python语言(八)多线程、多进程、虚拟环境、unittest、生成测试报告
多线程
进程与线程
进程:进程是资源(CPU、内存等)分配的最小单位,进程有独立的地址空间与系统资源,一个进程可以包含一个或多个线程
线程:线程是CPU调度的最小单位,是进程的一个执行流,线程依赖于进程而存在,线程共享所在进程的地址空间和系统资源,每个线程有自己的堆栈和局部变量
并发与并行
并发:当系统只有一个CPU时,想执行多个线程,CPU就会轮流切换多个线程执行,当有一个线程被执行时,其他线程就会等待,但由于CPU调度很快,所以看起来像多个线程同时执行
并行:当系统有多个CPU时,执行多个线程,就可以分配到多个CPU上同时执行
同步与异步
同步:调用者调用一个功能时,必须要等到这个功能执行完返回结果后,才能再调用其他功能
异步:调用者调用一个功能时,不会立即得到结果,而是在调用发出后,被调用功能通过状态、通知来通告调用者,或通过回调函数处理这个调用
多线程模块 threading模块
threading模块常用函数
- threading.current_thread(): 返回当前的线程对象。
- threading.enumerate(): 返回一个包含正在运行的线程的list。正在运行指线程启动后、结束前,不包括启动前和终止后的线程。
- threading.active_count(): 返回正在运行的线程数量,与len(threading.enumerate())有相同的结果。
Thread类
通过threading.Thread()创建线程对象
主要参数:
threading.Thread(group=None, target=None, name=None, args=(), kwargs={}, *, daemon=None)
- group 默认为 None,为了日后扩展 ThreadGroup 类实现而保留。
- target 是用于 run() 方法调用的可调用对象。默认是 None,表示不需要调用任何方法。
- name 是线程名称。默认情况下,由 "Thread-N" 格式构成一个唯一的名称,其中 N 是小的十进制数
- args 是用于调用目标函数的参数元组。默认是 ()
- kwargs 是用于调用目标函数的关键字参数字典。默认是 {}。
- daemon表示线程是不是守护线程。
Thread类常用方法与属性
- run(): 用以表示线程活动的方法。
- start():启动线程活动。
- join(timeout=None): 等待至线程中止。这阻塞调用线程直至线程的join() 方法被调用中止-正常退出或者抛出未处理的异常-或者是可选的超时发生。
- isAlive(): 返回线程是否活动的。
- getName(): 返回线程名。
- setName(): 设置线程名。
- name:线程对象名字
- setDaemon():设置是否为守护线程
创建线程
1 import threading # 导入线程模块 2 import time 3 4 # 线程是多个资源的集合 5 # 线程就是进程里面具体干活的 6 # 线程和线程之间是互相独立的 7 8 def down_load(): 9 time.sleep(5) # 假设线程要执行5秒结束 10 print('运行完了') 11 12 def movie(): 13 print('movie') 14 15 for i in range(10): # 启动10个线程 16 t = threading.Thread(target=down_load) # 实例化线程 17 t.start() # 启动它 18 19 for i in range(10): # 启动10个线程 20 t = threading.Thread(target=movie) 21 t.start()
movie
movie
movie
movie
movie
movie
movie
movie
movie
movie
运行完了
运行完了
运行完了
运行完了
运行完了
运行完了
运行完了
运行完了
运行完了
运行完了
查看当前线程数、当前线程
1 import threading # 导入线程模块 2 import time 3 4 def down_load(): 5 print(threading.current_thread()) # 显示当前线程 6 time.sleep(5) # 假设线程要执行5秒结束 7 print('运行完了') 8 9 def movie(): 10 print('movie') 11 12 for i in range(10): # 启动10个线程 13 t = threading.Thread(target=down_load) 14 t.start() 15 16 for i in range(10): # 启动10个线程 17 t = threading.Thread(target=movie) 18 t.start() 19 20 print(threading.activeCount()) # 查看当前线程数 21 print(threading.current_thread()) # 查看当前线程
<Thread(Thread-1, started 20128)> <Thread(Thread-2, started 9024)> <Thread(Thread-3, started 20484)> <Thread(Thread-4, started 20488)> <Thread(Thread-5, started 20492)> <Thread(Thread-6, started 20496)> <Thread(Thread-7, started 20500)> <Thread(Thread-8, started 20504)> <Thread(Thread-9, started 20508)> <Thread(Thread-10, started 20512)> movie movie movie movie movie movie movie movie movie movie 11 <_MainThread(MainThread, started 1900)> 运行完了 运行完了 运行完了 运行完了 运行完了 运行完了 运行完了 运行完了 运行完了 运行完了
实现线程同步join()
1 import threading # 导入线程模块 2 import time 3 4 def down_load(): 5 print(threading.current_thread()) # 显示当前线程 6 time.sleep(5) # 假设线程要执行5秒结束 7 print('运行完了') 8 9 def movie(): 10 print('movie') 11 12 for i in range(10): # 启动10个线程 13 t = threading.Thread(target=down_load) 14 t.start() 15 t.join() # 使用join() 来实现线程同步 16 17 for i in range(10): # 启动10个线程 18 t = threading.Thread(target=movie) 19 t.start() 20 t.join()
使用join()需等上一个线程执行完,才会开始执行
针对上述,我希望:在所有线程都执行完后,一起结束
使用thread_list[]来解决
