Vue05-Vuex
01. 什么是状态管理
在开发中,我们的应用程序需要处理各种各样的数据,这些数据需要保存在我们应用程序的某一个位置,对于这些数据的管理我们就称之为 状态管理。
在Vue开发中,我们使用组件化的开发方式:
在组件中我们定义data或者在setup中返回使用的数据,这些数据我们称之为state(状态);
在模块template中我们可以使用这些数据,模块最终会被渲染成DOM,我们称之为View;
在模块中我们会产生一些行为事件,处理这些行为事件时,有可能会修改state,这些行为事件我们称之为actions;
JavaScript开发的应用程序,已经变得越来越复杂了,这意味着JavaScript需要管理的状态越来越多了,
这些状态包括服务器返回的数据、缓存数据、用户操作产生的数据;
也包括一些UI的状态,比如某些元素是否被选中,是否显示加载动效,当前分页等等;
与此同时,状态之间相互会存在依赖,一个状态的变化会引起另一个状态的变化,这些都在加大状态管理的难度。
对于一些简单的状态,我们可以通过props的传递或者Provide的方式来共享状态;
但是对于复杂的状态管理,显然单纯通过传递和共享的方式是不足以解决问题的,这时候就需要专门的状态管理库了。
状态管理的第三方库有vuex和Pinia。
02. Vuex简介
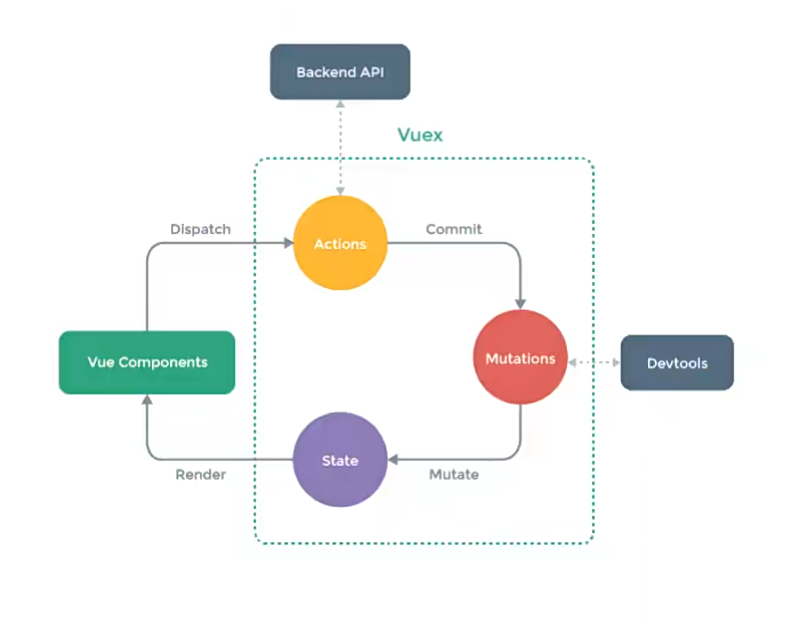
Vuex的状态管理图:
vuex将所有的state抽离存放于一个仓库Store,任何组件都可以去访问state。
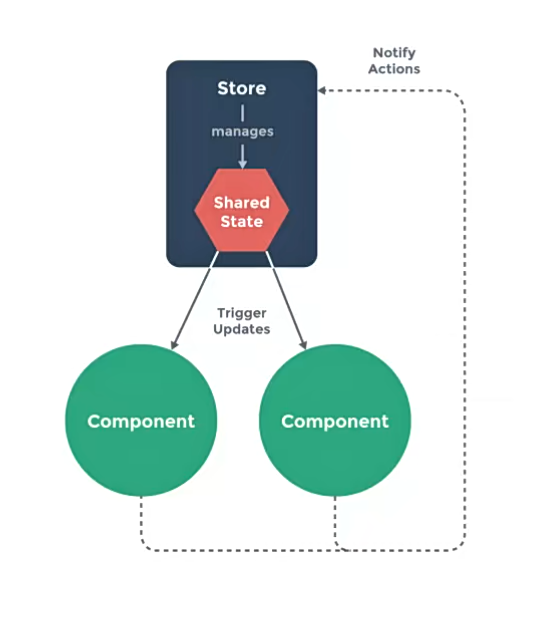
- 组件读取state,进行渲染;组件不能直接修改state;
- 组件需要修改state时,需要派发(dispatch)一个行为(actions);
- 行为(actions)一般为访问服务器获取数据;
- 通过mutations修改state。
03. 安装vuex
npm install vuex
04. 从案例入手
我们从一个简单案例入手:在setup中定义了一个counter,在模板中显示这个counter。
常规写法
<template> <div class="app"> <!-- 以前写法 --> <h2>App当前计数: {{ counter }}</h2> </div> </template> <script setup> import {ref} from 'vue' const counter = ref(0) </script>
运用vuex
每一个Vuex应用的核心就是store(仓库),store本质上是一个容器,它包含着应用中大部分的状态(state)。
按照编程习惯,一般会在项目的src目录中,创建store目录,在store目录中创建index.js,在index.js中书写关于状态管理的逻辑。
Vuex和单纯的全局对象有什么区别呢?
