Nginx
1. nginx简介
nginx(发音同engine x)是一款轻量级的Web服务器/反向代理服务器及电子邮件(IMAP/POP3)代理服务器,并在一个BSD-like协议下发行。
nginx由俄罗斯的程序设计师Igor Sysoev所开发,最初供俄国大型的入口网站及搜寻引擎Rambler使用。
第一个公开版本0.1.0发布于2004年10月4日。其将源代码以类BSD许可证的形式发布,因它的稳定性、丰富的功能集、示例配置文件和低系统资源的消耗而闻名。2011年6月1日,nginx 1.0.4发布。
nginx的特点是占有内存少,并发能力强,事实上nginx的并发能力确实在同类型的网页服务器中表现较好
2. nginx的特性与优点
2.1 nginx的特性
nginx是一个很牛的高性能Web和反向代理服务器,它具有很多非常优越的特性:
- 在高连接并发的情况下,nginx是Apache服务器不错的替代品,能够支持高达50000个并发连接数的响应
- 使用epoll and kqueue作为开发模型
- nginx作为负载均衡服务器:nginx既可在内部直接支持和PHP程序对外进行服务,也可支持作为HTTP代理服务器对外进行服务
- nginx采用C进行编写,不论系统资源开销还是CPU使用效率都比Perlbal要好很多
2.2 nginx的优点
- 高并发连接:官方测试能够支撑5万并发连接,在实际生产环境中跑到2-3万并发连接数
- 内存消耗少:在3万并发连接下,开启的10个nginx进程才消耗150M内存(15M*10=150M)
- 配置文件非常简单:风格跟程序一样通俗易懂
- 成本低廉:nginx为开源软件,可以免费使用。而购买F5 BIG-IP、NetScaler等硬件负载均衡交换机则需要十多万至几十万人民币
- 支持Rewrite重写规则:能够根据域名、URL的不同,将HTTP请求分到不同的后端服务器群组
- 内置的健康检查功能:如果Nginx Proxy后端的某台Web服务器宕机了,不会影响前端访问
- 节省带宽:支持GZIP压缩,可以添加浏览器本地缓存的Header头
- 稳定性高:用于反向代理,宕机的概率微乎其微
- 模块化设计:模块可以动态编译
- 外围支持好:文档全,二次开发和模块较多
- 支持热部署:可以不停机重载配置文件
- 支持事件驱动、AIO(AsyncIO,异步IO)、mmap(Memory Map,内存映射)等性能优化
- 同步:可以理解为在执行完一个函数或方法之后,一直等待系统返回值或消息,这时程序是出于阻塞的,只有接收到返回的值或消息后才往下执行其他的命令,同步,就是实时处理(如打电话)
- 同步在一定程度上可以看做是单线程,这个线程请求一个方法后就待这个方法给他回复,否则他不往下执行
- 异步:执行完函数或方法后,不必阻塞性地等待返回值或消息,只需要向系统委托一个异步过程,那么当系统接收到返回值或消息时,系统会自动触发委托的异步过程,从而完成一个完整的流程。异步,就是分时处理(如收发短信)
- 异步在一定程度上可以看做是多线程的,请求一个方法后,就不管了,继续执行其他的方法
- 内存映射:有一份数据在内存中放着,有多个位置需要使用,没有内存映射,同一份数据要生成多份,有的话,可以指向数据存放位置中
2.2.1 代理
-
正向代理
- 正向代理时,由客户端发送对某一个目标服务器的请求,代理服务器在中间将请求转发给该目标服务器,目标服务器将结果返回给代理服务器,代理服务器再将结果返回给客户端。
- 使用正向代理时,客户端是需要配置代理服务的地址、端口、账号密码(如有)等才可使用的。
- ①租客(用户)、②中介(代理服务器)、③房东(国外网站,目标服务器)
租房子一般会很难找到房东(目标服务器),但是房东却会把房屋信息、钥匙给中介(代理服务器)。对于房东(目标服务器)来说,他可能不知道要租他房子的人(用户)是谁,他只知道中介(代理服务器)在联系他。
引入中介(代理服务器)其实也就是因为租客(用户)无法直接联系房东(目标服务器)
-
反向代理,负载均衡
- 服务器根据客户端的请求,从其关系的一组或多组后端服务器(如Web服务器)上获取资源,然后再将这些资源返回给客户端,客户端只会得知代理服务器的IP地址,而不知道在代理服务器后面的服务器集群的存在。
- 反向代理整个流程:由客户端发起对代理服务器的请求,代理服务器在中间将请求转发给某一个服务器,服务器将结果返回给代理服务器,代理服务器再将结果返回给客户端。
- 还是租房子:假如没有中介:只有①房东、②二房东(放房东对外租房)、③租客,Web开发中就经常有这种反向代理:客户端(租客)发送请求到负载均衡服务器(二房东),负载均衡服务器(二房东)再把请求转发给一台真正的服务器(房东)来执行,再把执行结果返回给客户端(租客)
-
透明代理
- 透明代理也叫做内网代理(inline proxy)、拦截代理(intercepting proxy)以及强制代理(force proxy),所谓透明,即代理对客户端具有无感知性,即不需要客户端进行额外配置。
透明代理和正向代理基本相似,甚至是透明代理可以作为正向代理的一种。 - 透明代理技术经常作为一种备选模式存在,如在防火墙中作为策略,对部分流量进行过滤拦截;一般公司内的上网行为管理系统也是透明代理的应用。
- 透明代理也叫做内网代理(inline proxy)、拦截代理(intercepting proxy)以及强制代理(force proxy),所谓透明,即代理对客户端具有无感知性,即不需要客户端进行额外配置。
3. nginx的工作原理
nginx的模块直接被编译进nginx,所以属于静态编译方式。
启动nginx后,nginx的模块被自动加载,与apache不一样,首先将模块编译为一个so文件,然后在配置文件 中指定是否进行加载。
在解析配置文件的时候,nginx的每个模块都有可能去处理某个请求,但是同一个处理请求只能由一个模块来完成
nginx的进程架构
启动nginx时,会启动一个Master进程,这个进程不会处理任何客户端请求,主要用来产生Worker线程,一个Worker线程用来处理n个request
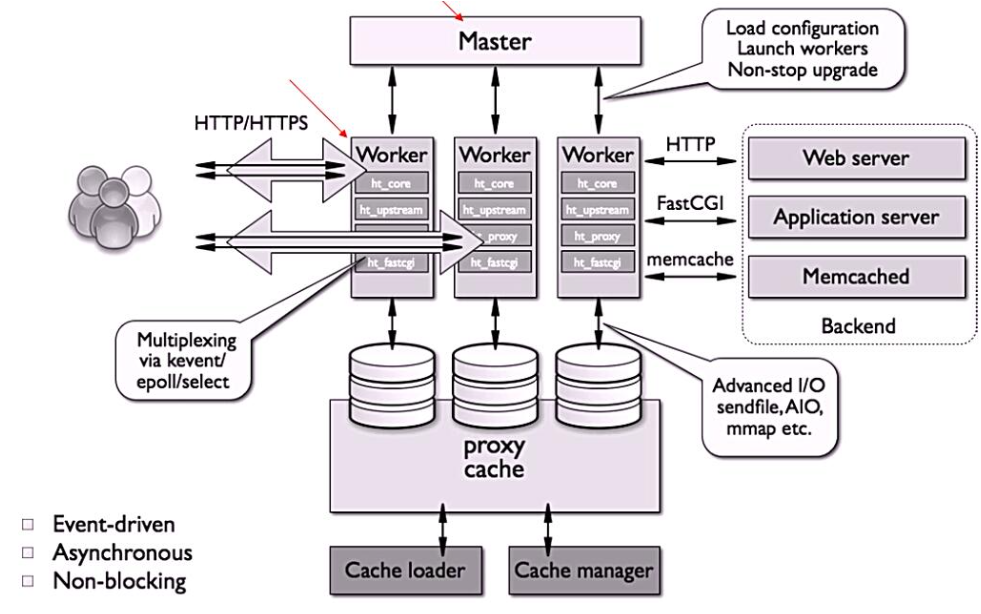
用户先找到nginx,nginx交给master,master生成很多worker,worker包括很多模块,核心功能
worker查看信息是本地处理还是其他人处理。如果是本地处理直接找到硬盘缓存下来处理,下次再请求静态资源直接将缓存资源给他
如果是动态的就通过fastcgi交给应用服务器,应用服务器处理完返还给他
本地缓存没有mencache强大,所以放入mencache中,如果有请求,直接查看mencache缓存
mencache没有持久化
中间的master和proxy是nginx,前端,做负载均衡,worker首先查看资源是动态的还是静态的,是静态的用http交给web server直接处理
nginx模块一次常规的http请求响应过程
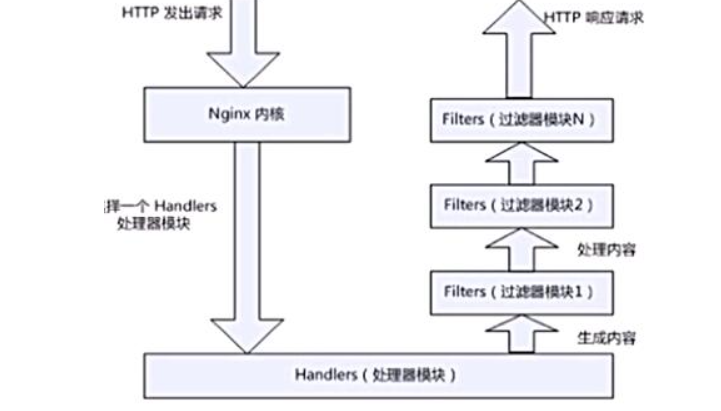
用户通过http发出请求,nginx内核建立一个handlers处理器模块,用模块处理,处理完之后,用过滤器进行过滤,得到结果响应用户
处理器模块还会用到代理模块
基本的web服务请求步骤
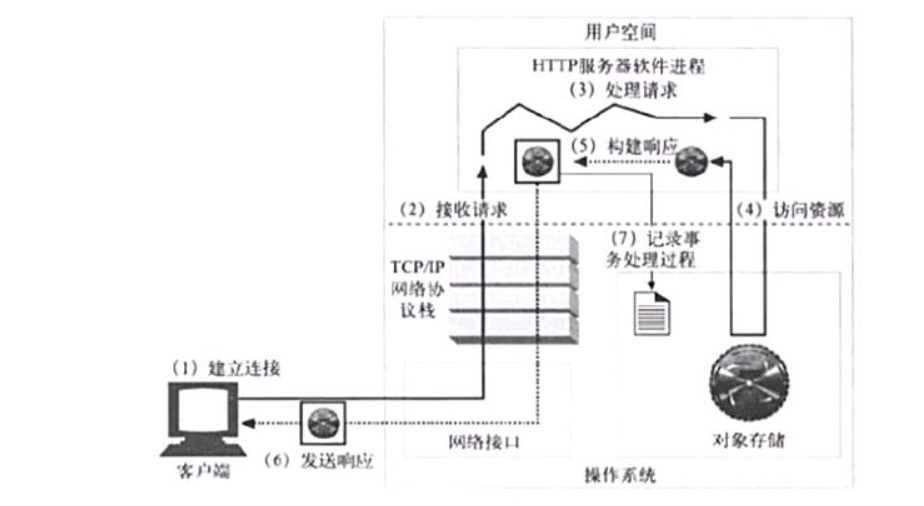
通过用户的浏览器跟服务器的nginx建立连接,建立连接用的是tcp/ip协议
建立连接通道之后可以发送请求,nginx收到请求,处理请求,访问资源(资源存放在硬盘上),取出资源之后构建响应,发送响应,然后将所有的事件记录下来(日志)
4. nginx的部署
//下载nginx源码包
[root@localhost ~]# wget https://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.20.2.tar.gz
//创建nginx用户
[root@localhost ~]# useradd -rMs /sbin/nologin nginx
//安装编译环境
[root@localhost ~]# dnf -y install gcc gcc-c++ make pcre-devel openssl openssl-devel gd-devel
//创建nginx日志存放目录
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir -p /var/log/nginx
[root@localhost ~]# chown -R nginx.nginx /var/log/nginx
//解压nginx源码包
