142. Linked List Cycle II
- Total Accepted: 102820
- Total Submissions: 331280
- Difficulty: Medium
- Contributors: Admin
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null.
Note: Do not modify the linked list.
Follow up:
Can you solve it without using extra space?
分析
1.判断单链表是否有环
使用两个slow, fast指针从头开始扫描链表。指针slow 每次走1步,指针fast每次走2步。如果存在环,则指针slow、fast会相遇;如果不存在环,指针fast遇到NULL退出。
就是所谓的追击相遇问题: 相遇时,slow 并没有走完一圈,fast领先slow一圈,第一次相遇在Pos处
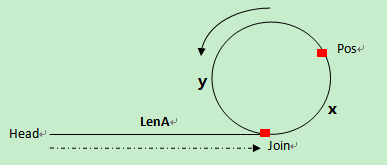
2.求有环单链表的环长
在环上相遇后,记录第一次相遇点为Pos,之后指针slow继续每次走1步,fast每次走2步。在下次相遇的时候fast比slow正好又多走了一圈,也就是多走的距离等于环长。
设从第一次相遇到第二次相遇,设slow走了len步,则fast走了2*len步,相遇时多走了一圈:
环长=2*len-len。
3.求有环单链表的环连接点位置
第一次碰撞点Pos到连接点Join的距离 = 头指针到连接点Join的距离,因此,分别从第一次碰撞点Pos、头指针head开始走,相遇的那个点就是连接点。
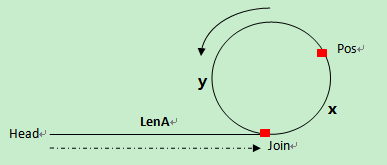
在环上相遇后,记录第一次相遇点为Pos,连接点为Join,假设头结点到连接点的长度为LenA,连接点到第一次相遇点的长度为x,环长为R。
第一次相遇时,slow走的长度 S = LenA + x;
第一次相遇时,fast走的长度 2S = LenA + n*R + x;
所以可以知道,LenA + x = n*R; LenA = n*R -x; 亦可以看成 LenA = m*R + y
4.求有环单链表的链表长
上述2中求出了环的长度;3中求出了连接点的位置,就可以求出头结点到连接点的长度。两者相加就是链表的长度。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */class Solution {public: ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) { if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL) return NULL; ListNode* slow = head, * fast = head; while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL){ slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; if(slow == fast) break; } if(slow != fast) return NULL; while(head != slow){ head = head->next; slow = slow->next; } return slow; }}; |