第一:Vuex的状态存储是响应式的。当Vue组件从store中读取状态的时候,若store中的状态发生变化,那么相应的组件也会被更新;
第二:不能直接改变store中的状态。改变store中的状态的唯一途径就显示提交 (commit) mutation;
这样我们就可以方便跟踪每一个状态的变化,从而让我们能够通过一些工具帮助我们更好的管理应用的状态。
需要注意的是,一个项目只能创建一个store,这种官方的描述中被称为“单一状态树”。
单一状态树(SSOT,Single Source of Truth),也称为“单一数据源”。
这是vuex中的一个概念,指vuex用一个对象(一个store),就包含了全部的应用层级的状态。
App.vue:
<template> <div class="app"> <!-- store中的counter:用 $store 访问--> <h2>App当前计数: {{ $store.state.counter }}</h2> </div> </template> <script setup> // 代码中需要先导入useStore import {useStore} from 'vuex' const store = useStore() function printCounter(){ console.log(store.state.counter) } </script>
index.js
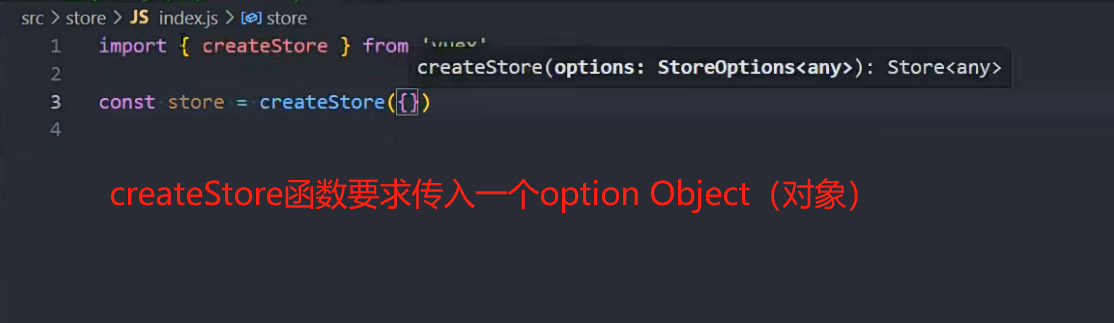
import { createStore } from 'vuex' const store = createStore({ state: () => ({ counter: 100, }) export default store
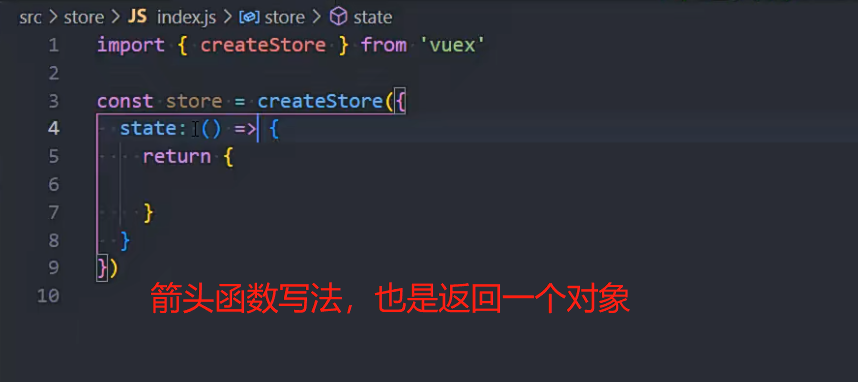
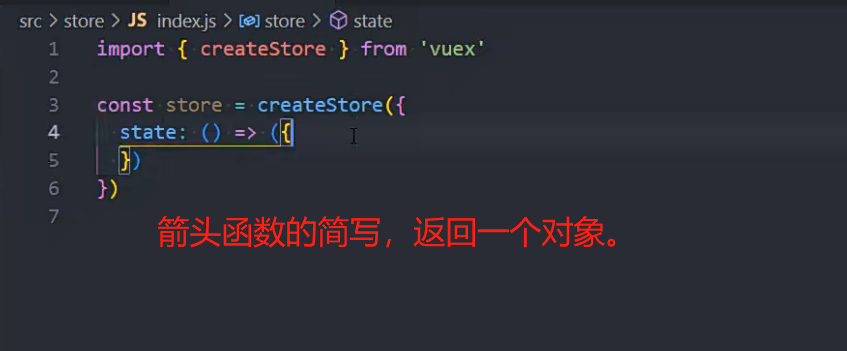
createStore函数的写法

05. mapState
在模板中访问state,一般的写法 $store.state.name,显得很冗长。
<template> <div class="app"> <!-- 在模板中直接访问state --> <h2>name: {{ $store.state.name }}</h2> <h2>age: {{ $store.state.age }}</h2> <h2>avatar: {{ $store.state.avatarURL }}</h2> </div> </template>
有没有更好的办法呢?你可能会想到computed。
<template> <div class="app"> <!-- 通过computed访问state --> <h2>name: {{ name }}</h2> <h2>age: {{ age }}</h2> <h2>avatar: {{ avatar }}</h2> </div> </template> <script> export default { computed: { name(){ return $store.state.name }, age(){ return $store.state.age }, avatar(){ return $store.state.avatarURL }, } } </script>
这种写法虽然简化了模板中的书写,但又需要在computed中定义函数,并没有优化多少。
vuex考虑到这种情况,提供了更简洁的写法,mapState函数。
mapState函数用于映射state到组件中,返回的是数组,内含一个个函数。
- 数组写法:需要保证state不与data中其他数据重名;
- 对象写法:可以给state取别名。
<template> <div class="app"> <!-- mapState的数组写法 --> <h2>name: {{ name }}</h2> <h2>age: {{ age }}</h2> <h2>avatar: {{ avatarURL }}</h2> <!-- mapState的对象写法 --> <h2>name: {{ sName }}</h2> <h2>age: {{ sAge }}</h2> </div> </template> <script> import { mapState } from 'vuex' export default { computed: { // 舍弃这种繁琐的写法 // name() { // return this.$store.state.name // }, // computed中可正常定义其他函数 fullname() { return "xxx" }, // 1. mapState的数组写法 ...mapState(["name", "age", "avatarURL"]), // 2. mapState的对象写法:用于给变量取别名 ...mapState({ sName: state => state.name, sAge: state => state.age }) } } </script>
vuex适用于Vue2,或Vue3的optionAPI写法,
在setup中适用vuex,会略微繁琐。
官方推荐Vue3使用Pinia库作状态管理。
<template> <div class="app"> <h2>name: {{ name }}</h2> <h2>age: {{ age }}</h2> </div> </template> <script setup> import { computed, toRefs } from 'vue' import { mapState, useStore } from 'vuex' import useState from "../hooks/useState" // 1.一步步完成 // const { name, level } = mapState(["name", "level"]) // 注意:name,level是函数,这个函数的执行需要传入store // setup中的computed函数要求传入一个函数,所以可以直接把上面的name和level传递进入,同时绑定所需要的store // const store = useStore() // const cName = computed(name.bind({ $store: store })) // const cLevel = computed(level.bind({ $store: store })) // 2.简洁写法:直接对store.state进行解构,同时赋予响应式。 const store = useStore() const { name, age } = toRefs(store.state) </script>
