基于keras的双层LSTM网络和双向LSTM网络
1.使用RBF神经网络实现函数逼近2.使用BP神经网络实现函数逼近3.使用CNN实现MNIST数据集分类4.tensorflow解决回归问题简单案列5.自然语言建模与词向量6.使用多层RNN-LSTM网络实现MNIST数据集分类及常见坑汇总7.基于tensorflow的RBF神经网络案例8.快速傅里叶变换(FFT)和小波分析在信号处理上的应用9.Python三次样条插值与MATLAB三次样条插值简单案例10.使用TensorFlow实现MNIST数据集分类11.数值积分原理与应用12.keras建模的3种方式——序列模型、函数模型、子类模型13.基于keras的残差网络
14.基于keras的双层LSTM网络和双向LSTM网络
15.seq2seq模型案例分析16.基于keras的卷积神经网络(CNN)17.基于keras的时域卷积网络(TCN)18.基于keras的胶囊网络(CapsNet)1 前言
基于keras的双层LSTM网络和双向LSTM网络中,都会用到 LSTM层,主要参数如下:
LSTM(units,input_shape,return_sequences=False)
- units:隐藏层神经元个数
- input_shape=(time_step, input_feature):time_step是序列递归的步数,input_feature是输入特征维数
- return_sequences: 取值为True,表示每个时间步的值都返回;取值为False,表示只返回最后一个时间步的取值
本文以MNIST手写数字分类为例,讲解双层LSTM网络和双向LSTM网络的实现。关于MNIST数据集的说明,见使用TensorFlow实现MNIST数据集分类。
笔者工作空间如下:

代码资源见--> 双隐层LSTM和双向LSTM
2 双层LSTM网络
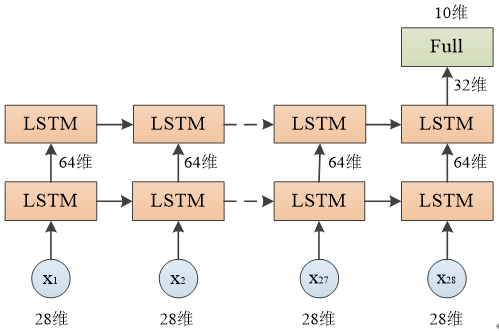 双层LSTM网络结构
双层LSTM网络结构
DoubleLSTM.py
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense,LSTM
#载入数据
def read_data(path):
mnist=input_data.read_data_sets(path,one_hot=True)
train_x,train_y=mnist.train.images.reshape(-1,28,28),mnist.train.labels,
valid_x,valid_y=mnist.validation.images.reshape(-1,28,28),mnist.validation.labels,
test_x,test_y=mnist.test.images.reshape(-1,28,28),mnist.test.labels
return train_x,train_y,valid_x,valid_y,test_x,test_y
#双层LSTM模型
def DoubleLSTM(train_x,train_y,valid_x,valid_y,test_x,test_y):
#创建模型
model=Sequential()
model.add(LSTM(64,input_shape=(28,28),return_sequences=True)) #返回所有节点的输出
model.add(LSTM(32,return_sequences=False)) #返回最后一个节点的输出
model.add(Dense(10,activation='softmax'))
#查看网络结构
model.summary()
#编译模型
model.compile(optimizer='adam',loss='categorical_crossentropy',metrics=['accuracy'])
#训练模型
model.fit(train_x,train_y,batch_size=500,nb_epoch=15,verbose=2,validation_data=(valid_x,valid_y))
#评估模型
pre=model.evaluate(test_x,test_y,batch_size=500,verbose=2)
print('test_loss:',pre[0],'- test_acc:',pre[1])
train_x,train_y,valid_x,valid_y,test_x,test_y=read_data('MNIST_data')
DoubleLSTM(train_x,train_y,valid_x,valid_y,test_x,test_y)
每层网络输出尺寸:
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
lstm_5 (LSTM) (None, 28, 64) 23808
_________________________________________________________________
lstm_6 (LSTM) (None, 32) 12416
_________________________________________________________________
dense_5 (Dense) (None, 10) 330
=================================================================
Total params: 36,554
Trainable params: 36,554
Non-trainable params: 0
由于第一个LSTM层设置了 return_sequences=True,每个节点的输出值都会返回,因此输出尺寸为 (None, 28, 64)