[root@localhost ~]# tar xf nginx-1.20.2.tar.gz
[root@localhost ~]# cd nginx-1.20.2/
//编译nginx
[root@localhost nginx-1.20.2]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx \
--user=nginx \
--group=nginx \
--with-debug \
--with-http_ssl_module \
--with-http_realip_module \
--with-http_image_filter_module \
--with-http_gunzip_module \
--with-http_gzip_static_module \
--with-http_stub_status_module \
--http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log \
--error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log
[root@localhost nginx-1.20.2]# make && make install
[root@localhost nginx-1.20.2]# cd /usr/local/nginx/
[root@localhost nginx]# ls
conf html logs sbin
//配置环境变量
[root@localhost nginx]# echo 'export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/nginx/sbin' > /etc/profile.d/nginx.sh
[root@localhost nginx]# source /etc/profile.d/nginx.sh
[root@localhost nginx]# which nginx
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
//服务控制方式,使用nginx命令
-t //检查配置文件语法
-v //输出nginx的版本
-c //指定配置文件的路径
-s //发送服务控制信号,可选值有{stop|quit|reopen|reload}
//启动nginx
[root@localhost nginx]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
[root@localhost nginx]# ss -antl
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port Process
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:111 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:*
//停止nginx
[root@localhost nginx]# nginx -s stop //因为前面配置了环境变量,所以可以直接使用nginx命令
//使用systemd风格管理nginx
[root@localhost nginx]# cp /usr/lib/systemd/system/sshd.service /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service
[root@localhost nginx]# vim /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service
[Unit]
Description=Nginx server daemon
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
ExecStart=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
ExecStop=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s stop
ExecReload=/bin/kill -HUP $MAINPID
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
[root@localhost nginx]# systemctl daemon-reload
[root@localhost nginx]# systemctl start nginx.service
[root@localhost nginx]# ss -antl
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port Process
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:111 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:*
在浏览器进行访问
5. nginx平滑升级
5.1 平滑升级流程
- 获取老版本的编译信息
- 获取新版本安装包或者功能包
- 配置新版本或功能,配置时附加上老版本的编译信息和新版本的功能
- 编译,编译后不执行安装操作
- 备份老版本的程序
- 停止老版本程序
- 将新版本复制到老版本所在位置替换老版本
- 启动新版本
5.2 nginx平滑升级实例
//查看老版本的编译信息
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -V
nginx version: nginx/1.20.2
built by gcc 8.5.0 20210514 (Red Hat 8.5.0-4) (GCC)
built with OpenSSL 1.1.1k FIPS 25 Mar 2021
TLS SNI support enabled
configure arguments: --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-debug --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_image_filter_module --with-http_gunzip_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_stub_status_module --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log
//下载新版的源码包和echo模块的功能包
[root@localhost ~]# dnf -y install git
[root@localhost ~]# wget https://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.22.0.tar.gz
[root@localhost ~]# git clone https://github.com/openresty/echo-nginx-module.git
//编译新版和功能
[root@localhost ~]# tar xf nginx-1.22.0.tar.gz
[root@localhost ~]# cd nginx-1.22.0
[root@localhost nginx-1.22.0]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx \
--user=nginx \
--group=nginx \
--with-debug \
--with-http_ssl_module \
--with-http_realip_module \
--with-http_image_filter_module \
--with-http_gunzip_module \
--with-http_gzip_static_module \
--with-http_stub_status_module \
--add-module=../echo-nginx-module
[root@localhost nginx-1.22.0]# make