06. getters
如果我们在输出state之前,需要对数据进行逻辑处理,可以使用getters。
import {createStore} from 'vuex' const store = createStore({ state: () => ({ name: "Mark", age: 18, height: 173, avatarURL: "http://xxxxxx", scores: [ {id: 111, name: "语文", score: 89}, {id: 112, name: "英语", score: 90}, {id: 113, name: "数学", score: 96} ], }), getters: { // 1.基本使用:对身高进行格式化输出 formatHeight(state) { return state.height / 100 }, // 1.复杂逻辑:计算总分 totalScores(state) { return state.scores.reduce((preValue, item) => { return preValue + item.score }, 0) }, // 3.在该getters属性中, 获取其他的getters message(state, getters) { return `name:${state.name} age:${state.age} height:${getters.height}` }, // 4.getters也可以返回一个函数, 调用这个函数可以传入参数(了解) getScoreById(state) { return function (id) { // 数组的find用法。 const score = state.scores.find(item => item.id === id) return score } } }, }) export default store
07. mapGetters
为了方便对getters的使用,vuex也提供了mapGetters函数,使用方法于mapState类似。
<template> <div class="app"> <h2>formatHeight: {{ formatHeight }}</h2> <h2>totalScores: {{ totalScores }}</h2> <h2>message: {{ message }}</h2> <!-- 根据id获取某一科目的成绩 --> <h2>id-111的科目分数: {{ getScoreById(111) }}</h2> <h2>id-112的科目分数: {{ getScoreById(112) }}</h2> </div> </template> <script> import { mapGetters } from 'vuex' export default { computed: { ...mapGetters(["formatHeight", "totalScores",'message']), ...mapGetters(["getScoreById"]) } } </script>
setup中使用:
<script setup> import { computed, toRefs } from 'vue'; import { mapGetters, useStore } from 'vuex' const store = useStore() // 1.使用mapGetters // const { message: messageFn } = mapGetters(["message"]) // const message = computed(messageFn.bind({ $store: store })) // 2.直接解构, 并且包裹成ref,提供响应式 // const { message } = toRefs(store.getters) // 3.针对某一个getters属性使用computed,比mapGetters好用 const message = computed(() => store.getters.message) </script>
08. mutations
更改 Vuex 的 store 中的状态的唯一方法是提交 mutation。
在mutations中书写对应的函数,默认会传入一个参数state,用于获取所有的state
import {createStore} from 'vuex' import {CHANGE_INFO} from './mutation_types' import homeModule from './modules/home' import counterModule from './modules/counter' import {CHANGE_INFO} from "@/store/mutation_types" const store = createStore({ state: () => ({ name: "Mark", age: 18, height: 173, avatarURL: "http://xxxxxx", scores: [ {id: 111, name: "语文", score: 89}, {id: 112, name: "英语", score: 90}, {id: 113, name: "数学", score: 96} ], }), getters: { // 1.基本使用:对身高进行格式化输出 formatHeight(state) { return state.height / 100 }, // 1.复杂逻辑:计算总分 totalScores(state) { return state.scores.reduce((preValue, item) => { return preValue + item.score }, 0) }, // 2.在该getters属性中, 获取其他的getters message(state, getters) { return `name:${state.name} age:${state.age} height:${getters.height}` }, // 3.getters也可以返回一个函数, 调用这个函数可以传入参数(了解) getScoreById(state) { return function (id) { const score = state.scores.find(item => item.id === id) return score } } }, mutations: { incrementAge(state) { state.age++ }, changeName(state, payload) { state.name = payload }, changeInfo(state, newInfo) { state.age = newInfo.age state.name = newInfo.name }, // 使用常量的写法: [CHANGE_INFO](state, newInfo) { state.age = newInfo.age state.name = newInfo.name }, }, }) export default store
