计算机图形学笔记三——橡皮筋技术和椭圆扫描算法
橡皮筋技术
橡皮筋技术就是可以使得用户进行可视化编辑,也就是在编辑的时候,图像能够进行实时的变化。这是一种非常实用的技术,接下来和大家讲解一下这个技术。
我们有鼠标点击回调函数,还有鼠标移动回调函数。我们需要的是在鼠标点击过后,移动鼠标能够预览我们绘制的图像。比如这是有无橡皮筋技术的对比:
有橡皮筋技术
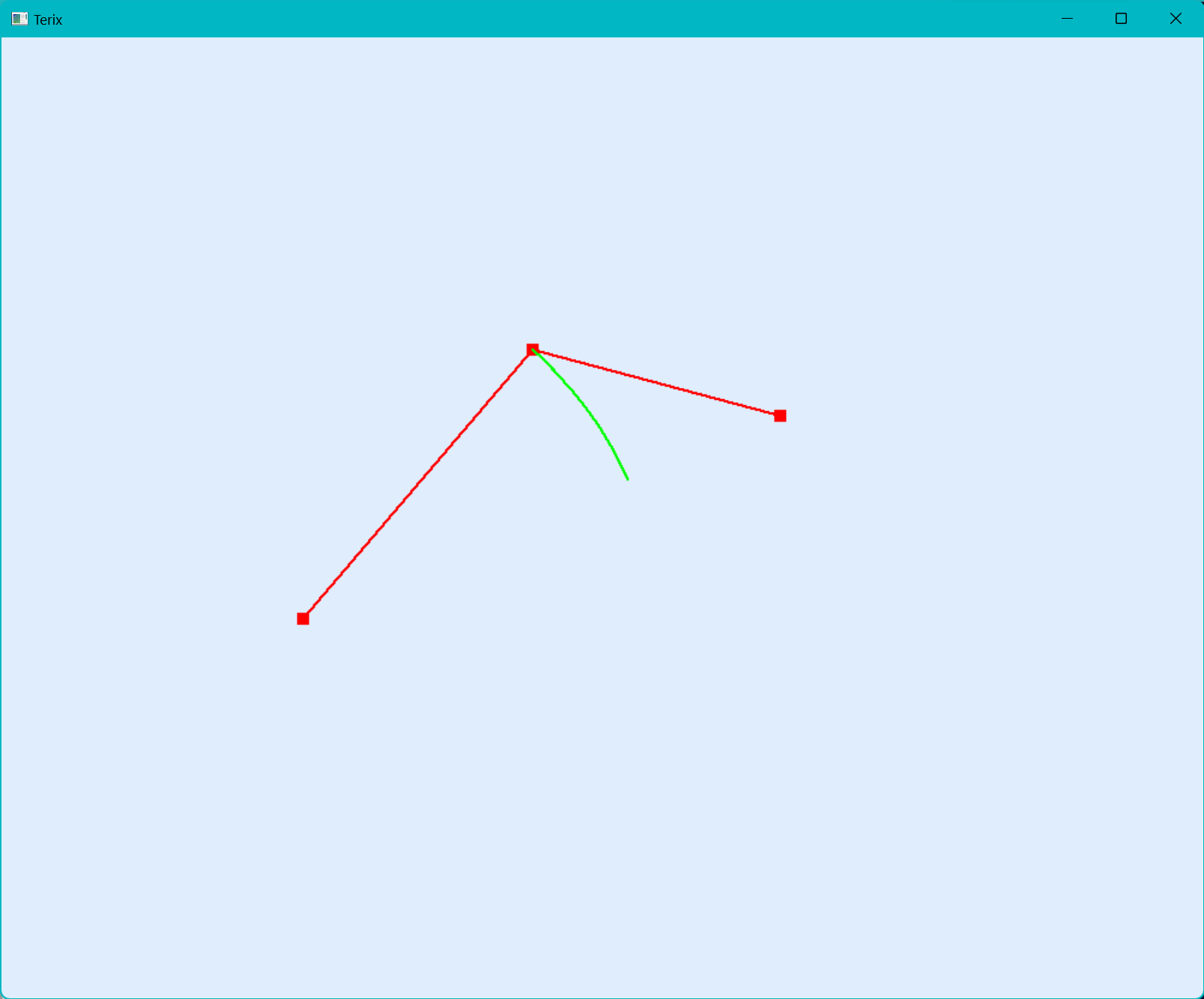
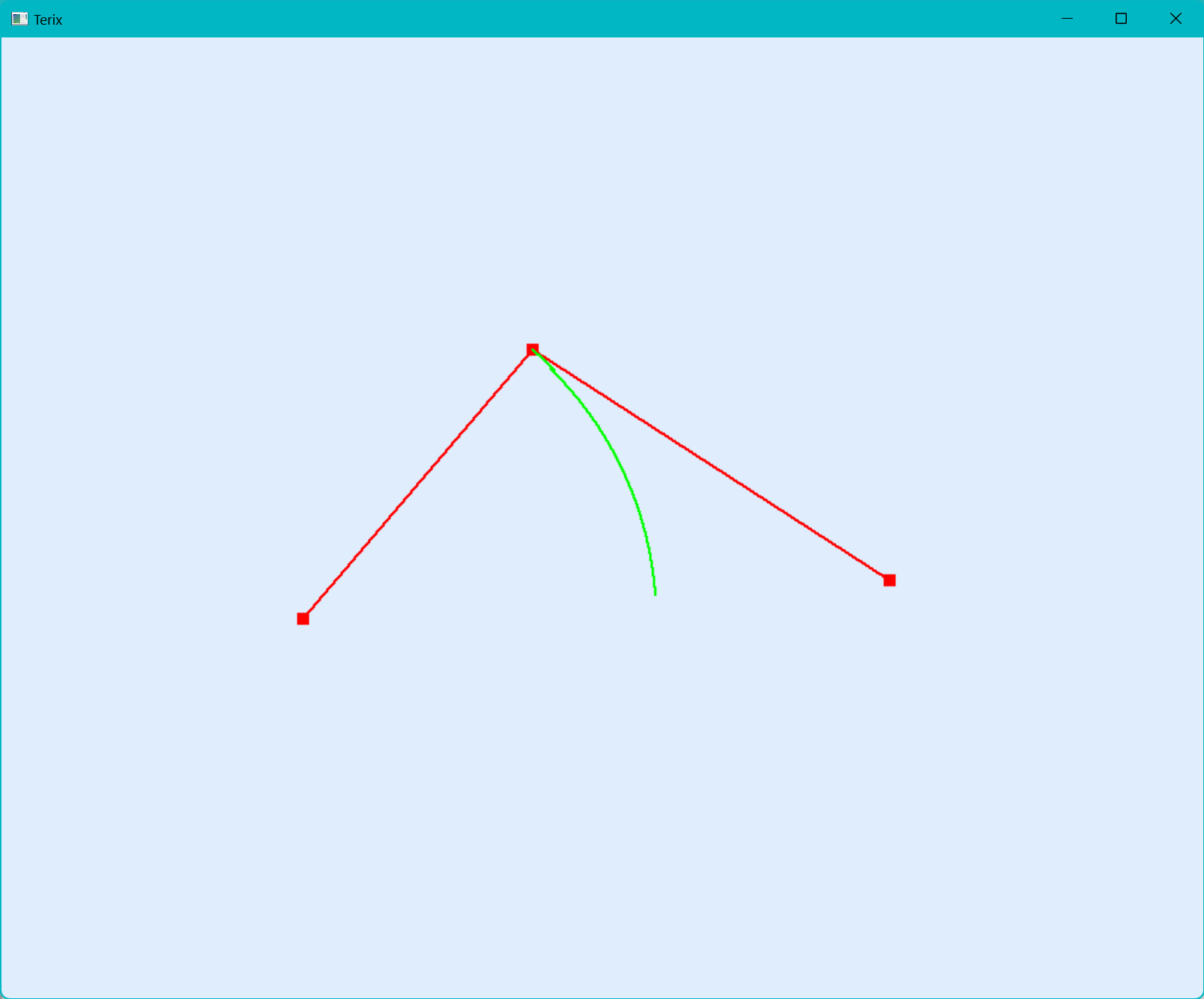
随着鼠标的移动,我们的最后一个顶点会跟着移动,可以达到很好的编辑效果。
没有橡皮筋技术
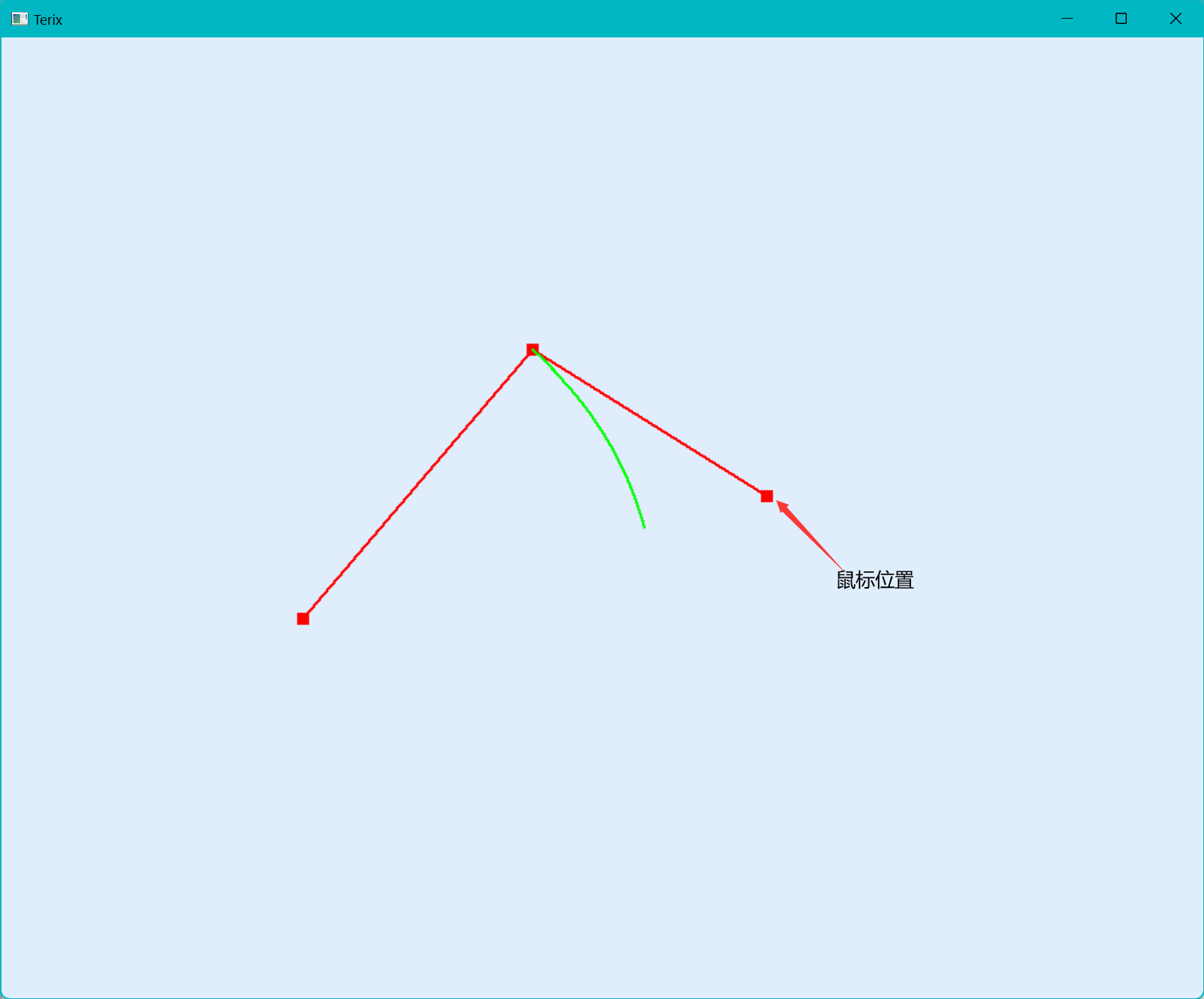
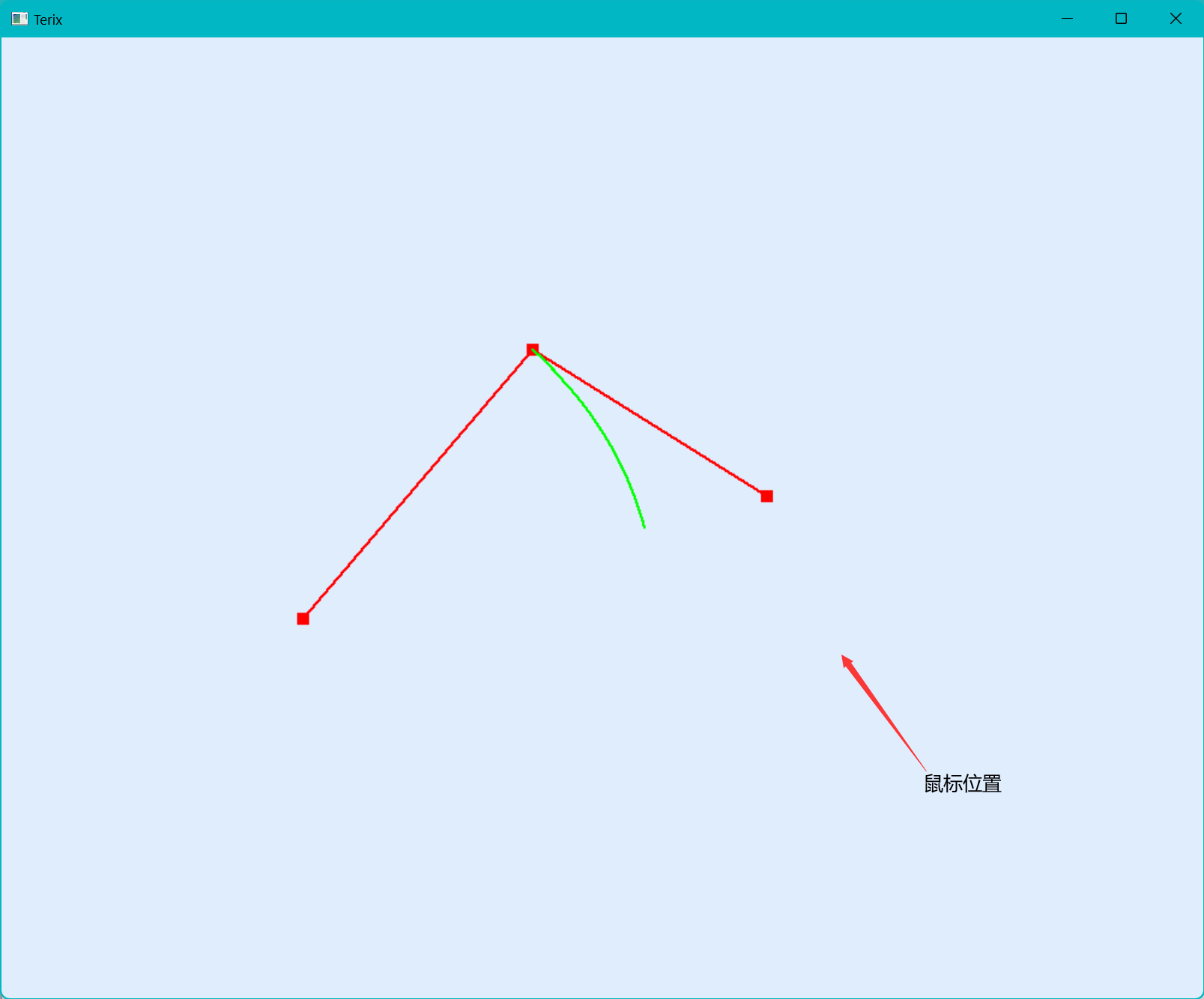
每次都会确定一个顶点位置,不能进行实时的更改。
橡皮筋技术的实现需要的两个函数和一个枚举:
//鼠标点击回调函数
glutMouseFunc(onMouse);
//鼠标移动回调函数
glutPassiveMotionFunc(onMouseMove);
typedef enum {
MOVE,
NONE
}MOUSEMODE;
鼠标点击回调函数
处理点击事件时,我们设置第一次点击创建两个顶点。想象一下,点击一次后,我们移动会带动第二个点移动,也就是说我们第一次点击需要创建两个顶点。在后面的点击只需要创建一个。并且把MouseMode更新为MOVE
/*这里是onMouse(GLint button, GLint state, GLint x, GLint y)*/
//如果点击状态是按下
if (state == GLUT_DOWN) {
//如果是鼠标左键
if (button == GLUT_LEFT_BUTTON) {