1 import threading # 导入线程模块 2 import time 3 4 def down_load(): 5 print(threading.current_thread()) # 显示当前线程 6 time.sleep(5) # 假设线程要执行5秒结束 7 print('运行完了') 8 9 def movie(): 10 print('movie') 11 12 thread_list = [] 13 for i in range(5): # 启动10个线程 14 t = threading.Thread(target=down_load) 15 t.start() 16 thread_list.append(t) #把每个线程加入列表 17 print('thread_list',thread_list) 18 19 for thread in thread_list: 20 thread.join() # 等待子线程结束,然后同时结束 21 22 23 for i in range(10): # 启动10个线程 24 t = threading.Thread(target=movie) 25 t.start() 26 t.join()
或者
1 for i in range(5): # 启动10个线程 2 t = threading.Thread(target=movie) 3 t.start() 4 5 while threading.activeCount()!=1: # 当执行线程数=1时,线程循环结束 6 pass
多线程下载图片
先不用多线程
1 import requests 2 import time 3 from hashlib import md5 4 5 6 def down_load_pic(url): 7 req = requests.get(url) 8 m = md5(url.encode()) 9 with open(m.hexdigest() + '.png', 'wb') as fw: 10 fw.write(req.content) 11 12 13 url_list = ['http://www.nnzhp.cn/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/b23755cdea210cfec903333c5cce6895.png', 14 'http://www.nnzhp.cn/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/481b5135e75c764b32b224c5650a8df5.png', 15 'http://www.nnzhp.cn/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/542824dde1dbd29ec61ad5ea867ef245.png', 16 'http://www.nnzhp.cn/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/f410afea8b23fa401505a1449a41a133.png'] 17 18 start_time = time.time() 19 for url in url_list: 20 down_load_pic(url) 21 end_time = time.time() 22 23 print(end_time - start_time)
然后用多线程下载
1 import requests 2 import time 3 import threading 4 from hashlib import md5 5 6 7 def down_load_pic(url): 8 req = requests.get(url) 9 m = md5(url.encode()) 10 with open(m.hexdigest() + '.png', 'wb') as fw: 11 fw.write(req.content) 12 13 14 url_list = ['http://www.nnzhp.cn/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/b23755cdea210cfec903333c5cce6895.png', 15 'http://www.nnzhp.cn/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/481b5135e75c764b32b224c5650a8df5.png', 16 'http://www.nnzhp.cn/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/542824dde1dbd29ec61ad5ea867ef245.png', 17 'http://www.nnzhp.cn/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/f410afea8b23fa401505a1449a41a133.png'] 18 19 start_time = time.time() 20 for url in url_list: 21 t = threading.Thread( 22 target=down_load_pic, args=( 23 url,)) # 如果只有一个参数的话,url后面要加一个逗号 24 t.start() 25 26 while threading.activeCount != 1: 27 pass 28 29 end_time = time.time() 30 print(end_time - start_time)
守护线程
无论是进程还是线程,都遵循:守护xx会等待主xx运行完毕后被销毁。需要强调的是:运行完毕并非终止运行。
- 对主进程来说,运行完毕指的是主进程代码运行完毕
- 对主线程来说,运行完毕指的是主线程所在的进程内所有非守护线程统统运行完毕,主线程才算运行完毕
详细解释
-
主进程在其代码结束后就已经算运行完毕了(守护进程在此时就被回收),然后主进程会一直等非守护的子进程都运行完毕后回收子进程的资源(否则会产生僵尸进程),才会结束。
-
主线程在其他非守护线程运行完毕后才算运行完毕(守护线程在此时就被回收)。因为主线程的结束意味着进程的结束,进程整体的资源都将被回收,而进程必须保证非守护线程都运行完毕后才能结束。
.setDaemon(True) # 设置子线程为守护线程
1 # 主线程结束,守护线程立马死掉 2 import threading,time 3 4 def down_load(): 5 print(threading.current_thread()) # 显示当前线程 6 time.sleep(5) # 假设线程要执行5秒结束 7 print('运行完了') 8 9 for i in range(5): # 启动10个线程 10 t = threading.Thread(target=down_load) 11 t.setDaemon(True) # 设置子线程为守护线程 12 t.start() # 把子守护线程设置在主线程前 13 14 print('over')# 主线程结束,守护线程立马结束
多进程
进程:正在进行的一个过程或者说一个任务,二负责执行任务则是cpu。
1 import multiprocessing 2 import time 3 4 5 def down_load(): 6 time.sleep(5) 7 print("运行完了") 8 9 # windows系统要求写 __main__ 10 if __name__ == '__main__': 11 for i in range(5): 12 p = multiprocessing.Process(target=down_load) 13 p.start() 14 print(multiprocessing.current_process())
多线程
适用于IO密集型任务(网络下载、等待...)
