数据结构 LeetCode 232 用栈实现队列
232.用栈实现队列
一、一开始没想到好的做法,就用了三个栈去做到输入输出
代码:
1 class MyQueue { 2 public: 3 stack<int>a; 4 MyQueue() { 5 6 } 7 8 void push(int x) { 9 a.push(x); 10 11 } 12 13 int pop() { 14 stack<int>b; 15 stack<int>temp = a; 16 while (!temp.empty()) 17 { 18 b.push(temp.top()); 19 temp.pop(); 20 } 21 int ans = b.top(); 22 b.pop(); 23 while (!b.empty()) 24 { 25 temp.push(b.top()); 26 b.pop(); 27 } 28 a = temp; 29 return ans; 30 } 31 32 int peek() { 33 stack<int>b; 34 stack<int>temp=a; 35 while (!temp.empty()) 36 { 37 b.push(temp.top()); 38 temp.pop(); 39 } 40 return b.top(); 41 42 } 43 44 bool empty() { 45 return a.empty(); 46 } 47 };
也AC了,时间复杂度也很低,只是多用了一个栈。
二、
后面发现直接两个栈,一个in栈存进来的,一个out栈存要出去的,每次有执行pop指令就从出out栈出去,如果out栈为空,就把in栈的元素都pop到out,所以一共有n个元素,总的也只是把n个元素从inpop到out,总的时间复杂度应该是n,也满足了题目的进阶要求:

我的AC代码:
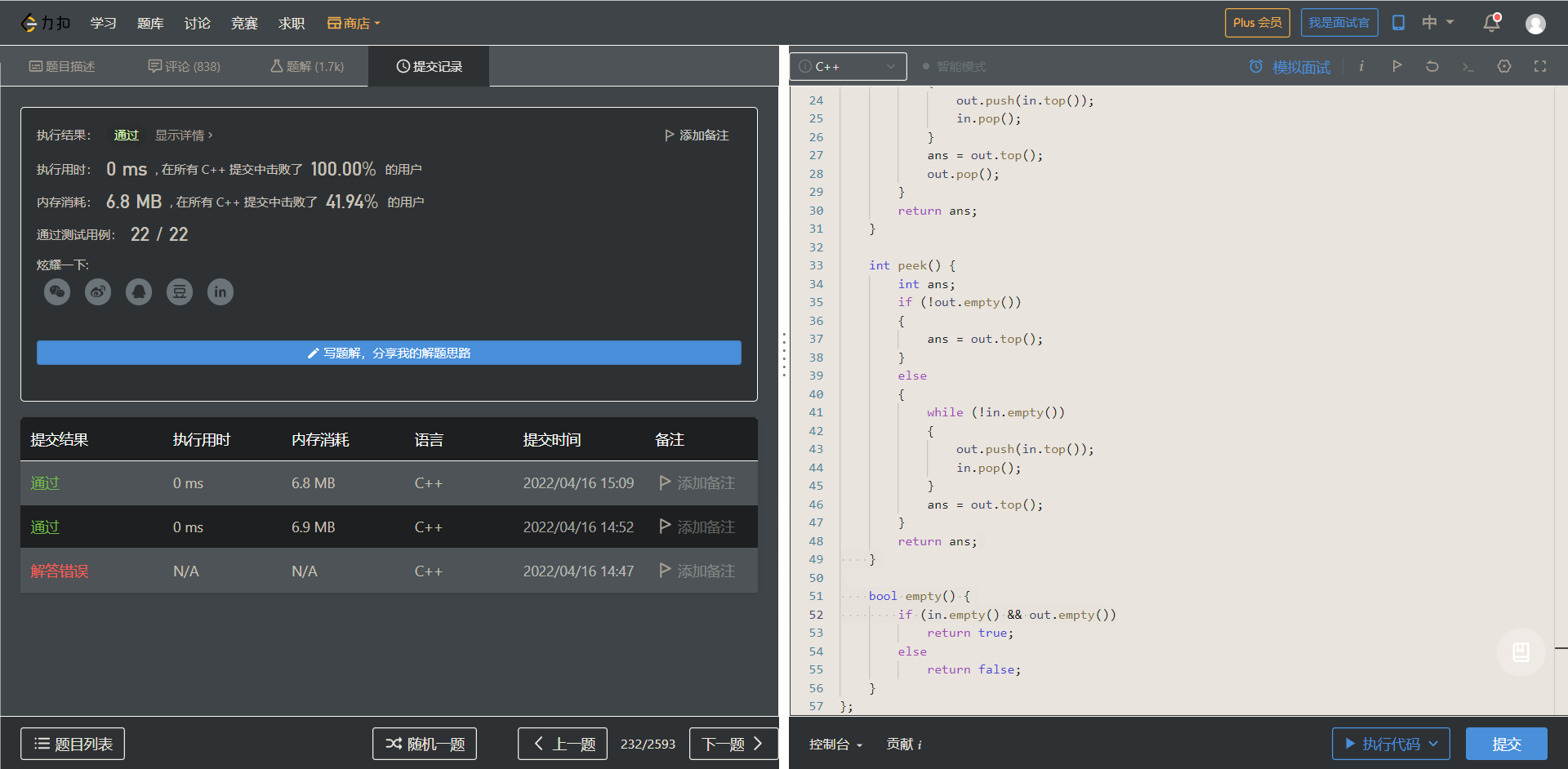
class MyQueue { public: stack<int>in; stack<int>out; MyQueue() { } void push(int x) { in.push(x); } int pop() { int ans; if (!out.empty()) { ans = out.top(); out.pop(); } else { while (!in.empty()) { out.push(in.top()); in.pop(); } ans = out.top(); out.pop(); } return ans; } int peek() { int ans; if (!out.empty()) { ans = out.top(); } else { while (!in.empty()) { out.push(in.top()); in.pop(); } ans = out.top(); } return ans; } bool empty() { if (in.empty() && out.empty()) return true; else return false; } };