Java之方法引用笔记
方法引用实际上是Lambda表达式的一种语法糖
方法引用分为4类:
1.类名::静态方法名
public class Student { private String name; private int mark; public Student(String name, int mark) { this.name = name; this.mark = mark; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getMark() { return mark; } public void setMark(int mark) { this.mark = mark; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", mark=" + mark + '}'; } //静态方法名 public static int computerByName(Student student1, Student student2){ return student1.getName().compareToIgnoreCase(student2.getName()); } public static int computerByMark(Student student1,Student student2){ return student2.getMark() - student1.getMark(); } }
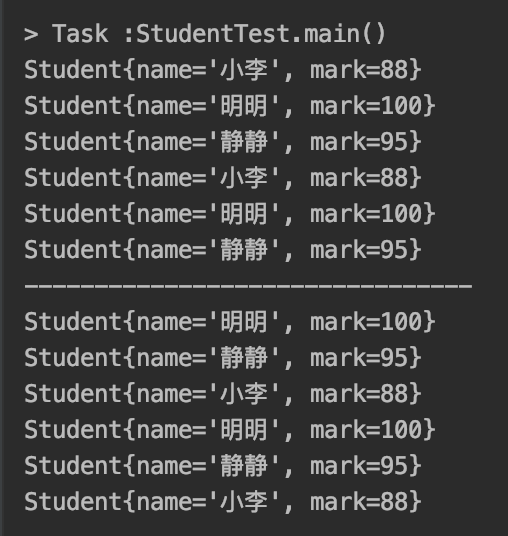
public static void main(String[] args) { Student student1 = new Student("明明",100); Student student2 = new Student("小李",88); Student student3 = new Student("静静",95); List<Student> studentList = Arrays.asList(student1,student2,student3); studentList.sort((theStudent1,theStudent2)-> Student.computerByName(theStudent1,theStudent2)); studentList.forEach(student -> System.out.println(student)); //等价于: studentList.sort(Student::computerByName); studentList.forEach(student -> System.out.println(student)); System.out.println("--------------------------------"); studentList.sort((theStudent1,theStudent2)-> Student.computerByMark(theStudent1,theStudent2)); studentList.forEach(student -> System.out.println(student)); //等价于 studentList.sort(Student::computerByMark); studentList.forEach(student -> System.out.println(student)); }
2.引用名::实例方法名
public class StudentComparator { //实例方法名 public int computerByName(Student student1, Student student2){ return student1.getName().compareToIgnoreCase(student2.getName()); } public int computerByMark(Student student1,Student student2){ return student2.getMark() - student1.getMark(); } }
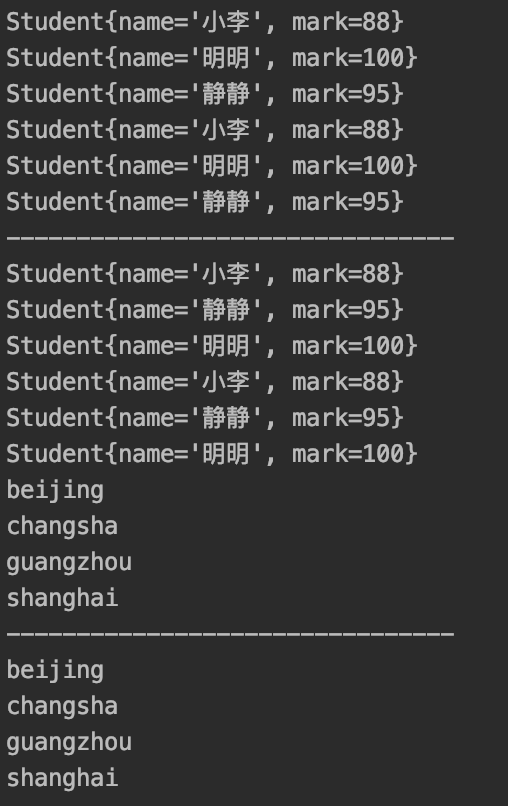
public static void main(String[] args) { Student student1 = new Student("明明",100); Student student2 = new Student("小李",88); Student student3 = new Student("静静",95); List<Student> studentList = Arrays.asList(student1,student2,student3); StudentComparator studentComparator = new StudentComparator(); studentList.sort((theStudent1, theStudent2) -> studentComparator.computerByMark(theStudent1,theStudent2)); studentList.forEach(student -> System.out.println(student)); //等价于: studentList.sort(studentComparator::computerByMark); studentList.forEach(student -> System.out.println(student)); System.out.println("--------------------------------"); studentList.sort((theStudent1, theStudent2) -> studentComparator.computerByName(theStudent1,theStudent2)); studentList.forEach(student -> System.out.println(student)); //等价于: studentList.sort(studentComparator::computerByName); studentList.forEach(student -> System.out.println(student)); }

3.类名::实例方法名
public class Student { private String name; private int mark; public Student(String name, int mark) { this.name = name; this.mark = mark; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getMark() { return mark; } public void setMark(int mark) { this.mark = mark; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", mark=" + mark + '}'; } //实例方法名 public int computerByName2(Student student){ return getName().compareToIgnoreCase(student.getName()); } public int computerByMark2(Student student){ return getMark() - student.getMark(); } }
public static void main(String[] args) { Student student1 = new Student("明明",100); Student student2 = new Student("小李",88); Student student3 = new Student("静静",95); List<Student> studentList = Arrays.asList(student1,student2,student3); //实例方法 为什么方法只有一个参数 是Lambda中第一个参数调用了这个方法,剩下的参数作为入参传入这个实例方法 studentList.sort(Student::computerByName2); studentList.forEach(student -> System.out.println(student)); //等价于: studentList.sort((theStudent1,theStudent2) -> theStudent1.computerByName2(student2)); studentList.forEach(student -> System.out.println(student)); System.out.println("--------------------------------"); studentList.sort(Student::computerByMark2); studentList.forEach(student -> System.out.println(student)); //等价于: studentList.sort((theStudent1,theStudent2) -> theStudent1.computerByMark2(student2)); studentList.forEach(student -> System.out.println(student)); //比如这个方法调用 List<String> citys = Arrays.asList("beijing","shanghai","guangzhou","changsha"); citys.sort((city1,city2) -> { return city1.compareToIgnoreCase(city2); }); citys.forEach(city -> System.out.println(city)); System.out.println("--------------------------------"); //等价于: citys.sort(String::compareToIgnoreCase); citys.forEach(city -> System.out.println(city)); }
4.构造方法引用 类名::new
public class MethodReferenceTest { public static void main(String[] args) { MethodReferenceTest methodReferenceTest = new MethodReferenceTest(); System.out.println(methodReferenceTest.getString(() -> new String())); //等价于: System.out.println(methodReferenceTest.getString(String::new)); } public String getString(Supplier<String>supplier){ return supplier.get() + "test"; } }
@FunctionalInterface public interface Supplier<T> { /** * Gets a result. * * @return a result */ T get(); }
Supplier<T>不接收参数,但是返回一个类型,在上面测试代码中吗就是返回一个String类型。用方法引用就可以简写为:String::new