组件中应用:
<template> <div class="app"> <button @click="changeName">修改name</button> <button @click="incrementAge">递增age</button> <button @click="changeInfo">修改info</button> <h2>Store Name: {{ $store.state.name }}</h2> <h2>Store Level: {{ $store.state.level }}</h2> </div> </template> <script> import {CHANGE_INFO} from "@/store/mutation_types" export default { computed: {}, methods: { changeName() { // 这种写法虽然可以修改值,但不推荐。 // this.$store.state.name = "Tom" this.$store.commit("changeName", "Tom") // 第一个参数为mutations中的名称,第二个参数为值 }, incrementAge() { this.$store.commit("incrementAge") }, changeInfo() { this.$store.commit(changeInfo, { name: "Tom", age: 20 }) }, // 使用常量的写法: changeInfo() { this.$store.commit(CHANGE_INFO, { name: "Tom", age: 20 }) } } } </script>
store/mutation_types.js:
export const CHANGE_INFO = "changeInfo"
mutation是重要原则: mutation 必须是同步函数,不要执行异步操作。
这是因为devtool工具会记录mutation的日志;
每一条mutation被记录,devtools都需要捕捉到前一状态和后一状态的快照;
但是在mutation中执行异步操作,就无法追踪到数据的变化;
对于异步操作,vuex放在action中。
09. mapMutations
为了方便对Mutations的使用,vuex也提供了mapMutations函数,使用方法于mapState类似。
<template> <div class="app"> <button @click="changeName('王小波')">修改name</button> <button @click="incrementAge">递增Age</button> <button @click="changeInfo({ name: '王二', age: 22 })">修改info</button> <h2>Store Name: {{ $store.state.name }}</h2> <h2>Store Level: {{ $store.state.level }}</h2> </div> </template> <script> import { mapMutations } from 'vuex' import { CHANGE_INFO } from "@/store/mutation_types" export default { computed: { }, methods: { btnClick() { console.log("btnClick") }, // 注意这里通过CHANGE_INFO取出常量,但模板中使用的是changeInfo // ...mapMutations(["changeName", "incrementAge", CHANGE_INFO]) } } </script> <script setup> import { mapMutations, useStore } from 'vuex' import { CHANGE_INFO } from "@/store/mutation_types" const store = useStore() // 手动的映射和绑定 const mutations = mapMutations(["changeName", "incrementLevel", CHANGE_INFO]) const newMutations = {} Object.keys(mutations).forEach(key => { newMutations[key] = mutations[key].bind({ $store: store }) }) const { changeName, incrementLevel, changeInfo } = newMutations </script>
10. actions
Action类似于mutation,不同在于:
-
Action提交的是mutation,而不是直接变更状态;
-
Action可以包含任意异步操作;
在actions中书写函数,默认会传入一个参数context(上下文)。可以通过context访问到当前的state和getters。
context.commit(mutation名称) 用于提交mutation
import {createStore} from 'vuex' const store = createStore({ // ... actions: { incrementAction(context) { // console.log(context.commit) // 用于提交mutation // console.log(context.getters) // 访问getters // console.log(context.state) // 访问state context.commit("incrementAge") }, changeNameAction(context, payload) { context.commit("changeName", payload) }, }, // ... }