//备份老版本文件,升级并启动nginx,一条命令解决,可以在一瞬间完成,让用户没有感知
[root@localhost nginx-1.22.0]# cp /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx{,bak};pkill nginx;\cp objs/nginx /usr/local/nginx/sbin;systemctl restart nginx
//查看nginx版本信息,升级成功
[root@localhost nginx-1.22.0]# cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin/
[root@localhost sbin]# nginx -V
nginx version: nginx/1.22.0
built by gcc 8.5.0 20210514 (Red Hat 8.5.0-4) (GCC)
built with OpenSSL 1.1.1k FIPS 25 Mar 2021
TLS SNI support enabled
configure arguments: --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-debug --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_image_filter_module --with-http_gunzip_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_stub_status_module --add-module=../echo-nginx-module
6. nginx配置文件详解
主配置文件:/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
- 默认启动nginx时,使用配置文件是:安装路径/conf/nginx.conf
- 在启动nginx时可以使用-c选项来指定要读取的配置文件
nginx常见的配置文件及作用
| 配置文件 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| nginx.conf | nginx的基本配置文件 |
| mime.types | MIME类型关联的扩展文件 |
| fastcgi.conf | 与fastcgi相关的配置 |
| proxy.conf | 与proxy相关的配置 |
| sites.conf | 配置nginx提供的网站,包括虚拟主机 |
6.1 nginx.conf配置详解
nginx.conf的内容分为以下几段:
- main配置段:全局配置段。其中main配置段中可能包含event配置段
- event {}:定义event模型工作特性
- http {}:定义http协议相关的配置
配置指令:要以分号结尾,语法格式如下:
derective value1 [value2 ...];
支持使用变量
- 内置变量:模块会提供内建变量定义
- 自定义变量:set var_name=value
6.2 用于调试、定位问题的配置参数
daemon {on|off}; //是否以守护进程的方式运行nginx,调试nginx的时候应该设置为off
master_process {on|off} //是否以master/worker模式来运行nginx,调试时可以设置为off
error_log 位置 级别; //配置错误日志
例如:error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log info; //级别可以不需要
error_log里的位置和级别可能有以下选项
| 位置 | 级别 |
|---|---|
| file stderr syslog:server=address[,parameter=value] memory:size |
debug:若要使用debug级别,需要在编译nginx时使用--with-debug选项 info notice warn error crit alert emerg |
6.3 正常运行必备的配置参数
user USERNAME [GROUPNAME]; //指定运行worker进程的用户和组,组一般不写
例如:user nginx;
pid file; //指定nginx守护进程的pid文件
例如:pid logs/nginx.pid; //这里的logs目录时nginx安装路径下的目录,如果路径是属于nginx安装路径下的子目录,可以使用相对 路径
worker_rlimit_nofile number; //设置所有worker进程最大可以打开的文件数,默认为1024
例如:
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
worker_rlimit_nofile 65535;
//不仅要设置nginx的配置文件,还要修改/etc/security/limits.conf文件,保证系统和nginx的最大读取文件数的一致性,就像一个柱体一样
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/security/limits.conf
# End of file
* soft nofile 65535
* hard nofile 65535
//重新加载nginx配置文件
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl reload nginx.service
//重新打开一个终端
[root@localhost ~]# ulimit -n
65535
worker_rlimit_core size; //指明所有worker进程所能够使用的总体的最大核心文件大小,保持默认即可
6.4 性能优化的配置参数
worker_processes n; //启动n个worker进程,这里的n为了避免上下文切换,通常设置为cpu总核心数-1或等于总核心数
//将系统的CPU核心数调整到8核
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
worker_processes 8;
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl reload nginx.service
[root@localhost ~]# ps -ef | grep nginx
root 1154 1 0 20:24 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
nginx 3772 1154 0 20:25 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 3773 1154 0 20:25 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 3774 1154 0 20:25 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 3775 1154 0 20:25 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 3776 1154 0 20:25 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 3777 1154 0 20:25 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 3778 1154 0 20:25 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 3779 1154 0 20:25 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
worker_cpu_affinity cpumask ...; //将进程绑定到某cpu中,避免频繁刷新缓存
//cpumask:使用8位二进制表示cpu核心,如:
0000 0001 //第一颗cpu核心
0000 0010 //第二颗cpu核心
0000 0100 //第三颗cpu核心
0000 1000 //第四颗cpu核心
