统计学习方法学习(四)--KNN及kd树的java实现
K近邻法
1基本概念
K近邻法,是一种基本分类和回归规则。根据已有的训练数据集(含有标签),对于新的实例,根据其最近的k个近邻的类别,通过多数表决的方式进行预测。
2模型相关
2.1 距离的度量方式
定义距离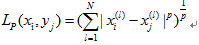
(1)欧式距离:p=2。
(2)曼哈顿距离:p=1。
(3)各坐标的最大值:p=∞。
2.2 K值的选择
通常使用交叉验证法来选取最优的k值。
k值大小的影响:
k越小,只有距该点较近的实例才会起作用,学习的近似误差会较小。但此时又会对这些近邻的实例很敏感,如果紧邻点存在噪声,预测就会出错,即学习的估计误差大,泛化能力不好。
K越大,距该点较远的实例也会起作用,造成近似误差增大,使预测发生错误。
2.3 k近邻法的实现:kd树
Kd树是二叉树。kd树是一种对K维空间中的实例点进行存储以便对其进行快速检索的树形数据结构.
Kd树是二叉树, 表示对K维空间的一个划分( partition).构造Kd树相 当于不断地用垂直于坐标轴的超平面将k维空间切分, 构成一系列的k维超矩形区域.Kd树的每个结点对应于一个k维超矩形区域
其中,创建kd树时,垂直于坐标轴的超平面垂直的坐标轴选择是:
L=(J mod k)+1。其中,j为当前节点的节点深度,k为k维空间(给定实例点的k个维度)。根节点的节点深度为0.此公式可看为:依次循环实例点的k个维所对应的坐标轴。
Kd树的节点(分割点)为L维上所有实例点的中位数。
2.4 Kd树的实现
别处代码实现基于其他博客,但是纠正了其中的错误,能够返回前k个近邻。如果要求最近邻,只需要将k=1即可。
1 public class BinaryTreeOrder { 2 3 public void preOrder(Node root) { 4 if(root!= null){ 5 System.out.print(root.toString()); 6 preOrder(root.left); 7 preOrder(root.right); 8 } 9 } 10 }
public class kd_main { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Node> nodeList=new ArrayList<Node>(); nodeList.add(new Node(new double[]{5,4})); nodeList.add(new Node(new double[]{9,6})); nodeList.add(new Node(new double[]{8,1})); nodeList.add(new Node(new double[]{7,2})); nodeList.add(new Node(new double[]{2,3})); nodeList.add(new Node(new double[]{4,7})); nodeList.add(new Node(new double[]{4,3})); nodeList.add(new Node(new double[]{1,3})); kd_main kdTree=new kd_main(); Node root=kdTree.buildKDTree(nodeList,0); new BinaryTreeOrder().preOrder(root); for (Node node : nodeList) { System.out.println(node.toString()+"-->"+node.left.toString()+"-->"+node.right.toString()); } System.out.println(root); System.out.println(kdTree.searchKNN(root,new Node(new double[]{2.1,3.1}),2)); System.out.println(kdTree.searchKNN(root,new Node(new double[]{2,4.5}),1)); System.out.println(kdTree.searchKNN(root,new Node(new double[]{2,4.5}),3)); System.out.println(kdTree.searchKNN(root,new Node(new double[]{6,1}),5)); } /** * 构建kd树 返回根节点 * @param nodeList * @param index * @return */ public Node buildKDTree(List<Node> nodeList,int index) { if(nodeList==null || nodeList.size()==0) return null; quickSortForMedian(nodeList,index,0,nodeList.size()-1);//中位数排序 Node root=nodeList.get(nodeList.size()/2);//中位数 当做根节点 root.dim=index; List<Node> leftNodeList=new ArrayList<Node>();//放入左侧区域的节点 包括包含与中位数等值的节点-_- List<Node> rightNodeList=new ArrayList<Node>(); for(Node node:nodeList) { if(root!=node) { if(node.getData(index)<=root.getData(index)) leftNodeList.add(node);//左子区域 包含与中位数等值的节点 else rightNodeList.add(node); } } //计算从哪一维度切分 int newIndex=index+1;//进入下一个维度 if(newIndex>=root.data.length) newIndex=0;//从0维度开始再算 root.left=buildKDTree(leftNodeList,newIndex);//添加左右子区域 root.right=buildKDTree(rightNodeList,newIndex); if(root.left!=null) root.left.parent=root;//添加父指针 if(root.right!=null) root.right.parent=root;//添加父指针 return root; } /** * 查询最近邻 * @param root kd树 * @param q 查询点 * @param k * @return */ public List<Node> searchKNN(Node root,Node q,int k) { List<Node> knnList=new ArrayList<Node>(); searchBrother(knnList,root,q,k); return knnList; } /** * searhchBrother * @param knnList * @param k * @param q */ public void searchBrother(List<Node> knnList, Node root, Node q, int k) { // Node almostNNode=root;//近似最近点 Node leafNNode=searchLeaf(root,q); double curD=q.computeDistance(leafNNode);//最近近似点与查询点的距离 也就是球体的半径 leafNNode.distance=curD; maintainMaxHeap(knnList,leafNNode,k); System.out.println("leaf1"+leafNNode.getData(leafNNode.parent.dim)); while(leafNNode!=root) { if (getBrother(leafNNode)!=null) { Node brother=getBrother(leafNNode); System.out.println("brother1"+brother.getData(brother.parent.dim)); if(curD>Math.abs(q.getData(leafNNode.parent.dim)-leafNNode.parent.getData(leafNNode.parent.dim))||knnList.size()<k) { //这样可能在另一个子区域中存在更加近似的点 searchBrother(knnList,brother, q, k); } } System.out.println("leaf2"+leafNNode.getData(leafNNode.parent.dim)); leafNNode=leafNNode.parent;//返回上一级 double rootD=q.computeDistance(leafNNode);//最近近似点与查询点的距离 也就是球体的半径 leafNNode.distance=rootD; maintainMaxHeap(knnList,leafNNode,k); } } /** * 获取兄弟节点 * @param node * @return */ public Node getBrother(Node node) { if(node==node.parent.left) return node.parent.right; else return node.parent.left; } /** * 查询到叶子节点 * @param root * @param q * @return */ public Node searchLeaf(Node root,Node q) { Node leaf=root,next=null; int index=0; while(leaf.left!