在组件中运用:通过 $store.dispatch
<template> <div class="home"> <h2>当前计数: {{ $store.state.counter }}</h2> <button @click="counterBtnClick">发起action修改counter</button> <h2>name: {{ $store.state.name }}</h2> <button @click="nameBtnClick">发起action修改name</button> </div> </template> <script> export default { methods: { counterBtnClick() { this.$store.dispatch("incrementAction") }, nameBtnClick() { this.$store.dispatch("changeNameAction", "aaa") } } } </script>
setup直接定义函数即可。
action中进行网络请求,继而处理请求得到的数据。
import {createStore} from 'vuex' const store = createStore({ actions: { incrementAction(context) { // console.log(context.commit) // 用于提交mutation // console.log(context.getters) // getters // console.log(context.state) // state context.commit("increment") }, changeNameAction(context, payload) { context.commit("changeName", payload) }, // 以下模拟网络请求 // fetchHomeMultidataAction(context) { // // 1.返回Promise, 给Promise设置then // // fetch("http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/multidata").then(res => { // // res.json().then(data => { // // console.log(data) // // }) // // }) // // 2.Promise链式调用 // // fetch("http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/multidata").then(res => { // // return res.json() // // }).then(data => { // // console.log(data) // // }) // return new Promise(async (resolve, reject) => { // // 3.await/async // const res = await fetch("http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/multidata") // const data = await res.json() // // 修改state数据 // context.commit("changeBanners", data.data.banner.list) // context.commit("changeRecommends", data.data.recommend.list) // resolve("aaaaa") // }) // } }, }) export default store
11. mapActions
<template> <div class="home"> <h2>当前计数: {{ $store.state.counter }}</h2> <button @click="incrementAgeBtn">发起action修改Age</button> <h2>name: {{ $store.state.name }}</h2> <button @click="changeNameBtn('bbbb')">发起action修改name</button> </div> </template> <script> import { mapActions } from 'vuex' export default { methods: { // incrementAgeBtn() { // this.$store.dispatch("incrementAction") // }, // changeNameBtn() { // this.$store.dispatch("changeNameAction", "aaa") // } // 这种方法需要注意的调用名称需一致 // ...mapActions(["incrementAction", "changeNameAction"]) } } </script> <!-- ↓ setup写法 ↓ --> <script setup> import { useStore, mapActions } from 'vuex' const store = useStore() // 1.在setup中使用mapActions辅助函数 // const actions = mapActions(["incrementAction", "changeNameAction"]) // const newActions = {} // Object.keys(actions).forEach(key => { // newActions[key] = actions[key].bind({ $store: store }) // }) // const { incrementAction, changeNameAction } = newActions // 2.使用默认的做法 function increment() { store.dispatch("incrementAction") } </script>
12. module
由于使用单一状态树,应用的所有状态会集中到一个比较大的对象,当应用变得非常复杂时,store 对象就有可能变得相当臃肿;
为了解决以上问题,Vuex 允许我们将 store 分割成模块(module);