由于第二个LSTM层设置了 return_sequences=False,只有最后一个节点的输出值会返回,因此输出尺寸为 (None, 32)
训练结果:
Epoch 13/15
- 17s - loss: 0.0684 - acc: 0.9796 - val_loss: 0.0723 - val_acc: 0.9792
Epoch 14/15
- 18s - loss: 0.0633 - acc: 0.9811 - val_loss: 0.0659 - val_acc: 0.9822
Epoch 15/15
- 17s - loss: 0.0597 - acc: 0.9821 - val_loss: 0.0670 - val_acc: 0.9812
test_loss: 0.0714278114028275 - test_acc: 0.9789000034332276
3 双向LSTM网络
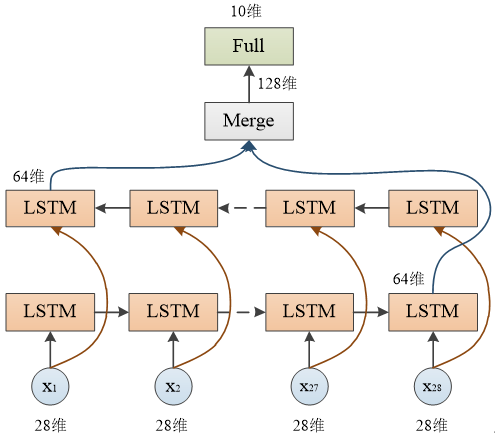 双向LSTM网络结构
双向LSTM网络结构
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense,LSTM,Bidirectional
#载入数据
def read_data(path):
mnist=input_data.read_data_sets(path,one_hot=True)
train_x,train_y=mnist.train.images.reshape(-1,28,28),mnist.train.labels,
valid_x,valid_y=mnist.validation.images.reshape(-1,28,28),mnist.validation.labels,
test_x,test_y=mnist.test.images.reshape(-1,28,28),mnist.test.labels
return train_x,train_y,valid_x,valid_y,test_x,test_y
#双向LSTM模型
def BiLSTM(train_x,train_y,valid_x,valid_y,test_x,test_y):
#创建模型
model=Sequential()
lstm=LSTM(64,input_shape=(28,28),return_sequences=False) #返回最后一个节点的输出
model.add(Bidirectional(lstm)) #双向LSTM
model.add(Dense(10,activation='softmax'))
#编译模型
model.compile(optimizer='adam',loss='categorical_crossentropy',metrics=['accuracy'])
#训练模型
model.fit(train_x,train_y,batch_size=500,nb_epoch=15,verbose=2,validation_data=(valid_x,valid_y))
#查看网络结构
model.summary()
#评估模型
pre=model.evaluate(test_x,test_y,batch_size=500,verbose=2)
print('test_loss:',pre[0],'- test_acc:',pre[1])
train_x,train_y,valid_x,valid_y,test_x,test_y=read_data('MNIST_data')
BiLSTM(train_x,train_y,valid_x,valid_y,test_x,test_y)
每层网络输出尺寸:
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
bidirectional_5 (Bidirection (None, 128) 47616
_________________________________________________________________
dense_6 (Dense) (None, 10) 1290
=================================================================
Total params: 48,906
Trainable params: 48,906
Non-trainable params: 0
由于LSTM层设置了 return_sequences=False,只有最后一个节点的输出值会返回,每层LSTM返回64维向量,两层合并共128维,因此输出尺寸为 (None, 128)
训练结果:
Epoch 13/15
- 22s - loss: 0.0512 - acc: 0.9839 - val_loss: 0.0632 - val_acc: 0.9790
Epoch 14/15
- 22s - loss: 0.0453 - acc: 0.9865 - val_loss: 0.0534 - val_acc: 0.9832
Epoch 15/15
- 22s - loss: 0.0418 - acc: 0.9869 - val_loss: 0.0527 - val_acc: 0.9830
test_loss: 0.06457789749838412 - test_acc: 0.9795000076293945
声明:本文转自基于keras的双层LSTM网络和双向LSTM网络





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享4款.NET开源、免费、实用的商城系统
· 全程不用写代码,我用AI程序员写了一个飞机大战
· MongoDB 8.0这个新功能碉堡了,比商业数据库还牛
· 白话解读 Dapr 1.15:你的「微服务管家」又秀新绝活了
· 上周热点回顾(2.24-3.2)