 2 && h[u] < h[u / 2])
{
heap_swap(u, u / 2);
u >>= 1;
}
}
int main()
{
int n, m = 0;
scanf("%d", &n);
while (n -- )
{
char op[5];
int k, x;
scanf("%s", op);
if (!strcmp(op, "I"))
{
scanf("%d", &x);
cnt ++ ;
m ++ ;
ph[m] = cnt, hp[cnt] = m;
h[cnt] = x;
up(cnt);
}
else if (!strcmp(op, "PM")) printf("%d\n", h[1]);
else if (!strcmp(op, "DM"))
{
heap_swap(1, cnt);
cnt -- ;
down(1);
}
else if (!strcmp(op, "D"))
{
scanf("%d", &k);
k = ph[k];
heap_swap(k, cnt);
cnt -- ;
up(k);
down(k);
}
else
{
scanf("%d%d", &k, &x);
k = ph[k];
h[k] = x;
up(k);
down(k);
}
}
return 0;
}
哈希
840. 模拟散列表

//: # (打卡模板,上面预览按钮可以展示预览效果 ^^)
拉链法
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int M=1e5+3;//打表找出的符合条件的最小质数
int h[M],idx,e[M],ne[M];//数组模拟链表
void insert(int x)
{
int t=(x%M+M)%M;//让所有数的余数都为正
e[idx]=x;
ne[idx]=h[t];//链表操作
h[t]=idx++;
}
bool find(int x)
{
int t=(x%M+M)%M;
for(int i=h[t];i!=-1;i=ne[i])//遍历链表
{
if(e[i]==x) return true;
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
memset(h,-1,sizeof h);//初始化:格式化数组默认为空
while(n--)
{
string op;
int x;
cin>>op>>x;
if(op=="I")
{
insert(x);
}
if(op=="Q")
{
if(find(x)) cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
else cout<<"No"<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
开放寻址法
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int M = 2e5+3;//打表找最小质数,开放寻址法的范围一般是数据范围的2-3倍
int h[M];
int find(int x)
{
int t=(x%M+M)%M;//让所有数的余数都为正数
while(h[t]!=x&&h[t]!=-1)//若位置被其他数占用
{
t++;
if(t==M) t=0;//走到范围边界后从头开始找位置
}
return t;//若x在哈希表中返回下标,不在哈希表中返回应该插入的位置
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
memset(h,-1,sizeof h);//初始化:格式化数组默认为空
while(n--)
{
string op;
int x;
cin>>op>>x;
int t=find(x);
if(op=="I")
{
h[t]=x;
}
if(op=="Q")
{
if(h[t]!=-1) cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
else cout<<"No"<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
841. 字符串哈希



#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10,P = 131;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
ULL h[N],p[N];
int n,m;
char str[N];
ULL get(int l,int r)
{
return h[r] - h[l-1] * p[r-l+1]; //取区间字符串的哈希值 h[r] - h[l-1] * p^(r-l+1)
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d%s", &n, &m,str+1);
p[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
p[i] = p[i-1] * P; //预处理P的n次幂
h[i] = h[i-1] * P + str[i]; //计算哈希值
}
while (m -- )
{
int l1,r1,l2,r2;
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &l1, &r1,&l2,&r2);
if(get(l1,r1) == get(l2,r2)) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}
return 0;
}



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)