0001 0000 //第五颗cpu核心
0010 0000 //第六颗cpu核心
0100 0000 //第七颗cpu核心
1000 0000 //第八颗cpu核心
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
worker_processes 8;
worker_cpu_affinity 00000001 00000010 00000100 00001000 00010000 00100000 01000000 10000000;
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl reload nginx.service
//查看8个worker进程都工作在那些CPU核心上
//使用top命令,按下F键,使用上下键找到P选项,然后空格选中,按q退出,输入L查找nginx
Tasks: 206 total, 1 running, 205 sleeping, 0 stopped, 0 zombie
%Cpu(s): 0.1 us, 0.3 sy, 0.0 ni, 99.5 id, 0.0 wa, 0.0 hi, 0.0 si, 0.0 st
MiB Mem : 940.9 total, 421.1 free, 298.2 used, 221.6 buff/cache
MiB Swap: 2048.0 total, 2048.0 free, 0.0 used. 484.0 avail Mem
13035 nginx 20 0 114312 6296 4712 S 0.0 0.7 0:00.00 nginx 0
13036 nginx 20 0 114312 5964 4388 S 0.0 0.6 0:00.00 nginx 1
13037 nginx 20 0 114312 5992 4416 S 0.0 0.6 0:00.00 nginx 2
13038 nginx 20 0 114312 6296 4712 S 0.0 0.7 0:00.00 nginx 3
13039 nginx 20 0 114312 6296 4712 S 0.0 0.7 0:00.00 nginx 4
13040 nginx 20 0 114312 6296 4712 S 0.0 0.7 0:00.00 nginx 5
13041 nginx 20 0 114312 6296 4712 S 0.0 0.7 0:00.00 nginx 6
13042 nginx 20 0 114312 6296 4712 S 0.0 0.7 0:00.00 nginx 7
timer_resolution interval; //计时器解析度。降低此值,可减少gettimeofday()系统调用的次数
worker_priority number; //指明worker进程的nice值
//例如:
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
worker_priority -10; //指定worker进程的nice值为-10
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl reload nginx.service
[root@localhost ~]# ps -elf | grep nginx
1 S root 1154 1 0 80 0 - 20417 - 20:24 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
5 S nginx 30322 1154 0 70 -10 - 28580 do_epo 20:39 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
5 S nginx 30323 1154 0 70 -10 - 28580 do_epo 20:39 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
5 S nginx 30324 1154 0 70 -10 - 28580 do_epo 20:39 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
5 S nginx 30325 1154 0 70 -10 - 28580 do_epo 20:39 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
5 S nginx 30326 1154 0 70 -10 - 28580 do_epo 20:39 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
5 S nginx 30327 1154 0 70 -10 - 28580 do_epo 20:39 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
5 S nginx 30328 1154 0 70 -10 - 28580 do_epo 20:39 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
5 S nginx 30329 1154 0 70 -10 - 28580 do_epo 20:39 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
6.5 事件相关的配置:event{}段中的配置参数
accept_mutex {off|on}; //master调度用户请求至各worker进程时使用的负载均衡锁;on表示能让多个worker轮流地、序列化地去响应新请求
lock_file file; //accept_mutex用到的互斥锁锁文件路径
use [epoll | rtsig | select | poll]; //指明使用的事件模型,建议让nginx自行选择
worker_connections #; //每个进程能够接受的最大连接数
//例如:
在上面我们配置了nginx的worker进程为8个,在企业中我们一般会让nginx的并发量保持在30000左右,那么每个worker进程最大连接数就用30000/8=3750
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
events {
worker_connections 3750;
}
6.6 网络连接相关的配置参数
keepalive_timeout number; //长连接的超时时长,默认为65s
keepalive_requests number; //在一个长连接上所能够允许请求的最大资源数
keepalive_disable [msie6|safari|none]; //为指定类型的UserAgent禁用长连接
tcp_nodelay on|off; //是否对长连接使用TCP_NODELAY选项,为了提升用户体验,通常设为on
client_header_timeout number; //读取http请求报文首部的超时时长
client_body_timeout number; //读取http请求报文body部分的超时时长
send_timeout number; //发送响应报文的超时时长
6.7 fastcgi相关配置参数
LNMP:php要启用fpm模型
配置示例如下:
location ~ \.php$ {
root html;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; //定义反向代理
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
6.8 常需要进行调整的参数
- worker_processes
- worker_connections
- worker_cpu_affinity
- worker_priority
6.9 nginx作为web服务器时使用的配置:http{}段的配置参数
http{...}:配置http相关,由ngx_http_core_module模块引入。nginx的HTTP配置主要包括四个区块,结构如下:
http {//协议级别
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
keepalive_timeout 65;
gzip on;
upstream {//负载均衡配置
...