//如果是第一个点,多创建一个顶点
if (!Vertex.size())
Vertex.push_back(make_pair(x, y));
Vertex.push_back(make_pair(x, y));
//设置控制点的位置
ctrlPoint = Vertex.size();
//修改控制模式
MouseMode = MOVE;
}
}
鼠标移动回调函数
在创建顶点过后,我们在鼠标移动回调函数中对最后一格顶点进行位置的更改,我们也可以叫最后一个顶点为临时顶点。
/*这里是onMouseMove(GLint xMouse, GLint yMouse)*/
//如果控制装填是移动
if (MouseMode == MOVE) {
Vertex[ctrlPoint - 1].first = xMouse, Vertex[ctrlPoint - 1].second = yMouse;
//发送重绘信息
glutPostRedisplay();
}
额外的——使用右键进行顶点的消除和暂停绘制
/*这里是onMouse(GLint button, GLint state, GLint x, GLint y)*/
//如果按下的是右键
else if (button == GLUT_RIGHT_BUTTON) {
//如果正在进行橡皮筋操作
if (MouseMode == MOVE) {
//停止橡皮筋操作(停止实时绘画)
MouseMode = NONE;
return;
}
//否则为删除模式,判断顶点位置
auto ibeg = Vertex.begin();
while (ibeg != Vertex.end()) {
//模糊搜索,先绘制的顶点先删除(距离都满足条件的话)
if (((x - ibeg->first) * (x - ibeg->first)) + ((y - ibeg->second) * (y - ibeg->second)) < 400) {