网络IO
磁盘IO
多进程
适用于CPU密集型任务(查询、排序、计算、分析...)
import multiprocessing import time def down_load(): time.sleep(5) print("运行完了") # windows系统要求写 __main__ if __name__ == '__main__': for i in range(5): p = multiprocessing.Process(target=down_load) p.start() while len(multiprocessing.active_children())!=0: # 等待子进程结束 pass print(multiprocessing.current_process()) print('end')
<_MainProcess(Process-3, started)> end <_MainProcess(Process-1, started)> end <_MainProcess(Process-2, started)> end <_MainProcess(Process-4, started)> end <_MainProcess(Process-5, started)> end 运行完了 运行完了 运行完了 运行完了 运行完了 <_MainProcess(MainProcess, started)> end
虚拟环境
pip3.5 install virtualenv
pip3.5 install parameterized
python虚拟环境
在电脑上创建一个目录
cmd命令进入到该目录
virtualenv UTP # 在该目录下创建一个叫UTP的虚拟环境
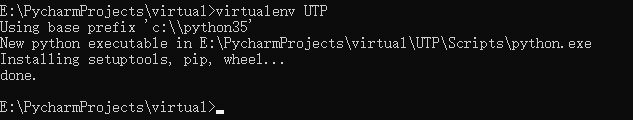
搭建测试环境
搭建测试环境
1、申请服务器
2、安装依赖软件:jdk1.8\redis\mysql\tomcat等等
3、获取代码,修改配置文件,(编译、打包)
4、导入基础数据(建表、导入数据)
5、代码放到服务器上,启动
日常部署
1、拉去最新代码,修改配置文件(编译、打包)
2、如果右边的sql,执行
3、服务器上代码替换成最新的,重启
生成安装python环境的txt方法
1.python项目中必须包含一个 requirements.txt 文件,用于记录所有依赖包及其精确的版本号。以便新环境部署。
requirements.txt可以通过pip命令自动生成和安装。
2.生成requirements.txt文件:
pip freeze > requirements.txt
3.安装requirements.txt依赖:
pip install -r requirements.txt
单元测试
TestCase 也就是测试用例
TestSuite 多个测试用例集合在一起,就是TestSuite
TestLoader 是用来加载TestCase到TestSuite中的
TestRunner 是来执行测试用例的,测试的结果会保存到TestResult实例中,包括运行了多少测试用例,成功了多少,失败了多少等信息
1 import unittest 2 import HTMLTestRunner 3 4 5 def add(a, b): 6 return a + b 7 8 9 class AddTest(unittest.TestCase): # unittest.TestCase 副类 10 @classmethod 11 def setUpClass(cls): # 所有用例执行前,执行它 12 print("setUpClass") 13 14 @classmethod 15 def tearDownClass(cls): # 所有用例执行完,执行它 16 print("tearDownClass") 17 18 def setUp(self): # 每条用例执行前,执行它 19 print('setUP') 20 21 def tearDown(self): # 每条用例执行后,执行它 22 print('tearDown') 23 24 def test_normal(self): # 用例必须以test 开头运行 25 result = add(1, 1) 26 self.assertEqual(1, result) 27 28 def test_error(self): 29 result = add(1, 1) 30 self.assertEqual(1, result, '结果计算错误') # 可以传错误提示参数 31 32 33 if __name__ == '__main__': 34 file = open('report.html', 'wb') 35 runner = HTMLTestRunner.HTMLTestRunner(file, title='测试报告') 36 test_suite = unittest.makeSuite(AddTest) # 变成测试集合 37 runner.run(test_suite)
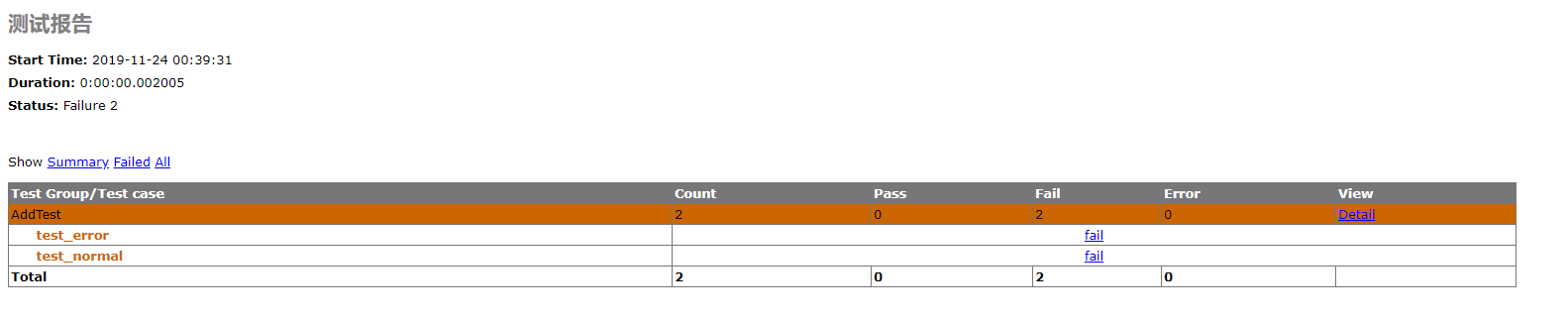
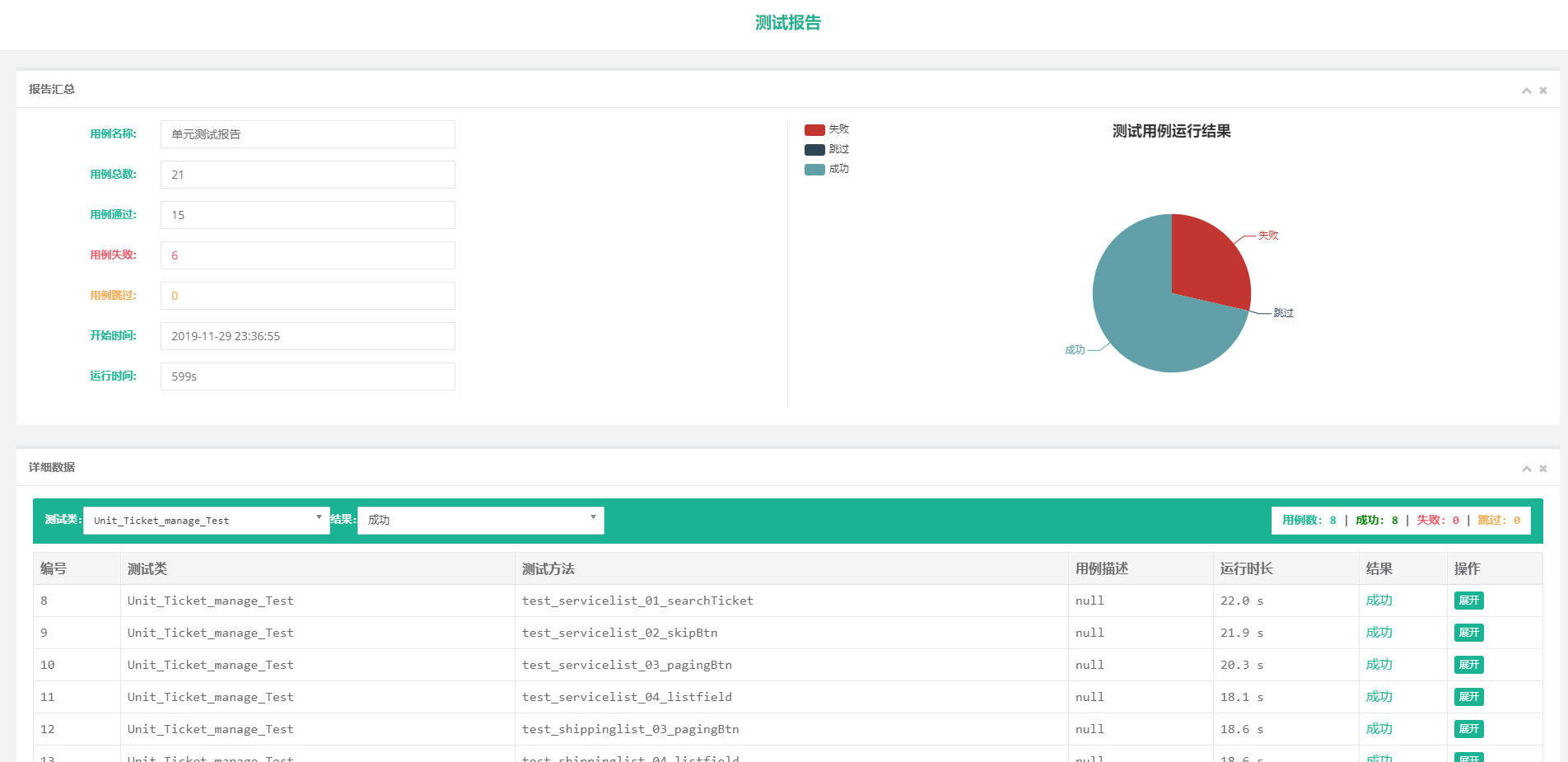
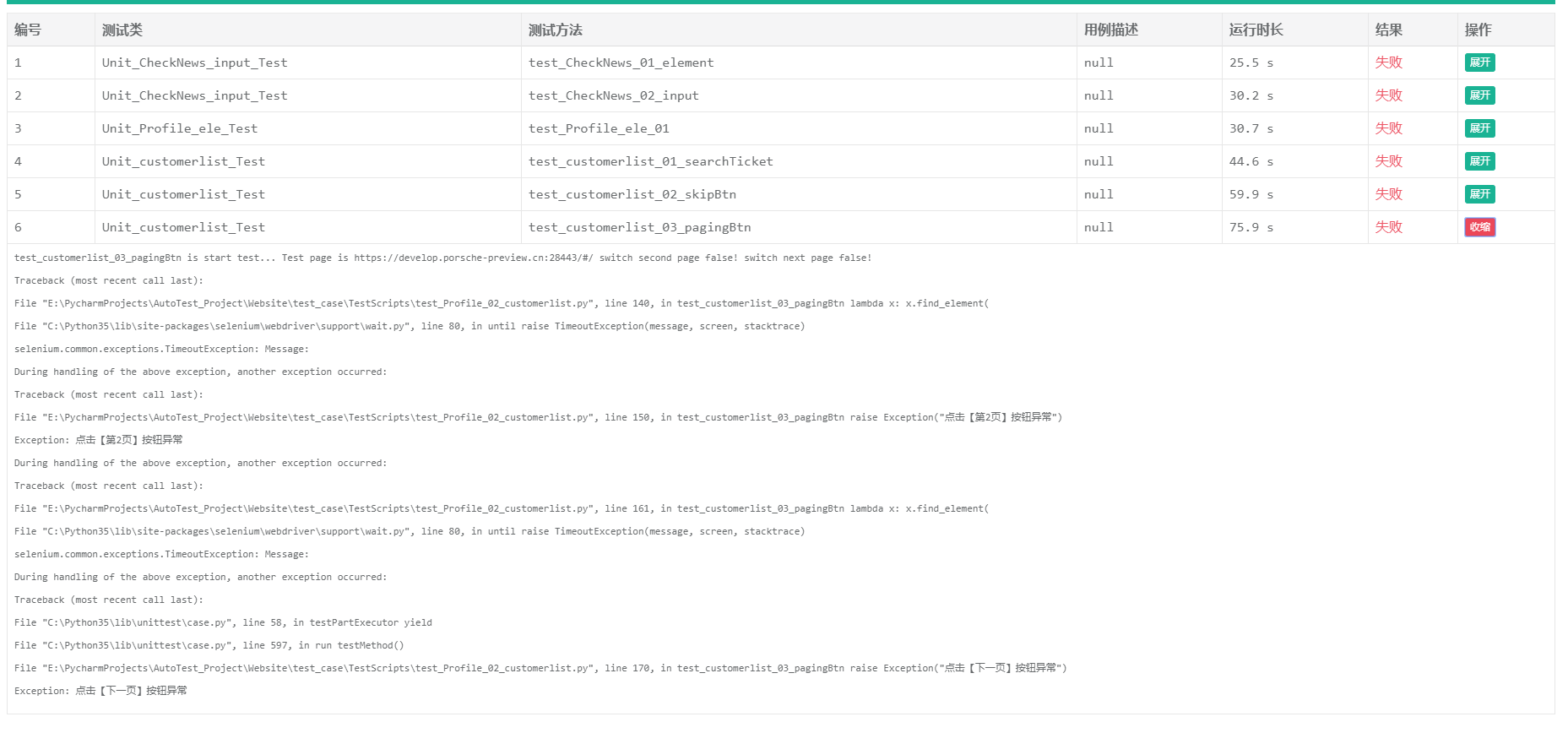
BeautifulReport