=null || leaf.right!=null) { if(q.getData(index)<leaf.getData(index)) { next=leaf.left;//进入左侧 }else if(q.getData(index)>leaf.getData(index)) { next=leaf.right; }else{ //当取到中位数时 判断左右子区域哪个更加近 if(q.computeDistance(leaf.left)<q.computeDistance(leaf.right)) next=leaf.left; else next=leaf.right; } if(next==null) break;//下一个节点是空时 结束了 else{ leaf=next; if(++index>=root.data.length) index=0; } } return leaf; } /** * 维护一个k的最大堆 * @param listNode * @param newNode * @param k */ public void maintainMaxHeap(List<Node> listNode,Node newNode,int k) { if(listNode.size()<k) { maxHeapFixUp(listNode,newNode);//不足k个堆 直接向上修复 }else if(newNode.distance<listNode.get(0).distance){ //比堆顶的要小 还需要向下修复 覆盖堆顶 maxHeapFixDown(listNode,newNode); } } /** * 从上往下修复 将会覆盖第一个节点 * @param listNode * @param newNode */ private void maxHeapFixDown(List<Node> listNode,Node newNode) { listNode.set(0, newNode); int i=0; int j=i*2+1; while(j<listNode.size()) { if(j+1<listNode.size() && listNode.get(j).distance<listNode.get(j+1).distance) j++;//选出子结点中较大的点,第一个条件是要满足右子树不为空 if(listNode.get(i).distance>=listNode.get(j).distance) break; Node t=listNode.get(i); listNode.set(i, listNode.get(j)); listNode.set(j, t); i=j; j=i*2+1; } } private void maxHeapFixUp(List<Node> listNode,Node newNode) { listNode.add(newNode); int j=listNode.size()-1; int i=(j+1)/2-1;//i是j的parent节点 while(i>=0) { if(listNode.get(i).distance>=listNode.get(j).distance) break; Node t=listNode.get(i); listNode.set(i, listNode.get(j)); listNode.set(j, t); j=i; i=(j+1)/2-1; } } /** * 使用快排进进行一个中位数的查找 完了之后返回的数组size/2即中位数 * @param nodeList * @param index * @param left * @param right */ @Test private void quickSortForMedian(List<Node> nodeList,int index,int left,int right) { if(left>=right || nodeList.size()<=0) return ; Node kn=nodeList.get(left); double k=kn.getData(index);//取得向量指定索引的值 int i=left,j=right; //控制每一次遍历的结束条件,i与j相遇 while(i<j) { //从右向左找一个小于i处值的值,并填入i的位置 while(nodeList.get(j).getData(index)>=k && i<j) j--; nodeList.set(i, nodeList.get(j)); //从左向右找一个大于i处值的值,并填入j的位置 while(nodeList.get(i).getData(index)<=k && i<j) i++; nodeList.set(j, nodeList.get(i)); } nodeList.set(i, kn); if(i==nodeList.size()/2) return ;//完成中位数的排序了,但并不是完成了所有数的排序,这个终止条件只是保证中位数是正确的。去掉该条件,可以保证在递归的作用下,将所有的树 //将所有的数进行排序 else if(i<nodeList.size()/2) { quickSortForMedian(nodeList,index,i+1,right);//只需要排序右边就可以了 }else{ quickSortForMedian(nodeList,index,left,i-1);//只需要排序左边就可以了 } // for (Node node : nodeList) { // System.out.println(node.getData(index)); // } } }
public class Node implements Comparable<Node>{ public double[] data;//树上节点的数据 是一个多维的向量 public double distance;//与当前查询点的距离 初始化的时候是没有的 public Node left,right,parent;//左右子节点 以及父节点 public int dim=-1;//维度 建立树的时候判断的维度 public Node(double[] data) { this.data=data; } /** * 返回指定索引上的数值 * @param index * @return */ public double getData(int index) { if(data==null || data.length<=index) return Integer.MIN_VALUE; return data[index]; } @Override public int compareTo(Node o) { if(this.distance>o.distance) return 1; else if(this.distance==o.distance) return 0; else return -1; } /** * 计算距离 这里返回欧式距离 * @param that * @return */ public double computeDistance(Node that) { if(this.data==null || that.data==null || this.data.length!=that.data.length) return Double.MAX_VALUE;//出问题了 距离最远 double d=0; for(int i=0;i<this.data.length;i++) { d+=Math.pow(this.data[i]-that.data[i], 2); } return Math.sqrt(d); } public String toString() { if(data==null || data.length==0) return null; StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder(); for(int i=0;i<data.length;i++) sb.append(data[i]+" "); sb.append(" d:"+this.distance); return sb.toString(); } }
参考文献:
[1]李航.统计学习方法



