C#基础 继承和实例化
有代码如下,问输出的是多少:
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { B b = new B(); Console.ReadKey(); } class A { public A() { PrintFields(); } public virtual void PrintFields() { } } class B : A { int x = 1; int y; public B() { y = -1; } public override void PrintFields() { Console.WriteLine("x={0},y={1}", x, y); } } }
结果:x=1;y=0;
刚开始有点不理解,觉得输出是x=1;y=-1;然后反编译看了下IL代码,然而。。还是没看出来,IL代码如下:

.class private auto ansi beforefieldinit Program extends [mscorlib]System.Object { .method public hidebysig specialname rtspecialname instance void .ctor() cil managed { .maxstack 8 L_0000: ldarg.0 L_0001: call instance void [mscorlib]System.Object::.ctor() L_0006: nop L_0007: ret } .method private hidebysig static void Main(string[] args) cil managed { .entrypoint .maxstack 1 .locals init ( [0] class ConsoleApplication1.Program/B b) L_0000: nop L_0001: newobj instance void ConsoleApplication1.Program/B::.ctor() L_0006: stloc.0 L_0007: call valuetype [mscorlib]System.ConsoleKeyInfo [mscorlib]System.Console::ReadKey() L_000c: pop L_000d: ret } .class auto ansi nested private beforefieldinit A extends [mscorlib]System.Object { .method public hidebysig specialname rtspecialname instance void .ctor() cil managed { .maxstack 8 L_0000: ldarg.0 L_0001: call instance void [mscorlib]System.Object::.ctor() L_0006: nop L_0007: nop L_0008: ldarg.0 L_0009: callvirt instance void ConsoleApplication1.Program/A::PrintFields() L_000e: nop L_000f: ret } .method public hidebysig newslot virtual instance void PrintFields() cil managed { .maxstack 8 L_0000: nop L_0001: ret } } .class auto ansi nested private beforefieldinit B extends ConsoleApplication1.Program/A { .method public hidebysig specialname rtspecialname instance void .ctor() cil managed { .maxstack 8 L_0000: ldarg.0 L_0001: ldc.i4.1 L_0002: stfld int32 ConsoleApplication1.Program/B::x L_0007: ldarg.0 L_0008: call instance void ConsoleApplication1.Program/A::.ctor() L_000d: nop L_000e: nop L_000f: ldarg.0 L_0010: ldc.i4.m1 L_0011: stfld int32 ConsoleApplication1.Program/B::y L_0016: ret } .method public hidebysig virtual instance void PrintFields() cil managed { .maxstack 8 L_0000: nop L_0001: ldstr "x={0},y={1}" L_0006: ldarg.0 L_0007: ldfld int32 ConsoleApplication1.Program/B::x L_000c: box int32 L_0011: ldarg.0 L_0012: ldfld int32 ConsoleApplication1.Program/B::y L_0017: box int32 L_001c: call void [mscorlib]System.Console::WriteLine(string, object, object) L_0021: nop L_0022: ret } .field private int32 x .field private int32 y } }
最后打断点,找到了原因
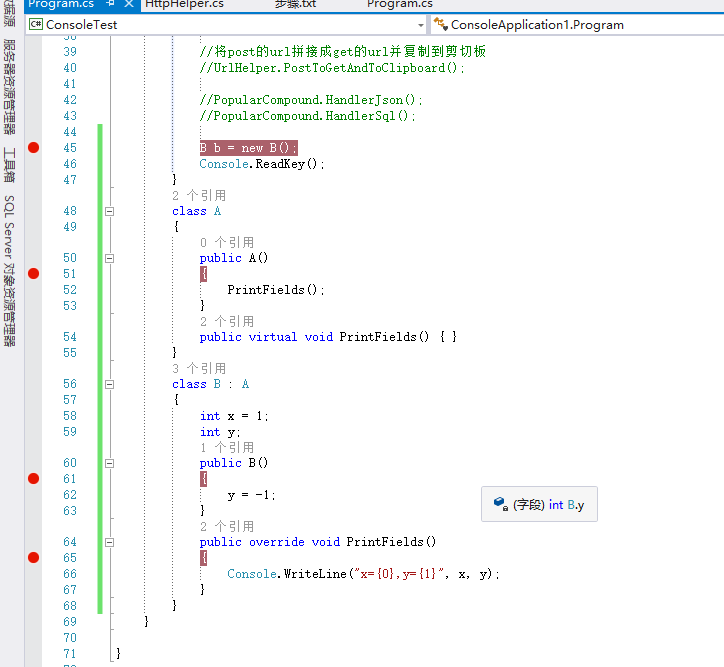
原因分析:
B b = new B();
执行顺序:
1、int x = 1;int y;给x赋值1,给y赋值默认为0(int类型)
2、public B(),然后关键点来了
3、public A(),执行A里面的PrintFields();但是A里面的这个方法是个虚方法,会调用B里面重写的方法
4、public override void PrintFields()这个是B里面的然后Console.WriteLine("x={0},y={1}", x, y);结果当然就是x=1;y=0;
5、然后才回到了B的public B(),接着给y赋值y = -1;这个时候y才变了,如果这个时候打印y的值才是-1,这个时候B的实例化就完成了
关键点:实例化类的时候,会先执行继承的父类的构造函数,如果父类构造函数含有虚方法又会回调子类的重写方法,之后才回到初始类的构造函数




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号