生成HTML测试报告的BeautifulReport 源码Clone地址为 https://github.com/TesterlifeRaymond/BeautifulReport,其中BeautifulReport.py和其template是我们需要的关键。
BeautifulReport.py
1 import os 2 import sys 3 from io import StringIO as StringIO 4 import time 5 import json 6 import unittest 7 import platform 8 import base64 9 from distutils.sysconfig import get_python_lib 10 import traceback 11 from functools import wraps 12 13 __all__ = ['BeautifulReport'] 14 15 HTML_IMG_TEMPLATE = """ 16 <a href="data:image/png;base64, {}"> 17 <img src="data:image/png;base64, {}" width="800px" height="500px"/> 18 </a> 19 <br></br> 20 """ 21 22 23 class OutputRedirector(object): 24 """ Wrapper to redirect stdout or stderr """ 25 26 def __init__(self, fp): 27 self.fp = fp 28 29 def write(self, s): 30 self.fp.write(s) 31 32 def writelines(self, lines): 33 self.fp.writelines(lines) 34 35 def flush(self): 36 self.fp.flush() 37 38 39 stdout_redirector = OutputRedirector(sys.stdout) 40 stderr_redirector = OutputRedirector(sys.stderr) 41 42 SYSSTR = platform.system() 43 SITE_PAKAGE_PATH = get_python_lib() 44 45 FIELDS = { 46 "testPass": 0, 47 "testResult": [ 48 ], 49 "testName": "", 50 "testAll": 0, 51 "testFail": 0, 52 "beginTime": "", 53 "totalTime": "", 54 "testSkip": 0 55 } 56 57 58 class PATH: 59 """ all file PATH meta """ 60 # config_tmp_path = SITE_PAKAGE_PATH + '/BeautifulReport/template/template' 61 # config_tmp_path = SITE_PAKAGE_PATH + '/BeautifulReport/template/template' 62 config_tmp_path = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)) + '/template/template' 63 64 65 class MakeResultJson: 66 """ make html table tags """ 67 68 def __init__(self, datas: tuple): 69 """ 70 init self object 71 :param datas: 拿到所有返回数据结构 72 """ 73 self.datas = datas 74 self.result_schema = {} 75 76 def __setitem__(self, key, value): 77 """ 78 79 :param key: self[key] 80 :param value: value 81 :return: 82 """ 83 self[key] = value 84 85 def __repr__(self) -> str: 86 """ 87 返回对象的html结构体 88 :rtype: dict 89 :return: self的repr对象, 返回一个构造完成的tr表单 90 """ 91 keys = ( 92 'className', 93 'methodName', 94 'description', 95 'spendTime', 96 'status', 97 'log', 98 ) 99 for key, data in zip(keys, self.datas): 100 self.result_schema.setdefault(key, data) 101 return json.dumps(self.result_schema) 102 103 104 class ReportTestResult(unittest.TestResult): 105 """ override""" 106 107 def __init__(self, suite, stream=sys.stdout): 108 """ pass """ 109 super(ReportTestResult, self).