}
server {//服务器级别,每个server类似于httpd中的一个<VirtualHost>
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {//请求级别,类似于httpd中的<Location>,用于定义URL与本地文件系统的映射关系
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
}
http{}段配置指令:
server {}:定义一个虚拟主机,示例如下:
server {
listen 80;
server_name zzd.example.com;
root "/opt/zzd";
}
listen:指定监听的地址和端口
listen address[:port];
listen port;
server_name NAME [...]; 后面可跟多个主机,名称可使用正则表达式或通配符
当有多个server时,匹配顺序如下:
- 先做精确匹配检查
- 左侧通配符匹配检查,如*.example.com
- 右侧通配符匹配检查,如mail.*
- 正则表达式匹配检查,如~ ^.*.idfsoft.com$
- default_server
root path; 设置资源路径映射,用于指明请求的URL所对应的资源所在的文件系统上的起始路径
alisa path; 用于location配置段,定义路径别名
index file; 默认主页面
index index.php index.html
error_page code [...] [=code] URI | @name 根据http响应状态码来指明特用的错误页面
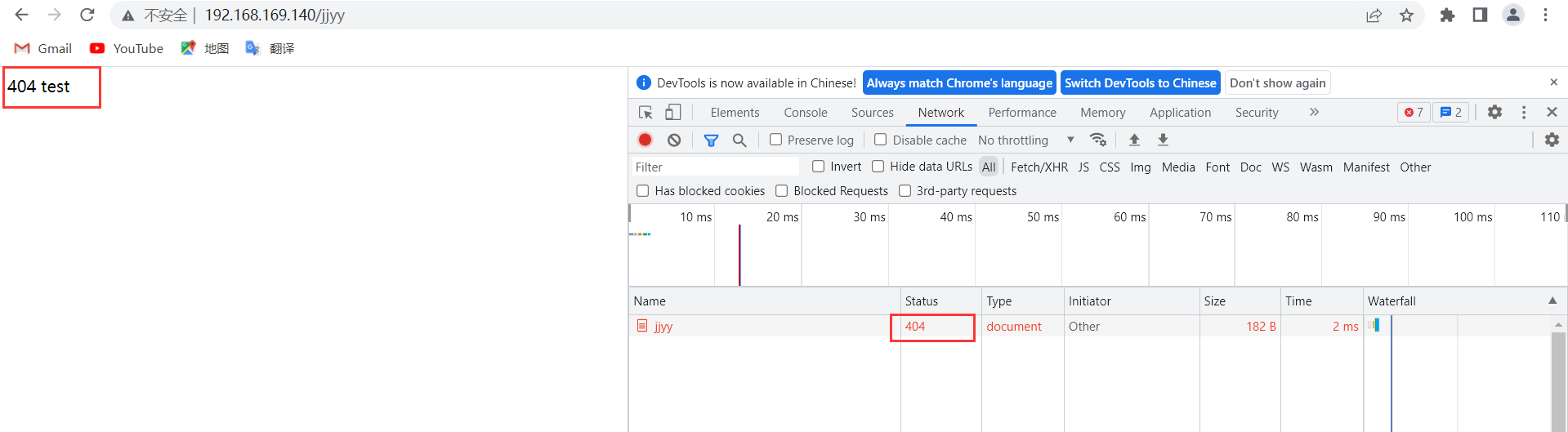
[root@localhost nginx]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
error_page 404 /404.html;
[root@localhost nginx]# echo "404 test" > html/404.html
[root@localhost nginx]# systemctl restart nginx.service
在浏览器输入一个不存在的URL进行访问,然后F12查看状态码
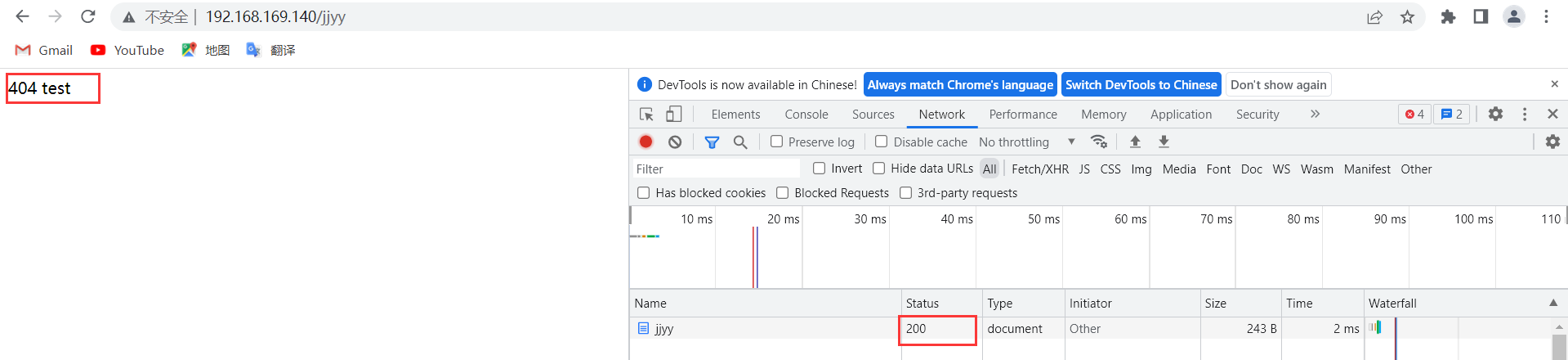
[=code]:以指定的响应码进行响应,而不是默认的原来的响应,默认表示以新资源的响应码为其响应码
[root@localhost nginx]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
error_page 404 =200 /404.html;
[root@localhost nginx]# systemctl reload nginx.service
回到浏览器,刷新页面,再次查看
log_format定义日志格式
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log logs/access.log main;
//注意:此处可用变量为nginx各模块内建变量
location区段,通过指定模式来与客户端请求的URI相匹配
//功能:允许根据用户请求的URI来匹配定义的各location,匹配到时,此请求将被相应的location配置块中的配置所处理,例如做访问控制等功能
//语法:location [ 修饰符 ] pattern {......}
常用修饰符说明:
| 修饰符 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| = | 精确匹配 |
| ~ | 正则表达式模式匹配,区分大小写 |
| ~* | 正则表达式模式匹配,不区分大小写 |
| ^~ | 前缀匹配,类似于无修饰符的行为,也是以指定模块开始,不同的是,如果模式匹配,那么就停止搜索其他模式了,不支持正则表达式 |
| @ | 定义命名location区段,这些区段客户端不能访问,只可以由内部产生的请求来访问,如try_files或error_page等 |
没有修饰符表示必须以指定模式开始,如:
location /abc {
echo "Hello World!";
}
那么如下内容就可正确匹配:
//http://192.168.169.140/abc
[root@localhost nginx]# curl http://192.168.169.140/abc
Hello World!
//http://192.168.169.140/abc?p1=11&p2=22
[root@localhost nginx]# curl http://192.168.169.140/abc\?a\&b //‘&’需要加上转义字符
Hello World!
//http://192.168.169.140/abc/
[root@localhost nginx]# curl http://192.168.169.140/abc/
Hello World!
=:表示必须与指定的模式精确匹配,如:
location = /abc {
echo "Hello World!";
}
那么如下内容就可正确匹配:
[root@localhost nginx]# curl http://192.168.169.140/abc?p1=11\&p2=22
Hello World!
[root@localhost nginx]# curl http://192.168.169.140/abc
Hello World!
~:表示指定的正则表达式要区分大小写,如:
location ~ ^/abc$ {
echo "Hello World!";
}
那么如下内容就可正确匹配:
[root@localhost nginx]# curl http://192.168.169.140/abc?p1=11\&p2=22
Hello World!
[root@localhost nginx]# curl http://192.168.169.140/abc
Hello World!
如果是大写的话,就不能匹配
[root@localhost nginx]# curl http://192.168.169.140/aBC
404 test
[root@localhost nginx]# curl http://192.168.169.140/abC
404 test
~*:表示指定的正则表达式不区分大小写,如:
location ~* ^/abc$ {
echo "Hello World!";
}
这样的话,就不会区分大小写,大写也可以匹配
[root@localhost nginx]# curl http://192.168.169.140/abC
Hello World!
[root@localhost nginx]# curl http://192.168.169.140/aBC
Hello World!
