爬虫(六)多线程爬虫
创建多线程类
import threading # 引入多线程模块
import time
def run(name):
print(name,"线程执行了!")
time.sleep(5)
# 创建2个线程对象
t1 = threading.Thread(target=run,args=("t1",))
t2 = threading.Thread(target=run,args=("t2",))
# 启动线程
t1.start()
t2.start()
# 等待子线程执行完毕后再继续执行主线程后的内容
t1.join()
t2.join()
使用threading 模块创建线程
创建一个新的子类继承threading、Thread
实例化后调用 start() 方法启动新线程,即它调用了线程的 run() 方法
import threading # 引入多线程模块
import time
class myThread(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self,name):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.name = name
def run(self):
print('开始线程')
print('线程执行中---1')
time.sleep(1)
print('线程执行中---2')
time.sleep(1)
print('线程执行中---3')
time.sleep(1)
print('线程执行中---4')
time.sleep(1)
print('线程执行中---5')
time.sleep(1)
print('结束线程',self.name)
# 创建线程
t1 = myThread("t1")
t2 = myThread("t2")
t3 = myThread("t3")
# 开启线程
t1.start()
t2.start()
t3.start()
t1.join()
t2.join()
t3.join()
队列
队列Queue
Queue 是python标准集中的线程安全的实现
提供了一个适用于多线程编程的先进先出的数据结构
即队列
用来在生产者和消费者之间的信息传递
对于资源,加锁是个重要的环节
因为python原生的list,dict等,都是非线程安全的
而Queue,是线程安全的,因此在满足使用条件下,建议使用队列
import queue
# 创建队列
q = queue.Queue(maxsize=10) # 队列最多对象数是10
for i in range(1,11):
q.put(i) # 往队列里放值
# 判断队列是否为空,循环取出所有值
while not q.empty():
print(q.get())

实战:多线程糗事百科爬虫
# 使用了线程库
import threading
# 队列
import queue
import os
import time
import requests
from lxml import etree
# https://www.qiushibaike.com/8hr/page/1/
# https://www.qiushibaike.com/8hr/page/2/
# https://www.qiushibaike.com/8hr/page/3/
# 爬取网页线程--获取段子列表所在的网页,放进队列
file = os.path.abspath(__file__) # 1、获取当前文件路径
path = file.split('多线程爬虫')[0] # 2、获取共同路径部分
filepath = path + '多线程爬虫/多线程.txt'
class Thread1(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, threadName, pageQueue, dataQueue):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.threadName = threadName # 线程名
self.pageQueue = pageQueue # 页码
self.dataQueue = dataQueue # 数据队列
self.headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/85.0.4183.83 Safari/537.36 Edg/85.0.564.44"}
def run(self):
print("启动线程" + self.threadName)
while not flag1:
try:
page = self.pageQueue.get()
url = "https://www.qiushibaike.com/8hr/page/" + str(page) + "/"