__init__() 110 self.begin_time = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime()) 111 self.start_time = 0 112 self.stream = stream 113 self.end_time = 0 114 self.failure_count = 0 115 self.error_count = 0 116 self.success_count = 0 117 self.skipped = 0 118 self.verbosity = 1 119 self.success_case_info = [] 120 self.skipped_case_info = [] 121 self.failures_case_info = [] 122 self.errors_case_info = [] 123 self.all_case_counter = 0 124 self.suite = suite 125 self.status = '' 126 self.result_list = [] 127 self.case_log = '' 128 self.default_report_name = '自动化测试报告' 129 self.FIELDS = None 130 self.sys_stdout = None 131 self.sys_stderr = None 132 self.outputBuffer = None 133 134 @property 135 def success_counter(self) -> int: 136 """ set success counter """ 137 return self.success_count 138 139 @success_counter.setter 140 def success_counter(self, value) -> None: 141 """ 142 success_counter函数的setter方法, 用于改变成功的case数量 143 :param value: 当前传递进来的成功次数的int数值 144 :return: 145 """ 146 self.success_count = value 147 148 def startTest(self, test) -> None: 149 """ 150 当测试用例测试即将运行时调用 151 :return: 152 """ 153 unittest.TestResult.startTest(self, test) 154 self.outputBuffer = StringIO() 155 stdout_redirector.fp = self.outputBuffer 156 stderr_redirector.fp = self.outputBuffer 157 self.sys_stdout = sys.stdout 158 self.sys_stdout = sys.stderr 159 sys.stdout = stdout_redirector 160 sys.stderr = stderr_redirector 161 self.start_time = time.time() 162 163 def stopTest(self, test) -> None: 164 """ 165 当测试用力执行完成后进行调用 166 :return: 167 """ 168 self.end_time = '{0:.3} s'.format((time.time() - self.start_time)) 169 self.result_list.append(self.get_all_result_info_tuple(test)) 170 self.complete_output() 171 172 def complete_output(self): 173 """ 174 Disconnect output redirection and return buffer. 175 Safe to call multiple times. 176 """ 177 if self.sys_stdout: 178 sys.stdout = self.sys_stdout 179 sys.stderr = self.sys_stdout 180 self.sys_stdout = None 181 self.sys_stdout = None 182 return self.outputBuffer.getvalue() 183 184 def stopTestRun(self, title=None) -> dict: 185 """ 186 所有测试执行完成后, 执行该方法 187 :param title: 188 :return: 189 """ 190 FIELDS['testPass'] = self.success_counter 191 for item in self.result_list: 192 item = json.loads(str(MakeResultJson(item))) 193 FIELDS.get('testResult').append(item) 194 