实验6
task4
代码:

#pragma once #include <iostream> #include <stdexcept> #include <iomanip> // 模板类 Vector 的定义 template <typename T> class Vector { public: // 构造函数 Vector(int size); Vector(int size, T value); Vector(const Vector<T>& other); // 深复制构造函数 // 析构函数 ~Vector(); // 成员函数 int get_size() const; // 获取大小 T& at(int index); // 按索引访问元素 const T& at(int index) const; // 常量版本 T& operator[](int index); // 重载 [] // 友元函数 template <typename U> friend void output(const Vector<U>& vec); private: int size; // 数组大小 T* data; // 动态数组 }; // 构造函数 template <typename T> Vector<T>::Vector(int size) : size(size) { if (size < 0) { throw std::length_error("Size cannot be negative."); } data = new T[size]; } // 构造函数(指定初始值) template <typename T> Vector<T>::Vector(int size, T value) : size(size) { if (size < 0) { throw std::length_error("Size cannot be negative."); } data = new T[size]; for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) { data[i] = value; } } // 深复制构造函数 template <typename T> Vector<T>::Vector(const Vector<T>& other) : size(other.size) { data = new T[size]; for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) { data[i] = other.data[i]; } } // 析构函数 template <typename T> Vector<T>::~Vector() { delete[] data; } // 获取大小 template <typename T> int Vector<T>::get_size() const { return size; } // 按索引访问元素 template <typename T> T& Vector<T>::at(int index) { if (index < 0 || index >= size) { throw std::out_of_range("Index out of range."); } return data[index]; } template <typename T> const T& Vector<T>::at(int index) const { if (index < 0 || index >= size) { throw std::out_of_range("Index out of range."); } return data[index]; } // 重载运算符 [] template <typename T> T& Vector<T>::operator[](int index) { return at(index); } // 输出 Vector 中的元素 template <typename T> void output(const Vector<T>& vec) { for (int i = 0; i < vec.size; ++i) { std::cout << vec.data[i] << " "; } std::cout << std::endl; }

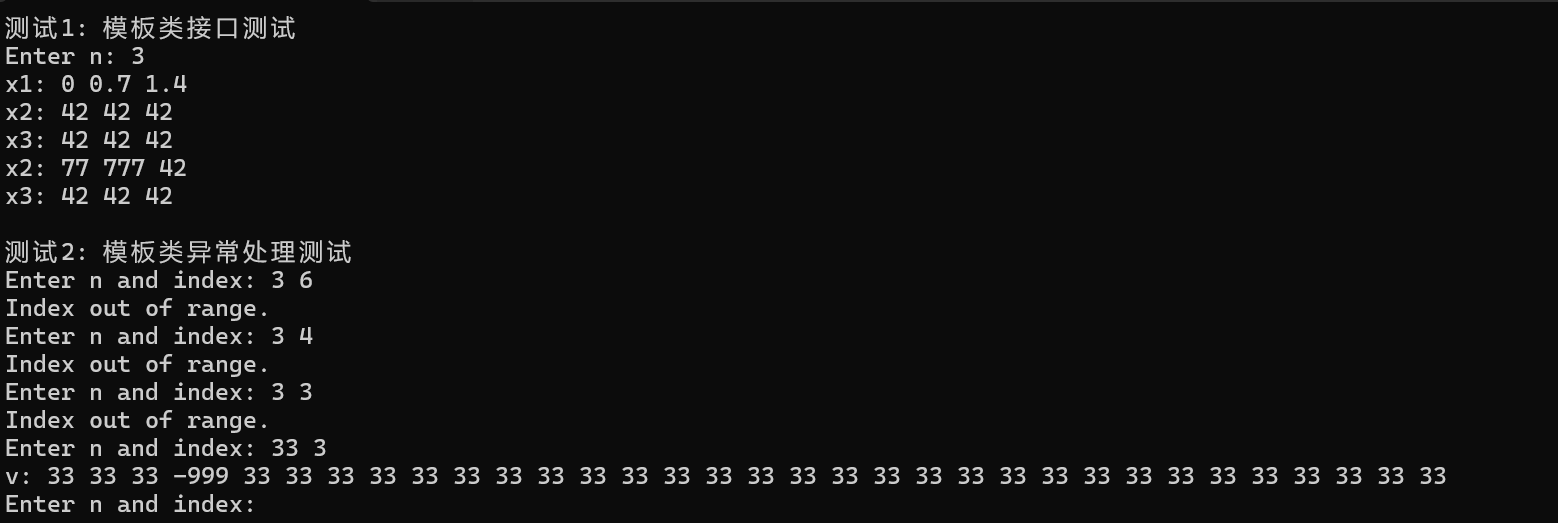
#include <iostream> #include "Vector.hpp" void test1() { using namespace std; int n; cout << "Enter n: "; cin >> n; Vector<double> x1(n); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) x1.at(i) = i * 0.7; cout << "x1: "; output(x1); Vector<int> x2(n, 42); const Vector<int> x3(x2); cout << "x2: "; output(x2); cout << "x3: "; output(x3); x2.at(0) = 77; x2.at(1) = 777; cout << "x2: "; output(x2); cout << "x3: "; output(x3); } void test2() { using namespace std; int n, index; while (cout << "Enter n and index: ", cin >> n >> index) { try { Vector<int> v(n, n); v.at(index) = -999; cout << "v: "; output(v); } catch (const exception& e) { cout << e.what() << endl; } } } int main() { cout << "测试1: 模板类接口测试\n"; test1(); cout << "\n测试2: 模板类异常处理测试\n"; test2(); }
运行截图:
task5
代码:

#include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <vector> #include <string> #include <algorithm> struct Student { std::string name, major; double score; bool operator<(const Student& other) const { if (major == other.major) { return score > other.score; // 降序 } return major < other.major; // 按字典序升序 } }; void load_data(const std::string& filename, std::vector<Student>& students) { std::ifstream file(filename); if (!file) { throw std::runtime_error("Failed to open file."); } Student student; while (file >> student.name >> student.major >> student.score) { students.push_back(student); } } void save_data(const std::string& filename, const std::vector<Student>& students) { std::ofstream file(filename); if (!file) { throw std::runtime_error("Failed to open file."); } for (const auto& student : students) { file << student.name << " " << student.major << " " << student.score << "\n"; } } int main() { try { std::vector<Student> students; load_data("data5.txt", students); std::sort(students.begin(), students.end()); save_data("ans5.txt", students); for (const auto& student : students) { std::cout << student.name << " " << student.major << " " << student.score << "\n"; } } catch (const std::exception& e) { std::cerr << e.what() << std::endl; } return 0; }
运行截图: