选择结构
1.多选择结构
#include <stdio.h> int main() { float c; scanf("%f",&c); if(c>700) { printf("我要上清华"); } else if(c>680 & c<700) { printf("我要上北大"); } else{ printf("我要上武汉大学"); } return 0; }

2. switch选择结构
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int a; scanf("%d",&a); switch(a) { case 1 : printf("今天温度3摄氏度,有点冷"); break; case 2: printf("今天温度36摄氏度,非常热"); break; default: printf("今天温度25摄氏度,气候宜人"); break; } return 0; }

当结果不满足case的任意一项值,执行默认default
3.条件嵌套
#include <stdio.h> int main() { float c; scanf("%f",&c); if(c>700) { if(c>=720) { printf("我要上清华"); } else if(c>=710 & c<=720) { printf("我要上北大"); } } else{ printf("我要上武汉大学"); } return 0; }

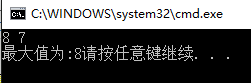
4. 条件表达式
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int a ,b ; scanf("%d%d",&a,&b); printf("最大值为:%d",a>b?a:b); return 0; }