FIELDS['testAll'] = len(self.result_list) 195 FIELDS['testName'] = title if title else self.default_report_name 196 FIELDS['testFail'] = self.failure_count 197 FIELDS['beginTime'] = self.begin_time 198 end_time = int(time.time()) 199 start_time = int(time.mktime(time.strptime(self.begin_time, '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'))) 200 FIELDS['totalTime'] = str(end_time - start_time) + 's' 201 FIELDS['testError'] = self.error_count 202 FIELDS['testSkip'] = self.skipped 203 self.FIELDS = FIELDS 204 return FIELDS 205 206 def get_all_result_info_tuple(self, test) -> tuple: 207 """ 208 接受test 相关信息, 并拼接成一个完成的tuple结构返回 209 :param test: 210 :return: 211 """ 212 return tuple([*self.get_testcase_property(test), self.end_time, self.status, self.case_log]) 213 214 @staticmethod 215 def error_or_failure_text(err) -> str: 216 """ 217 获取sys.exc_info()的参数并返回字符串类型的数据, 去掉t6 error 218 :param err: 219 :return: 220 """ 221 return traceback.format_exception(*err) 222 223 def addSuccess(self, test) -> None: 224 """ 225 pass 226 :param test: 227 :return: 228 """ 229 logs = [] 230 output = self.complete_output() 231 logs.append(output) 232 if self.verbosity > 1: 233 sys.stderr.write('ok ') 234 sys.stderr.write(str(test)) 235 sys.stderr.write('\n') 236 else: 237 sys.stderr.write('.') 238 self.success_counter += 1 239 self.status = '成功' 240 self.case_log = output.split('\n') 241 self._mirrorOutput = True # print(class_name, method_name, method_doc) 242 243 def addError(self, test, err): 244 """ 245 add Some Error Result and infos 246 :param test: 247 :param err: 248 :return: 249 """ 250 logs = [] 251 output = self.complete_output() 252 logs.append(output) 253 logs.extend(self.error_or_failure_text(err)) 254 self.failure_count += 1 255 self.add_test_type('失败', logs) 256 if self.verbosity > 1: 257 sys.stderr.write('F ') 258 sys.stderr.write(str(test)) 259 sys.stderr.write('\n') 260 else: 261 sys.stderr.write('F') 262 263 self._mirrorOutput = True 264 265 def addFailure(self, test, err): 266 """ 267 add Some Failures Result and infos 268 :param test: 269 :param err: 270 :return: 271 """ 272 logs = [] 273 output = self.complete_output() 274 logs.append(output) 275 logs.extend(self.error_or_failure_text(err)) 276 self.failure_count += 1 277 self.add_test_type('失败', logs) 278 if self.verbosity > 1: 279 sys.stderr.write('F ') 280 sys.stderr.write(str(test)) 281 sys.stderr.write('\n') 282 else: 283 sys.stderr.write('F') 284 285 self._mirrorOutput = True 286 287 def addSkip(self, test, reason) -> None: 288 """ 289 获取全部的跳过的case信息 290 :param test: 291 :param reason: 292 :return: None 293 """ 294 logs = [reason] 295 self.complete_output() 296 self.skipped += 1 297 self.add_test_type('跳过', logs) 298 299 if self.verbosity > 1: 300 sys.stderr.write('S ') 301 sys.stderr.write(str(test)) 302 sys.stderr.write('\n') 303 else: 304 sys.stderr.write('S') 305 self._mirrorOutput = True 306 307 def add_test_type(self, status: str, case_log: list) -> None: 308 """ 309 abstruct add test type and return tuple 310 :param status: 311 :param case_log: 312 :return: 313 """ 314 self.status = status 315 self.case_log = case_log 316 317 @staticmethod 318 def get_testcase_property(test) -> tuple: 319 """ 320 接受一个test, 并返回一个test的class_name, method_name, method_doc属性 321 :param test: 322 :return: (class_name, method_name, method_doc) -> tuple 323 """ 324 class_name = test.__class__.__qualname__ 325 method_name = test.__dict__['_testMethodName'] 326 method_doc = test.__dict__['_testMethodDoc'] 327 return class_name, method_name, method_doc 328 329 330 class BeautifulReport(ReportTestResult, PATH): 331 img_path = 'img/' if platform.system() != 'Windows' else 'img\\' 332 333 def __init__(self, suites): 334 super(BeautifulReport, self).__init__(suites) 335 self.suites = suites 336 self.log_path = None 337 self.title = '自动化测试报告' 338 self.filename = 'report.html' 339 340 def report(self, description, filename: str = None, log_path='.'): 341 """ 342 生成测试报告,并放在当前运行路径下 343 :param log_path: 生成report的文件存储路径 344 :param filename: 生成文件的filename 345 :param description: 生成文件的注释 346 :return: 347 """ 348 if filename: 349 self.filename = filename if filename.endswith('.html') else filename + '.html' 350 351 if description: 352 self.title = description 353 354 self.log_path = os.path.abspath(log_path) 355 self.suites.run(result=self) 356 self.stopTestRun(self.title) 357 self.output_report() 358 text = '\n测试已全部完成, 可前往{}查询测试报告'.format(self.log_path) 359 print(text) 360 361 def output_report(self): 362 """ 363 生成测试报告到指定路径下 364 :return: 365 """ 366 template_path = self.config_tmp_path 367 # template_path = "D:\\PythonUnittest\\Template\\template" 368 override_path = os.path.abspath(self.log_path) if \ 369 os.path.abspath(self.log_path).endswith('/') else \ 370 os.path.abspath(self.log_path) + '/' 371 372 with open(template_path, 'rb') as file: 373 body = file.readlines() 374 with open(override_path + self.filename, 'wb') as write_file: 375 for item in body: 376 if item.strip().startswith(b'var resultData'): 377 head = ' var resultData = ' 378 item = item.decode().split(head) 379 item[1] = head + json.dumps(self.FIELDS, ensure_ascii=False, indent=4) 380 item = ''.join(item).encode() 381 item = bytes(item) + b';\n' 382 write_file.write(item) 383 384 @staticmethod 385 def img2base(img_path: str, file_name: str) -> str: 386 """ 387 接受传递进函数的filename 并找到文件转换为base64格式 388 :param img_path: 通过文件名及默认路径找到的img绝对路径 389 :param file_name: 用户在装饰器中传递进来的问价匿名 390 :return: 391 """ 392 pattern = '/' if platform != 'Windows' else '\\' 393 394 with open(img_path + pattern + file_name, 'rb') as file: 395 data = file.read() 396 return base64.b64encode(data).decode() 397 398 def add_test_img(*pargs): 399 """ 400 接受若干个图片元素, 并展示在测试报告中 401 :param pargs: 402 :return: 403 """ 404 405 def _wrap(func): 406 @wraps(func) 407 def __wrap(*args, **kwargs): 408 img_path = os.path.abspath('{}'.format(BeautifulReport.img_path)) 409 try: 410 result = func(*args, **kwargs) 411 except Exception: 412 if 'save_img' in dir(args[0]): 413 save_img = getattr(args[0], 'save_img') 414 save_img(func.__name__) 415 data = BeautifulReport.img2base(img_path, pargs[0] + '.png') 416 print(HTML_IMG_TEMPLATE.format(data, data)) 417 sys.exit(0) 418 print('<br></br>') 419 420 if len(pargs) > 1: 421 for parg in pargs: 422 print(parg + ':') 423 data = BeautifulReport.img2base(img_path, parg + '.png') 424 print(HTML_IMG_TEMPLATE.format(data, data)) 425 return result 426 if not os.path.exists(img_path + pargs[0] + '.png'): 427 return result 428 data = BeautifulReport.img2base(img_path, pargs[0] + '.png') 429 print(HTML_IMG_TEMPLATE.format(data, data)) 430 return result 431 return __wrap 432 return _wrap
template
template文件是和BeautifulReport.py一起使用的,他将unittest的测试结果按照template的样式转换成HTML格式的报告
调用BeautifulReport
run_all_cases.py
1 import unittest 2 from BeautifulReport import BeautifulReport 3 4 if __name__ == '__main__': 5 test_suite = unittest.defaultTestLoader.discover('TestScripts', pattern='test*.py') 6 result = BeautifulReport(test_suite) 7 result.report(filename='HC_Unittest测试报告', description='单元测试报告')