//找到了,删除该顶点
Vertex.erase(ibeg);
break;
}
ibeg++;
}
}
这里是可以用于前面圆和圆弧绘制的测试代码
/*
你可以使用左键绘制顶点
你可以使用右键删除顶点
直线的绘制沿着顶点顺序
*/
#include <gl/glut.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
#include "DrawLine.hpp"
#include "DrawRound.hpp"
using namespace std;
#define m_POINT_SIZE 10
#define m_LINE_SIZE 2
typedef enum {
MOVE,
NONE
}MOUSEMODE;
vector<pair<GLint, GLint >>Vertex;
MOUSEMODE MouseMode = NONE;
GLint ctrlPoint = 0;
void onDisplay();
void onReshape(GLint w, GLint h);
void onMouse(GLint button, GLint state, GLint x, GLint y);
void onMouseMove(GLint xMouse, GLint yMouse);
void onReshape(GLint w, GLint h)
{
// 设置视口大小
glViewport(0, 0, w, h);
// 切换矩阵模式为投影矩阵
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
// 载入单位矩阵
glLoadIdentity();
// 进行二维平行投影
gluOrtho2D(0, w, h, 0);
// 切换矩阵模式为模型矩阵
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
// 发送重绘
glutPostRedisplay();
}
void onMouse(GLint button, GLint state, GLint x, GLint y){
if (state == GLUT_DOWN) {
if (button == GLUT_LEFT_BUTTON) {
if(!Vertex.size())
Vertex.push_back(make_pair(x, y));
Vertex.push_back(make_pair(x, y));
ctrlPoint = Vertex.size();
MouseMode = MOVE;
}
else if (button == GLUT_RIGHT_BUTTON) {
if (MouseMode == MOVE) {
MouseMode = NONE;
return;
}
auto ibeg = Vertex.begin();
while (ibeg != Vertex.end()) {
if (((x - ibeg->first) * (x - ibeg->first)) + ((y - ibeg->second) * (y - ibeg->second)) < 400) {
Vertex.erase(ibeg);
break;
}
ibeg++;
}
}
}
glutPostRedisplay();
}
void onMouseMove(GLint xMouse, GLint yMouse) {
if (MouseMode == MOVE) {
Vertex[ctrlPoint-1].first = xMouse, Vertex[ctrlPoint-1].second = yMouse;
