Timer:定时
1.Timer基础
1.1Timer简介
1.2Timer实战
2.Timer的定时调度函数
2.1schedule
2.1.1 schedule(task,time)
2.1.2 schedule(task,time,period)
2.1.3 schedule(task,delay)
2.1.4 schedule(task,delay,period)
2.2scheduleAtFixedRate的两种用法
2.2.1 scheduleAtFixedRate(task,time,period)
2.2.2 scheduleAtFixedRate(task,delay,period)
2.3其他重要函数
2.3.1 TimerTask的cancel()
2.3.2 TimerTask的scheduledExecutionTime()
2.3.3 Timer的cancel()
2.3.4 Timer的purge()
2.4 schedule与scheduleAtFixedRate的区别
2.4.1 首次计划执行的时间早于当前的时间
2.4.2 任务执行所需时间超出任务的执行周期间隔
3.Timer综合应用,实战:
3.1 任务介绍
3.2 源码:
3.2.1 跳舞机器人:DancingRobot
3.2.2灌水机器人:WaterRobot
3.2.3timer实例:
4.Timer的缺陷
4.1 Timer的两个缺陷
4.2Timer的使用禁区
1.1Timer简介
1.2Timer实战
2.Timer的定时调度函数
2.1schedule
2.1.1 schedule(task,time)
2.1.2 schedule(task,time,period)
2.1.3 schedule(task,delay)
2.1.4 schedule(task,delay,period)
2.2scheduleAtFixedRate的两种用法
2.2.1 scheduleAtFixedRate(task,time,period)
2.2.2 scheduleAtFixedRate(task,delay,period)
2.3其他重要函数
2.3.1 TimerTask的cancel()
2.3.2 TimerTask的scheduledExecutionTime()
2.3.3 Timer的cancel()
2.3.4 Timer的purge()
2.4 schedule与scheduleAtFixedRate的区别
2.4.1 首次计划执行的时间早于当前的时间
2.4.2 任务执行所需时间超出任务的执行周期间隔
3.Timer综合应用,实战:
3.1 任务介绍
3.2 源码:
3.2.1 跳舞机器人:DancingRobot
3.2.2灌水机器人:WaterRobot
3.2.3timer实例:
4.Timer的缺陷
4.1 Timer的两个缺陷
4.2Timer的使用禁区
1.Timer基础
1.1Timer简介
概述:
是jdk提供的,只有一个后台线程,可以对多个任务定时定频率的调度。
主要构件:
Timer和TimerTask,Timer定时调用TimerTask来对任务定时调度。
1.2Timer实战
- 创建一个类继承TimerTask类
import java.util.TimerTask;
public class MyTimerTask extends TimerTask{
private String name;
public MyTimerTask(String inputName) {
this.name = inputName;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// 打印当前的name的内容
System.out.println("current name is:"+name);
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}- 创建一个Timer实例
import java.util.Timer;
public class MyTimer{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建一个timer实例
Timer timer=new Timer();
//2.创建一个MyTimerTask实例
MyTimerTask myTimerTask=new MyTimerTask("NO.1");
//3.通过Etimer定时定频率调用myTimerTask的业务逻辑
//即第一一次执行是在当前时间的两秒之后,之后每隔一秒钟执行一次
timer.schedule(myTimerTask, 2000L,1000L);//执行的任务,第一次执行间隔,循环间隔
}
}2.Timer的定时调度函数
2.1schedule
2.1.1 schedule(task,time)
- 参数:
task:所要安排的任务time:执行任务的时间
- 作用:在时间≥time的时候,执行一次task(只执行一次)
»实战
- TimerTask
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.TimerTask;
public class MyTimerTask extends TimerTask{
private String name;
public MyTimerTask(String inputName) {
this.name = inputName;
}
@Override
public void run() {
//以yyyy-MM-ddHH:mm:SS的格式打印当前执行时间
//如2016一11一11 00:00:00
Calendar calendar=Calendar.getInstance();//当前时间
SimpleDateFormat sf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-ddHH:mm:ss");
System.out.println("current exec time is:"+sf.format(calendar.getTime()));
////打印当前name的内容
System.out.println("current exec name is:"+name);
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}- Task调用任务
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Timer;
public class MyTimer{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建一个timer实例
Timer timer=new Timer();
//2.创建一个MyTimerTask实例
MyTimerTask myTimerTask=new MyTimerTask("NO.1");
/**
* 获取当前时间,并设置成距离当前时间三秒之后的时间
*如当前时间是2016一11一10 23:59:57
则设置后的时间则为2016一11一11 00:00:00
*/
Calendar calendar=Calendar.getInstance();
SimpleDateFormat sf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-ddHH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(sf.format(calendar.getTime()));
calendar.add(calendar.SECOND, 3);//添加3s
/**
*1.在时间等于或超过time的时候执行且仅执行一次task
如在2016一11一11 00:00:00执行一次task:打印任务的名字
*/
myTimerTask.setName("schedule1");
timer.schedule(myTimerTask, calendar.getTime());//这个calendar是3s后的
}
}- 运行结果:

2.1.2 schedule(task,time,period)
- 参数:
task:所要安排的任务time:首次执行任务的时间period:执行一次task的时间间隔,ms
- 作用:
- 时间等于或超过time时首次执行task
- 之后每隔period毫秒重复执行一次task
»实战
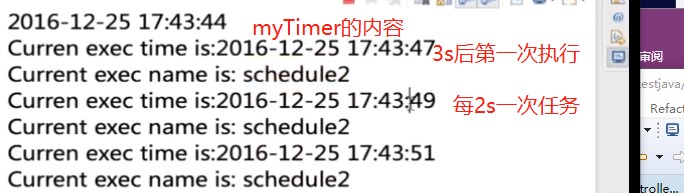
- MyTimer定义
myTimerTask.setName("schedule2");
//这个calendar是3s后的
//3s之后第一次执行,之后,每隔2s执行一次
timer.schedule(myTimerTask, calendar.getTime(),2000L);- 运行结果:
2.1.3 schedule(task,delay)
- 参数:
task:所要安排的任务delay:执行任务前的延迟时间,单位是ms
- 作用:
- 等待delay毫秒后执行且仅执行一次task
» 实战
- MyTimer
myTimerTask.setName("schedule3");
//1s之后执行这个任务
timer.schedule(myTimerTask, 1000);- 结果:

2.1.4 schedule(task,delay,period)
- 参数:
task:所要安排的任务delay:执行任务前的延迟时间,单位是msperiod:执行任务的间隔,单位是ms
- 作用:
- 等待de|ay毫秒后首次执行task
- 之后每隔period毫秒重复执行一次task
»实战
- MyTimer
myTimerTask.setName("schedule4");
//3s之后执行这个任务,之后每隔2s执行一次
timer.schedule(myTimerTask, 3000,2000);- 结果

2.2scheduleAtFixedRate的两种用法
2.2.1 scheduleAtFixedRate(task,time,period)
- 参数:
task:所要安排的任务time:首次执行任务的具体时间period:执行时间间隔,ms
- 作用:
- 在时间≥time的时候,首次执行task;
- 之后,每隔period ms执行一次task
»实战
- MyTimer
myTimerTask.setName("scheduleAtFixedRate1");
//在calendar的时候,首次执行;之后,每隔2s执行一次
timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(myTimerTask, calendar.getTime(), 2000);- 结果

2.2.2 scheduleAtFixedRate(task,delay,period)
- 参数:
task:所要安排的任务delay:执行任务前的延迟时间,单位是msperiod:执行时间间隔,ms
- 作用:
- 等待de|ay毫秒后首次执行task
- 之后每隔period毫秒重复执行一次task
»实战
- MyTimer
myTimerTask.setName("scheduleAtFixedRate2");
//在3s后,首次执行;之后,每隔2s执行一次
timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(myTimerTask, 3000, 2000);- 结果

2.3其他重要函数
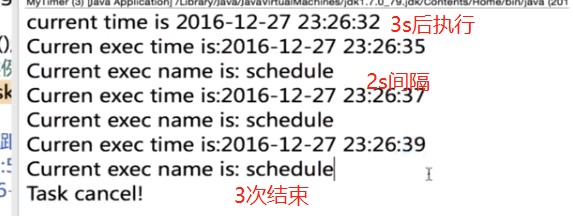
2.3.1 TimerTask的cancel()
- 作用::取消当前TimerTask里的任务
»实战
- MyTimerTask
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.TimerTask;
public class MyTimerTask extends TimerTask{
private String name;//任务名
private Integer count=0;//计时器
public MyTimerTask(String inputName) {
this.name = inputName;
}
@Override
public void run() {
if (count<3) {
//以yyyy-MM-ddHH:mm:SS的格式打印当前执行时间
//如2016一11一1100:00℃0
Calendar calendar=Calendar.getInstance();
SimpleDateFormat sf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-ddHH:mm:ss");
System.out.println("current exec time is:"+sf.format(calendar.getTime()));
////打印当前name的内容
System.out.println("current exec name is:"+name);
count++;//每次任务,数+1
}else {
cancel();//超过三次,取消任务
System.out.println("Task cancel!");
}
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}- MyTimer
myTimerTask.setName("schedule4");
//3s之后执行这个任务,之后每隔2s执行一次
timer.schedule(myTimerTask, 3000,2000);- 结果
2.3.2 TimerTask的scheduledExecutionTime()
- 作用::返回此任务最近实际执行的已安排执行的时间(设置的任务真正执行时间)
- 返回值:long型
»实战
- MyTimer
timer.schedule(myTimerTask, 3000);
System.out.println("scheduled time is:"+sf.format(myTimerTask.scheduledExecutionTime()));//返回的是刚运行完的任务的运行时间- 结果

2.3.3 Timer的cancel()
- 作用::终止此计时器,丢弃
所有当前已安排的任务(Timer下是所有的任务)
»实战
- Timer
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Timer;
public class CancelTest{
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//1.创建一个timer实例
Timer timer=new Timer();
//2.创建TimerTask实例
MyTimerTask task1=new MyTimerTask("task1");
MyTimerTask task2=new MyTimerTask("task2");
Date startTime=new Date();
SimpleDateFormat sf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-ddHH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(sf.format(startTime));//当前时间
//taskl首次执行是距湍现在时间3秒后执行,之后每隔2秒执行一次;
//task2首次执行是距离现在时间1秒后执行,之后每隔2秒执行一次
timer.schedule(task1,3000,2000);
timer.schedule(task2,1000,2000);
//休眠5秒
Thread.sleep(5000);
//获取当前的执行时间并打印
Date cancelTime=new Date();
System.out.println("cancel time is:"+sf.format(cancelTime));
//取消所有任务
timer.cancel();
System.out.println("Tasks all cancled!");
}
}- 结果

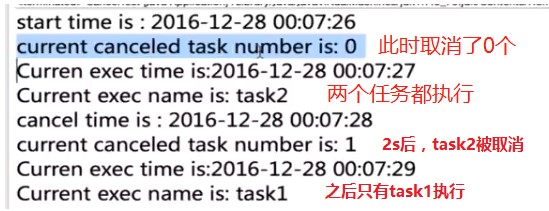
2.3.4 Timer的purge()
- 作用::从此计时器的任务队列中移除所有
已取消的任务 - 返回值::从队列中移除的任务数
»实战
- Timer
public class CancelTest{
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//1.创建一个timer实例
Timer timer=new Timer();
//2.创建TimerTask实例
MyTimerTask task1=new MyTimerTask("task1");
MyTimerTask task2=new MyTimerTask("task2");
Date startTime=new Date();
SimpleDateFormat sf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-ddHH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(sf.format(startTime));//当前时间
//taskl首次执行是距湍现在时间3秒后执行,之后每隔2秒执行一次;
//task2首次执行是距离现在时间1秒后执行,之后每隔2秒执行一次
timer.schedule(task1,3000,2000);
timer.schedule(task2,1000,2000);
//当前已取消的任务数
System.out.println("current cancleld task number is:"+timer.purge());
//休眠5秒
Thread.sleep(2000);
//获取当前的执行时间并打印
Date cancelTime=new Date();
System.out.println("cancel time is:"+sf.format(cancelTime));
//取消task2任务(2s后,取消task2)
task2.cancel();
System.out.println("current cancleld task number is:"+timer.purge());
}
}- 结果
2.4 schedule与scheduleAtFixedRate的区别
2.4.1 首次计划执行的时间早于当前的时间
定义的时间已将过去了;
1.schedule
"fixed-delay";如果第一次执行时间被delay了,随后的执行时间按照上一次实际执行完成的时间点进行计算;
- 实战
public class DifferenceTest{
public static void main(String[] args) {
final SimpleDateFormat sf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-ddHH:mm:ss");
Calendar calendar=Calendar.getInstance();
System.out.println("Current time is"+sf.format(calendar.getTime()));
//设置成6秒前的时旬,若当前时间为2016-12-28 00:00:06,
//那么设置之后时间变成2016-12-28 00:00:00
calendar.add(Calendar.SECOND,-6);
Timer timer=new Timer();
//第一次执行时间为6秒前,之后每隔两秒钟执行一次
timer.schedule的时候,开始时间是现在就开始(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
//打印任务执行时间
System.out.println("Schedyle exec time is:"+sf.format(scheduledExecutionTime()));
System.out.println("Task is being executed!");
}
}, calendar.getTime(), 2000);
}
}- 结果

尽管设置的开始时间是6s前,但是用schedule的时候,开始时间是现在就开始
2.scheduleAtFixedRate方法
"fixed-rate";如果第一次执行时间被delay了,随后的执行时间按照上一次开始的时间点进行计算,并且为了赶上进度会多次执行任务,因此TimerTask中的执行体需要考虑同步.
- 实战
timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new TimerTask() {//只是换了一下方法名
@Override
public void run() {
//打印任务执行时间
System.out.println("Schedyle exec time is:"+sf.format(scheduledExecutionTime()));
System.out.println("Task is being executed!");
}
}, calendar.getTime(), 2000);-结果:
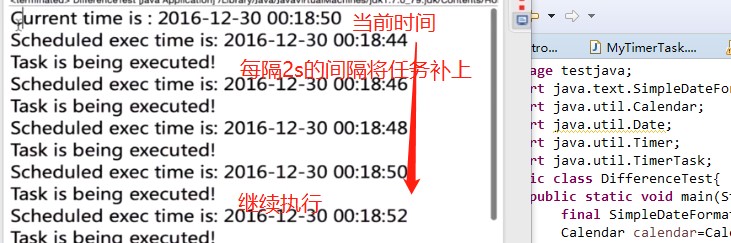
会将之前落下的任务补上,然后继续执行;
2.4.2 任务执行所需时间超出任务的执行周期间隔
任务2s,间隔1s,任务还没有执行完,就要进行下一次了
1.schedule
下一次执行时间相对于上一次实际执行完成的时间点,因此执行
时间会不断延后
- 实战
timer.schedule(new TimerTask() {//scheduleAtFixedRate
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//打印任务执行时间
System.out.println("Schedyle exec time is:"+sf.format(scheduledExecutionTime()));
System.out.println("Task is being executed!");
}
}, calendar.getTime(), 2000);- 结果:
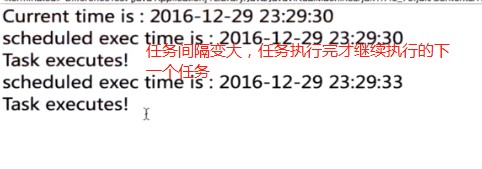
上一个任务执行完才执行
2.scheduleAtFixedRate方法
下一次执行时间相对于上一次开始的时间点,因此执行时间一般
不会延后,因此存在并发性;
---不会延后,会直接运行任务;
- 实战
timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//打印任务执行时间
System.out.println("Schedyle exec time is:"+sf.format(scheduledExecutionTime()));
System.out.println("Task is being executed!");
}
}, calendar.getTime(), 2000);- 结果