^~: 前缀匹配,似于无修饰符的行为,也是以指定模式开始,不同的是,如果模式匹配,则停止搜索其他模式
location ^~ /abc {
echo "Hello World!";
}
查找顺序和优先级:由高到底依次为
- 带有=的精确匹配优先
- 正则表达式按照他们在配置文件中定义的顺序
- 带有^~修饰符的,开头匹配
- 正则表达式按照他们在配置文件中定义的顺序带有或*修饰符的,如果正则表达式与URI匹配
- 没有修饰符的精确匹配
优先级次序如下:
( location = 路径 ) --> ( location ^~ 路径 ) --> ( location ~ 正则 ) --> ( location ~* 正则 ) --> ( location 路径 )
6.10 访问控制
allow:设定允许哪台或哪些主机访问
deny:设定禁止哪台或哪些主机访问
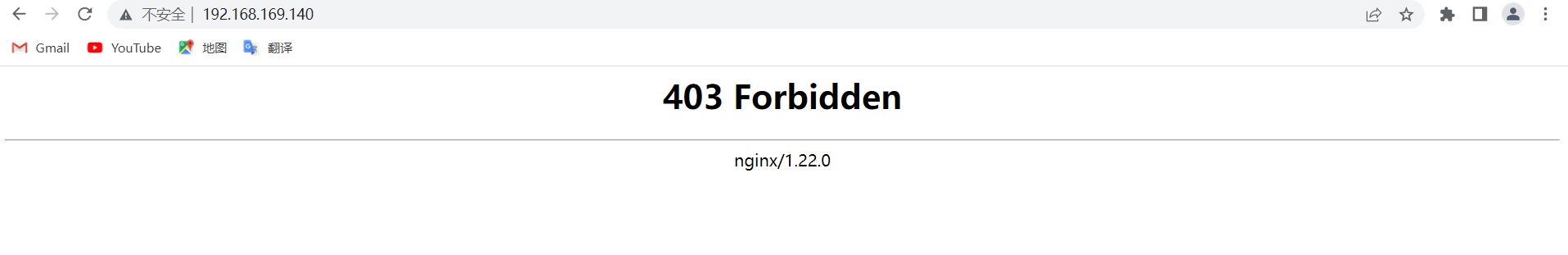
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
//在主页面配置进行修改
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
deny 192.168.169.1; //不允许192.168.169.1这台主机进行访问
allow all; //不包括上面拒绝的,允许所有主机访问
}
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl reload nginx.service
//先使用本机进行访问
[root@localhost ~]# curl http://192.168.169.140
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
…………
在192.168.169.1主机上访问,也就是我的物理机,访问不到
6.11 用户认证
auth_basic "欢迎信息";
auth_basic_user_file "/path/to/user_auth_file"
//建议用htpasswd来创建密码文件
//安装httpd-tools包
[root@localhost ~]# dnf -y install httpd-tools
//创建密码文件
[root@localhost ~]# htpasswd -c -m /usr/local/nginx/conf/.user_auth_file zzd //-m后面为文件存放路径,zzd为用户名
New password:
Re-type new password:
Adding password for user zzd
[root@localhost ~]# cat /usr/local/nginx/conf/.user_auth_file
zzd:$apr1$7f1VJ4ty$jPXNW/OcfLaNWFa4Ylvb0.
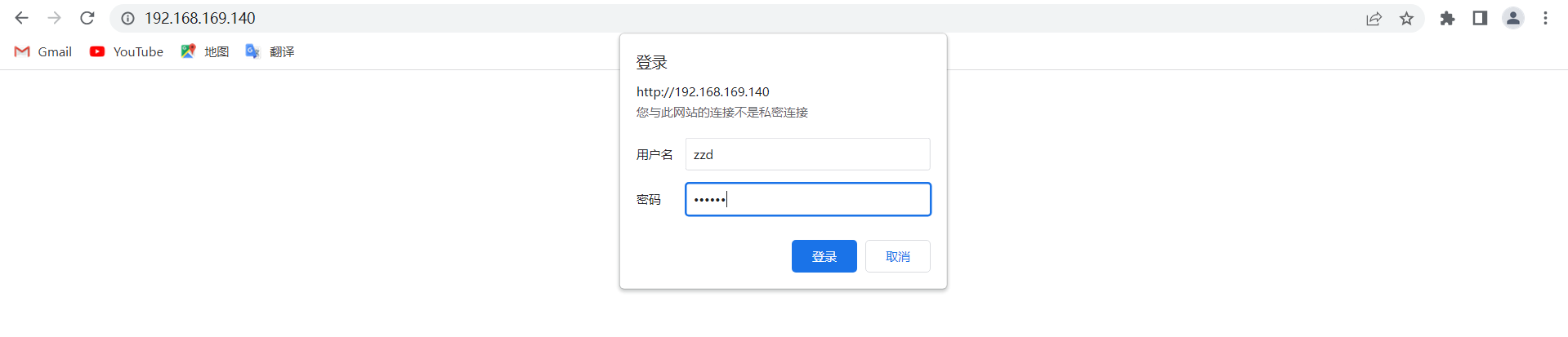
//配置用户认证,还是拿nginx默认主页进行测试
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
auth_basic "Hello!";
auth_basic_user_file /usr/local/nginx/conf/.user_auth_file
}
6.12 https配置
自签证书
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir -p /etc/pki/CA/private
[root@localhost ~]# cd /etc/pki/CA/
[root@localhost CA]# (umask 077;openssl genrsa -out private/cakey.pem 2048)
Generating RSA private key, 2048 bit long modulus (2 primes)
...........................................................................+++++
.............+++++
e is 65537 (0x010001)
[root@localhost CA]# openssl req -new -x509 -key private/cakey.pem -out cacert.pem -days 365
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:CN
State or Province Name (full name) []:HB
Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:WH
Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:zic-linux
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:zic-linux
Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:zzd@example.com
Email Address []:123@456.com
[root@localhost CA]# touch index.txt && echo 01 > serial
[root@localhost CA]# cd /usr/local/nginx/conf
[root@localhost conf]# mkdir ssl
[root@localhost conf]# cd ssl/
[root@localhost ssl]# (umask 077;openssl genrsa -out nginx.key 2048)
Generating RSA private key, 2048 bit long modulus (2 primes)
........+++++
............................................................................................+++++
e is 65537 (0x010001)
[root@localhost ssl]# openssl req -new -key nginx.key -days 365 -out nginx.csr
Ignoring -days; not generating a certificate
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:CN
State or Province Name (full name) []:HB
Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:WH
Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:zic-linux
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:zic-linux
Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:zzd@example.com
Email Address []:123@456.com
Please enter the following 'extra' attributes
to be sent with your certificate request
A challenge password []:
An optional company name []:
[root@localhost ssl]# cd /etc/pki/CA/
[root@localhost CA]# mkdir /etc/pki/CA/newcerts
[root@localhost CA]# openssl ca -in /usr/local/nginx/conf/ssl/nginx.csr -out /usr/local/nginx/conf/ssl/nginx.crt -days 365
Using configuration from /etc/pki/tls/openssl.cnf
Check that the request matches the signature
Signature ok
Certificate Details:
Serial Number: 1 (0x1)
Validity
Not Before: Oct 13 13:30:12 2022 GMT
Not After : Oct 13 13:30:12 2023 GMT
Subject:
countryName = CN
stateOrProvinceName = HB
organizationName = zic-linux
organizationalUnitName = zic-linux
commonName = zzd@example.com
emailAddress = 123@456.com
X509v3 extensions:
X509v3 Basic Constraints:
CA:FALSE
Netscape Comment:
OpenSSL Generated Certificate
X509v3 Subject Key Identifier:
60:41:EE:B6:85:6B:30:76:01:CE:2F:E3:DD:95:9D:A9:C9:9B:54:4C
X509v3 Authority Key Identifier:
keyid:55:13:51:28:30:CE:FB:93:19:89:7B:E1:DD:47:FE:25:C3:3A:C0:12
Certificate is to be certified until Oct 13 13:30:12 2023 GMT (365 days)
Sign the certificate? [y/n]:y
1 out of 1 certificate requests certified, commit? [y/n]y
Write out database with 1 new entries
Data Base Updated
//配置nginx
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name www.zzd.com;
ssl_certificate ssl/nginx.crt;
ssl_certificate_key ssl/nginx.key;
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
ssl_session_timeout 5m;
ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
访问https://host_ip
6.13 开启状态界面
location /status {
stub_status {on | off};
allow xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/16;
deny all;
}
//开启状态界面的前提是在安装nginx的时候开启了此功能
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -V
…………
………… --with-http_stub_status_module …………
//编辑nginx主配置文件
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
location /status {
stub_status on;
}
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl reload nginx.service
状态页面信息详解:
| 状态码 | 表示的意义 |
|---|---|
| Active connections 2 | 当前所有处于打开状态的连接数 |
| accepts | 总共处理了多少个连接 |
| handled | 成功创建多少握手 |
| requests | 总共处理了多少个请求 |
| Reading | nginx读取到客户端的Header信息数,表示正处于接收请求状态的连接数 |
| Writing | nginx返回给客户端的Header信息数,表示请求已经接收完成, 且正处于处理请求或发送响应的过程中的连接数 |
| Waiting | 开启keep-alive的情况下,这个值等于active - (reading + writing), 意思就是Nginx已处理完正在等候下一次请求指令的驻留连接 |
6.14 rewrite
语法:rewrite regex replacement flag;
rewrite ^/images/(.*\.jpg)$ /imgs/$1 break; 此处的$1用于引用(.*.jpg)匹配到的内容
rewrite ^/bbs/(.*)$ http://www.idfsoft.com/index.html redirect;
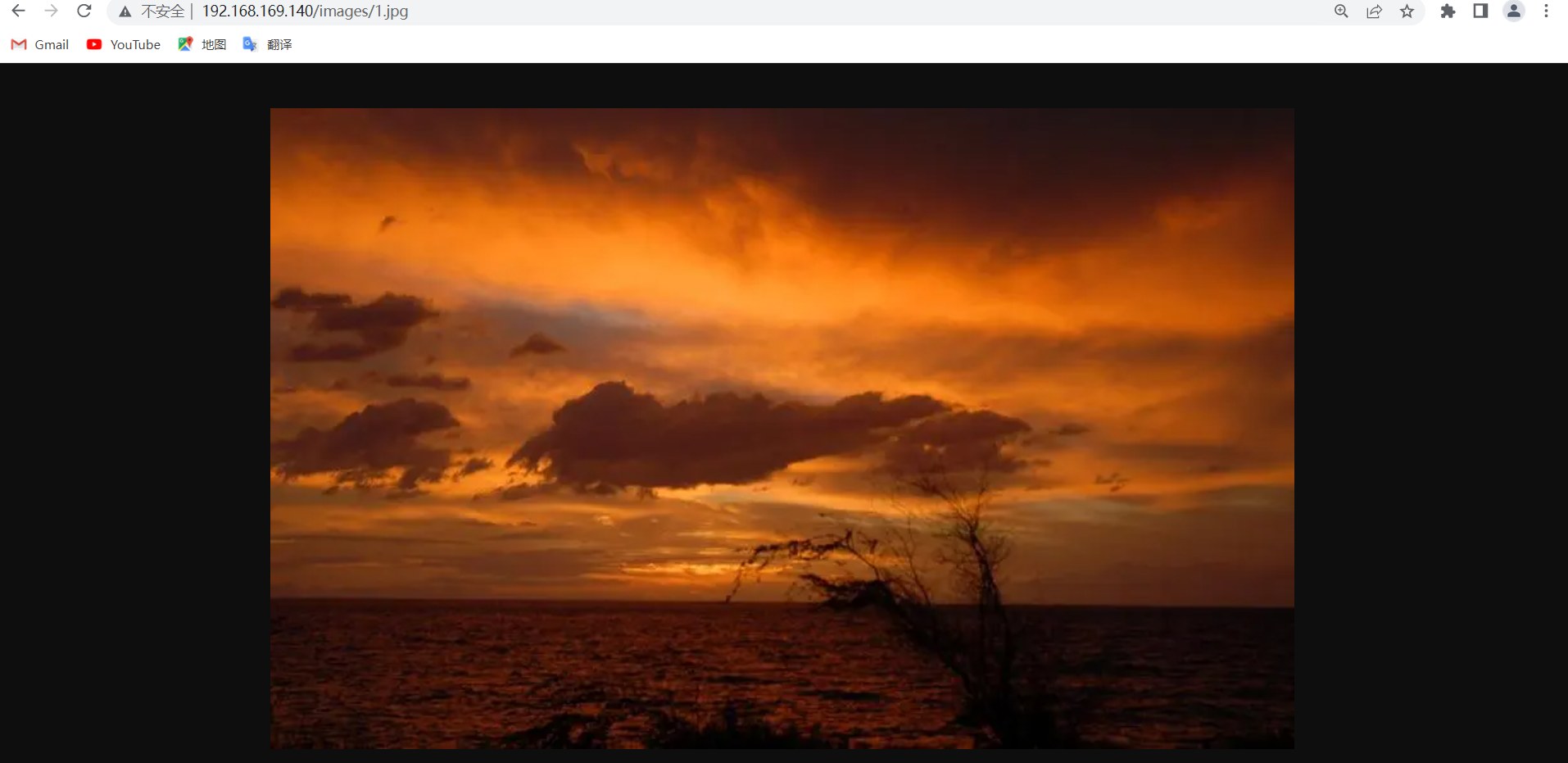
//此时nginx默认站点下images目录有一个图片1.jpg
[root@nginx ~]# ls /usr/local/nginx/html/images/
1.jpg
[root@nginx html]# chmod 644 images/1.jpg
[root@nginx html]# ll images/1.jpg
-rw-r--r-- 1 nginx nginx 20020 Oct 15 17:28 images/1.jpg
//我们可以通过ip加站点路径正常访问
试想一下,如果我们将此目录做了修改,将images修改为imge,那么用户使用原有的访问方式就访问不到了,而我们又不可能去告诉用户新的访问链接,所以,我们可以用rewrite去匹配用户输入的链接将其修改为新的链接,这样用户就相当于用旧的链接去访问到了新的连接,而用户并不知情
[root@nginx html]# mv images imge
[root@nginx html]# ls
404.html 50x.html imge index.html