glutPostRedisplay();
}
}
void onDisplay() {
glClearColor(224 / 255.0, 237 / 255.0, 253 / 255.0,1.0);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
glColor3f(1.0f, 0, 0);
auto ibeg = Vertex.begin(),jbeg=ibeg;
GLint VertexNum = Vertex.size();
while (ibeg != Vertex.end()) {
glPointSize(m_POINT_SIZE);
glBegin(GL_POINTS);
glVertex2i(ibeg->first, ibeg->second);
glEnd();
glPointSize(m_LINE_SIZE);
if(VertexNum>=2) {
//这里可以选择直线绘制方式
BRESENHAM_Line(ibeg->first, ibeg->second, jbeg->first, jbeg->second);
//TMP_Line(ibeg->first, ibeg->second, jbeg->first, jbeg->second);
//DDA_Line(ibeg->first, ibeg->second, jbeg->first, jbeg->second);
//这里是绘制圆形
//Mid_Circle( jbeg->first, jbeg->second,ibeg->first, ibeg->second);
//BRESENHAM_Circle(jbeg->first, jbeg->second, ibeg->first, ibeg->second);
}
jbeg = ibeg;
ibeg++;
}
//这里是绘制圆弧(只绘制前三个点,可以自己DIY)
if (VertexNum >= 3) {
cout << "Draw CircleArc" << endl;
DrawCircleArc(Vertex[0].first, Vertex[0].second, Vertex[1].first, Vertex[1].second, Vertex[2].first, Vertex[2].second);
}
glutSwapBuffers();
cout << "Once" << endl;
}
GLint main(GLint argc, char* argv[])
{
// 初始化 glut
glutInit(&argc, argv);
// 设置 OpenGL 显示模式(双缓存, RGB 颜色模式)
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_DOUBLE | GLUT_RGB);
// 设置窗口初始尺寸
glutInitWindowSize(1000,800);
// 设置窗口初始位置
glutInitWindowPosition(0, 0);
// 设置窗口标题
glutCreateWindow("Terix");
glutReshapeFunc(onReshape);
glutDisplayFunc(onDisplay);
glutMouseFunc(onMouse);
glutPassiveMotionFunc(onMouseMove);
// 设置菜单
// 进入 glut 事件循环
glutMainLoop();
return 0;
}
椭圆扫描算法
然后我们来介绍一下最后一个绘制圆锥曲线的算法(我的专栏里)——椭圆的绘制.
由于椭圆的对称性较圆稍差,它的对称性只有4份,也就是四个卦象内对称,也就是说我们得绘制出第一卦象一整个卦象的图像。当斜率绝对值小于1的时候使用x作为步长,反之为y轴。接下来来推导一下迭代方程和斜率的判别式:
设一个椭圆方程为
x轴
假设当前最佳迭代点为 \((x_i+1, y_i)\),那么对于下一个迭代点的两种情况:
d<0
d>=0
迭代终点为斜率的绝对值大于1
斜率判别式
转化为:
y轴
同样的我们可以得到:
d<0
d>0
迭代终点为y==0
因为单纯使用函数已经无法很好的维护数据了,所以从椭圆开始我会将所有的算法和所需要的数据结构封装成类。
Ellipt类
class Ellipt {
public:
Ellipt(GLint P1x=0,GLint P1y=0,GLint P2x=0,GLint P2y=0)
{
m_a = abs(static_cast<GLint>(P1x - P2x)/2);
m_b= abs(static_cast<GLint>(P1y - P2y)/2);
//四舍五入
m_R.x = static_cast<GLint>(((P1x + P2x) / 2.0 + 0.5));
m_R.y = static_cast<GLint>(((P1y + P2y) / 2.0 + 0.5));
}
void setData(GLint P1x, GLint P1y, GLint P2x, GLint P2y) {
m_a = abs(static_cast<GLint>(P1x - P2x)/2);
m_b = abs(static_cast<GLint>(P1y - P2y)/2);
//四舍五入
m_R.x = static_cast<GLint>(((P1x + P2x) / 2.0 + 0.5));
m_R.y = static_cast<GLint>(((P1y + P2y) / 2.0 + 0.5));
}
void Draw(){
MidPt_Elliptse(m_R, m_a, m_b);
}
private:
myPoint m_R;
GLint m_a,m_b;
void MidPt_Elliptse(myPoint cPt, GLint a, GLint b) {
glBegin(GL_POINTS);
GLint x, y, temp = a * 7 / 10, dir[4][2] = {
{ 1, 1 }, { 1,-1 },
{ -1,1}, {-1,-1 }
};
double d;
x = 0, y = b;
d = b * b + a * a * (-b + 0.25);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
glVertex2i(cPt.x + x * dir[i][0], cPt.y + y * dir[i][1]);
}
while ((b * b * (x + 1)<a * a * (y + 0.5))) {
if (d > 0)
{
x += 1;
y -= 1;
d += b * b * (2 * x + 3) + a * a * (-2 * y + 2);
}
else {
x += 1;
d += b * b * (2 * x + 3);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
glVertex2i(cPt.x + x * dir[i][0], cPt.y + y * dir[i][1]);
}
}
while (y > 0) {
if (d >= 0) {
y -= 1;
d += a * a * (-2 * y + 3);
}
else {
x += 1;
y -= 1;
d += a * a * (-2 * y + 3) + b * b * (2 * x + 2);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
glVertex2i(cPt.x + x * dir[i][0], cPt.y + y * dir[i][1]);
}
}
glFlush();
glEnd();
}
};
其中用到的myPoint类
class myPoint;
//A point or a vector in R^2
class myPoint {
public:
myPoint(GLint X=0,GLint Y=0 ):x(X),y(Y){}
GLint x, y;
};
myPoint operator+(const myPoint& a, const myPoint& b) {
return myPoint(a.x + b.x, a.y + b.y);
}
myPoint operator-(const myPoint& a, const myPoint& b) {
return myPoint(a.x - b.x, a.y - b.y);
}
GLint operator*(const myPoint& a, const myPoint& b) {
return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y;
}
代码汇总
你可以在这里找到目前为止所有的源代码
阿里云盘-代码汇总
gitee-代码汇总
下/上一篇
本文来自博客园,作者:zhywyt,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhywyt/p/17347089.html


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号