3.Timer综合应用,实战:
3.1 任务介绍
- 任务:
通过模拟两个机器人的定时行为来把我们前面所学的主要函数给结合起来,让大家加深对这些函数的理解。 - 实现两个机器人:
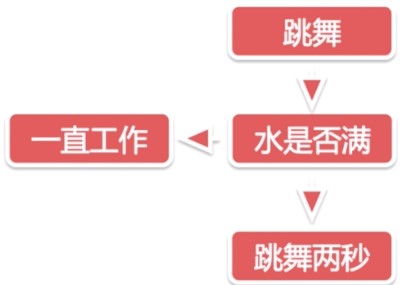
- 第一个机器人会
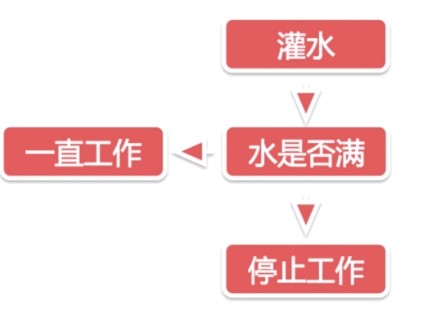
隔两秒打印最近一次计划的时间、执行内容 - 第二个机器人会模拟往捅里倒水,直到桶里的水满为止
- 第一个机器人会
- 工作流程:
- 灌水机器人的执行流程
- 跳舞机器人的执行流程
- 灌水机器人的执行流程
3.2 源码:
3.2.1 跳舞机器人:DancingRobot
public class DancingRobot extends TimerTask{
@Override
public void run() {
//获取最近的一次任务执行的时间,并将其格式化
SimpleDateFormat sf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-ddHH:mm:ss");
System.out.println("Scheduled exec time is:"
+sf.format(scheduledExecutionTime()));
System.out.println("Dancing happily!");
}
}3.2.2灌水机器人:WaterRobot
public class WaterRobot extends TimerTask{
//最大容量为5L
private Integer bucketCapacity=0;
@Override
@Override
public void run() {
//灌水直至桶满为止
if(bucketCapacity<5){
System.out.println("Add 1L water into the bucket!");
bucketCapacity++;
}else {
//水满之后就停止执行
System.out.println("The number of canceled task in timer is:"+timer.purge());//已取消的任务数
cancel();
System.out.println("The WaterRobot has bean aborted");
System.out.println("The number of canceled task in timer is:"+timer.purge());//已取消的任务数
System.out.println("current water is:"+bucketCapacity+"L");//已取消的任务数
//等待2s钟,终止timer的所有任务(2s后,停止跳舞机器人)
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
timer.cancel();
}
}
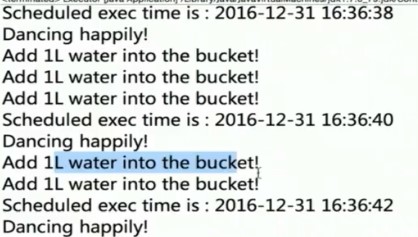
}3.2.3timer实例:
public class Executor{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Timer timer=new Timer();
Calendar calendar=Calendar.getInstance();
SimpleDateFormat sf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-ddHH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(sf.format(calendar.getTime()));
DancingRobot dancingRobot=new DancingRobot();
WaterRobot waterRobot=new WaterRobot(timer);
timer.schedule(dancingRobot,calendar.getTime(),2000);
timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(waterRobot, calendar.getTime(), 1000);
}
}

4.Timer的缺陷
4.1 Timer的两个缺陷
- 管理并发任务的缺陷
Timer有且仅有一个线程去执行定时任务,如果存在多任务,且任务时间过长,会导致执行效果与预期不符
只有一个线程,在定义的时候同时进行的任务实际上不能同时执行 - 当任务抛出异常时的缺陷
如果TimerTask抛出RuntimeException,Timer会停止所有任务的运行
4.2Timer的使用禁区
- 对时效性要求较高的多任务并发作业
- 对复杂的任务的调度




