content = requests.get(url, headers=self.headers).text
time.sleep(0.5)
self.dataQueue.put(content) # 将数据放入数据队列中
except Exception as e:
pass
print("结束线程" + self.threadName)
# 解析网页线程--从队列中拿到列表网页,进行解析,并存储到本地
class Thread2(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, threadName, dataQueue,filename):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.threadName = threadName # 线程名
self.filename = filename # 文件名
self.dataQueue = dataQueue # 数据队列
def run(self):
print("启动线程" + self.threadName)
while not flag2:
try:
data1 = self.dataQueue.get()
html = etree.HTML(data1)
node_list = html.xpath('//div/a[@class="recmd-content"]')
for node in node_list:
data = node.text
self.filename.write(data + '\n')
except Exception as e:
pass
print("结束线程" + self.threadName)
flag1 = False # 判断页码队列中是否为空
flag2 = False # 判断数据队列中是否为空
def main():
# 页码队列
pageQueue = queue.Queue(10)
for i in range(1, 11):
pageQueue.put(i)
# 存放采集结果的数据队列
dataQueue = queue.Queue()
# 保存到本地的文件
filename = open(filepath, "a")
t1 = Thread1("采集线程", pageQueue, dataQueue)
t1.start()
t2 = Thread2("解析线程", dataQueue, filename)
t2.start()
# 当pageQueue为空时,结束采集线程
while not pageQueue.empty():
pass
global flag1
flag1 = True
# 当dataQueue为空时,结束解析线程
while not dataQueue.empty():
pass
global flag2
flag2 = True
t1.join()
t2.join()
filename.close()
print("结束!")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
机器视觉体验-识别车牌号
人工智能:停车场管理系统-车进入停车场拍一张照片,通过这张照片就能把车牌号记录到本地;从停车场出去的时候再拍一张照片,把照片里的车牌号记录下来和进入停车场的车牌号进行匹配,计算出时间差来计算停车费。
安装第三方插件
pip install baidu-aip
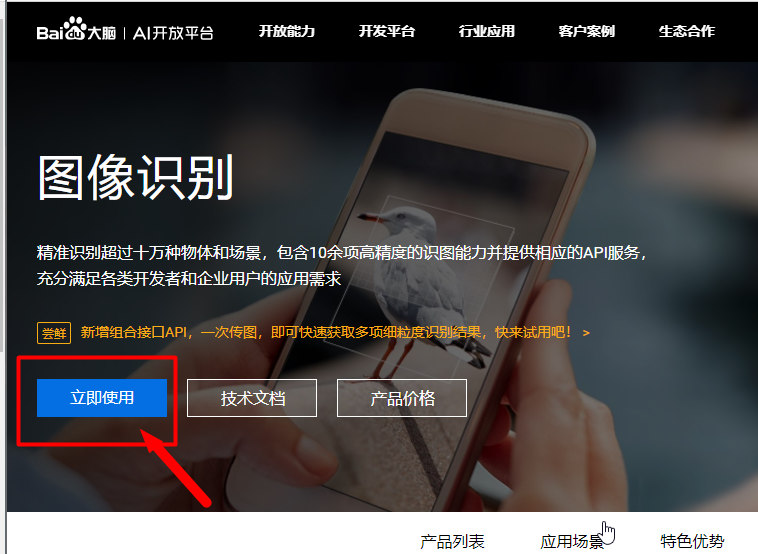
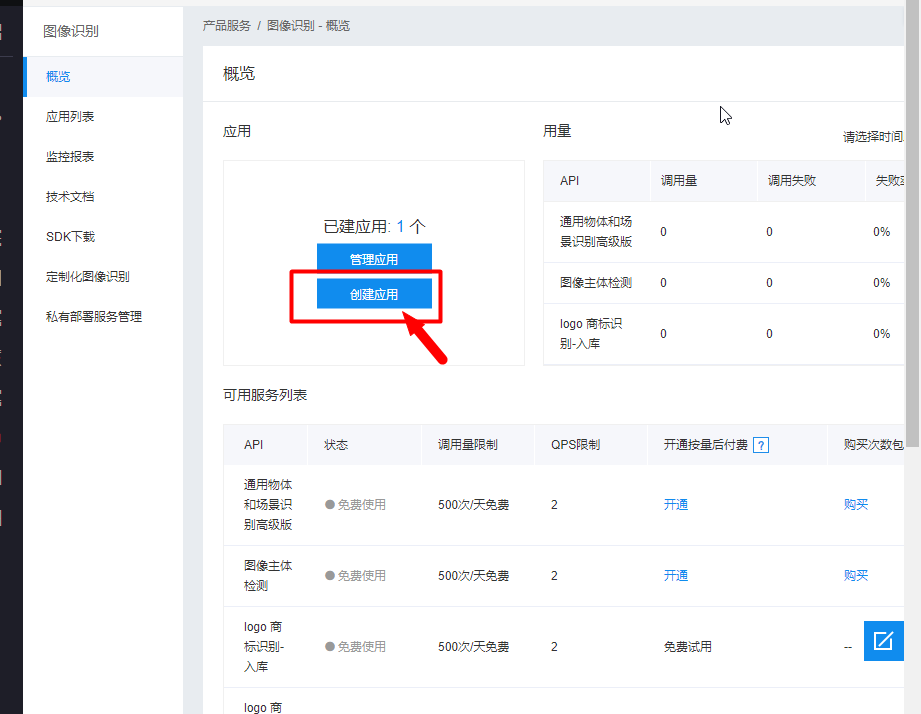
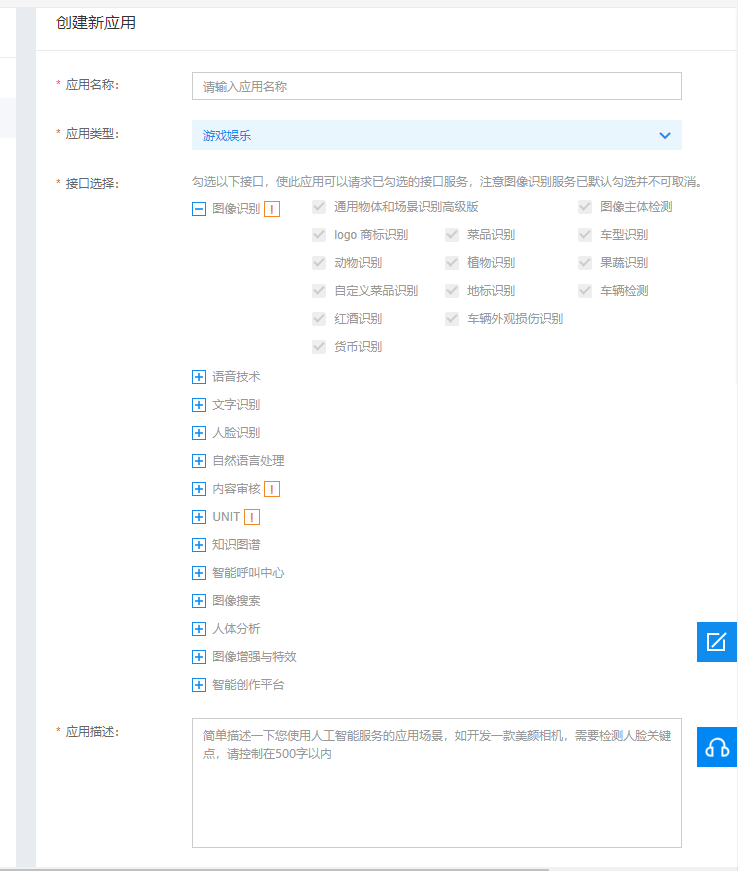
使用百度AI开发平台的接口来识别

import os
from aip import AipOcr
import re
file = os.path.abspath(__file__) # 1、获取当前文件路径
path = file.split('多线程爬虫')[0] # 2、获取共同路径部分
file1path = path + '多线程爬虫/aa.jpg'
file2path = path+ '多线程爬虫/bb.jpg'
APP_ID='22570407'
API_KEY='zh2SZGwHXG9dtMv4u7z8AynW'
SECRET_KEY='41jLzyhs1U656U5mm549nLzj8j1qZFkI'
client = AipOcr(APP_ID,API_KEY,SECRET_KEY)
with open(file2path,'rb') as f:
image = f.read()
data = str(client.basicGeneral(image)).replace(" ","")
pat = re.compile(r"{'words':'(.*?)'}")
result = pat.findall(data)[0]
print(result)