[root@nginx html]# ll imge/
total 20
-rw-r--r-- 1 nginx nginx 20020 Oct 15 17:28 1.jpg
[root@nginx html]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
location /images {
rewrite ^/images/(.*)$ /imge/$1 break;
}
[root@nginx html]# systemctl reload nginx.service
此时,我们就是用户,我并不知道images目录已经改为imge,让然用之前的链接去进行访问
可以看到,仍然可以正常进行访问
又或者说,还是进行了更改,不过是吧原本的目录拿出来,单独变成了一个网站,也就是说单独的一个server{}配置,用户仍然可以使用原有的链接进行访问
现在有一个nginx服务器,有一个虚拟主机的server_name为zic01.example.com,用户使用zic01.example.com/images/1.jpg可以访问到一个图片,但是现在将images这个目录进行了重命名,重命名后目录名为imge,并且将这个目录单独拿出来做了一个虚拟主机,server_name为zic02.example.com,但是用户并不知情,所以必须让用户使用原链接同样可以进行访问
//先配置另外一个网站,server_name为zic02.example.com
[root@nginx html]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name zic02.example.com;
location / {
root html/imge;
index index.html;
}
}
…………
//nginx默认的网站的server_name为zic01.example.com,也要进行修改
listen 80;
server_name zic01.example.com;
…………
location /images {
rewrite ^/images/.*\.jpg$ http://zic02.example.com/1.jpg break;
}
[root@nginx html]# systemctl reload nginx.service
在物理机的hosts文件里添加域名映射
192.168.169.140 zic01.example.com
192.168.169.140 zic02.example.com
先试试能不能使用域名正常访问
可以正常进行访问
现在我们使用原链接,看看能不能访问成功

我们输入的是原链接,但是回车进行访问后,URL被重写成了zic02.example.com/1.jpg
这就是因为rewrite配用户输入的URI所匹配到,并且将URI进行了重写,而我们刚才在上面的配置也明确说明进指定匹配到的URI重写为http://zic02.example.com/1.jpg
如上例所示,replacement可以是某个路径,也可以是某个URL
如果将上面两个实验结合起来,用户本来可以使用zic01.example.com/images/1.jpg进行访问。但是后来,images这个目录被重命名为imge,所以为了让用户能够正常进行访问,所以进行了如下重写操作,让用户输入的是zic01.example.com/images/1.jpg,但实际访问到的却是zic01.example.com/imge/1.jpg
location /images {
rewrite ^/images/(.*)$ /imge/$1 break;
}
后来又将imge这个目录单独拿出来做了一个网站,server_name为zic02.example.com,用户还是需要输入最开始的链接访问
location /images {
rewrite ^/images/(.*)$ /imge/$1 last;
}
location /imge {
rewrite ^/imge/(.*)$ http://zic02.example.com/$1 break;
}
可以正常进行访问
常见的flag
| flag | 作用 |
|---|---|
| last | 基本上都用这个flag,表示当前的匹配结束,继续下一个匹配,最多匹配10个到20个 一旦此rewrite规则重写完成后,就不再被后面其它的rewrite规则进行处理 而是由UserAgent重新对重写后的URL再一次发起请求,并从头开始执行类似的过程 |
| break | 中止Rewrite,不再继续匹配 一旦此rewrite规则重写完成后,由UserAgent对新的URL重新发起请求, 且不再会被当前location内的任何rewrite规则所检查 |
| redirect | 以临时重定向的HTTP状态302返回新的URL |
| permanent | 以永久重定向的HTTP状态301返回新的URL |
rewrite模块的作用是用来执行URL重定向。这个机制有利于去掉恶意访问的url,也有利于搜索引擎优化(SEO)
nginx使用的语法源于Perl兼容正则表达式(PCRE)库,基本语法如下:
| 标识符 | 意义 |
|---|---|
| ^ | 必须以^后的实体开头 |
| $ | 必须以$前的实体结尾 |
| . | 匹配任意字符 |
| [] | 匹配指定字符集内的任意字符 |
| [^] | 匹配任何不包括在指定字符集内的任意字符串 |
| | | 匹配 | 之前或之后的实体 |
| () | 分组,组成一组用于匹配的实体,通常会有 | 来协助 |
6.15 if
语法:if (condition) {...}
应用场景:
- server段
- location段
常见的condition
- 变量名(变量值为空串,或者以“0”开始,则为false,其它的均为true)
- 以变量为操作数构成的比较表达式(可使用=,!=类似的比较操作符进行测试)
- 正则表达式的模式匹配操作
- ~:区分大小写的模式匹配检查
- ~*:不区分大小写的模式匹配检查
- !和!*:对上面两种测试取反
- 测试指定路径为文件的可能性(-f,!-f)
- 测试指定路径为目录的可能性(-d,!-d)
- 测试文件的存在性(-e,!-e)
- 检查文件是否有执行权限(-x,!-x)
6.15.1 基于浏览器实现分离案例
if ($http_user_agent ~ Firefox) {
rewrite ^(.*)$ /firefox/$1 break;
}
if ($http_user_agent ~ MSIE) {
rewrite ^(.*)$ /msie/$1 break;
}
if ($http_user_agent ~ Chrome) {
rewrite ^(.*)$ /chrome/$1 break;
}
6.15.2 防盗链案例
location ~* \.(jpg|gif|jpeg|png)$ {
valid_referers none blocked www.idfsoft.com;
if ($invalid_referer) {
rewrite ^/ http://www.idfsoft.com/403.html;
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号