每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块。
使用module时,mutation、action和getter会自动合并到一起,所以在模板中可以直接通过
$store.getters.xxxx去调用;而state是独立的,在模板中需要用
$store.state.module_name.state_name去访问。由于mutation、action和getter会自动合并到一起,一起放到全局,所以对于这些函数的命名需要特别小心,重名就会被覆盖;
为了避免重名问题,也可以设置namespace。

index.js:
import {createStore} from 'vuex' import homeModule from './modules/home' import counterModule from './modules/counter' const store = createStore({ state: () => ({ name: "Mark", age: 18, height: 173, rootCounter: 100, avatarURL: "http://xxxxxx", scores: [ {id: 111, name: "语文", score: 89}, {id: 112, name: "英语", score: 90}, {id: 113, name: "数学", score: 96} ], }), // ...... modules: { home: homeModule, counter: counterModule } }) export default store
home.js:
export default { state: () => ({ // 服务器数据 banners: [], recommends: [] }), mutations: { changeBanners(state, banners) { state.banners = banners }, changeRecommends(state, recommends) { state.recommends = recommends } }, actions: { // 向服务器发起请求,获取home页面数据 fetchHomeMultidataAction(context) { return new Promise(async (resolve, reject) => { // 3.await/async const res = await fetch("http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/multidata") const data = await res.json() // 修改state数据 context.commit("changeBanners", data.data.banner.list) context.commit("changeRecommends", data.data.recommend.list) resolve("aaaaa") }) } } }
counter.js:
const counter = { namespaced: true, state: () => ({ count: 99 }), mutations: { incrementCount(state) { state.count++ } }, getters: { // 注意:module中,getters函数有第三个参数rootState doubleCount(state, getters, rootState) { return state.count + rootState.rootCounter } }, actions: { incrementCountAction(context) { context.commit("incrementCount") } } } export default counter
对store的代码逻辑进行拆分后,在组件中如何访问数据呢?
<template> <div class="home"> <h2>Home Page</h2> <ul> <!-- 获取数据: 需要从模块中获取 state.modulename.xxx --> <template v-for="item in $store.state.home.banners" :key="item.acm"> <li>{{ item.title }}</li> </template> </ul> <h2>Counter Page</h2> <!-- 使用state时, 是需要state.moduleName.xxx --> <h2>Counter模块的counter: {{ $store.state.counter.count }}</h2> <!-- 使用getters时, 默认可以直接getters.xxx --> <!-- <h2>Counter模块的doubleCounter: {{ $store.getters.doubleCount }}</h2>--> <!-- 如果设置了namespace,则需要用下面的方式: --> <h2>Counter模块的doubleCounter: {{ $store.getters["counter/doubleCount"] }}</h2> <button @click="incrementCount">count模块+1</button> </div> </template> <script> </script> <script setup> import { useStore } from 'vuex' const store = useStore() // 默认:dispatch一个action的时候,直接调用即可 store.dispatch("fetchHomeMultidataAction").then(res => { console.log("home中的then被回调:", res) }) // 如果module中设置了 namespaced: true, 那么dispatch时就需要加上模块名 function incrementCount() { store.dispatch("counter/incrementCountAction") } </script>
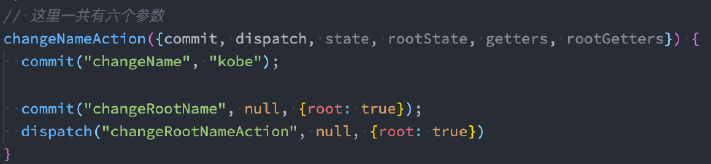
在module中,如果希望修改root中的state,有如下方式:
(完)






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律